CPR1 - Histology {1.02}
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
What is serum?
Plasma - clotting factors
What are the characteristics of erythrocytes/RBCs?
Biconcave disc, bag of hemoglobin with no nucleus and barely any organelles
What are the characteristics of the erythrocyte/RBC cell membrane?
Has antigenic sites (blood grouping), attached to spectrin and ankyrin
What is the function of erythrocytes/RBCs?
Transport of oxygen & carbon-di-oxide
What is Polycythemia?
the body makes too many red blood cells, thickening the blood and slowing flow
What is Hereditary Spherocytosis?
Defect in cytoskeleton – spectrin & ankyrin causing weakening of the lipid bilayer and premature destruction of RBCs
What is sickle cell anemia?
Mutation of beta globin chain of hemoglobin causing sickling & destruction of RBCs
What is hemolytic anemia?
blood disorder where red blood cells (RBCs) are destroyed faster than the bone marrow can replace them
What disorders are considered a part of hemolytic anemia?
Sickle cell anemia and hereditary spherocytosis
In order to study the morphology of leukocytes, which of the following blood fractions would you prefer?
Buffy coat
What is the microscopic shape of the nucleus of a neutrophil?
3-5 lobes
What is the microscopic shape of the nucleus of eosinophils and basophils?
Bilobed
What WBCs have specific/secondary granules?
Granulocytes (Neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils)
What percent of leukocytes are neutrophils?
50-70%
What percent of leukocytes are lymphocytes?
20-40%
What is the lifespan of neutrophils?
1-4 days
What are the characteristics of leukocytes in circulation?
Spherical and inactive
What are the characteristics of leukocytes after migration to tissues?
Amoeboid and motile
What is margination?
Leukocytes move from the center of the bloodstream to the periphery
What is diapedesis?
leukocytes squeeze out from blood vessels into inflamed tissues to fight infection
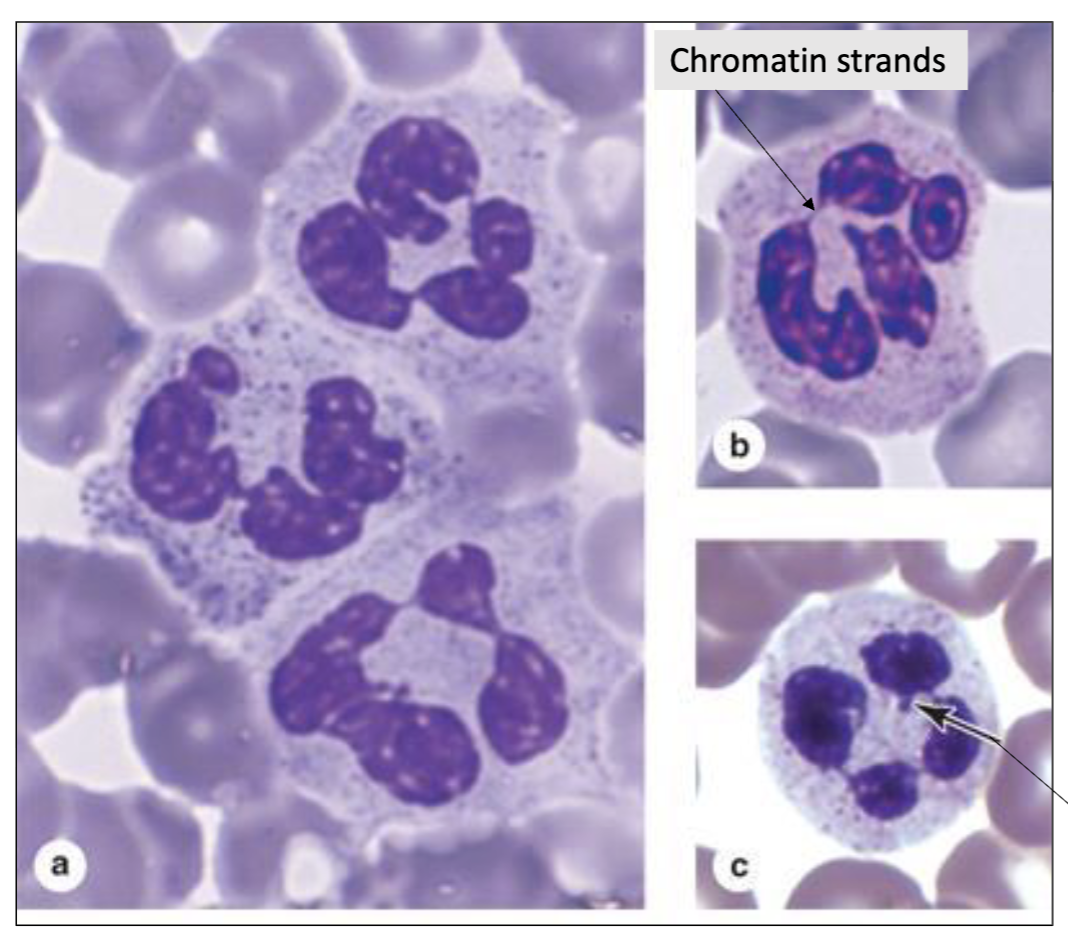
What type of cell is seen here?
Neutrophil
What type of cell is seen here?
Neutrophil
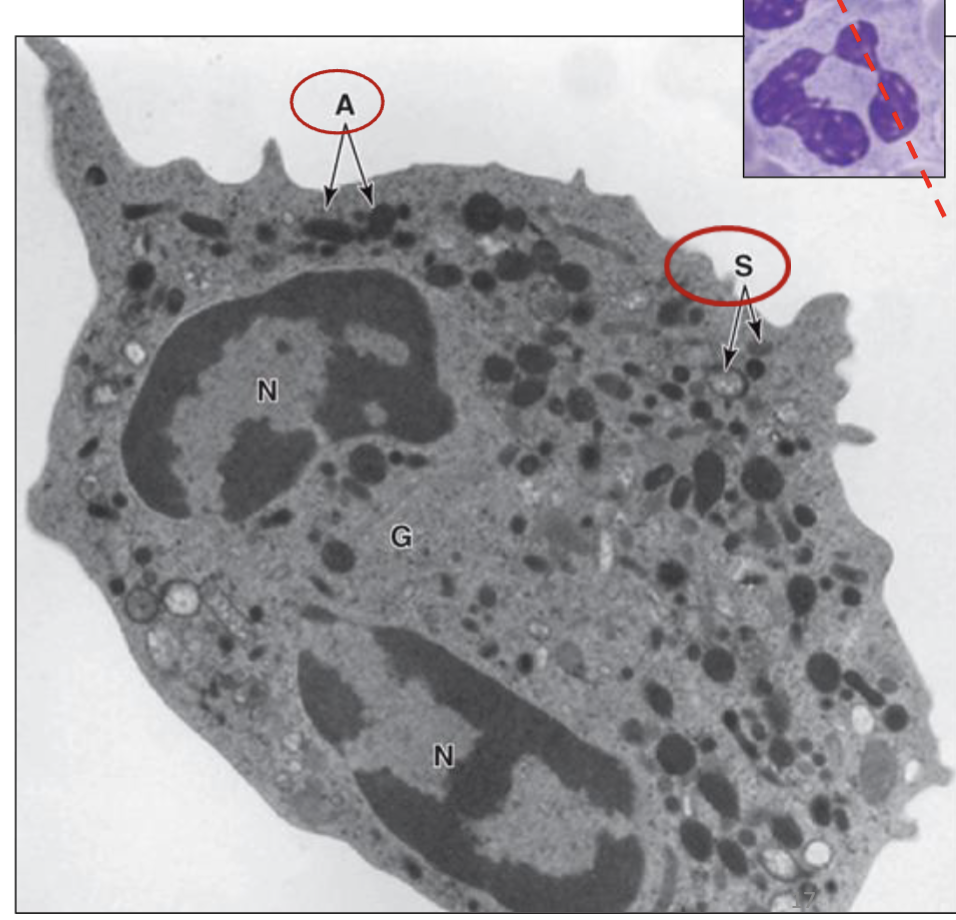
What type of granule of the neutrophil is seen in A?
