D2.1 Cell and nuclear division
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Where do all new cells come from?
From preexisting cells
Why do cells need to produce new cells?
For reproduction, growth and tissue repair
What are the 2 types of cell division?
Mitosis and Meiosis
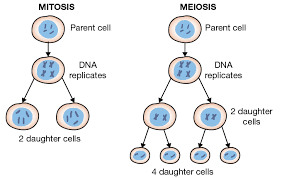
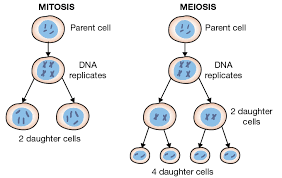
What is mitosis?
A single nuclear division that results in 2 genetically identical nuclei, with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell (Use the word nuclear division in the definition, rather than the word cell division, as mitosis and meiosis is when the nucleus divides, not the cell. That would be called cytokinesis)
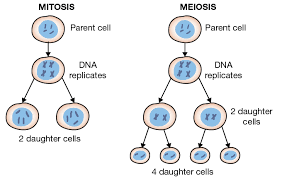
What is meiosis?
Two nuclear divisions that result in 4 different cells, with half as many chromosomes as the parent cell (Use the word nuclear division in the definition, rather than the word cell division, as mitosis and meiosis is when the nucleus divides, not the cell. That would be called cytokinesis)
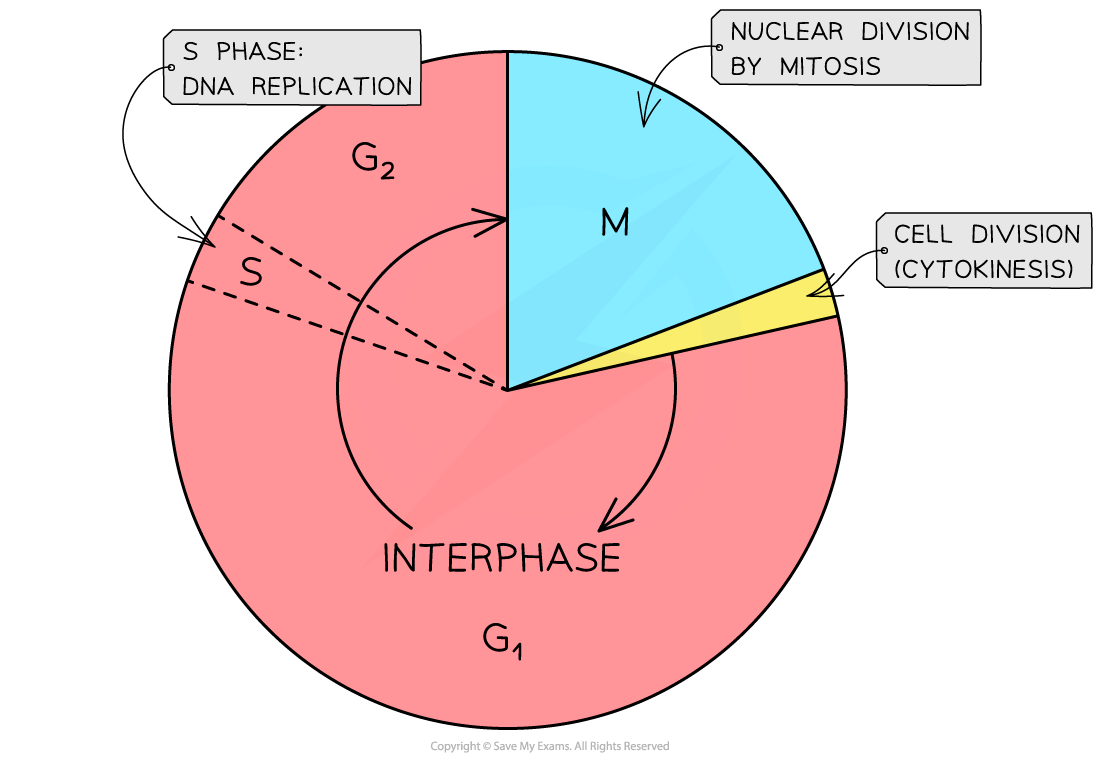
What are the main phases of the cell cycle ?
