chem 2- molecular orbital theory (*exam 1)
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
advanced theories of covalent bonding
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
what is paramagnetism
phenomenon in which a material is not magnetic itself but is attracted to a magnetic field
occurs when unpaired electrons are present
what is diamagnetism
phenomenon where a material is not magnetic but is repelled by a magnetic field
what does molecular orbital theory provide to us
an explanation of chemical bonding that accounts for the paramagnetism of the oxygen molecule
a model for describing the energies of electrons in a molecule and the probable location of these electrons
why is molecular orbital theory different from valence bond theory
valence bond theory used hybrid orbitals that are assigned to one specific atom
molecular orbital theory uses the combination of atomic orbitals to yield molecular orbitals that are delocalized over the entire molecule
how is the behavior of an electron described
a wave function, analogous to the behavior in an atom
what is a molecular orbital (wave function²)?
the region of space in which a valence electron in a molecule is likely to be found.
when is a molecular orbital full
when it contains two electrons with opposite spin (same as an atomic orbital)
what are homonuclear diatomic molecules
diatomic molecules where several types of molecular orbitals ocuur
what is the linear combination of atomic orbital (LCAO)
the mathematical process of combing
what are molecular obitals
combinations of atomic orbital wave functions
what can combining waves lead to
constructive interference or destructive interference
what is constructive interference
peaks line up with peaks
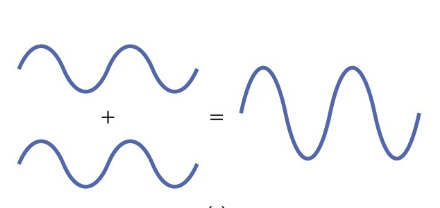
increases electron density
what is destructive interference
peaks line up with troughs
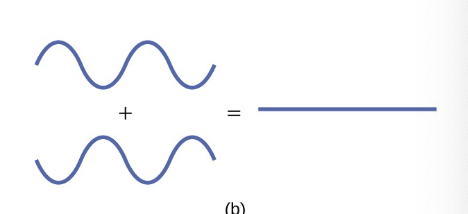
creates nodes
decreases electron density
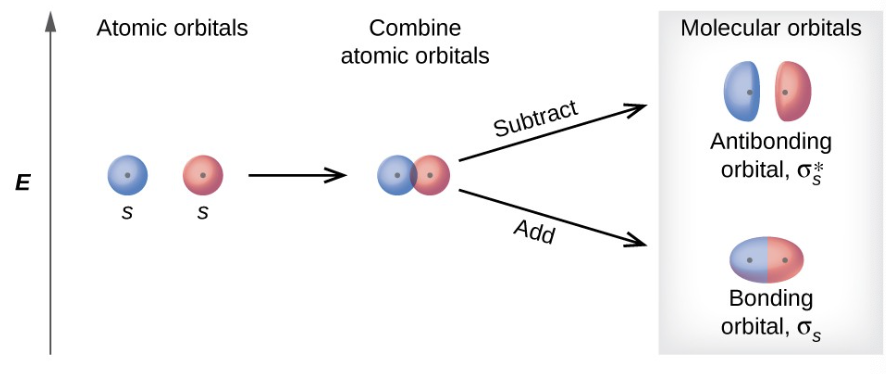
what are sigma s molecular orbitals
the in phase combination which is of lower energy and most of the electron density is directly between the nuclei
bonding orbital
more stable
what are sigma s* molecular orbitals
the out of phase addition ( can also be though of as subtracting the wave functions) which is of higher energy with a node between the nuclei
antibonding orbital
what is a bonding orbital
A molecular orbital formed by the constructive interference of atomic orbitals, resulting in lower energy and increased stability. It has electron density concentrated between the nuclei of the bonded atoms.
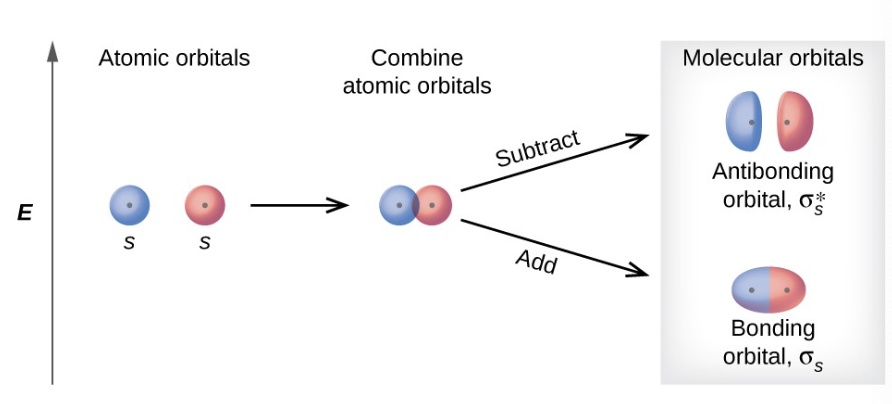
what is an antibonding orbital
A molecular orbital formed by the destructive interference of atomic orbitals, resulting in higher energy and decreased stability. It has a node between the nuclei, with electron density located outside the region between the bonded atoms.