Azurophilic (primary) granules/ Lysosomes
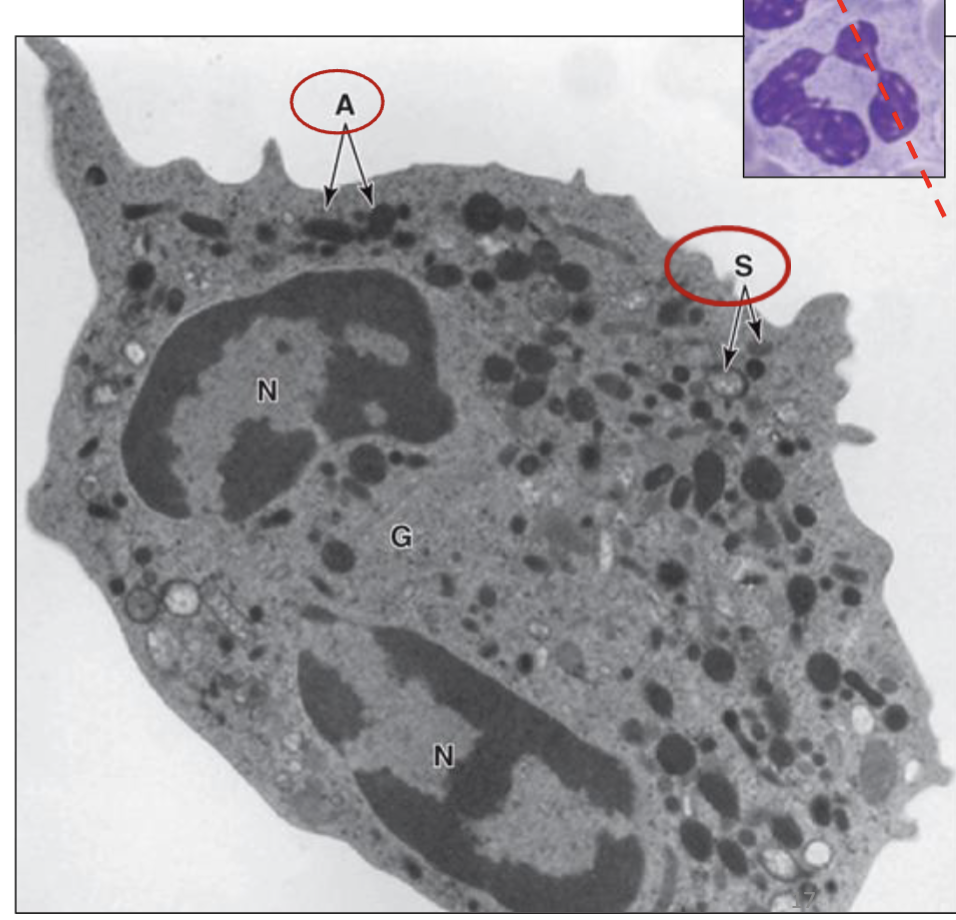
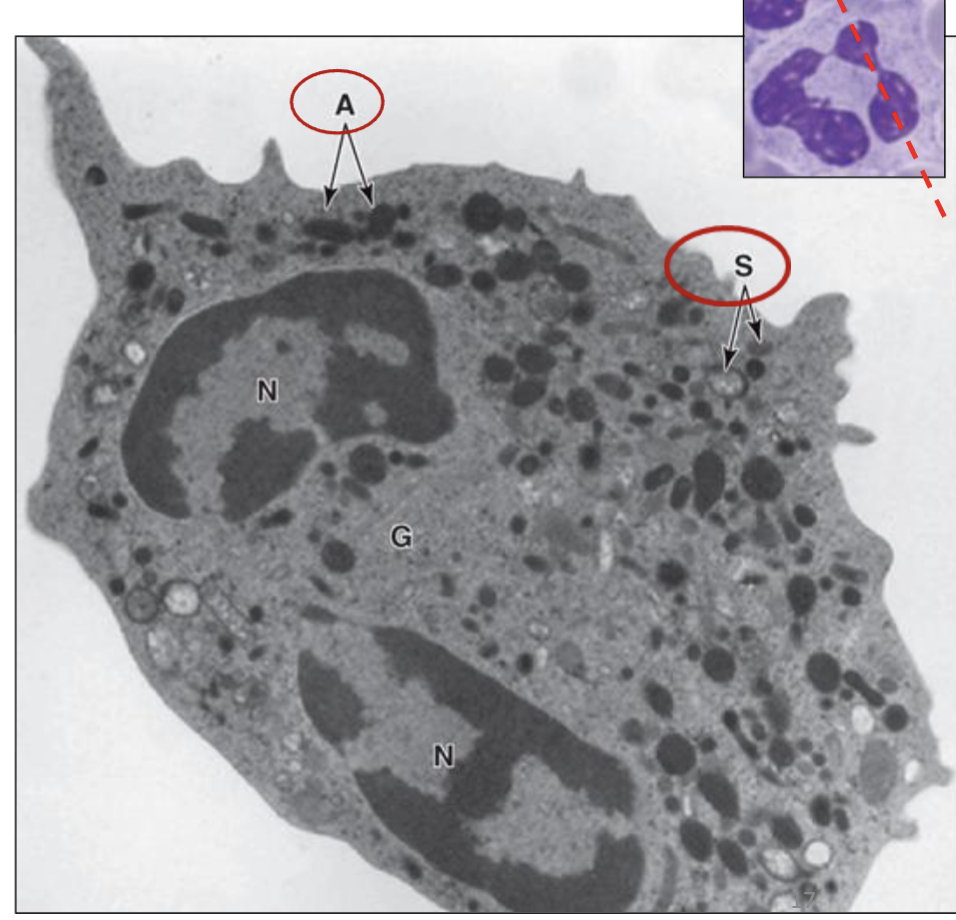
What type of granule of the neutrophil is seen in S?
Specific (secondary) granules
What is found in Azurophilic (primary) granules/ Lysosomes of neutrophils?
Myeloperoxidase, lysozyme, defensins
What is the function of Azurophilic (primary) granules/ Lysosomes of neutrophils?
Degrade phagocytosed microorganisms
What is the function of enzymes found in specific (secondary) granules?
Digest matrix & destroy bacteria
When is the enzymes of specific (secondary) granules released by neutrophils?