These are the overall stages to do with mitosis:
Interphase (the growth period before the cell divides, such as DNA replication)
Mitosis (nucleus divides)
Cytokinesis (cytoplasm and organelle divides)
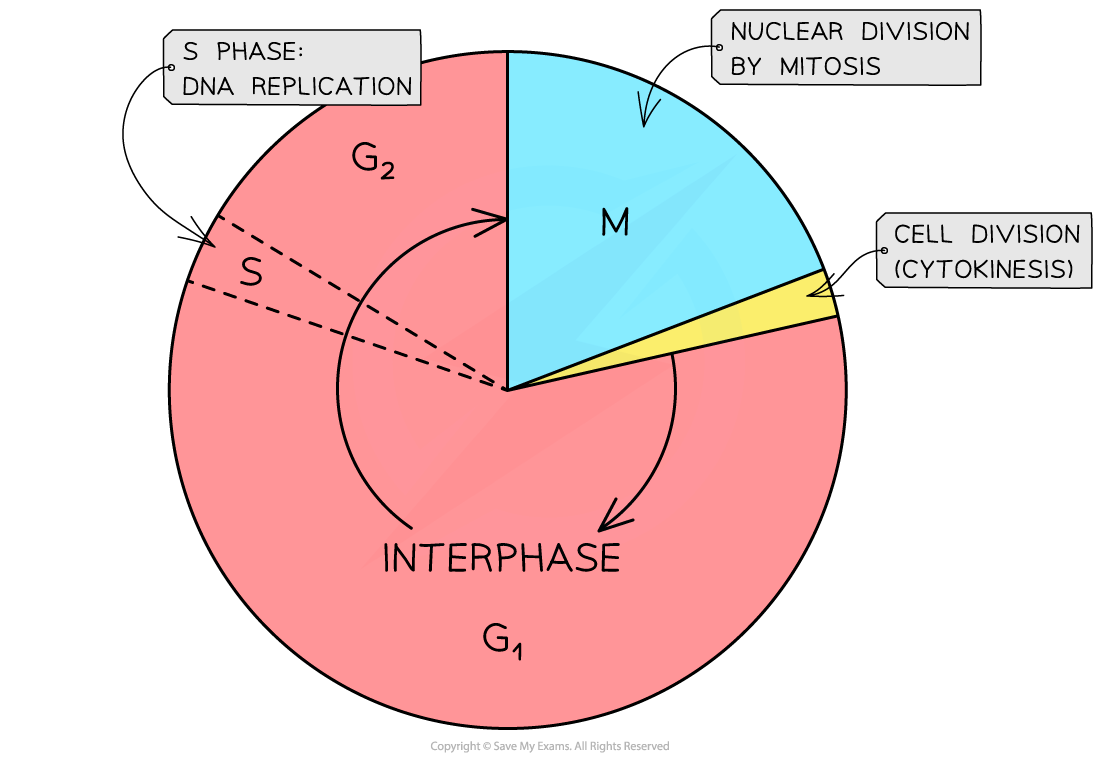
What is DNA replication?
It is when the number of chromosomes replicates before the cell divides, so that both cells after division have the same set of genetic information. This occurs during the interphase
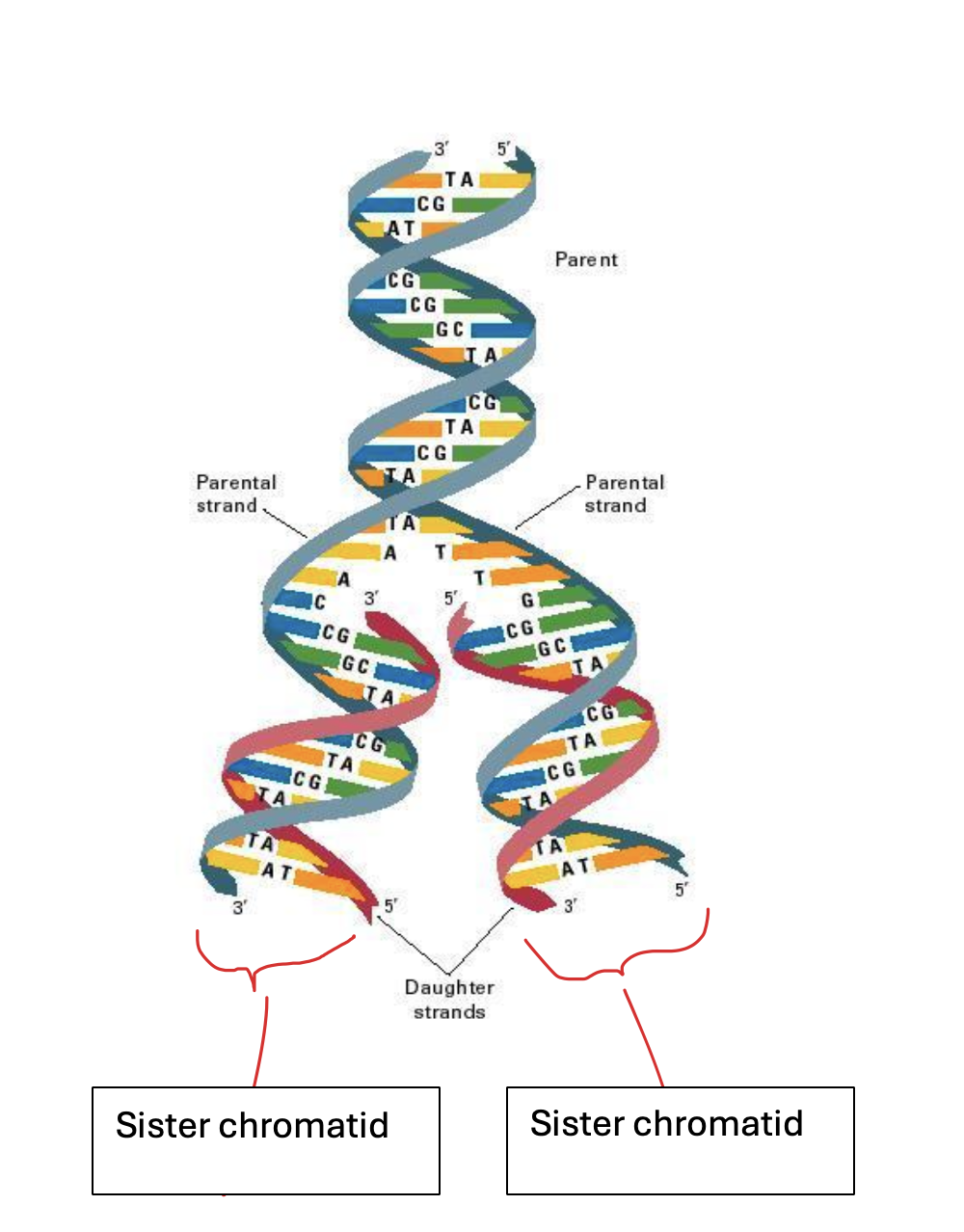
