Caldwell's large animal toxins
1/190
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
191 Terms
when working up a toxin case what populations do you want to look at
all species on farm
adult and young animal groups
how to differentiate central vs peripheral blindness
Central (visual cortex lesion): blindness with PLR (most toxicosis)
Peripheral (optic chiasm lesion): no opposite PLR
what are 4 diseases to think of with muscle fasciculations
Hypocalcemia stage 1 (milk fever)
Insecticide toxicity
WNV horses – facial tremors
listeria goat
cerebellar signs of large animals
CN 8: vestibulocochlear → nystagmus and head tilt
Intention tremor (↓fine motor control)
Ataxia, wide base stance
why might cows eat sand
soothe abomasal ulcer
Achromotrichia definition
speckled lightening of fur coat (red brown color instead of black)
Copper or sulfur toxicosis
photosensitization is a sign of what underlying problem
liver disease
what type of cardiogenic edema do cows vs horses get
cows - brisket edema
horses -ventral tummy edema
contraindication to providing supp O2
paraquat tox
drugs to control seizures
Diazepam
Phenobarbital
Propofol
Inhalant anesthesia
Often use: xylazine
contraindication to using dawn dish soap as derm scrub
do NOT use on sticky items - vegetable oil, peanut butter, mayo instead
contraindication to gastric lavage/decontamination
if worried that substance will do more damage on the way up
2 absorbants used in large animal
AC
kaopectate
3 types of cathartics/laxatives
Bulk – psyllium hydrophilic mucilloid (Metamucil) swells with intestinal contents to increase peristalsis when contact water
Osmotics – MgSO4 (Epson salt), MgOH, NaSO4, DSS (horses) – draw water into the GI tract
Lubricants – mineral oil (horses) – lubricates fecal contents and reduces water absorption
what is one thing always keep in mind when administering drugs and treating large animals
withdrawal times!
mycotoxins where found
moldy cereal grains or forage - warm temperature and high moisture
5 plant stressors
drought
flood
extreme temperatures
insects
herbicide damage
what species sensitive to mycotoxins
monogastrics
ruminants are kinda resistant
mycotoxicosis vs mycosis
mycotoxicosis - disease caused by mycotoxin exposure
mycosis - disease from fungal infxn
what are 9 mycotoxins we have to know
aflatoxin
ergot alkaloids
vomitoxin (DON)
