LAB MIDTERM
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:03 AM on 11/29/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
1
New cards
Independent variable
The variable that is altered by scientist
2
New cards
Dependent variable
The variable observed in response to changes made to the independent variable
3
New cards
Replication
Replicating an experiment increases accuracy of results
4
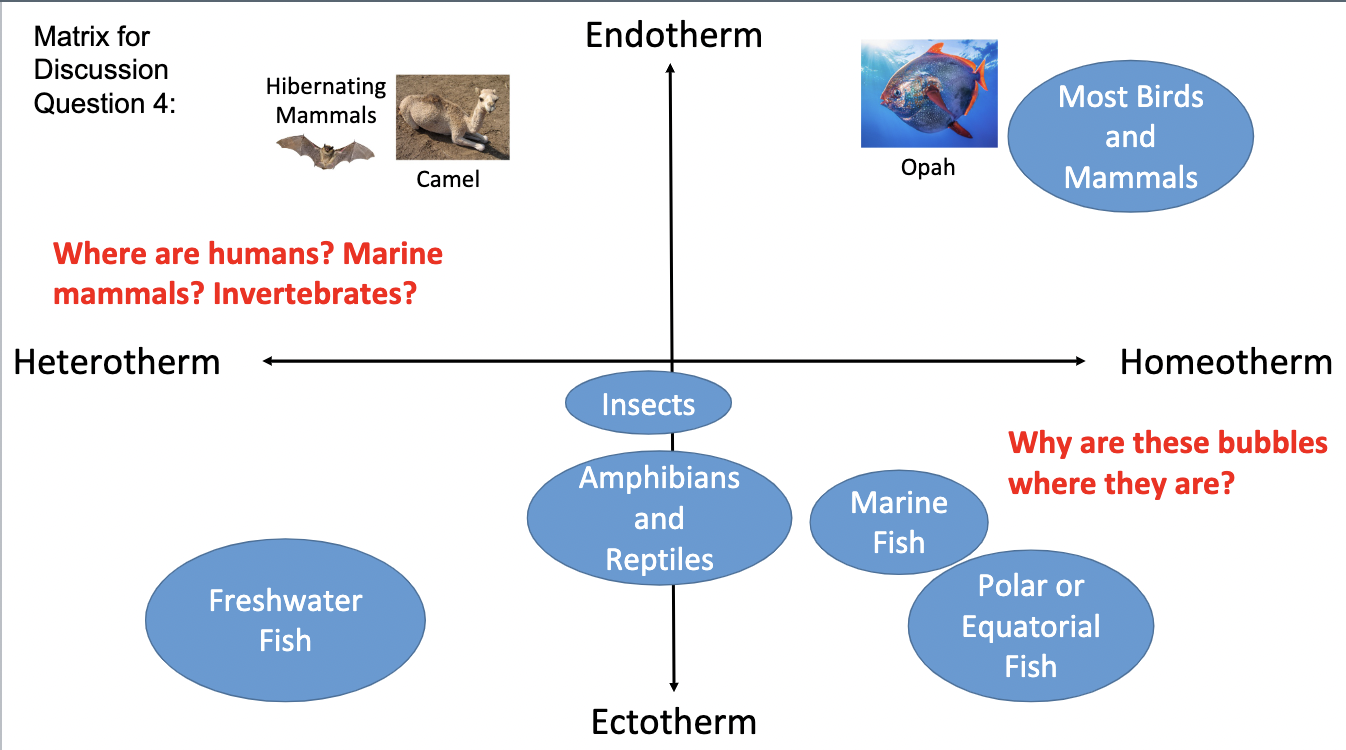
New cards
Control variable
the group compared to the independent group
5
New cards
The scientific method
Ask, research, hypothesis, test hypothesis, analyze data, report results
6
New cards
Cell
- The smallest structural and functional unit of an organism
- ALL living organisms composed of cells
- Typically microscopic and consisting of several key structures enclosed in a membrane.