After migration to tissues
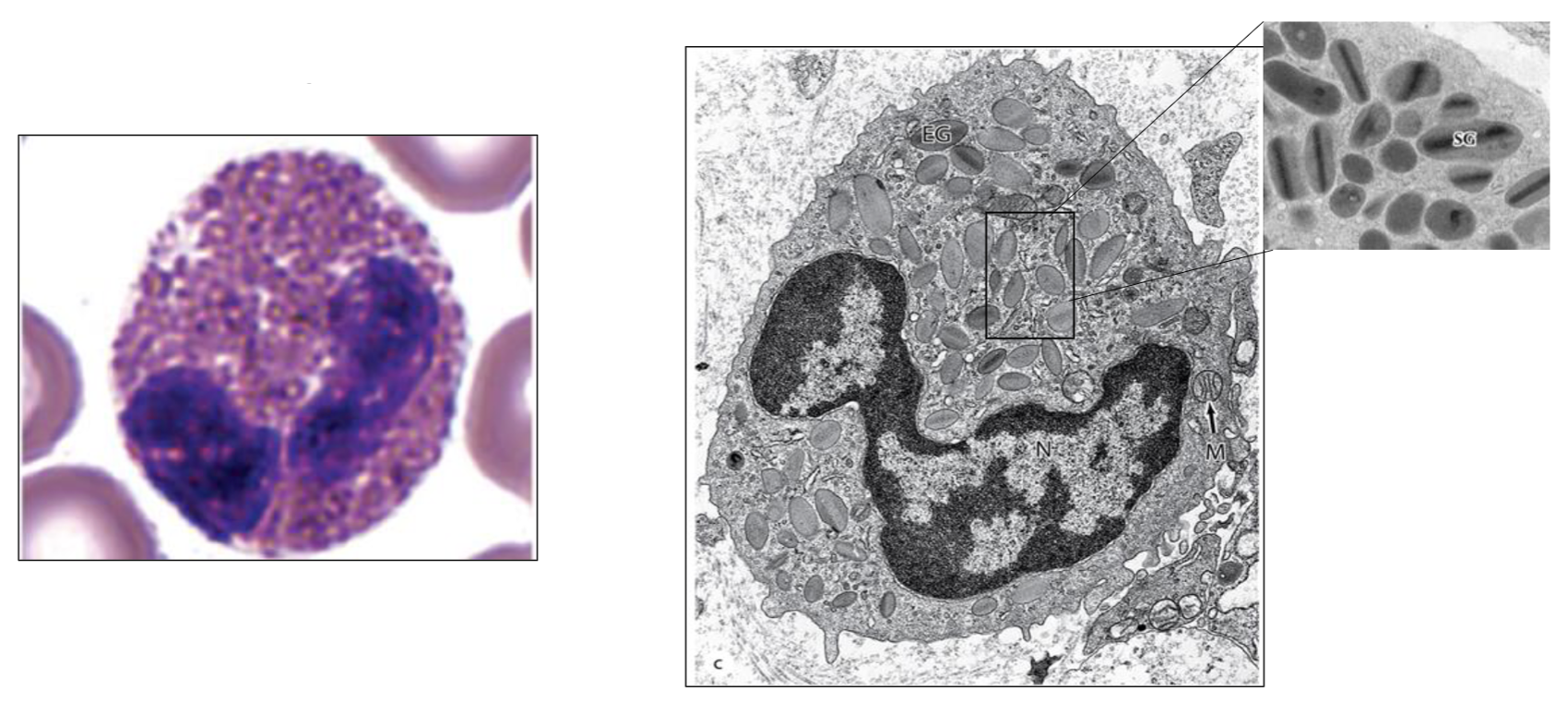
What type of cell is seen here?
Eosinophil
Where are eosinophils found?
Respiratory and gastrointestinal mucosa
What are the functions of eosinophils?
Kill parasites/helminthes, Local tissue damage & inflammation in allergic reactions
What enzymes are found in eosinophil granules?
Major basic protein, peroxidase
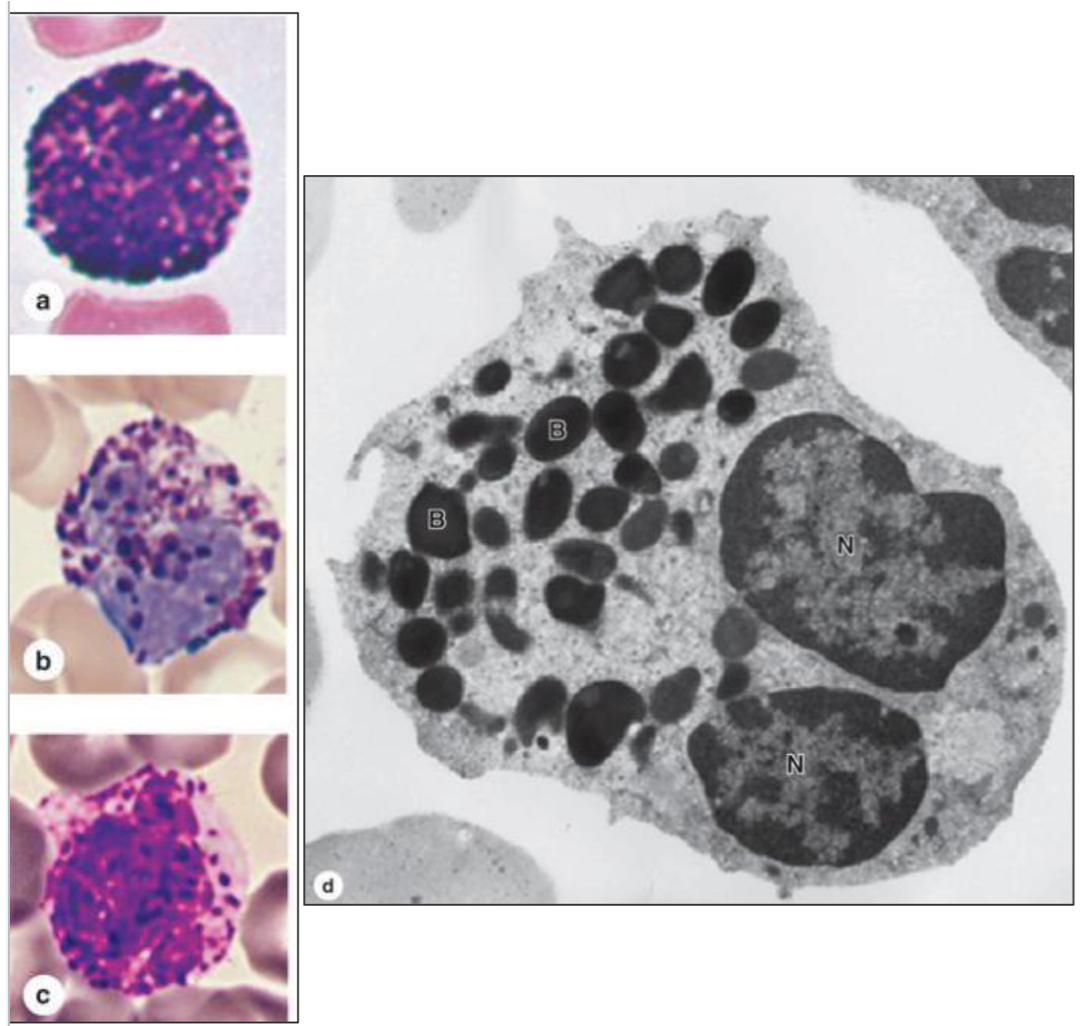
What type of cell is seen here?
Basophil
What is found in granules of basophils?
Histamine, heparin
What is the function of basophils?
Modulates inflammation in allergy, Supplements the action of mast cells
What receptor is found on the membrane of basophils?
IgE
When is neutrophilia seen?
Acute bacterial infections
When is eosinophilia seen?
Helminthic/worm infection, drug reaction, allergy
When is basophilia seen?