What are the genetically identical strands of DNA after DNA replication called?
Sister chromatids. One strand of DNA replication remains the parent strand, and the other one is the daughter strand, which is the new strand that has been added. Together, they are called a sister chromatid
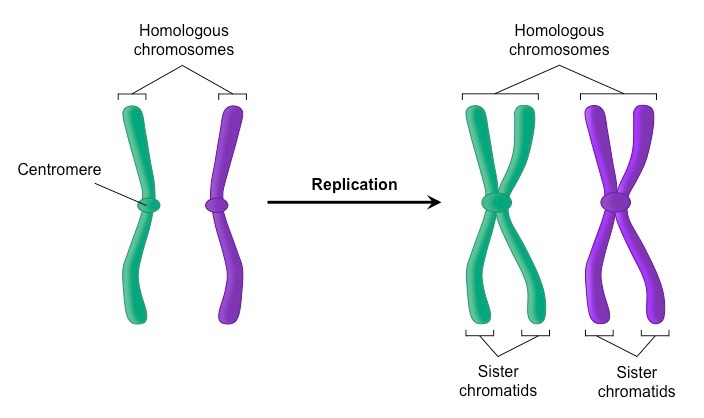
Daughter strand, parent strand and sister chromatid
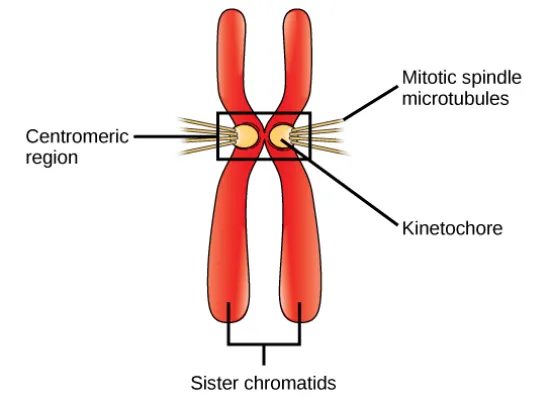
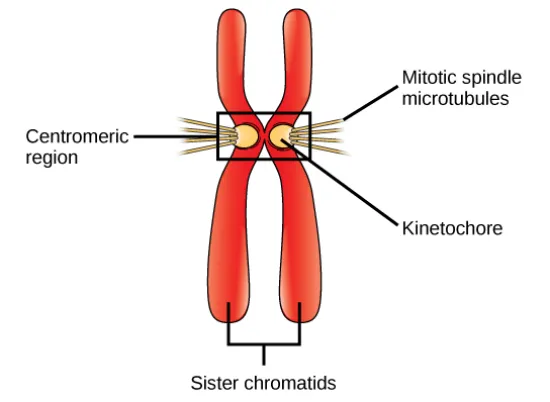
How are sister chromatids held together?