- ALL living organisms composed of cells
- Typically microscopic and consisting of several key structures enclosed in a membrane.
7
New cards
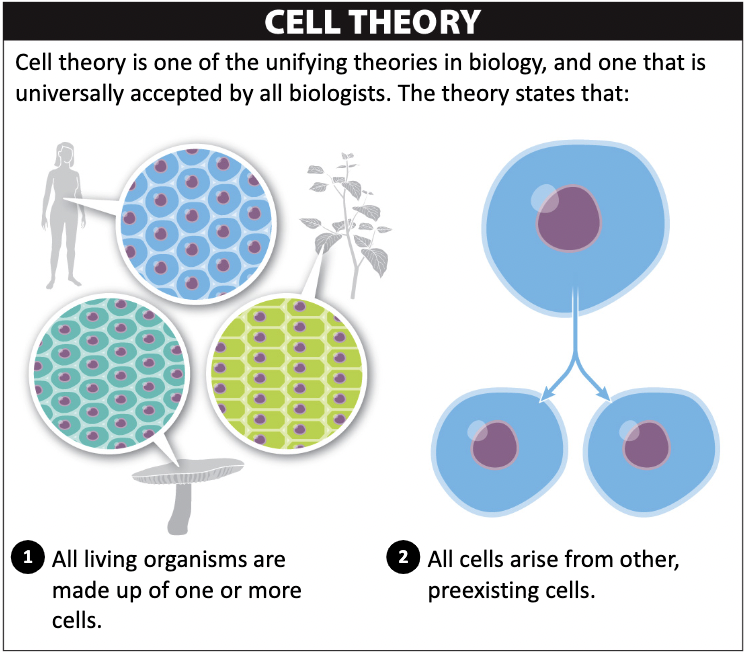
The Cell Theory
- All organisms are made of cells
- All cells arise from pre-existing cells
- Populations of single-celled organisms all have a common ancestor cell
- All cells in multicellular organism arose from a single cell All living organisms are
- All cells arise from pre-existing cells
- Populations of single-celled organisms all have a common ancestor cell
- All cells in multicellular organism arose from a single cell All living organisms are
8
New cards
Implications of Cell Theory
- All life is cellular
- All cells in a population of sing-celled organisms are related by common
ancestry
- All cells in a multicellular organisms are descended from a single cell
- Hereditary Info. (DNA) is passed on from cell to cell
- All cells in a population of sing-celled organisms are related by common
ancestry
- All cells in a multicellular organisms are descended from a single cell
- Hereditary Info. (DNA) is passed on from cell to cell
9
New cards
The 4 components present in all
Cells are:
Cells are:
- Cell membrane
- Nucleic Acids
- Ribosomes
- Enzymes
- Nucleic Acids
- Ribosomes
- Enzymes
10
New cards
Cell membrane
selectively permeable, keeps environment out!
11
New cards
Nucleic acids
information carrying molecules in the cell (DNA/RNA)
12
New cards
Enzymes
protein catalysts used to increase the rate of biological reactions
13
New cards
Ribosome
makes proteins needed for cellular function
14
New cards
Three Domains of Life
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
15
New cards
7 levels of taxonomic classification
Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species
16
New cards
Autotrophic
of or relating to organisms that can make complex organic nutritive compounds from simple inorganic sources by photosynthesis
17
New cards
Mixotrophic
an organism that can use a mix of different sources of energy and carbon, instead of having a single trophic mode (both autotroph and heterotroph)
18
New cards
Heterotrophic
requiring organic compounds of carbon and nitrogen for nourishment
19
New cards
Unicellular
having or consisting of a single cell
20
New cards
multicellular
consisting of many multicellular cells
21
New cards
colonial
an organism is composed of attached unicellular cells, but the cells are mostly similar in structure and function, can live on their own,
22
New cards
All plant cells have
cell walls, one vacuole, and chloroplast
23
New cards
Animal cells have
no cell walls, many vacuoles
24
New cards
Bacteria is
the most diverse domain of life
25
New cards
endothermic
an organism capable of internal generation of heat
26
New cards
ectohermic
an organism that regulates its body temp. by exchanging heat with environment
27
New cards
homeothermic
maintaining a constant body temp.