Myeloproliferative Disorders, Type I hypersensitivity (IgE)
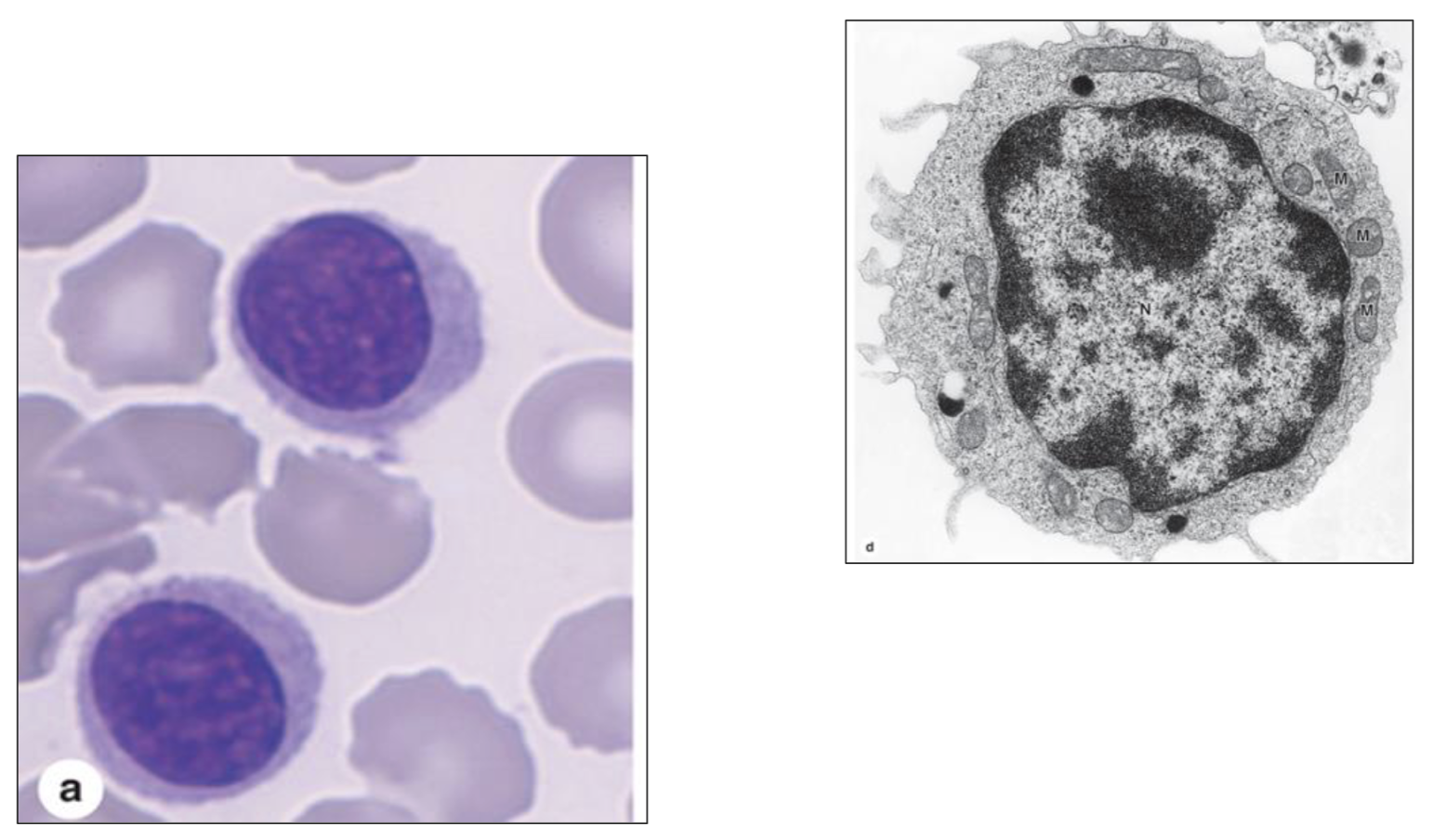
What type of cell is seen here?
Lymphocyte
What cells are lymphocytes?
B cells, T cells, NK cells
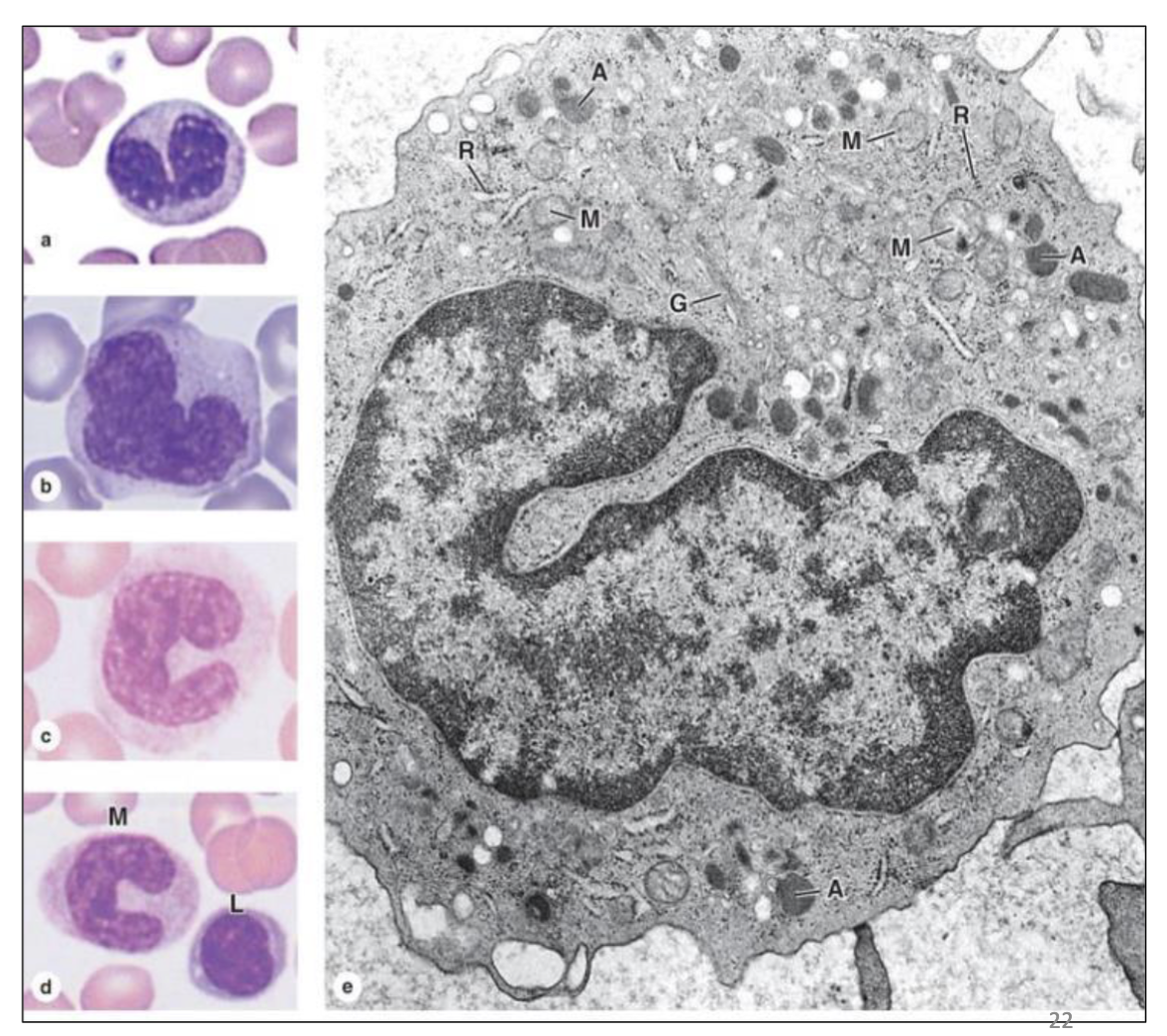
What type of cell is seen here?
Monocyte
The plasma cells are derivatives of which of the following cells?
B lymphocytes
What are monocytes precursors of?
mononuclear phagocyte system/ macrophages
What are the functions of monocytes?
