Lab Diagnostics Exam 4 - HEMATOLOGY
1/210
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
211 Terms
hematopoiesis
all cell lines originate from a pluripotent stem cell that is capable of maturing into many cell lines
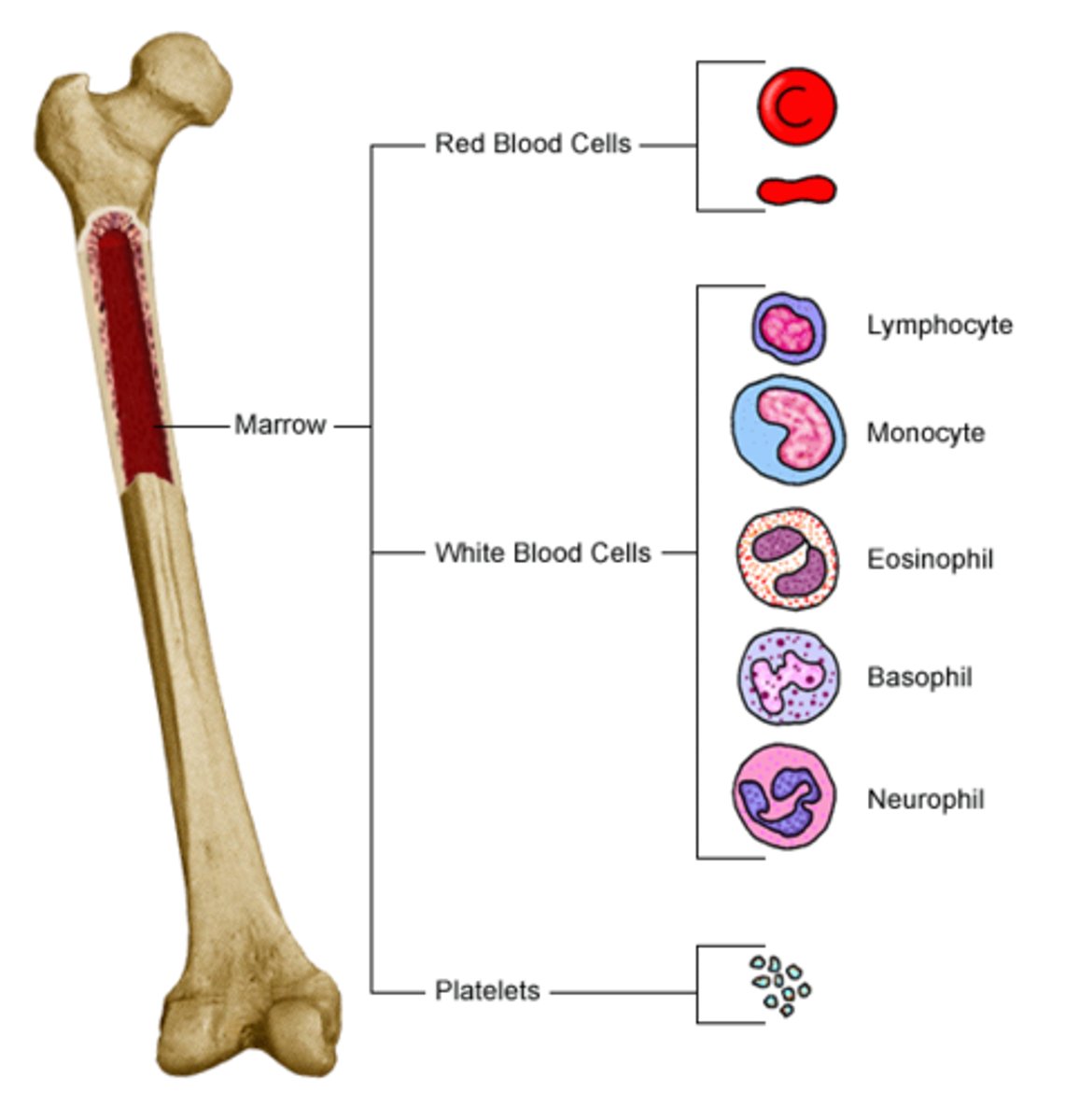
myeloid stem cells
multi-colony stimulating factors (multi-CSF) to stimulate differentiation to:
- erythroblasts > erythrocytes
- megakaryocytes > platelets
- myeloblasts > neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
- monoblasts > monocytes
lymphoid stem cells
differentiation into
- natural killer cells
- B-lymphocytes: antigen driven to form B-cells > plasma cells
- T-lymphocytes: antigen driven to form T-cells
leukocytes
aka "white blood cells;" indicator of infection and/or inflammation
diapedesis
aka "squeezing;" passage of blood cells (especially white blood cells) through intact capillary walls and into the surrounding tissue
leukocytosis
elevated leukocyte count generally associated with bacterial or viral infections
granulocytes
a group of leukocytes containing granules in their cytoplasm (i.e., neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils)
agranulocytes
a group of leukocytes without granules in their nuclei (i.e., lymphocytes, monocytes)
classification of WBC functionality
- myelocytic (granulocytes)
- monocytic
- lymphocytic
"never let monkeys eat bananas"
neutrophils (60%), lymphocytes (30%), monocytes (5%), eosinophils (4%), basophils (1%)
staining of neutrophils
pink (or neutral) granules
staining of eosinophils
red granules
staining of basophils
dark-blue granules
are cells functional in the maturation pool?
no; myelocyte > metamyelocyte > band neutrophil > segmented neutrophils
cardiovascular pool (CVP)