zeralenone
fumonisins
ochratoxins
tremorgens grass staggers
aflatoxins reside in what plant
In the seeds/kernels of nuts and grains
corn
cottonseed
peanuts
cereal grains
Toxic component of aflatoxin
hepatotoxin
B1 is the most common
pathophys of aflatoxin
eat it
direct damage to proteins, enzymes, DNA of hepatocytes
cellular necrosis, immune suppression, mutagenesis and neoplasm
what species most sensitive to aflatoxins
poultry, young piglets, growing animals and high producing (young and monogastric)
CS of aflatoxins
Acute
Sudden Death
Prolonged prothrombin time
Hemorrhage
Petechiation
Bloody diarrhea
Anorexia
Rumen atony
Ataxia
Tremors
Abortion
Liver failure (Icterus)
Chronic/vague
Poor growth
Poor milk production (damaged proteins)
Poor feed conversion (damaged proteins
Rough coats
Ill thrift
Immunosuppression
Hepatic fibrosis
Infertility
Carcinogenesis
production animals DO NOT produce with damaged livers
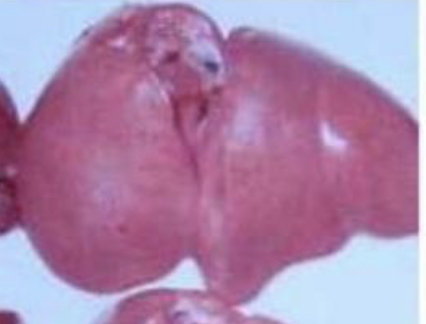
what mycotoxin caused this light and big liver
aflatoxin - poultry
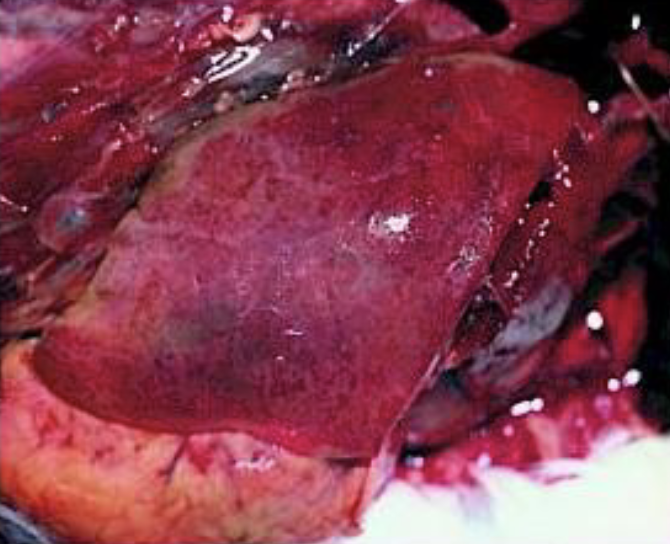
what mycotoxin caused this liver pathology
aflatoxin - focal hemorrhages
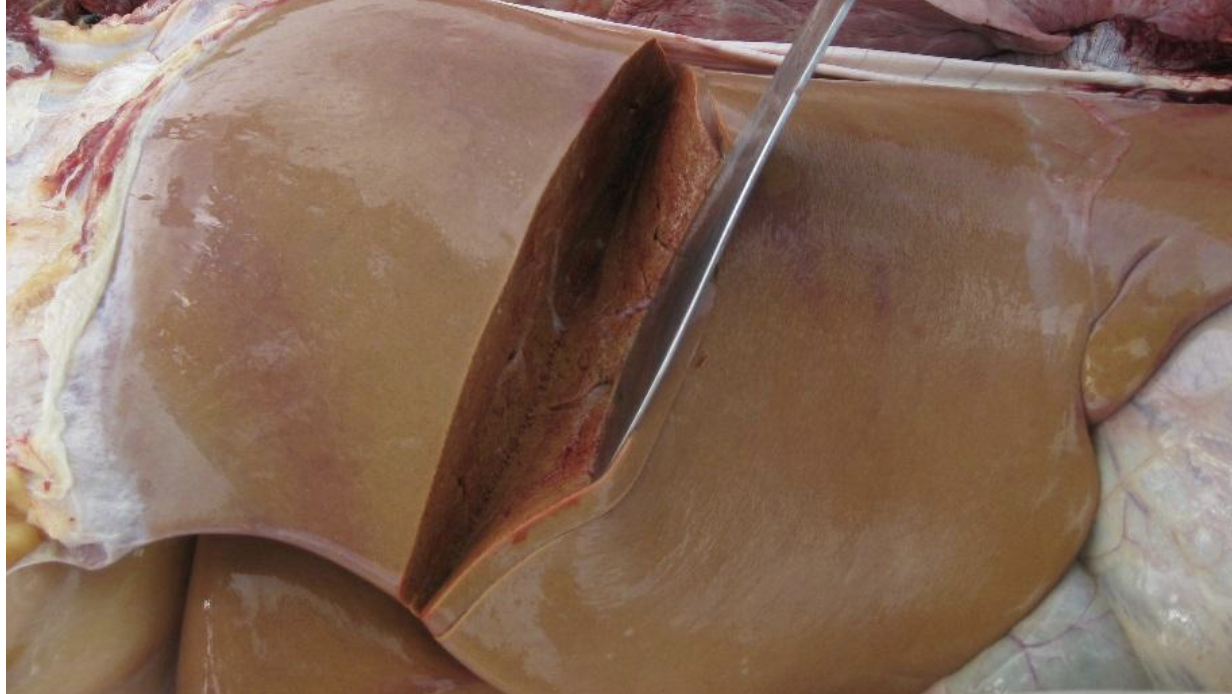
what mycotoxin did this cow die of
aflatoxin - nutmeg liver, yellow, mottled
dx aflatoxin
MDB
CBC
chem- liver failure
high leakage enzymes
sample the feed
tissue biopsy - kidney, liver
corn glows under blacklight sometimes
Tx aflatoxin
remove contaminated feeds
supplement with trace minerals and free radical scavengers (Vit E and Se)
fix storage and clean grain
ammoniation of feed to reduce fungal colonization
adding binders to TMR
ergot alkaloids affect what plant
fescue and cereal grains (rye, oats, wheat, triticale)
toxic components ergot alkaloids
Endophyte ergovaline
Claviceps purpurea
what are 3 pathologies associated with ergot alkaloids
vasoconstriction
hypoPRL
fat necrosis
pathophys for vasoconstriction, hypoPRL, fat necrosis
Pathophys vasoconstriction
EAs activate α1 – adrenergic and serotonin receptors (VC arteries)
inhibit D1-dopamine receptors (block VD)
=vasoconstriction of small vessels and poor peripheral blood flow
exacerbated by cold weather = ischemia and necrosis
hot weather = can’t dissipate heat normally (cannot move blood to periphery to cool)
Pathophys hypoprolactemia (low Prl)
Ergovaline induces overstimulation of D2-dopaminergic neurons (hypothalamus)
