Wiley Chp. 17: Aromatic Compounds
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Aromatic compounds include _____ and its derivatives.
Benzene
What is the usually the parent name of monosubstituted aromatic rings?
Benzene
Toluene is a benzene ring with what substituent?
Methyl
Phenol is a benzene ring with what substituent?
Hydroxyl
Anisole is a benzene ring with what substituent?
Methoxy
Aniline is a benzene ring with what substituent?
Primary amine
Benzoic acid is a benzene ring with what substituent?
Carboxylic acid
Benzaldehyde is a benzene ring with what substituent?
Aldehyde
Acetophenone is a benzene ring with what substituent?
Ketone
Styrene is a benzene ring with what substituent?
Ethene
If the parent chain is _____ than the benzene ring it's attached to, then it becomes the parent name.
Larger
When benzene rings are named as substituents, they are called _____.
Phenyl
Common name for dimethyl benzene derivatives
Xylene
Ortho, meta, and para are used to describe substitutents on ______ rings.
Disubstituted
Ortho means two substituents are in the _____ positions.
1,2
Meta means two substituents are in the _____ positions.
1,3
Para means two substituents are in the _____ positions.
1,4
Aromatic rings _____ undergo addition reactions.
Do not
Aromatic rings are ____ stable than cyclic dienes.
More
The first criterion for a compound to be aromatic is to be _____, fully conjugated, and planar.
Cyclic
The first criterion for a compound to be aromatic is to be cyclic, _____, and planar.
Fully conjugated
The first criterion for a compound to be aromatic is to be cyclic, fully conjugated, and _____.
Planar
For a compound to be aromatic, it must meet _____ rule.
Huckel's
Huckel's rule says that an aromatic compound must have _____ pi electrons.
4n+2
Huckel's rule says that an aromatic compound must have an _____ number of pairs of pi electrons.
Odd
Fully conjugated rings with _____ or more carbons adopt non planar conformations.
8
Fully conjugated rings with 8 or more carbons are nonplanar and _____.
Nonaromatic