2 sub-compartments
- marginal pool
- circulating pool
marginal pool (MP2)
made up of cells that adhere to the epithelial lining of the vessels (cells can enter or leave circulation)
circulating pool (CP)
- contains the cells which are actively circulating in the bloodstream
- main function is to locate, ingest, and kill bacteria and other foreign invaders
when does the shift from the MP2 to the CP occur?
stress, trauma, or catecholamine release resulting in transient leukocytosis that can last from 4-6 hours
neutrophil
- nuclei segmented (lobes)
- primary defense for bacterial infections
- phagocytic with an active metabolism
what are the major cellular constituent of pus?
neutrophils
neutropenia
decreased number of neutrophils
causes of neutropenia
- decreased production of WBC
- increased neutrophil destruction
- drugs (penicillin)
pseudoneutropenia
a decrease in the neutrophil count associated with cells shifting from the circulatory pool to the marginated pool
neutrophilia
increased numbers of neutrophils
causes of neutrophilia
- acute infection (mostly bacterial)
- acute inflammation
- drugs (steroids, lithium)
pseudoneutrophilia
elevation of the neutrophil count that is the result of cells shifting from the marginated pool to the circulatory pool
the "left shift"
an increase in the number of immature neutrophils in the CP in response to a severe acute bacterial infection
where are many banded neutrophils present?
bone marrow
eosinophils
- bilobed nucleus
- drawn to sites of hypersensitivity reactions by mast cells
- play a role in parasitic infections
- produce histaminase
histaminase
an enzyme that breaks down histamines released by basophils in an effort to reduce inflammation
eosinophilia