what do p orbitals create when they overlap
sigma and sigma* orbitals
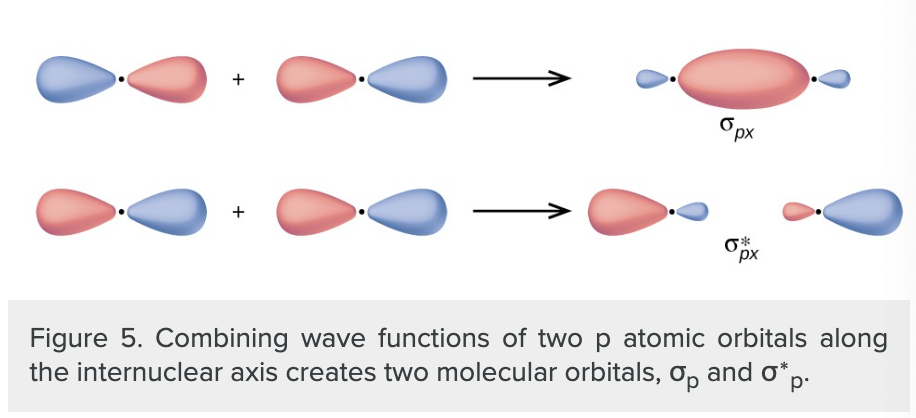
if the atoms are along the x-axis the two px orbitals overlap end to end to form sigma px and sigma*px orbitals
what does the side by side overlap of two p orbitals create
pi bonding molecular orbital and a pi antibonding molecular orbital.
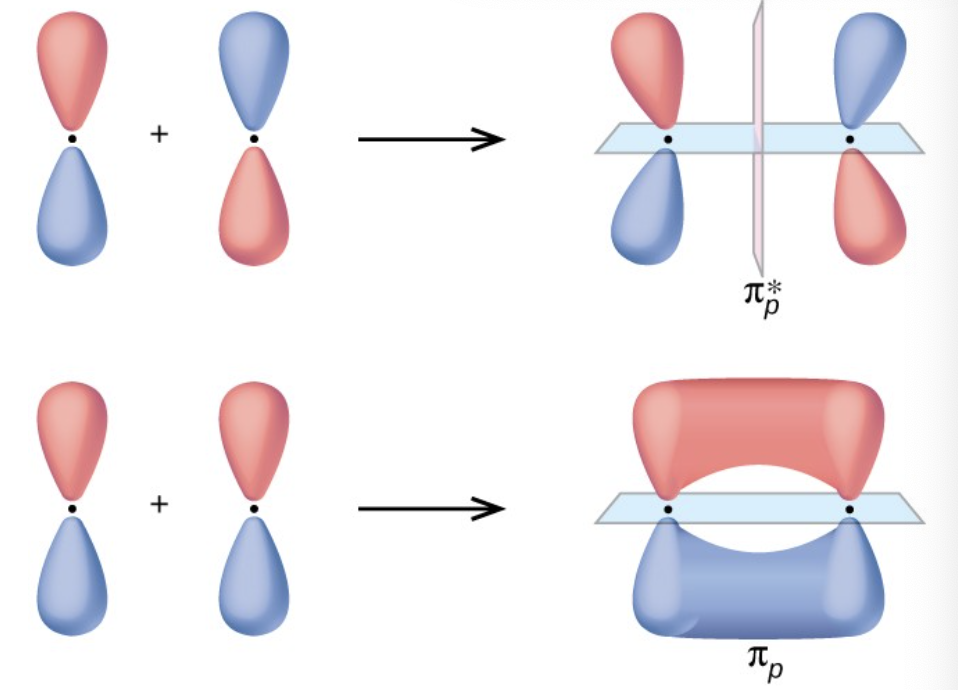
what are pi bonds
contains a nodal plane with the internuclear axis and is perpendicular to the lobes of p-pi orbitals, with electron density on either side of the node.