28
New cards
heterothermic
having body temp. that varies with environment
29
New cards
respiration rate
breathing rate of an organism
30
New cards
metabolic rate
rate at which an animal burns calories to produce energy
31
New cards
Specialized cell types
- Plants -> have guard cells
- Animals -> have muscle and nerve cells, etc.
- Volvox (algae) have different cells that have different functions in the colony as well!
- Animals -> have muscle and nerve cells, etc.
- Volvox (algae) have different cells that have different functions in the colony as well!
32
New cards
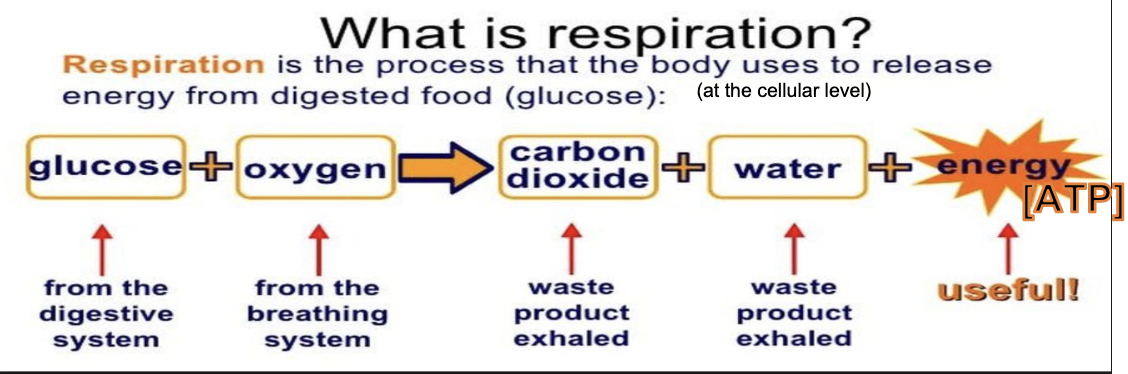
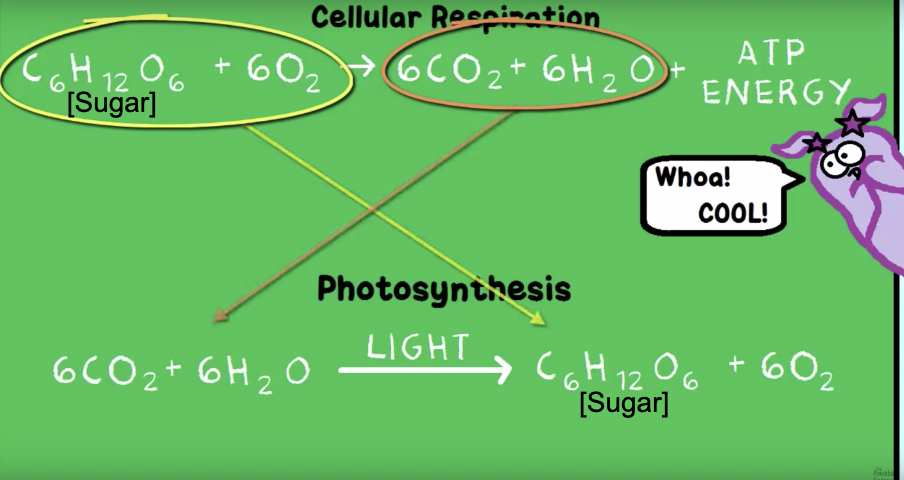
cellular respiration
(done by both plants and animals) how an organism can turn food into energy cells can use (aka ATP)
33
New cards
photosynthesis
synthesis of compounds with the aid of solar energy
34
New cards
Body temp. is regulated by...