increased number of eosinophils
causes of eosinophilia
- allergy (asthma, hay fever, urticaria)
- parasitic infections (tissue-invasive parasites such as trichinosis, visceral larva migrans, or filariasis)
- pernicious anemia
eosinopenia
decreased number of eosinophils
basophils
- least common of the WBCs
- can increase in response to same conditions that cause eosinophils to respond
- migrate into the peripheral tissue and become fixed (mast cells)
heparin
acts as an anticoagulant
histamine
induces vasodilation and increased capillary permeability to promote exudation of fluid into the tissues
SRS-A
slow-reacting substances of anaphylaxis
when you see tissue inflammation, think
basophils
causes of basophilia
- myeloproliferative disorders
- hypersensitivity reactions
- myxedema
- tuberculosis
- diabetes
primary role of monocytic line
phagocytosis; becoming "activated" when direct contact with microorganisms occurs
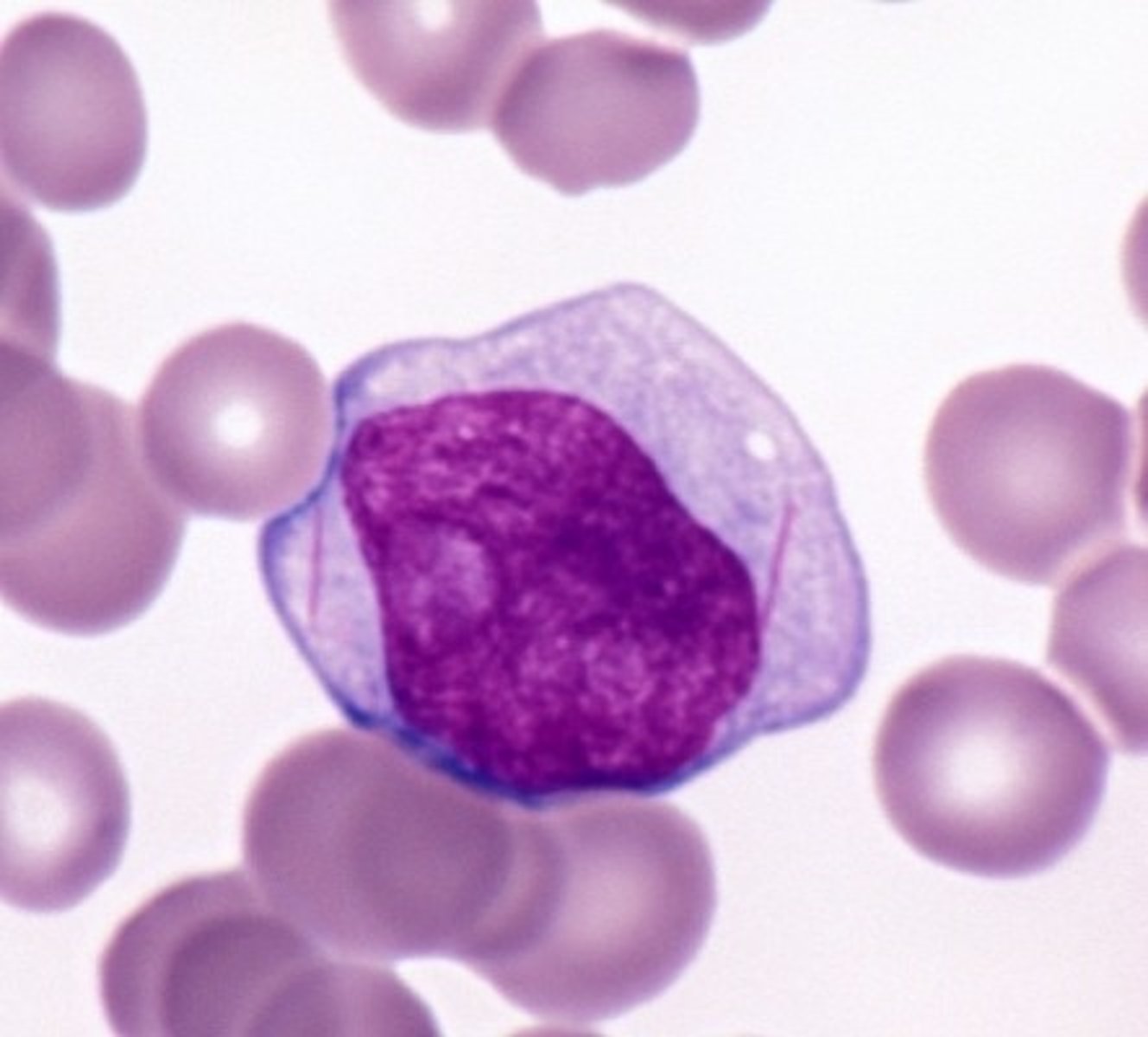
monocytes
- single, large nucleus with a "horseshoe" appearance
- cytoplasm is densely packed giving the cell a "frosted glass" appearance
monocytosis
increased number of monocytes
causes of monocytosis
- tuberculosis
- IBD
- chronic neutropenia
- sarcoidosis
main function of lymphocytic line
antigen recognition and immune response
2 phases of lymphocyte maturation
- antigen independent
- antigen dependent
antigen independent maturation
occurs in the bone marrow first where the lymphoblast gives rise to either pre-T or pre-B cells
maturation of natural killer cells
pre-T cells that move directly into the CP, bypassing the thymus
antigen dependent maturation
- T-cells migrate into lymphoid tissue
- B-cells migrate to germinal centers
what are the smallest WBCs?