Excess dopamine inhibits production and release of Prl (esp mares)
=↓Prl = agalactia, prolonged gestation, altered placental physio
Prolonged gestation = big foal = dystocia = no colostrum
Pathophys fat necrosis
Mature animals
Unknown pathopys —> Vasoconstrictive necrosis is suspected
Soaponification of fat
Pendulous mass in mares —> entrap SI
Hard mass mesentery of cow
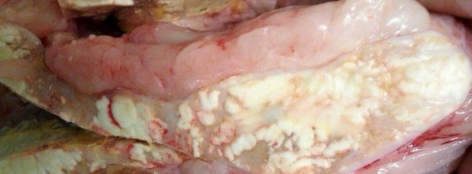
what mycotoxin causes this
ergot alkaloids
Hot weather CS of ergot alkaloids
aka summer slump
hyperthermia
Open-mouthed breathing
Lethargy
Unwillingness to graze → robs calves of rapid growth (poor hair coat, ↓shed)
Poor milk production/performance
Poor growth rates
Infertility/can’t stay preg
Cold weather CS of ergot alkaloids
aka frost bite - Vasoconstriction
Sloughing feet, ear tips, tails, teats
Swelling and erythema of affected tissues
Lameness – coronary bands
Mastitis
Hippo cows – no tips of ears (frostbite)
what CS does ergot alkaloids do in mares
prolonged gestation
dystocia
agalactia
dx ergot alkaloids
sample the feed at various depths of hay
Tx ergot alkaloids
remove suspect feed, clip seed heads and avoid excess fertilization
can use endophyte free fescue but will get infected eventually
only feed cleaned grains
ammoniate hay - reduce ergovaline conc.
supportive care -protect from heat/cold
antibiotics for secondary infections
domperidone within last 30-60 day gestation - cure hypoPRL
breed cow that are raised with it as they are more tolerant
what plant does vomitoxin/DON (Deoxynivalenol) live in
corn, wheat, barley in cool, wet and delayed harvest conditions
what species is susceptible to vomitoxin
swine > ruminants
pathophys of vomitoxin
stimulate CRTZ in medulla oblongata
inhibit protein synthesis - poor production and/or immunosuppression
CS of vomitoxin
Emesis
Diarrhea
Feed refusal
↓feed uptake
Impaired nutrient absorption
Poor production
Clin Path abnormalities reflect excessive vomiting: ↓ Na and K,
dehydration, metabolic alkalosis (throw up HCl → ↓Cl alkalosis)
dx vomitoxin
detection in feed
tx vomitoxin
remove DON and provide supportive care
properly storage conditions + add binders to feed
Zeralenone toxin grows in what plants
corn and other grains cooler conditions than DON
what species most sensitive to zeralenone
swine - delayed detox and enterohepatic recirc.