The sister chromatids are held together in a region called the centromere, and through a protein called cohesin to bind them together until they are separated at anaphase.
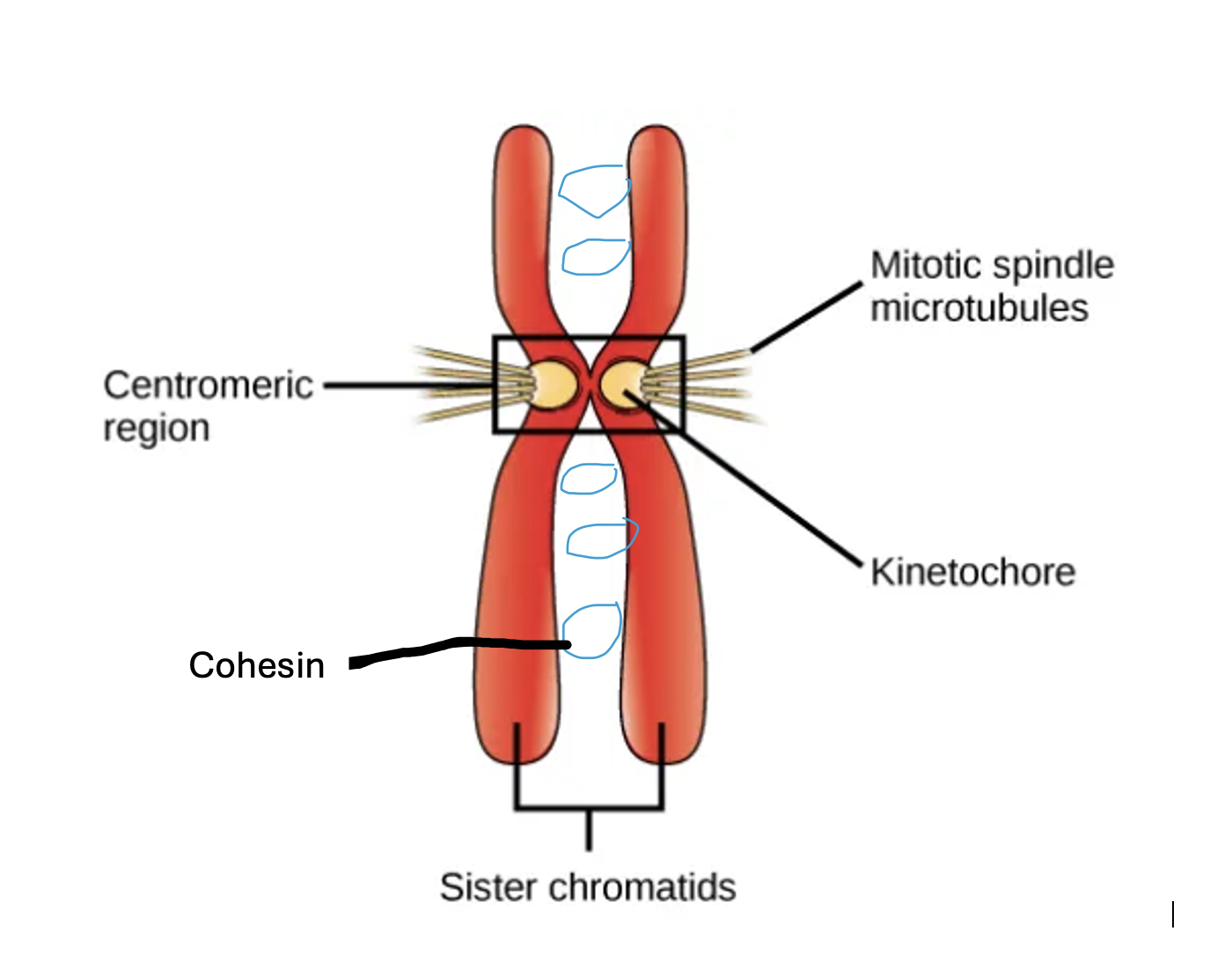
When is cohesin removed?