a pi bond exists when this orbital contains electrons
the electrons interact with both nuclei and help hold the atoms together
what do molecular orbitals or diatomic molecules contain
each atom with two sets of p orbitals oriented side by side (py and pz)
what do the 2 sets of py and pz combine to create
two pi orbitals and two pi* orbitals
the pi py and pi*pz orbitals are oriented at right angles to the sigmapz and pi*pz orbtials
what are degenerate orbitals
orbitals that have the same energy
ex) sigma py and sigma pz
what are the six molecular orbitals that result from the combination of the 6 atomic p orbitals in two atoms
sigma px and sigma*px
pi py and pi* py
sigma pz and pi* pz
what is a molecular orbital energy diagram
A graphical representation that shows the relative energy levels of molecular orbitals formed from atomic orbitals. It illustrates how atomic orbitals combine to form bonding, antibonding, and nonbonding molecular orbitals.
what do horizontal lines on the molecular orbital energy diagrams represent
one orbital that can hold two electrons
what do dashed lines show on the molecular orbital energy diagrams?
which of the atomic orbitals combine to form the molecular orbitals
what do a pair of atomic orbitals combining produce
the lower energy (bonding) and higher energy (anti bonding)
ex) combining six 2p orbitals results in three bonding orbitals one sigma and two pi and three antibonding orbitals one sigma* and two pi*