pathophys of zeralenone
estrogenic compound
dairy cow -delayed estrous, swollen vulva
often used as growth implant in steers to improve rate of gain
CS of zeralenone
Hyperestrogenism
Swollen vulva and mammary glands
Prolapsed rectum (repeat tenesmus)
Overdeveloped reproductive tracts
Nymphomania (heat, humping gilts)
Pseudopregnancy (fluid)
Early embryonic death (infertility) in older sows
↓litter size (8-10 when normally 12-18)
Estrogenization of males – ↓ testicular weight, ridden by other males
+/- V+ if DON toxin also involved
Tx of zeralenone
same as DON
remove offending feed
add binders to feed
Fumonisins like to grow in what plant
corn with broken kernels
pathophys of fumonisins
block sphingosine to become sphingosine lipid
blocks lipid rich cell membrane on neurons, myocardial, hepatocytes
= liquifactive necrosis of neurons - chronic exposure
= myocardial necrosis - PIGS
= direct hepatotoxicity - acute high exposure
= equine leukoencephalomalacia - white matter of cerebrum necrosis
CS of fumonisins
ELEM
Rapidly fatal neuro dz
CS appear at irreversible necrosis → horse die
Altered mentation – depression to excitability → “furious rabies”
Head pressing
Ataxia
Blindness
Seizures
Death
Porcine pul. Edema + LHF
Damage to the left ventricle induces congestive pulmonary hypertension and edema
Sudden death
Dyspnea
Cyanosis
Any species
Icterus
Ill thrift
Poor Production
dx fumonisims
necropsy
clin path suggestive of liver failure
tx of fumonisims
none once CS
prevention is straight forward
ochratoxin is found in what plants
cereal grains
dried fruit (figs)
coffee
wine
nuts/pistachios
what species are LEAST sensitive to ochratoxin
ruminants - can break down toxin
pathophys of ochratoxin
potent nephrotoxin
damage PCT - acute renal failure
= hyaline casts, dilated tubules, renal fibrosis
CS of ochratoxin
Acute renal failure
Uremia – ammonia smell
Depression
Anorexia
Reduced production
Diarrhea
Dehydration
Anuria/oliguria
dx of ochratoxin
based of CS and toxin detection
Clin path of renal failure
tx ochratoxin
like any other acute renal disease
remove offending feed
supportive care - fluids/plasmalyte, electrolyte correction
Tremorgenic grass stagger toxins grow in what type of plants
perenial ryegrass
bermuda grass
dallisgrass
bahia grass
**highest concentration in the seeds** in the dry weather
what species is affected by tremorgens grass staggers
ruminants mostly
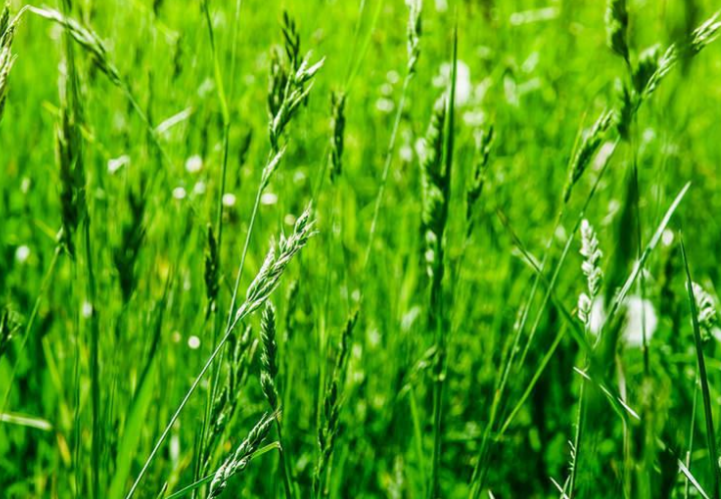

perennial ryegrass
clumped seed head
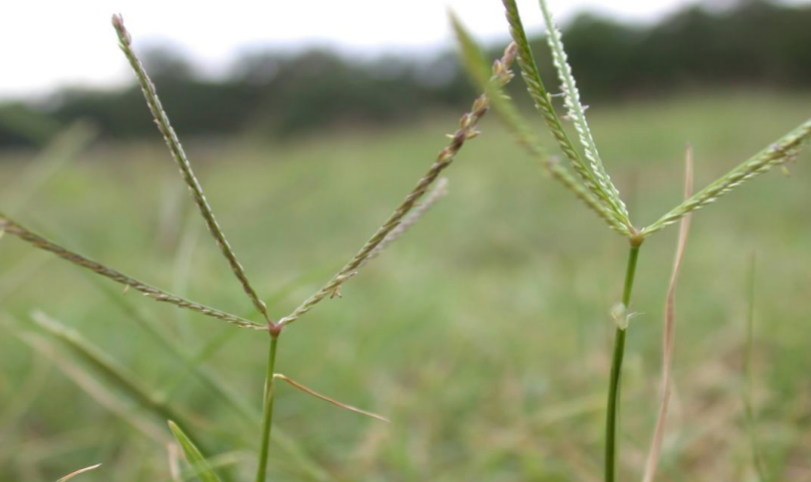

bermuda grass
looks like turkey foot