At the anaphase stage, where the sister chromatids are no longer held together, and are able to separate to opposite poles of the cell

What is the function of the centromere?
It holds the two sister chromatids together at this region, and it is where the kinetochore and microtubules are attached for the movement of chromosomes
How is the DNA condensed?
The DNA first wraps around histones to form a nucleosome. The nucleosomes coil and stack together to form chromatin. Chromatin only condenses to form chromosomes during prophase
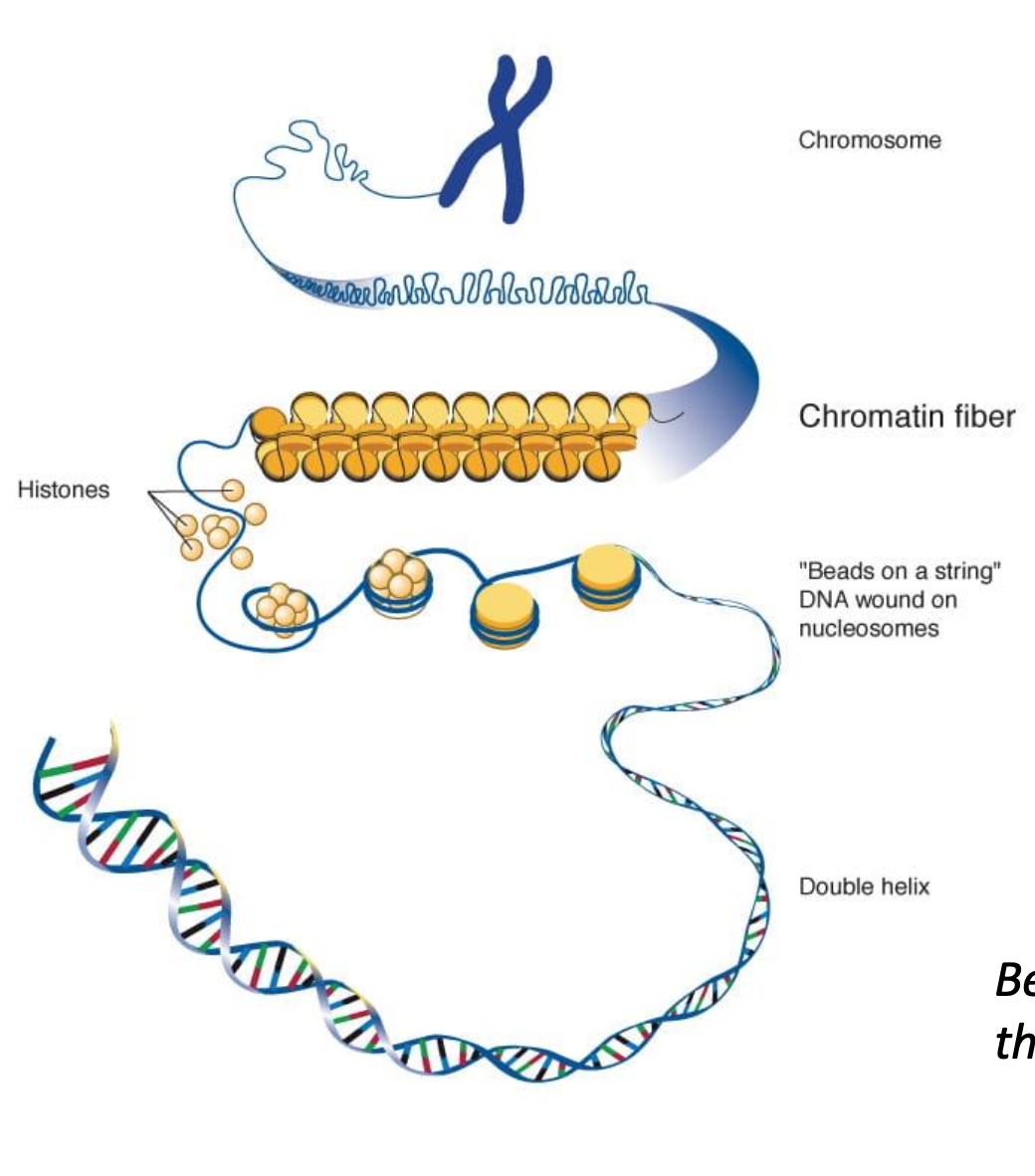
Why does DNA condense and supercoil?