lymphocytes
most common cause of lymphocytosis
viral infection (such as CMV or EBV)
causes of lymphopenia
- immunodeficiency (AIDS, chemo, transplant)
- acute bacterial infection
- increased steroids in circulation
which virus is associated with "atypical" or "reactive" lymphocytes?
an Epstein-Barr virus infectious mononucelosis
3 major divisions of a CBC used to evaluate illnesses
- WBC (infection and/or inflammation)
- RBC (weakness, shortness of breath, fatigue)
- platelets (easy bleeding, clotting disorders)
total white cell count
total number of all leukocytes in a sample
elevated levels of WBC
>11,000
leukemia
increased production of abnormal leukocytes and leukocyte precursors in the bone marrow and in the circulation
acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) on CBC
- hyperleukocytosis (>100,000) with markedly elevated levels of circulating blast cells
- pancytopenia (decreased number of the other WBC, RBC, and platelets)
acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) on blood smear
- increased number of immature cells with many myeloblasts and promyelocytes
- severe decrease in thrombocytes
- auer rods
acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL)
most common form of leukemia in children
acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) on CBC
pancytopenia
acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) on blood smear
decreased number of platelets and RBC
terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase stain (TdT)
if positive, aids in the diagnosis of ALL in children
chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) on CBC