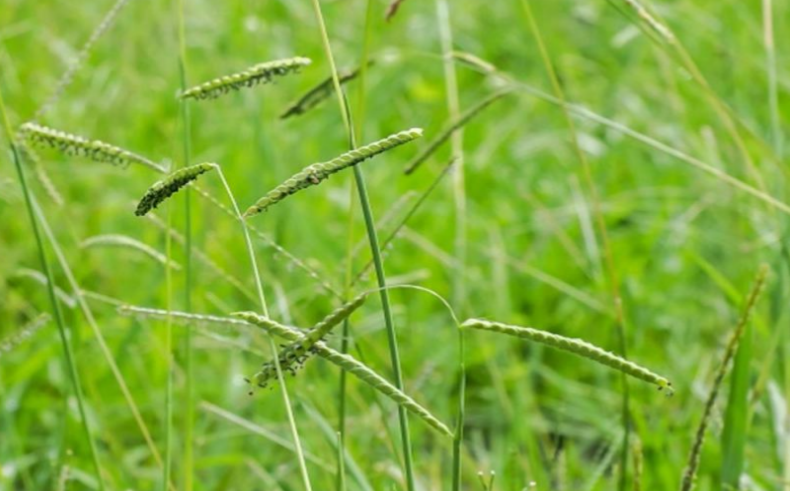

dallisgrass
alternating seed heads

bahia grass
“peace sign”
pathophys of grass staggers
neurotoxin = stagger toxins
stimulate GABA receptors in CNS —> impair motor neuroMSK control = tremors and incoordination
CS of grass staggers
Generally mild
Staggers – ataxia
Hypermetric gait, no feed under her when walk
Muscle fasciculation
Head, ear, flank tremor
Weakness
Proprioceptive deficits
Misadventures – lost cow cannot get out of ditch, fell of cliff
dx grass staggers
CS and Hx
feed or grass analysis
tx of grass staggers
remove from offending pastures and add hay
CS resolve in 2-3 days
clip seed heads
where in environment would animal have access to arsenic
old cotton farm sheds
rotted bags of pesticides
salt leached into env from arsenic
pathophys of arsenic tox
disrupts cellular metabolism
binds proteins and enzymes of krebs cycle
cells with high metabolic demand are selectively damaged (enterocytes, myocardial, hepatocytes, renal medullary cells)
how does arsenic act as a cardiotoxin
Acute exposure: vasodilation and capillary damage
congestion, edema, hemorrhage
Cardiotoxicity – direct damage to myocardial cells (left ventricle)
arrhythmia, ischemia, and heart failure
CS of peracute, acute, chronic arsenic exposure
Peracute
Sudden death
Within min to hrs of ingestion
Acute – GI tract hit first (absorbed here)
Colic
V+
Ataxia
Weakness
CV collapse
Blood D+
Death
Blisters and edema (dermal contact exposure)
Chronic – slow low dose, think red
Depression
Anorexia
Hemarthrosis: Stiff and enlarged joints
Profuse blood D+
Hematuria
Fatigue
Dyspnea
Intense thirst
Brick red MM
dx arsenic tox
blood or tissue sample ASAP
delayed sample has decreased concentration
necropsy - red erosions on everything
Tx arsenic tox
prevent absorption
removal from source
empty stomach contents -emesis, rumenotomy
AC
chelators - BAL, NaThiosulfate, D-penicillamine, CaEDTA
supportive care - fluids, pain meds, blood transfusion
copper where is it found in the env. for livestock to get exposed
soil and forage concentration (smokey mountain area)
what species is sensitive to copper tox
sheep
cattle and goats are less SN
monogastrics tolerate
pathophys of copper tox
directly damage cell membranes
forms free radicals
= cell necrosis
GI signs
CS of copper tox
acute - GI dz
GI irritation – acute
Mucosal erosions – necrosis
Blue-green discoloration to the bowel of lumen
Blood D+ - big mucosal damage
chronic - liver dz
intravascular hemolysis crisis
sudden death - RBC no carry O2
anemia
icterus
HgBuria
↑RR