So that it can be moved to opposite poles of the cell without getting tangled or broken
How are the sister chromatids pulled apart from each other?
The microtubules are attached to the kinetochore of each sister chromatid, and the microtubules (which are long protein fibers) pull these sister chromatids in opposite directions to each pole of the cell
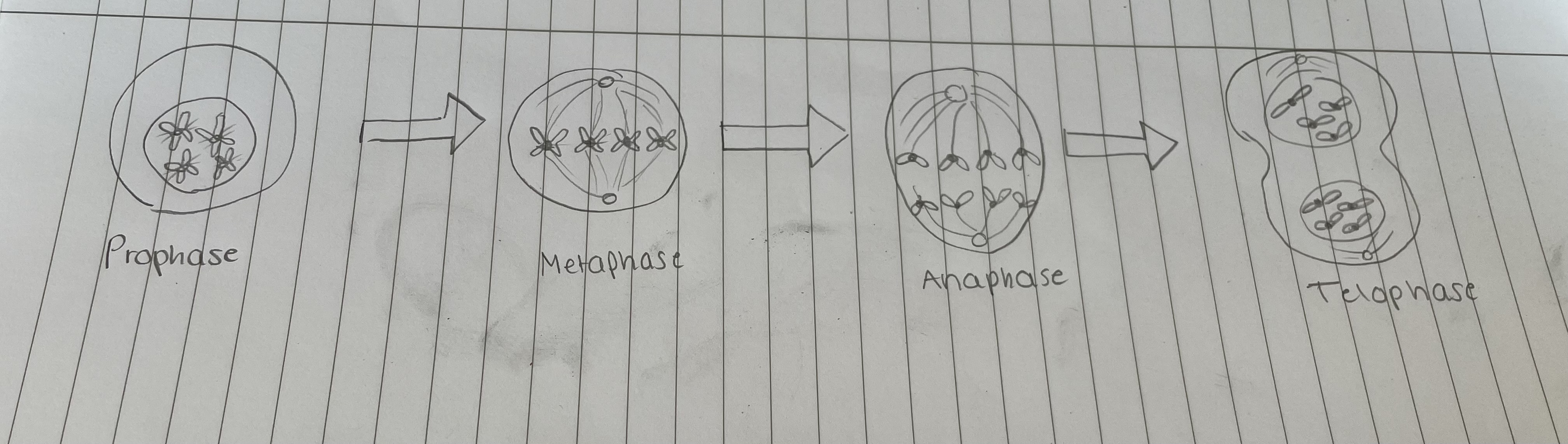
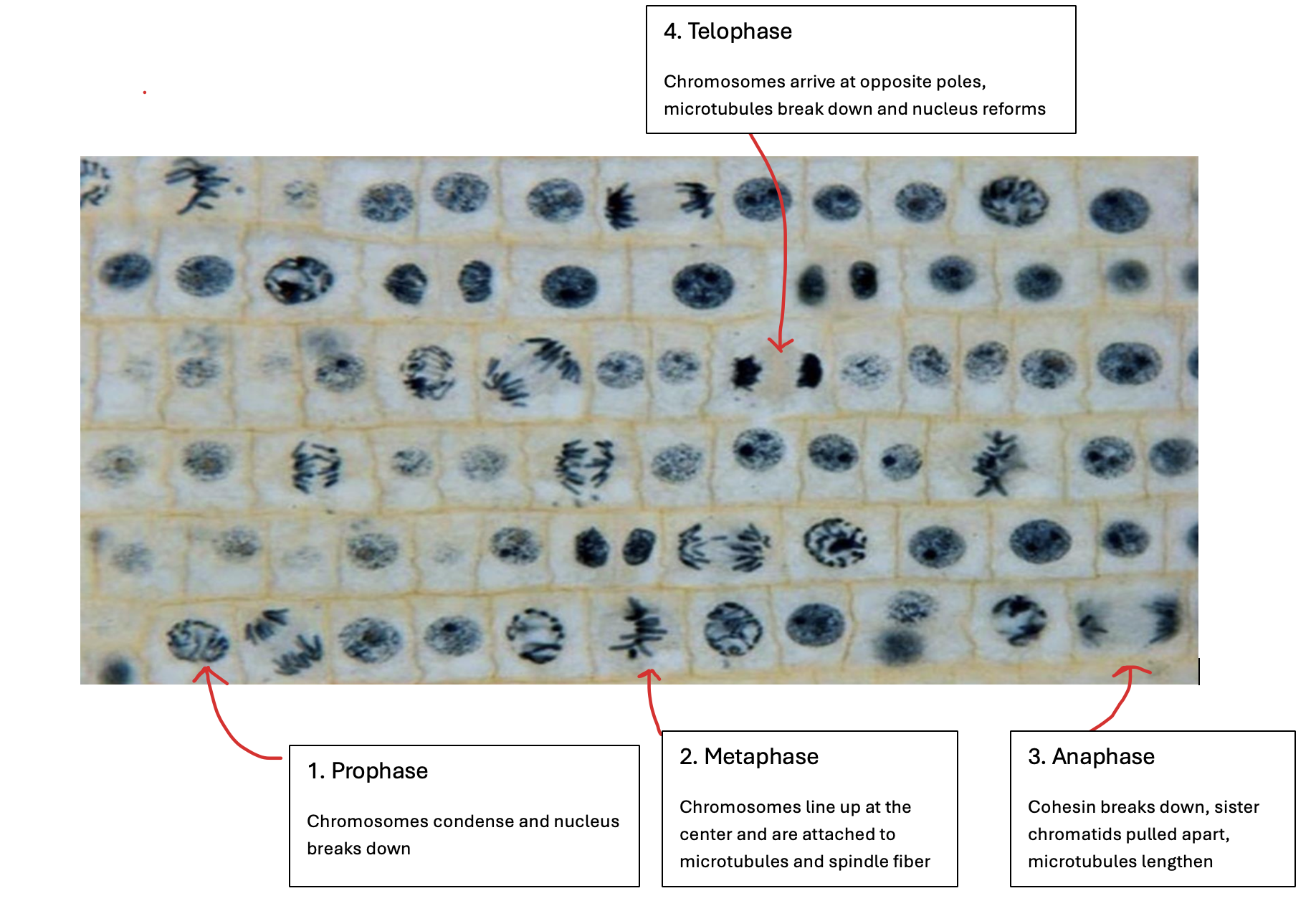
What are the phases of mitosis?
Prophase - chromatin condenses into chromosomes, and the nucleus breaks down
Metaphase - chromosomes line up at the center and each sister chromatid is attached to microtubules attached to a spindle fiber at opposite poles of the cell
Anaphase - cohesin which binds the sister chromatids together breaks down. Sister chromatids are pulled apart towards opposite poles, and microtubules lengthen, making the cell longer
Telophase - chromosomes arrive at opposite poles. Nucleus begins to form around each set of the chromosomes. Microtubules break down
When does cytokinesis occur?
It occurs when the cytoplasm and organelles divide. This can be at the same time as mitosis.
How is cytokinesis different in plant and animal cells?