leukocytosis with a median WBC count of 150,000
chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) on bone biopsy
- hypercellular with a left shift
- PCR used to identify BCR-ABL gene (aka Philadelphia gene)
chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) on CBC
isolated leukocytosis with a WBC >20,000
lymph cells involved in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
- B-cell CD19
- T-cell CD5
chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) on peripheral blood smear and bone biopsy
- increase in mature but small lymphocytes
- smear aka "smudge" cells
Hodgkin's lymphoma on lymph node biopsy
Reed-Sternberg cells
what virus is present in half the cases of Hodgkin's lymphoma?
EBV
non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
90% of cases are from B-cells
non-Hodgkin's lymphoma on lymph node biopsy
invasion of prolymphocytic-like cells
plasma cell myeloma
previously called "multiple myeloma;" produces an abundance of monoclonal paraprotein (M protein)
Bence-Jones protein
also referred to "M-proteins," "myeloma proteins," "paraproteins," and "free immunoglobulin light chains"
production of Bence-Jones protein
component of immunoglobulin produced in excess by B cell-derived clonal cell populations
diagnostic testing for PCM (multiple myeloma)
- serum protein electrophoresis
- CBC
- serum protein
- urine and serum Bence-Jones proteins
- serum free kappa to lambda ratio
- bone marrow biopsy
toxic vacuolization
round, clear spaces within granulocyte cytoplasm; seen in patients with severe bacterial infections
toxic granualization