hypoxia
acute renal failure
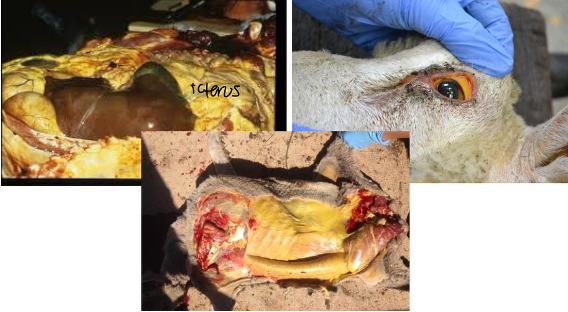
what heavy metal caused this
copper
dx copper tox
serum or liver biopsy
eval minerals/feed + water
necropsy -liver, kidneys gun metal sheen, portwine urine
Tx copper tox
blood transfusion
chelators - NaThiosulfate
↑dietary molybdenum, sulfur, zinc
ALWAYS check mineral label for sheep
source of fluoride tox for large animals
soil and forages near industrial centers
rodenticides
toothpaste
pathophys of fluoride tox
abnormal bone and tooth formation
binds with hydroxyapatite in bone
increased periosteal rxn and cortical thickening
teeth - soft chalky, weak enamel and dental dysplasia
CS of fluoride tox
lameness
abnormal hoof wear
abnormal keratin growth
mottled, chalky, soft enamel
early loss of dentition with wear
dx fluoride tox
bony lesions
tissue or urine conc.
rads/necropsy
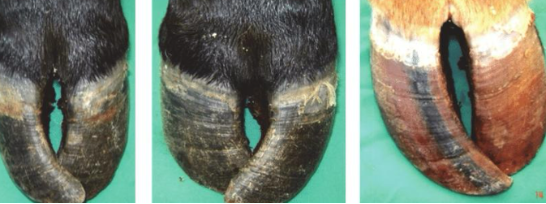
what heavy metal caused this
fluoride
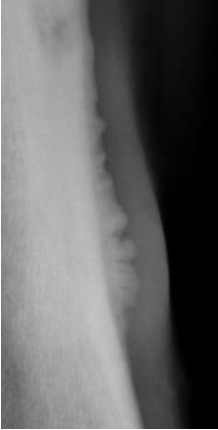
what heavy metal tox caused this
fluoride
Tx of fluoride tox
early lesions may resolve with time
dentition is permanent
avoid excess exposure or high risk env.
consider well water or filtered water instead of city water
source of iodine tox for large animals
bad mineral formulations
iatrogenic treatments from owners
goitergenic plants - soybeans, brassicas
what are 3 iatrogenic ways that large animals get iodine tox
Na I - treat lumpy jaw, wooden tongue, nasal granulomas
EDDI - added to mineral in excess
kelp supplement
pathophys of iodine tox
insufficient dietary iodine
low T3/T4
Low feedback stimulus
excess TSH made —> goiter
dietary excess
paradoxical suppression of T3/T4 production
still excess TSH —> goiter
CS of iodine tox in foals
knot on knot head foats - congenital hypothyroid
mom fed excess iodine during gestation —> foal with goiter
11 mo exposure
mare concentrate iodine in milk
CS of iodinism
Alopecia – face/head
Scaling of skin
Catarrhal – ropey nasal discharge
Excess tearing
Tachypnea
Abortion- One case of goiter present in an aborted fetus

what heavy metal caused this
iodine
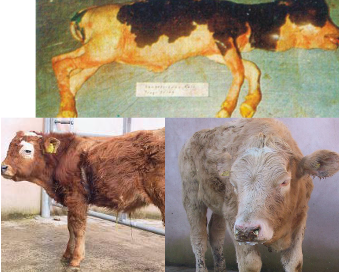
what heavy metal caused this
iodine
tx of iodine tox for foal vs livestock
Tx of congenital hypothyroid foals
Removal of iodine supplementation, milk replacer, foals typically resolve in time (couple weeks)
mares show no CS
Avoid soybean and brassica based diets - Especially in pregnant mares
Tx – no specific tx for livestock - Removal of excess will relate to ↓ CS over time
avoid excess iodine in the diet (put down supplements)