Antigen-antibody uptake, Antigen presenting cells, Phagocytosis, Wound healing, Bone resorption
What are Osteoclasts, Alveolar macrophage, Kupffer cells, Microglial cells derived from?
Monocytes
When is lymphocytosis seen?
Viral infection, Tuberculosis, Pertussis, Drug reaction
What diseases cause atypical lymphocytes?
Infectious mononucleosis, Epstein-Barr virus
When is monocytosis seen?
Chronic infections, Chronic inflammatory diseases, Malignancy
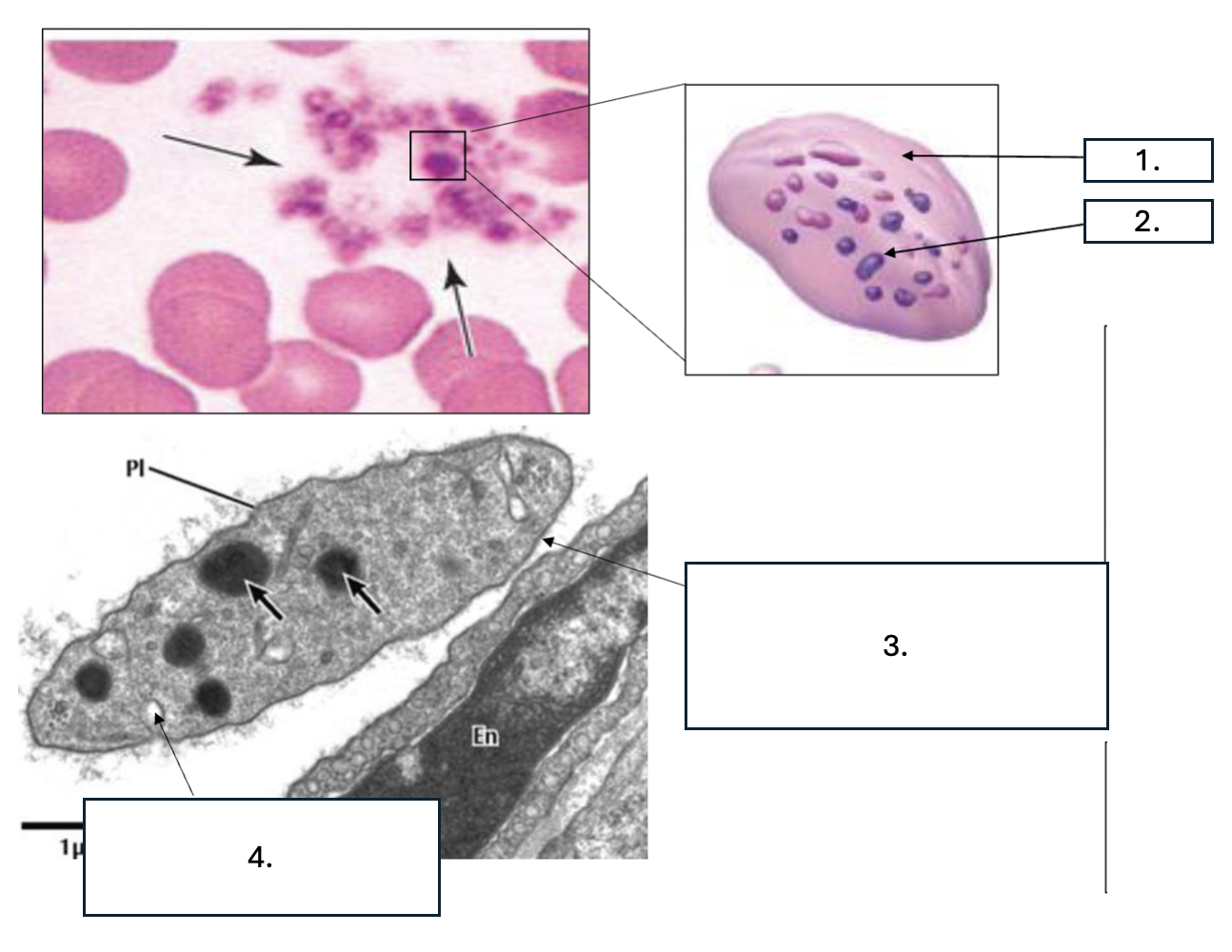
What cell is seen here?
Platelet/thrombocyte
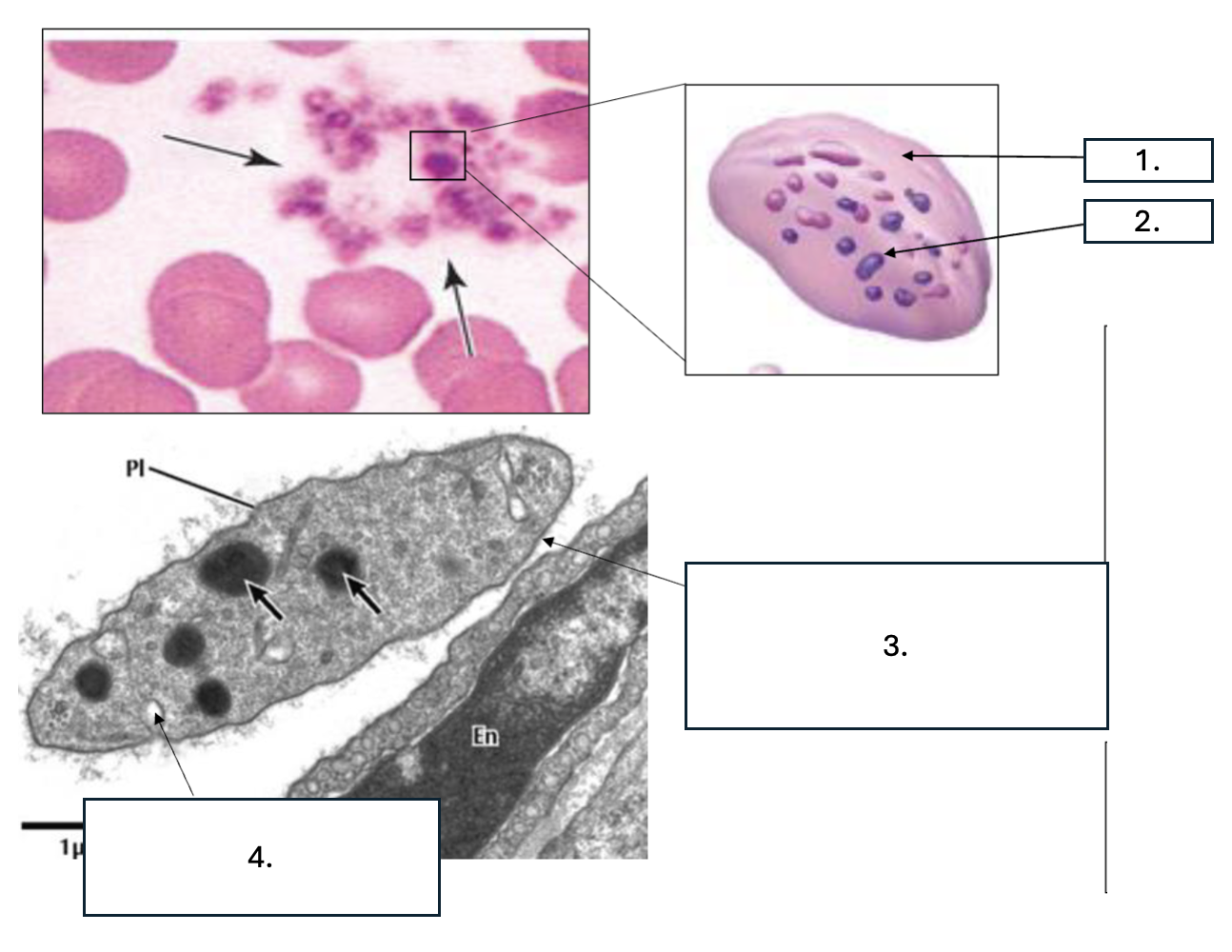
What zone is number 1?