why do we use the aufbau principle?
to predict the distribution of electrons in molecular orbitals
lower energy orbitals fill first, electrons spread out among degenerate orbitals before pairing
each orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons with opposite signs
how can tou write the molecular electronic configuration
listing the orbitals with superscripts indicating the number of electrons present
*place parenthesis around molecular orbitals with same energy
what is bond order?
Bond order is a measure of the stability of a bond, calculated as the difference between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons, divided by two. It indicates the strength and number of bonds between two atoms; for example, a bond order of 1 represents a single bond.
what is the bond order for a single bond, double bond, and triple bond?
1, 2, and 3
what is the equation for bond order?

for atoms with three or fewer electrons in the p orbitals (Li through N) what is the pattern observed?
the sigma p orbital is higher in energy than the pi p set
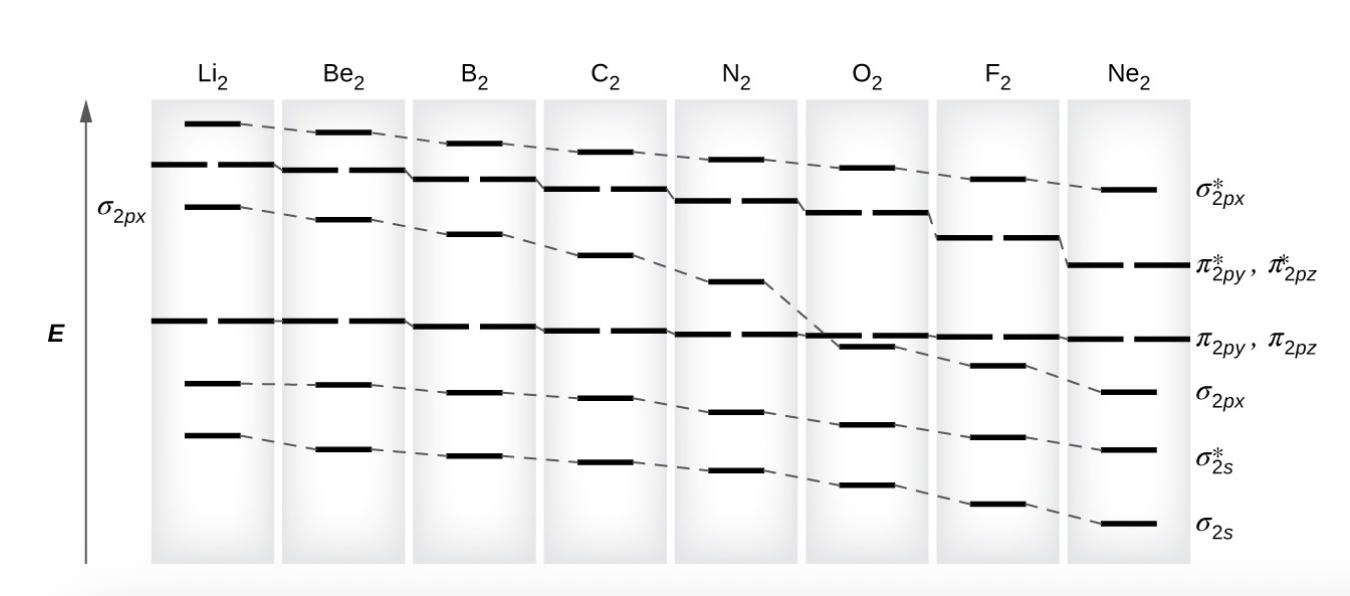
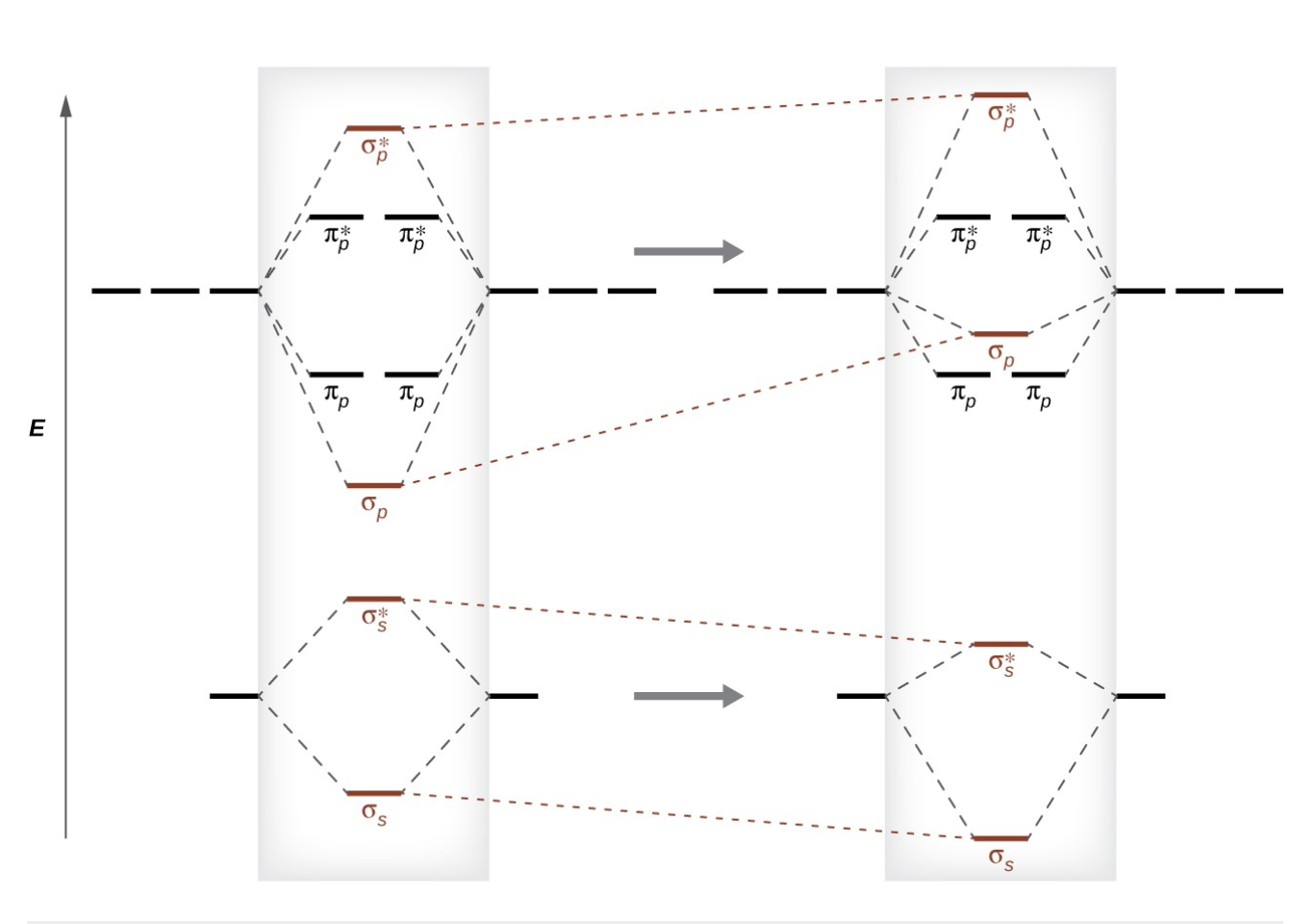
what is s-p mixing
change that cause sigma p orbitals to be less stable than pi p orbitals die to the mixing of s and p orbitals, affecting molecular stability.
also happens with sigma* p and pi* p orbitals
the turlets broken
