Key Concepts in Group Dynamics and Leadership
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Group Size
Number of individuals forming a group.
7 features of a group
interdependence, Goals, Influence, Size, Membership, Structure, Systems
Open Systems
Groups interact with their environment dynamically.
Equifinality
Same resources yield different outcomes in groups.
Self fufillment needs
self-actualization
pyschological needs
the urge to belong and to give and receive love, and the urge to acquire esteem
basic needs
Safety needs and physiological needs
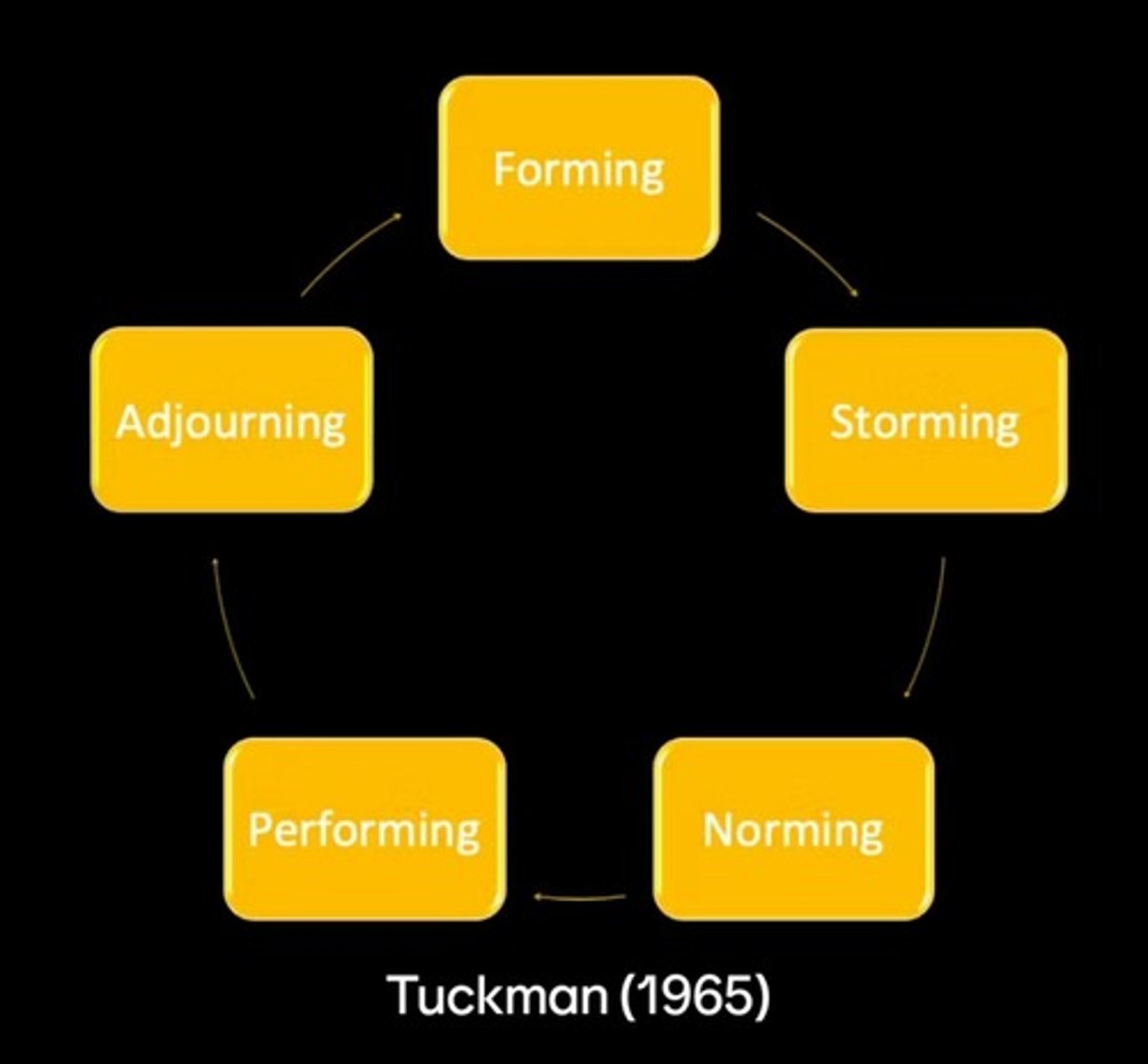
Group Development Stages
1. Forming
2. Storming
3. Norming
4. Performing
5. Adjourning
Role Diversity
Balance between task and socioemotional functions.
Role Differentiation
Process of assigning specific roles in a group.
Role Ambiguity
Uncertainty in expectations for a role.
Role Conflict
Competing expectations within a role.
Role Status
Power and perception associated with a role.
4 Stage Model
Framework for understanding group development stages.
Reflection/debriefing
what worked, what didn't, what should/would you change, what went well/didn't
Debrief Techniques
Methods for reflecting on group performance.