Hyalomere
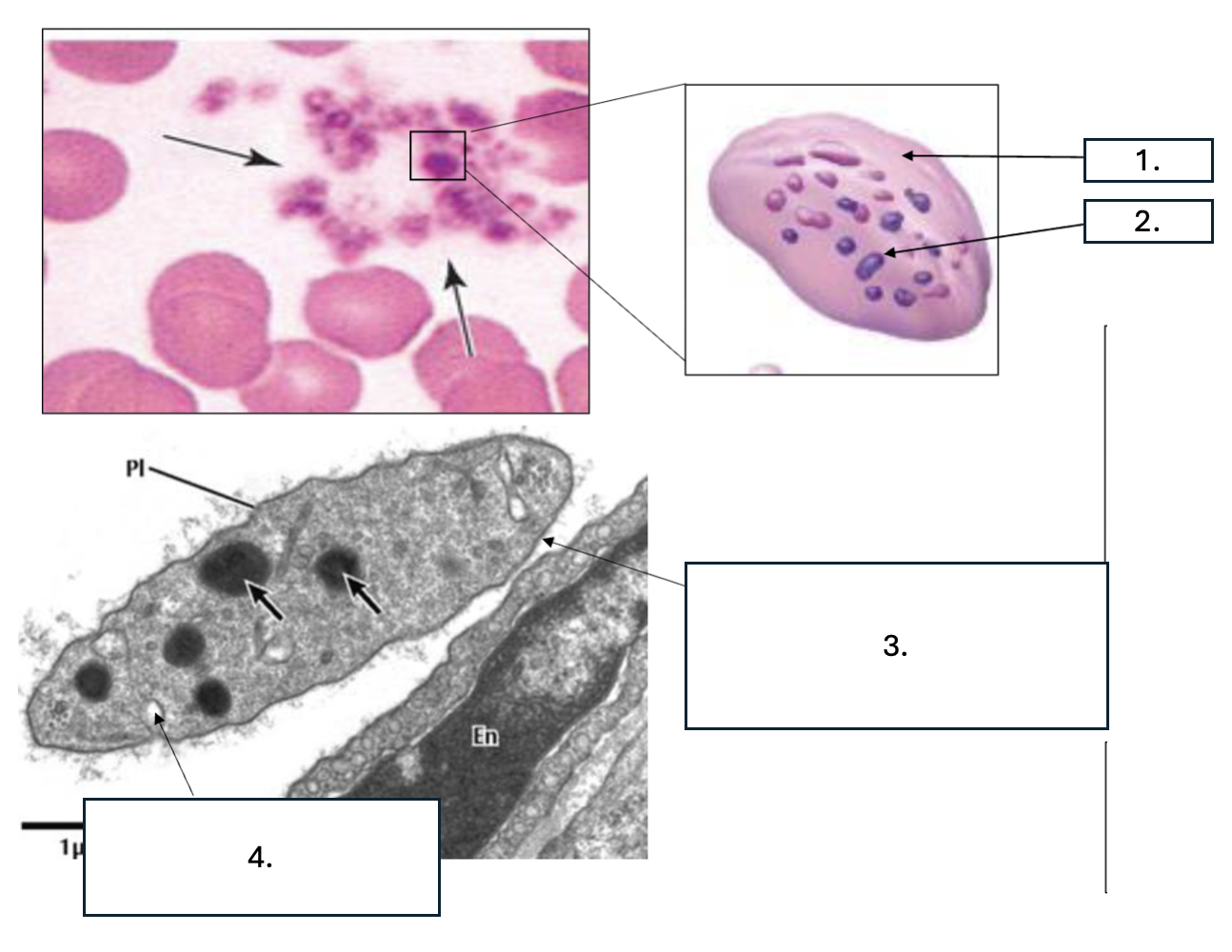
What zone is number 2?
Granulomere
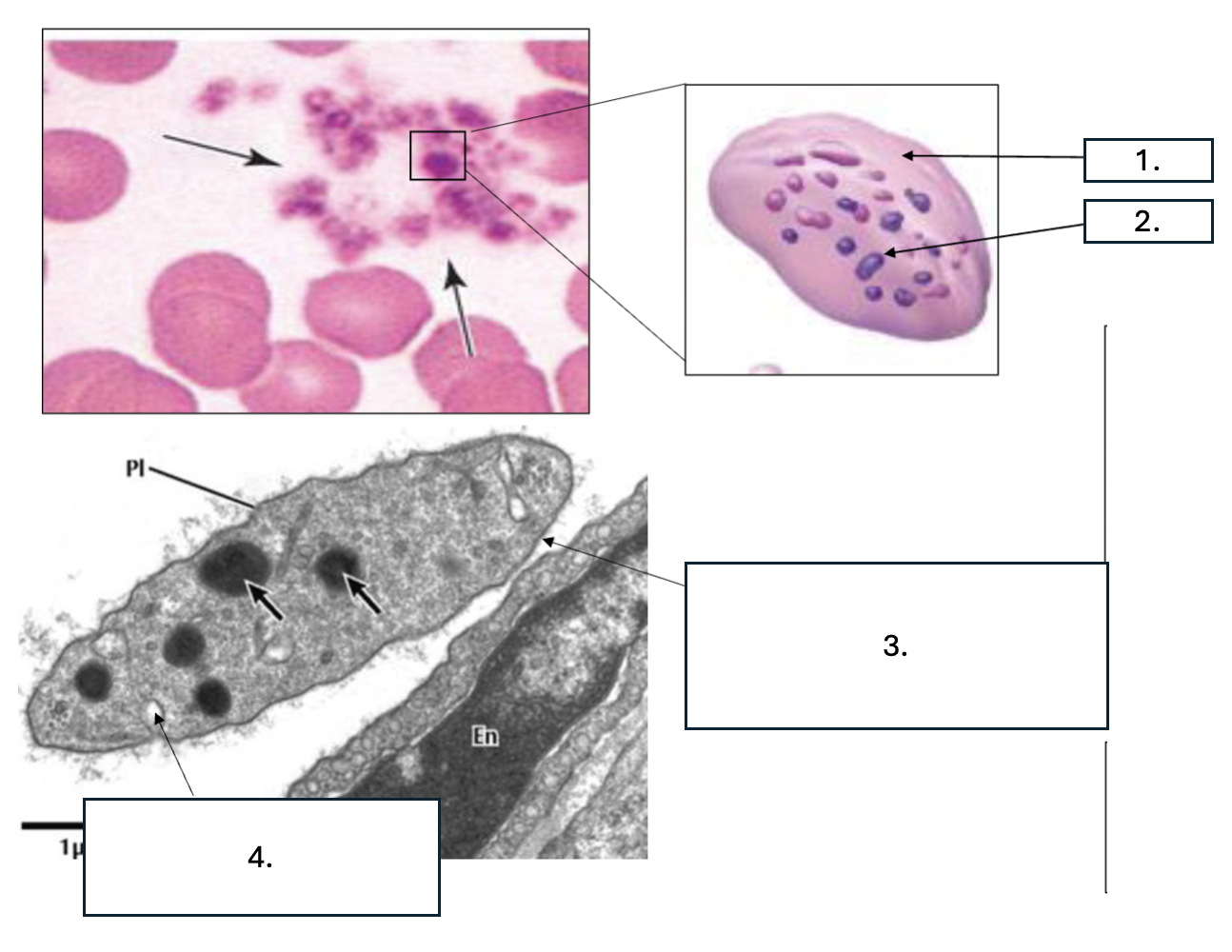
What is number 3?