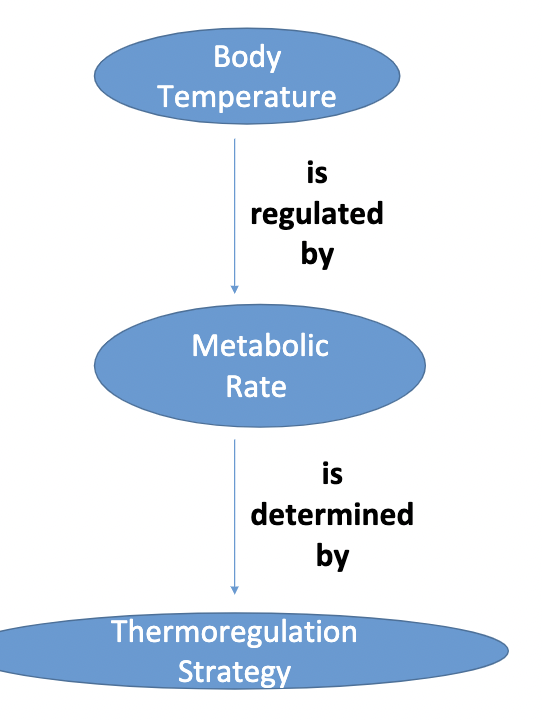
35
New cards
Reactions occur faster at higher
temperatures, but enzymes have an
optimal temperature at which they work the best.
temperatures, but enzymes have an
optimal temperature at which they work the best.
At temperatures too low or two high, enzymes will lose their ability to bind to substrate and eventually denature.
36
New cards
Alu-PV92
- Located on chromosome 16
- ~300 bp
- Transposon
- ~300 bp
- Transposon
37
New cards
Transposon
a chromosomal segment of DNA that can undergo transposition within a genome, can reverse/create a mutation
38
New cards
Exon
sequence of a gene's DNA that transcribes into protein structures (affects phenotype)
39
New cards
Intron
sequence of a eukaryotic gene's DNA that is NOT translated into a protein
40
New cards
Regulatory Sequences
segment of nucleic acid molecule that's able to increase/decrease expression of certain genes
41
New cards
DNA isolation
extraction of DNA from cortex and purify nucleic acid to remove any inhibitors
42
New cards