Compounds that fail the first aromatic critrion (conjugated, cyclic, planar) are _____.
Nonaromatic
Compounds that fail the second aromatc criterion/Huckel's rule are _____.
Antiaromatic
Antiaromatic compounds are _____ in energy than aromatic compounds.
Higher
Antiaromatic compounds are _____ in energy than nonaromatic compounds.
Higher
Nonaromatic compounds are _____ in energy than aromatic compounds.
Higher
Nonaromatic compounds are _____ in energy than antiaromatic compounds.
Lower
Aromatic compounds are _____ in energy than nonaromatic compounds.
Lower
Aromatic compounds are _____ in energy than antiromatic compounds.
Lower
_____ can be used to predict the shapes and energies of molecular orbitals.
Frost circles
Rings that are fully conjugated are known as _____.
Annuelenes
Rings containing carbanions and carbocations can be _____.
Aromatic
The cyclopentadienyl anion is an example of a _____ anion.
Aromatic
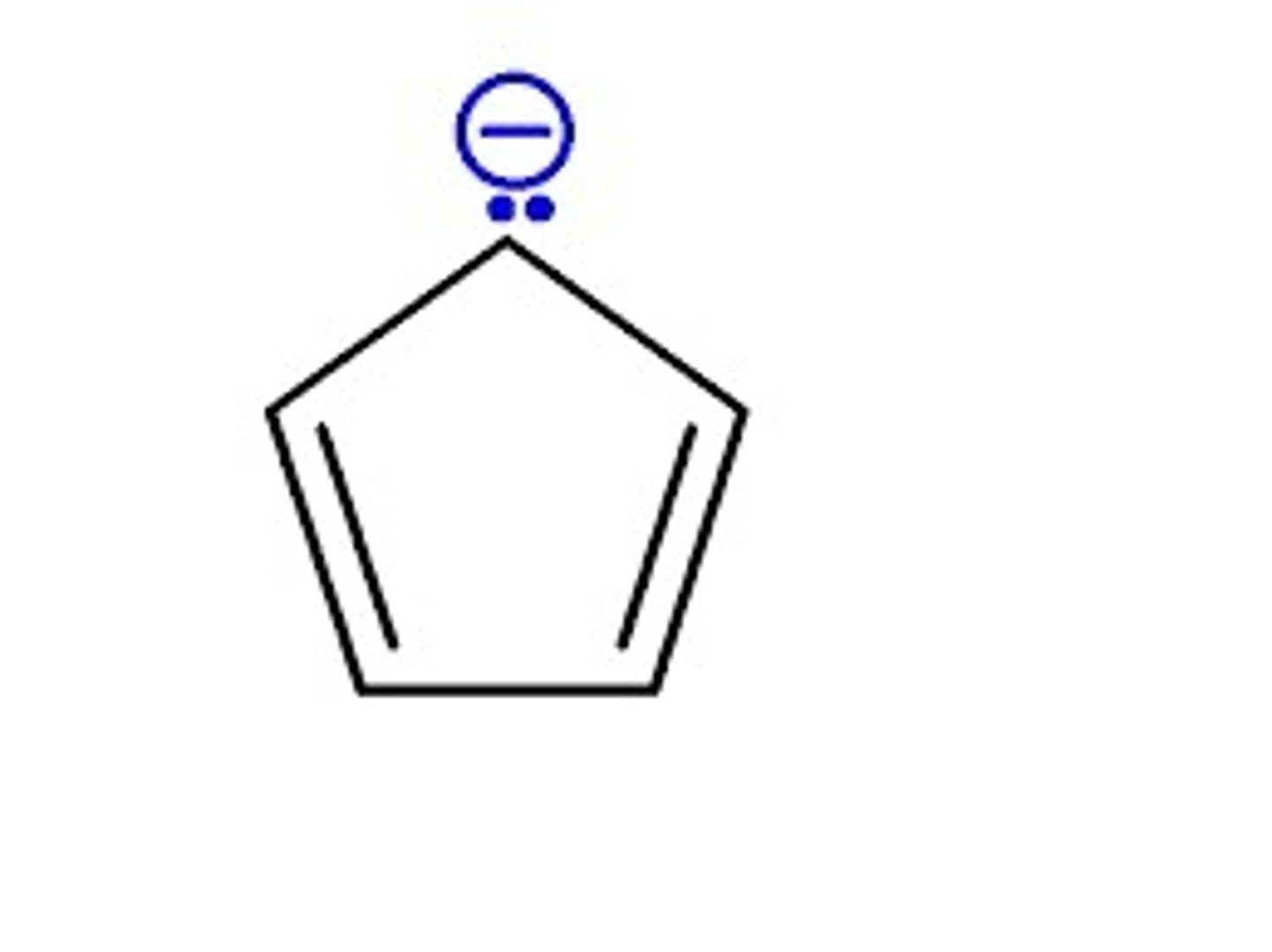
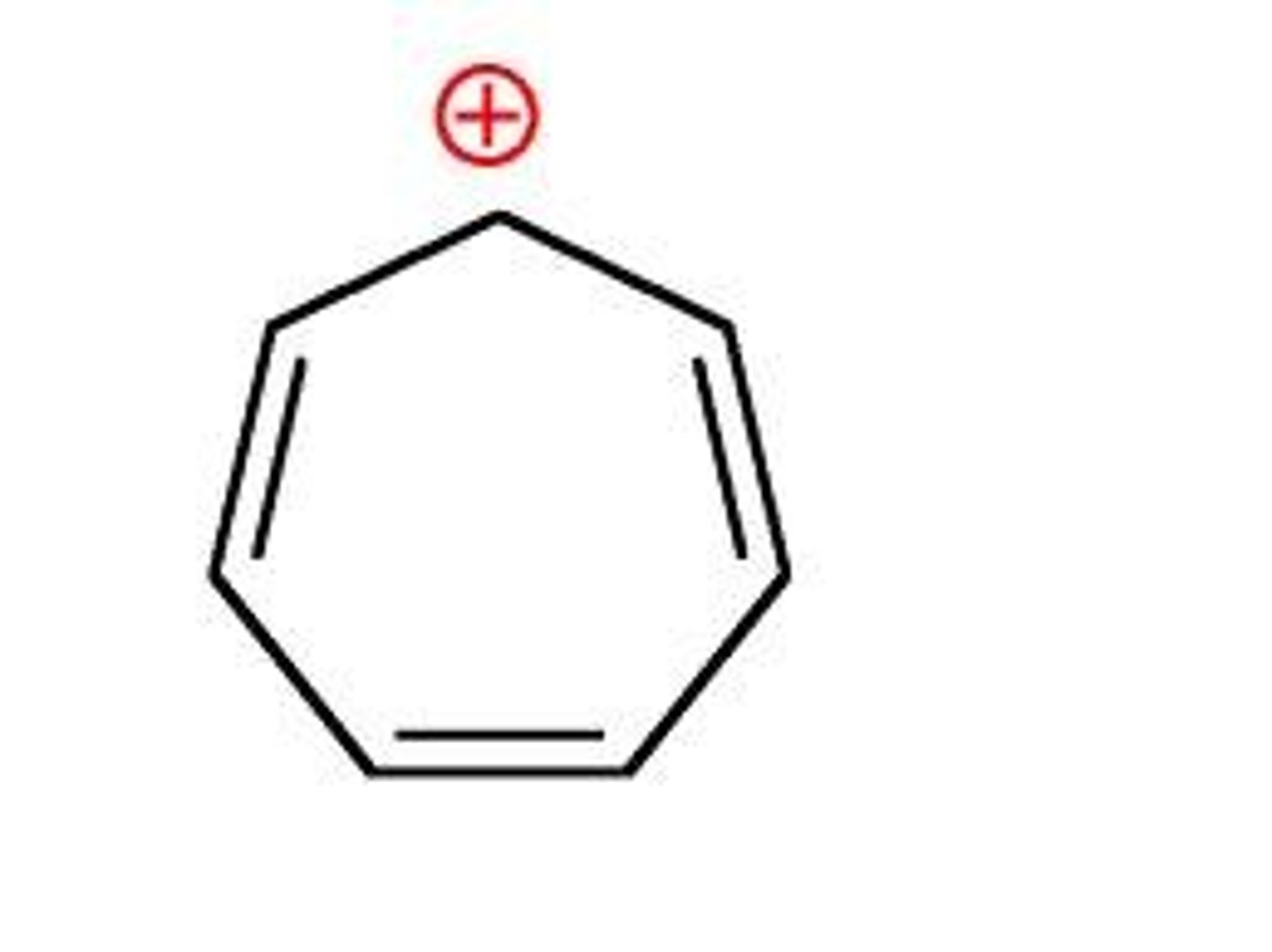
The tropylium cation is an example of an _____ cation.
Aromatic
Aromatic rings can also contain atoms other than C and H, called _____.
Heteroatoms
Pyridine and pyrrole are examples of aromatic rings containing _____.
Heteroatoms
If a heteroatom's lone pair is necessary for aromaticity, it is included in the calculation for _____.
Huckel's rule
If a lone pair is necessary for aromaticity, it is ____ basic than other lone pairs.
Less
A carbon attached directly to a benzene ring is in the _____ position.
Benzylic
Benzylic positions are readily _____ by chromic acid/Jone's reagent.
Oxidized
_____ positions are readily oxidized by chromic acid/Jone's reagent.
Benzylic
A benzylic position must have at least one _____ to undergo oxidation.
Hydrogen
Benzylic positions can be oxidized by chromic acid/Jone's reagent or what reagent(s)?
Permanganate (KMnO4)
Benzylic position readily undergo free radical _____.
Bromination
When benzylic positions undergo free radical bromination, they form _____.
Benzylic bromides
Benzylic _____ readily undergo substitution and elimination reactions.
Bromides