Glycocalyx
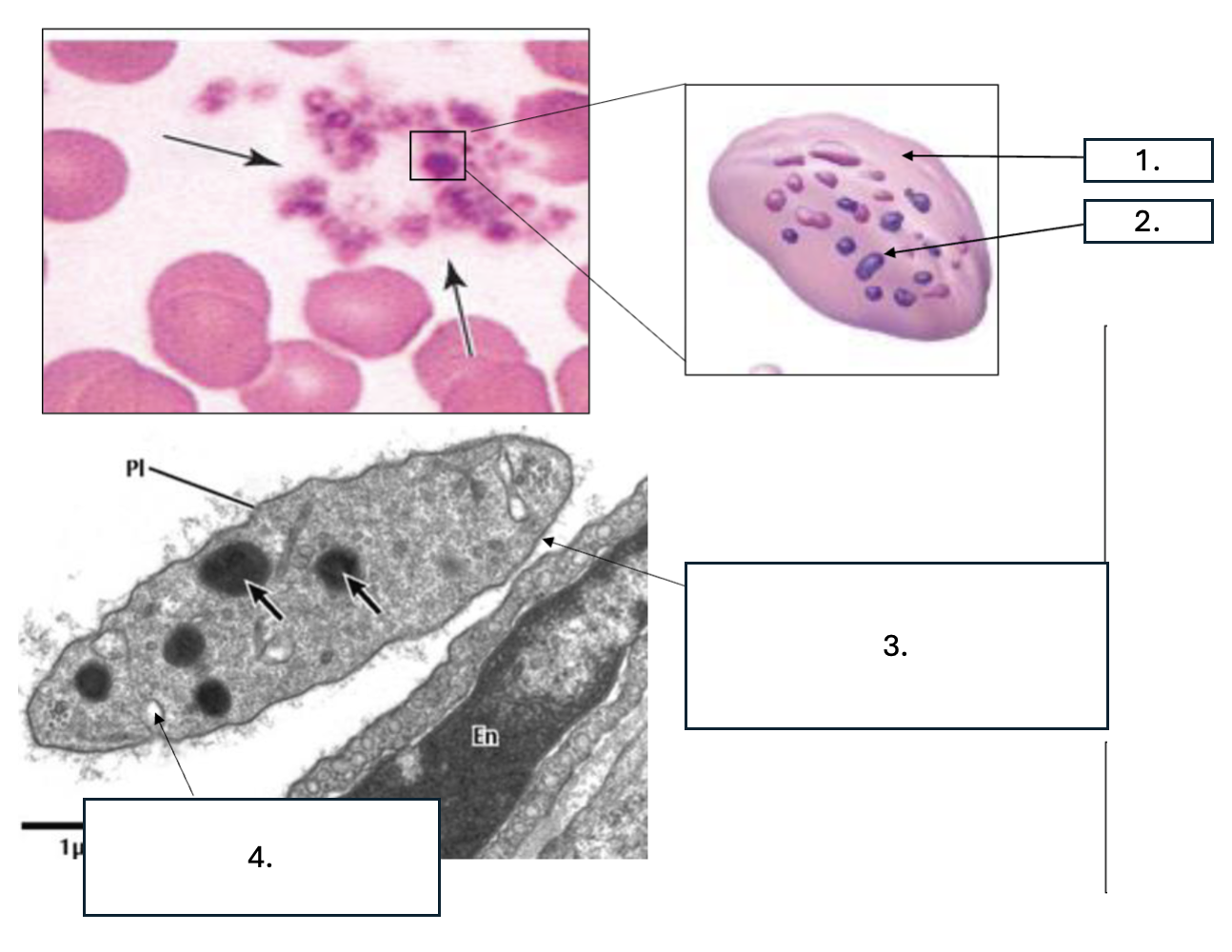
What is number 4?
Open canaliculus
What is the function of open canaliculus of platelets?
Releases granules
What is the function of the Glycocalyx of platelets?
Promotes adhesion & activation
What is the function of platelets/thrombocytes?
Promotes hemostasis, Platelet plug, Repair of microvascular injury
What is contained in the hyalomere zone of platelets?
Marginal bundle (microtubules & actin), Open canaliculi/Vesicles, Smooth ER (calcium)
What is contained in the granulomere zone of platelets?
α granules: PDGF, VWF, fibrinogen, factor V, Delta/ dense granules: ADP, serotonin
What is Thrombocytopenic purpura caused by?
Autoimmune
What is aspirins effect on platelets?
Increased bleeding tendency by blocking platelet activation
What is red marrow?
Active hemopoiesis
What is yellow marrow?
Adipose tissue
What is a bone marrow smear?
Fluid & cells of marrow for Cell count & morphology
What is a bone marrow biopsy?
Bone & marrow for Marrow cellularity & composition
What percent of a normal marrow smear show blasts?
<5%
When is Reticulocytosis seen?
Highly active bone marrow
When are Howell-Jolly Bodies seen?
Failure of extrusion of nucleus, Common following splenectomy
What are more band cells in circulation indicative of?
Immature neutrophils, indicate infection
What are more hypersegmented neutrophils in circulation indicative of?
Due to slowed DNA synthesis, Megaloblastic anemia
What are Auer rods in Myeloblasts indicative of?
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
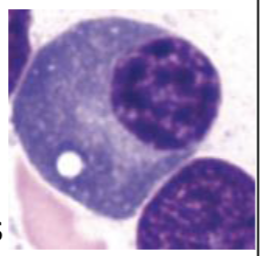
What type of cell is seen here?
Plasma Cell
What are plasma cells?
B cell derivatives that secrete immunoglobulin and are located next to the capillaries
What do platelets form from?