In plant cells, the cytoplasm and organelles are separated through a cell plate, which eventually forms a cell wall, splitting the cell into two daughter cells. In animal cells, a cleavage furrow forms, which splits the cell into two daughter cells.
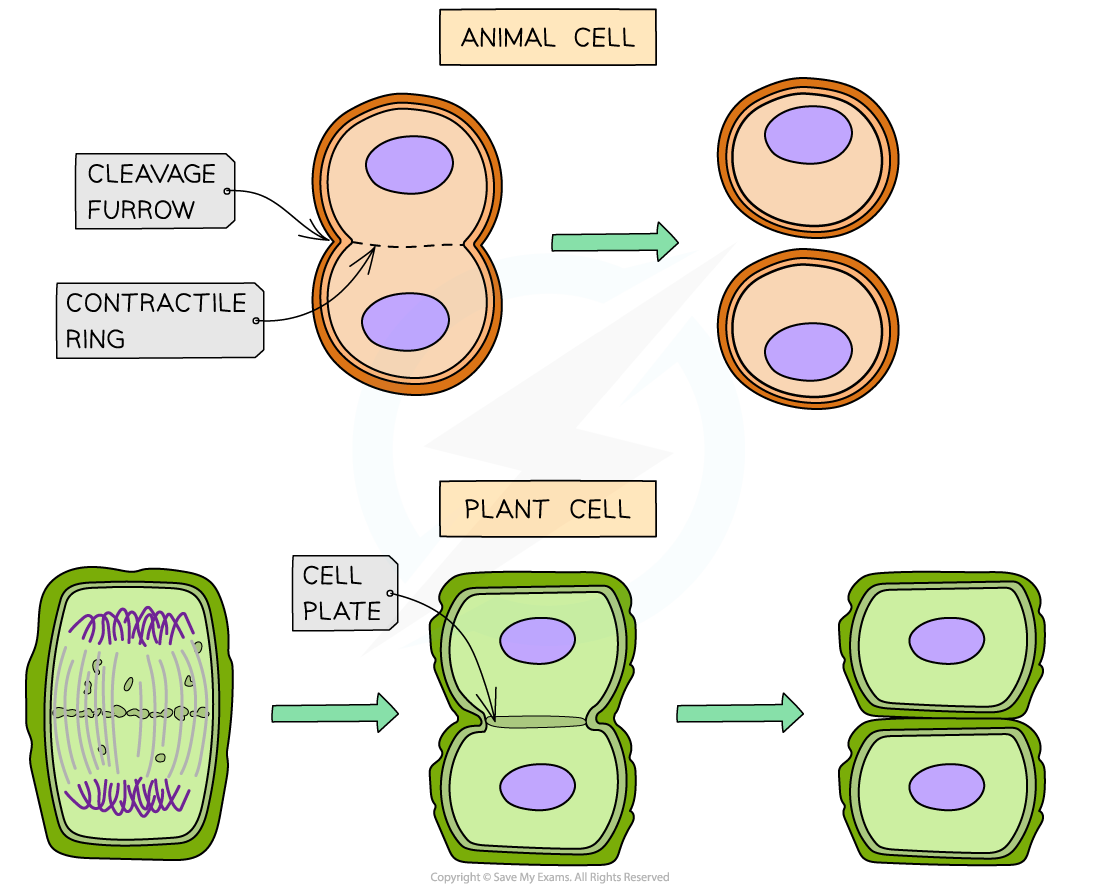
What is equal vs unequal cytokinesis?
Equal cytokinesis is when the cytoplasm and the organelles are equally separated into each new cell.
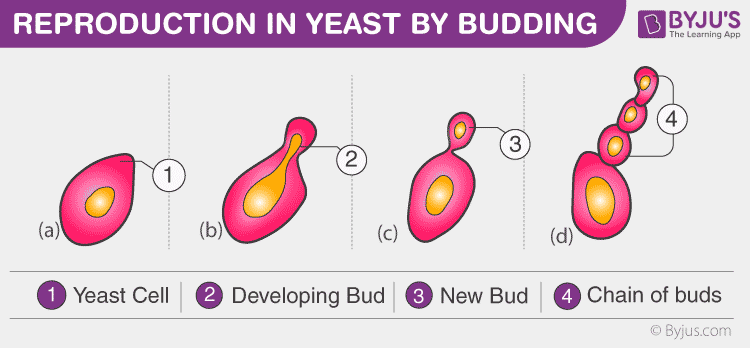
Unequal cytokinesis is when the cells are unequally divided and the daughter cell only receives a small part of the cytoplasm. This is called a bud, and is often used by yeast to reproduce asexually.
What is oogenesis?
When a new egg cell is produced. This is when during cytokinesis, the cytoplasm splits into one large egg cell and three small buds. The large volume of the egg cell contains all the nutrients for embryonic development
Identifying phases of mitosis under a microscope
What are homologous chromosomes and what alleles can they have?
Homologous chromosomes are the pair of chromosomes where one is inherited from the mother, and the other is inherited from the father. These can have the alleles of being homozygous (AA or aa) or heterozygous (Aa)
Where are homologous chromosomes found?
In every cell except for gametes, as they only have one set of chromosomes instead of pairs
Why does meiosis occur?
It is a reduction division, and it occurs to form gametes. This is because a diploid cell needs to turn into haploid gametes in sexual reproduction
Why is there meiosis I and meiosis II?
Because cell division occurs twice during meiosis. Meiosis I is the first cell division, whereas meiosis II is the second cell division. In each round of the cell division, the cells go through each of the four stages: Prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase
What are the meiosis stages?

What is a nondisjunction error in meiosis?
When chromosomes fail to separate in anaphase I or sister chromatids fail to separate in anaphase II
How can nondisjunction lead to down syndrome?
If chromosomes or sister chromatids don’t separate properly, some cells will have an extra chromosome. People with down syndrome have an extra chromosome
How is meiosis a source of variation?
The maternal and paternal chromosomes cross over and exchange genetic information. Any combination of these can be found in each of the four daughter cells. Genetic variation can also come from mutations, during interphase when the DNA is replicated