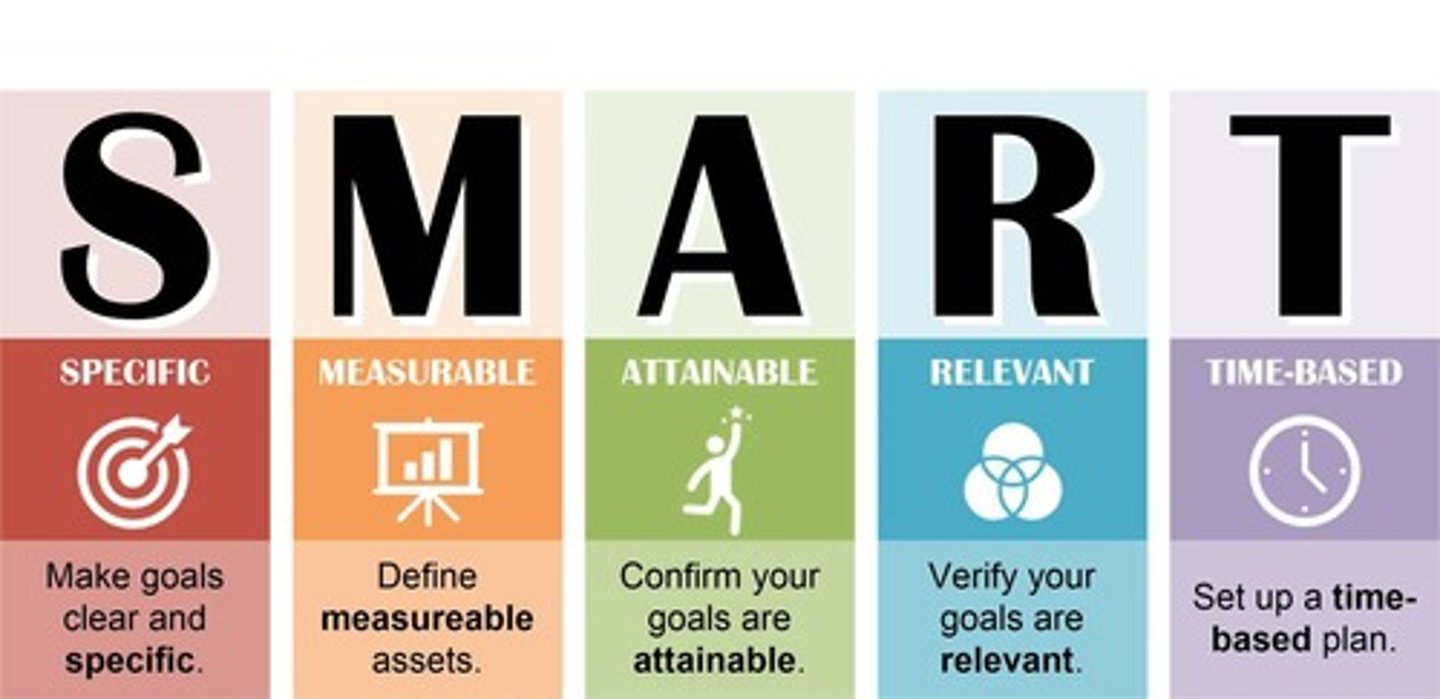
SMART Goals
Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound objectives.
Normative Ethics
Study of ethical action and moral principles.
Consequentialism
Ethical theory focusing on outcomes of actions.
Deontology
Ethical theory based on rules and duties.
Virtue Ethics
Focus on character and virtues in ethical behavior.
Group Decision Making Advantages
greater pool of knowledge, different perspectives, greater comprehension, increased acceptance, training ground
Group decision making disadvantages
social pressure, few people dominate, goal displacement, groupthink
Selective Information Sharing
Distributing information strategically within a group.
Social Loafing
Reduced effort by individuals in a group setting.
Production Blocking
Loss of contribution due to rapid topic changes.
Groupthink
Desire for consensus overrides critical thinking.
social facilitation
stronger responses on simple or well-learned tasks in the presence of others
group polarization
tendency of group members to move to an extreme position after discussing an issue as a group
7 methods of decision making
- decision by authority without discussion
- expert member
- average members' opinion
- decision by authority after discussion
- minority control
- majority control
- consensus: "no one is violated by decision"
coercive power
A power base that is dependent on fear of the negative results from failing to comply
reward power
Power to provide things people need to achievedesired results
legit power
Power that is derived from a formal position held within the hierarchy
referent power
power that comes from subordinates' and coworkers' respect, admiration, and loyalty
expert power
influence based on special skills or knowledge
procedural conflict
conflict that arises over how work should be completed
substantive conflict
involves fundamental disagreement over ends or goals to be pursued and the means for their accomplishment
interpersonal conflict
emotional conflict that occurs between two or more individuals
how people deal with conflict
Competing, Avoiding, Accommodating, Compromising, Collaborating
comfort = greater focus
People feel stressed when uncomfortable in their situation
Leadership Facets
Leadership requires competence, relationships, and goal orientation.
Trait Theory
Leadership based on inherent personal characteristics.
Style Theory
Leadership styles: Authoritarian, Democratic, Laissez-faire.
Contingency Theory
Effectiveness depends on leader and situational context.
Situational Leadership
Leadership style adapts to group and situation.
Conflict Management Styles
Approaches to resolving interpersonal conflicts.
Problem-Solving (Collaboration)
Win-win approach to conflict resolution.
Self-categorization theory
develops social identity theory's point that people categorize themselves, along with each other into groups, favoring their own group.
emergent norm theory
Act how others act
convergence theory
theory of collective action stating that collective action happens when people with similar ideas and tendencies gather in the same place
De-individuation
when immersion in a group causes people to become less aware of their individual values