Benzene can be forcely reduced to _____.
Cyclohexane
Reagents/conditions for the reduction of benzene to cyclohexane under forceful conditions
H2, Ni, 100 atm, 150C
In the presence of a benzene ring, _____ will be selectively hydrogenated.
Alkenes
Benzene can be reduced to _____ via Birch reduction.
1,4-cyclohexadiene
Benzene can be reduced to 1,4-cyclohexadiene via _____ reduction.
Birch
Reagents for Birch reduction
Na, MeOH, NH3
The mechanism of birch reduction is similar to the _____ reduction of an alkyne.
Dissolving metal
Birch reduction involves a _____ intermediate.
Radical anion
Substituents on the benzene ring affect the _____ of Birch reduction.
Regioselectivity
If there is an electron-donating substituent during Birch reduction, the product will have the EDG in a _____ position.
Vinylic
If there is an electron-withdrawing substituent during Birch reduction, the product will have the EDG in a _____ position.
Allyic
If there is an _____ during Birch reduction, the product will have the _____ in a vinylic position.
Electron-donating group
If there is an _____ during Birch reduction, the product will have the _____ in a allylic position.
Electron-withdrawing group
In H NMR, a Para-disubstituted benzene ring with identical substituents will produce a _____ with an integration of 4.
Singlet
In H NMR, a Para-disubstituted benzene ring with identical substituents will produce a singlet with an integration of _____.
4
In H NMR, a Para-disubstituted benzene ring with two different substituents will produce two_____ each with an integration of 2.
Doublets
In H NMR, a Para-disubstituted benzene ring with two different substituents will produce two doublets each with an integration of _____.
2
In 13C NMR, Benzene carbons typically appear at _____ ppm.
100-150
Graphite consists of layers of sheets of fused _____.
Aromatic rings
Buckyballs are C60 spheres made of interlocking _____.
Aromatic rings
Buckyballs are also known as
Buckminster fullerenes
Buckyballs can also be made into _____.
Nanotubes
_____ is the main soure of aromatic compounds used for energy.
Petroleum