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
a lab method used to make many copies of a DNA piece from a tiny sample
43
New cards
Gel electrophoresis
a lab method used to separate mixtures of DNA and RNA or proteins according to size
44
New cards
Alu insertions shared by different individuals are identical by descent...
so you can find a common ancestor
45
New cards
PCR steps
Denaturation (heat)- heat splits open DNA double helix
Annealing (cold)- primers bind to ends of target sequence of DNA. Primers tell DNA polymerase where to start copying DNA
Extension/Elongation- new nucleotides are added by a kind of DNA polymerase called Taq, making copies of DNA segment
Annealing (cold)- primers bind to ends of target sequence of DNA. Primers tell DNA polymerase where to start copying DNA
Extension/Elongation- new nucleotides are added by a kind of DNA polymerase called Taq, making copies of DNA segment
46
New cards
Animal cell
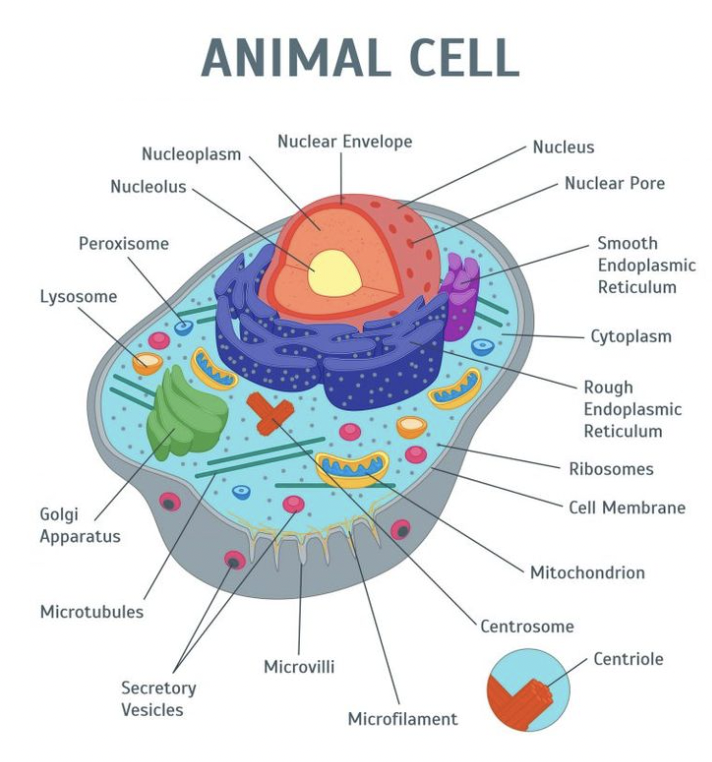
47
New cards
Plant cell
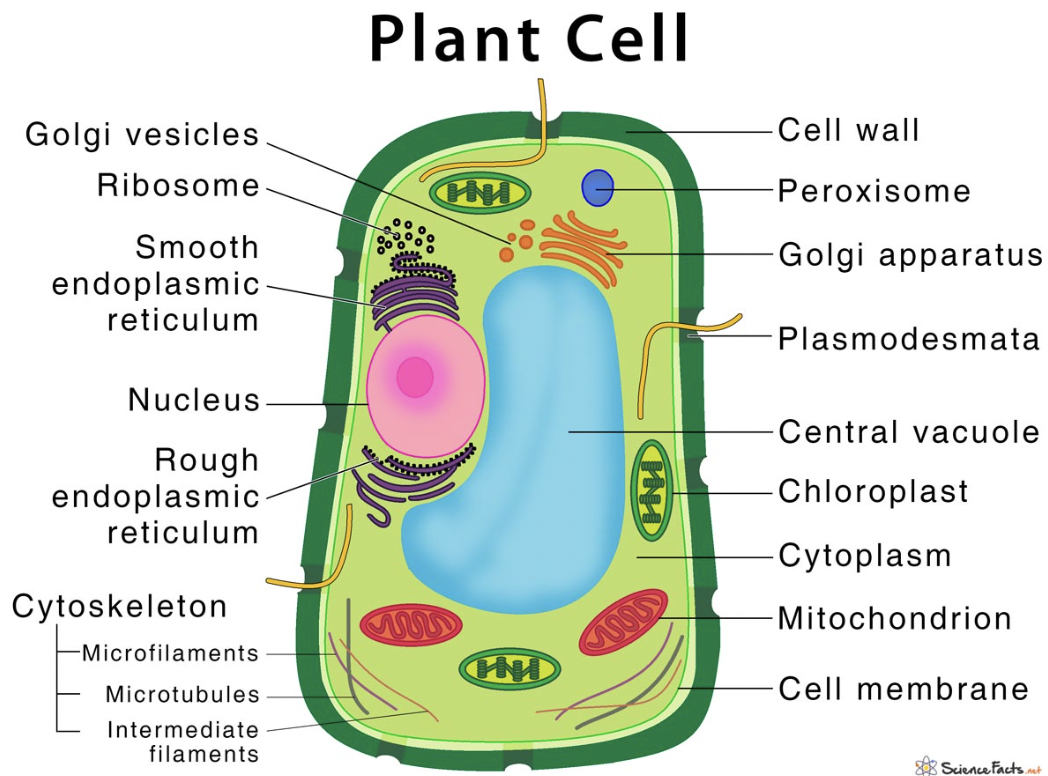
48
New cards
Matrix