Megakaryoblast → Megakaryocyte releases proplatelets
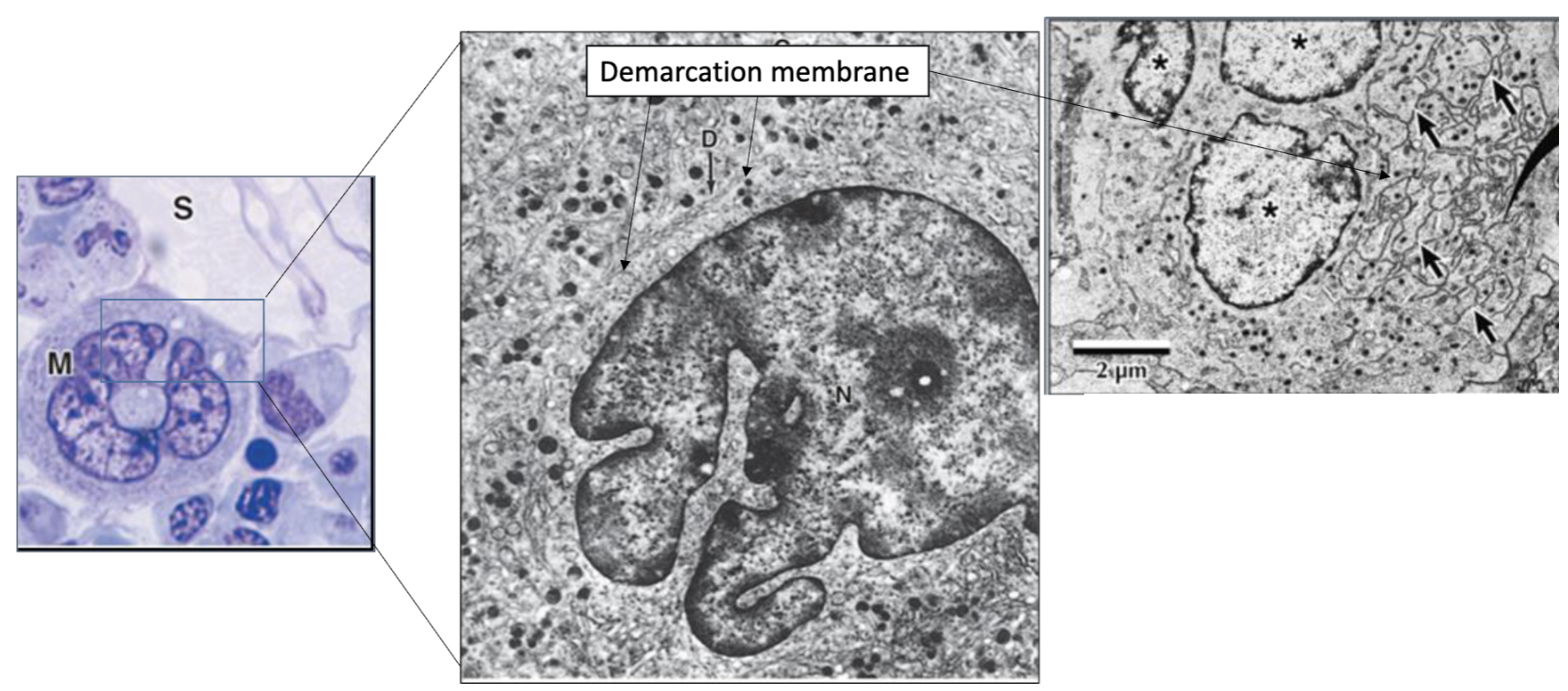
What type of cell is seen here?
Megakaryocyte
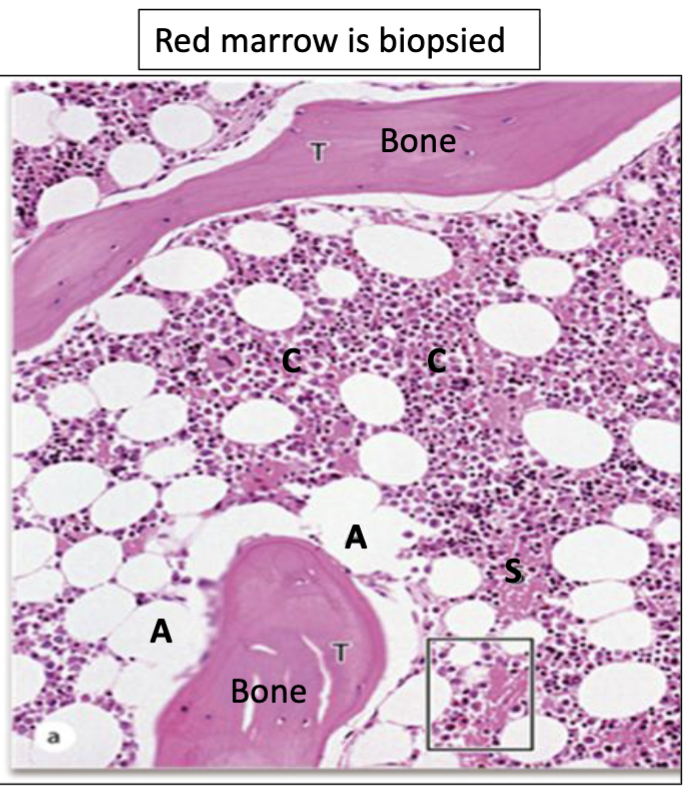
What is indicated by C?
Hematopoietic cords
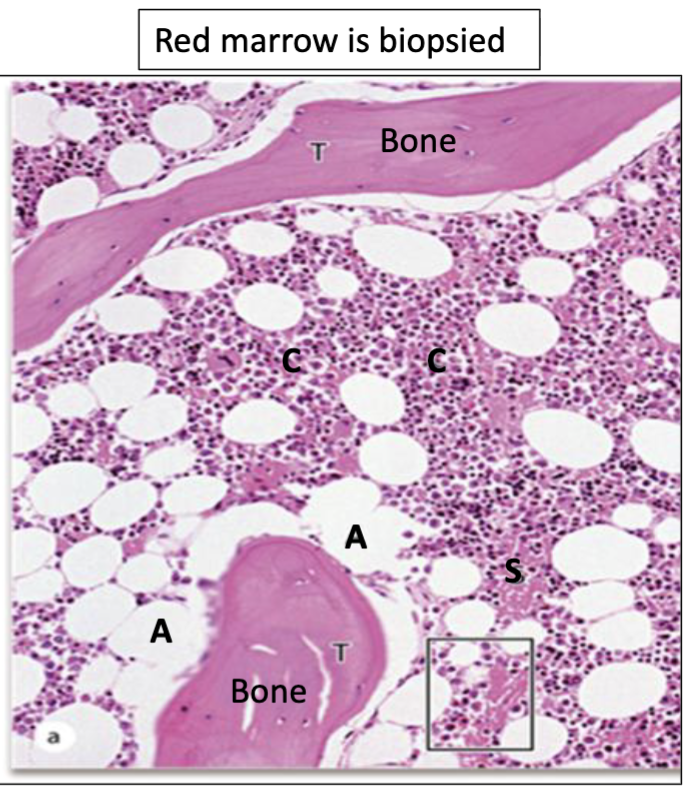
What is indicated by A?
Adipocytes
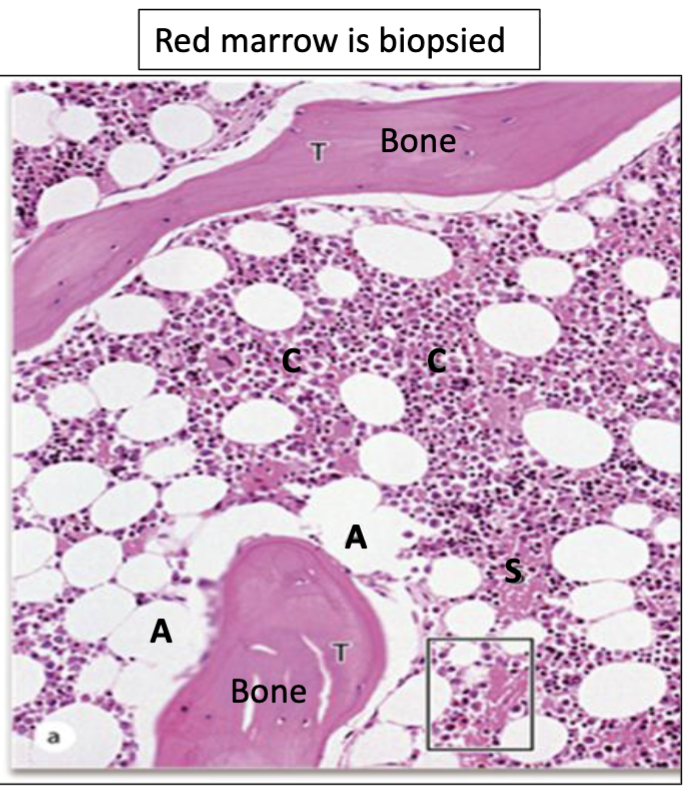
What is indicated by S?
Sinusoids
What is Erythroid Hyperplasia?
More hematopoietic cords, More erythroid series
What is Myeloid Hyperplasia?
More hematopoietic cords, More myeloid series
What is Aplastic Anemia?
Less hematopoietic cords, More stroma