presence associated with bacterial infections, drug poisoning, and burns
auer rods
slender, rod-shaped bodies within the cytoplasm, only seen in blasts
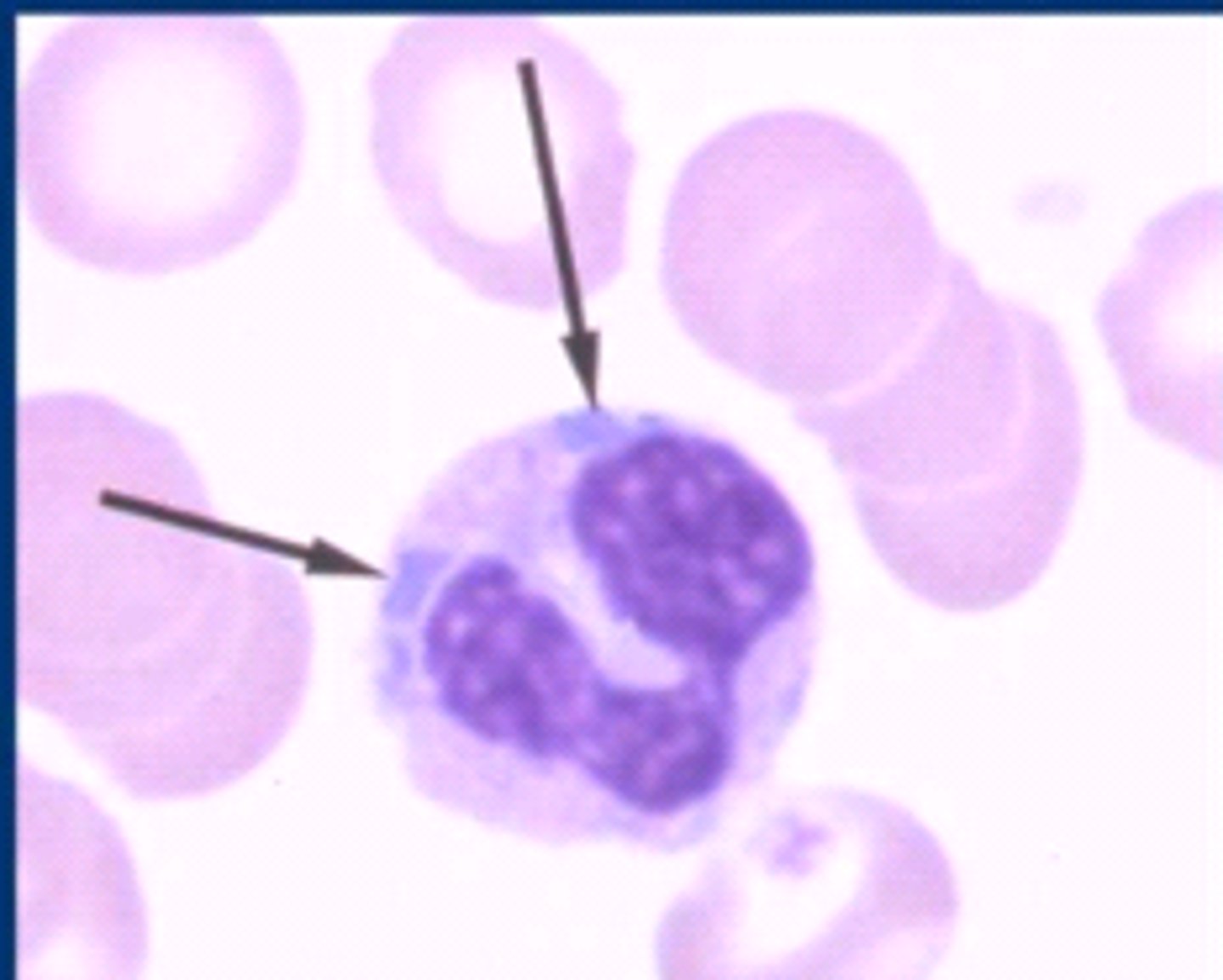
Dohle bodies
round-oval pale grayish-blue inclusions that are found in the periphery of the cytoplasm of neutrophils, accompanies toxic granulation
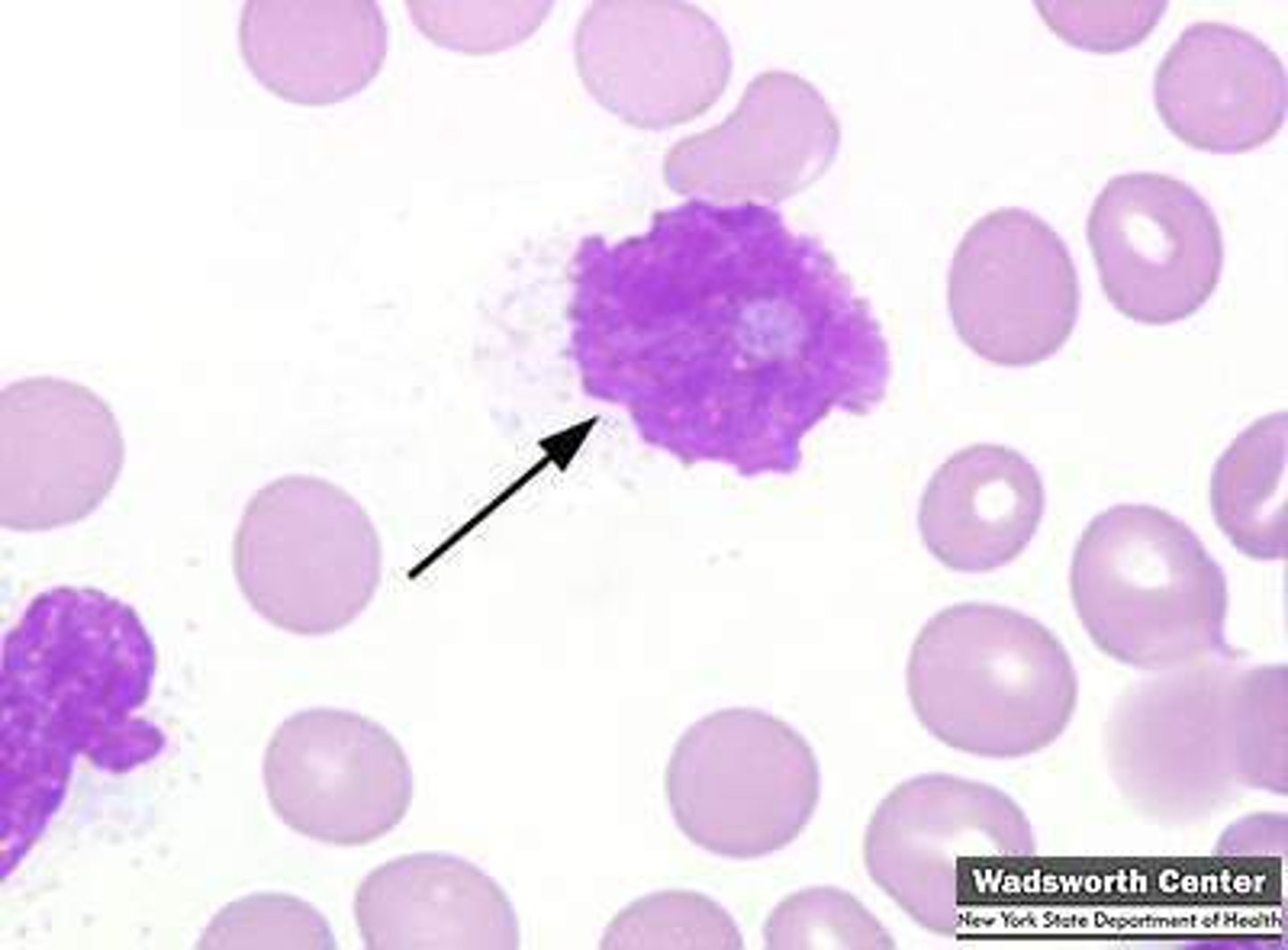
smudge cells
reflects the fragility of lymphocytes
erythrocytes
- red blood cells
- stimulated by erythropoietin from the kidneys
polycythemia
increased RBC count
hemoglobin
oxygen carrying capacity
hematocrit
represents the percentage of cells per fluid volume
the "rule of three"
RBC count x 3 = hemoglobin x 3 = hematocrit
mean corpuscular volume (MCV)
a gauge of cell size
normocytic
80-100
microcytic
<80
macrocyctic
>100
mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC)
average concentration of hemoglobin per erythrocyte
normochromic
30-35
hypochromic
- <30
- deficiency of Hgb in the red blood cells
mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH)
average weight of hemoglobin per erythrocyte
normal MCH
27-32
anemia
condition in which the blood is deficient in RBCs, in Hgb, or in total volume
erythropoietin
glycoprotein hormone that stimulates the production of RBC by bone marrow
anisocytosis
variation in RBC size
poikilocytosis
variation in RBC chape
polychromasia
- increased number of abnormal colored RBC
- indicative of increased reticulocytes in the peripheral circulation
reticulocytes
- immature erythrocytes that are produced from erythroblasts
- constitutes about 1-1.5% of RBC volume