Final Exam NURS3720
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Management
Getting the job done & ensuring people have resources to get their job done
Requires practice knowledge to know their pt. population
Set goals & objectives & achieve withing timelines & budgets
relational leadership
Building positive relationships w/ interprofessional team & supporting a positive workplace environment
Characteristics:
others-oriented
caring
active listening
Approachable & authentic
Ethical decision maker
Nurtruing
Open to feedback
Benefits
Builds trust with team members
Builds a supportive & engaged team
Leads to improved patient outcomes
Increases job satisfaction
Leadership approaches
Authentic leadership
Servant leadership
Transformational leader
Followership
Engaging w/ others who are leading or managing by contributing to the works that needs to be done
Involves actively participating & challenging leadership decisions
Personal Attributes needed to Lead, Manage & Follow
Sense of ethical responsibility
Code of ethics
Patient-centered care
Emotional intelligence
Appreciative Inquiry
Resilience
Mindfulness
Emotional intelligence
ability to know oneself and others
Characteristics
Self-awareness: emtotional awareness, accurate idea of self and self-confidence
Self management: self-control, adaptability, initiative, achievement drive
Social awareness: empathy, organizational awareness, service orientation
Relationship management: inspirational leadership, developing others, influence, change catalyst, conflict management, building bonds & teamwork
Appreciative Inquiry
Ongoing continuous study of what gives life to a human system when it is functioning at its best
Focuses on what is working, strengths and successes
Nursing Managers
Ensures task are completed efficiently & effectively
Oversees day-today operations & enforces policies
Relies of structured, evidence based decision making
Delegates responsibilities & monitors performance
Task-focused to enforce organizational and regulatory policy & procedures
Meeting deadlines & adhering to standards
Nursing Leaders
Inspire & motivate team towards shared vision & team goals
Encourage collaborative & creative problem solving
Builds relationships & empowers team members
Future-focused, fostering growth & adaptation
Communication, inspiration & emotional intelligence
Leadership Theories
Trait leadership
Style leadership
Situational-contingency leadership
Transformational leadership
Authentic leadership
Trait leadership Theories
The Great Man Theory
Leaders have certain set of physical & emotional traits crucial for inspiring other
Debate on whether these traits can be learned or are born w/
Application: Self-awareness of traits is useful to assess personal strength and apply them
Leadership theory
Traits Classified
Cardinal: rare; dominating personality
Central: personality not as dominating; honest, shy, etc.
Secondary: attitudes & personality preferences; anxiety & impatience
Style Theories
Focuses on how leaders behave
Based on task & relationship behaviors
Leaders need to be develop competences in completing task & maintaining relationships to be successful
Leadership Theory
Styles of leadership include:
task-oriented
People-oriented
Country club
Status quo
Dictatorial
Situational Contingency Theory
Leadership effectiveness depends on situational factors
Patho-goal theory: leader’s behaviors should be dependent on the task & followers characteristics
Leaders should asses each situation differently & determine appropriate actions
Leadership theory
Factors that impact a leader:
Type of company
Size of company
Innate leadership style
Customer feelings/satisfaction
Marketplace
Transformational Theory
Leaders inspire & motivate workers to embrace change
relationship focused leadership
Fosters workplace accountability, ownership & autonomy
Leaders have 4 attributes
Idealized & charismatic
Inspirational motivators
Intellectually stimulating
Considerate
Example: Uses effective communication skills to build trust & establish a shared vision around a culture of safety where everyone understands their role in working to protect patients.
Authentic Leadership Theory
Leaders are aware of own values & morals & are align their actions to match their values
Self-aware, transparent, genuine, ethical
Fosters trust & respect
Team members feel comfortable providing honest feedback
Examples: Champions initiatives to improve patient safety, openly shares concerns about staffing shortages & actively participates in team discussions to adrdress challenges
Management Theories
Taylor founder of scientific management & efficiency movement
Introduced concepts: labour division & specialization, systematic analysis of relationship between workers & assigned task, written standardized procedures, close supervision, shared manager-worker responsibility for goal achievement, etc.
Mintzberg: focused on organizational structures & process contributing to management theory
Proposed coordination mechanism to complete complex task, standardization of work processes outputs, worker skills & knowledge, etc.
Complexity Science
the study of complex systems: how they are sustained, self-organize, relationships within them & how outcomes emerge
Nurses must be flexible & dynamic to keep up w/ changing systems of people, health care, public policy, & human relationships
Achieve through networking, attractors, emergence, systems thinking & the Butterfly effect
Followship Theory
Competencies for Leadership & Management
Managing the business
Leading within
Leading people
Self Leadership (check textbook)
Journey of understanding who you are
Learning skills & abilities to guide personal leadership path
Strength based approach
Develop internal self-control, self-determination & self-regulation
rooted in emotional intelligence
Core characteristics
Understanding one’s values and how they influence decisions
Self-awareness, self control, self regulation
Knowing strengths & weaknesses
Growth mindset
Goal setting
Coaching oneself
Embrace failure
Group vs Team
Group: collection of people aware they belong together & have social ties
Team: collection of people who are working together to achieve a set goal
Interdisciplinary Team
Composed of members from different clinical disciplines with specialized knowledge, skills & abilities
Ex: nurses, surgeon & physiotherapists working together for the needs of a pt. receiving postoperative care after orthopedic surgery
Intraprofessiona team
Composed of individuals withing the same profession
Interprofessional Team
comprised of different health or social professions working together toward common goals to meet the needs of a patient population
Work is divided based on scope of practice
Canadian Interprofessional Health Collaborative Competency Framework
Relationship-focused care/service
team communication
role clarification & negotiation
Team functioning
Team differences/disagreements processing
Collaborative leadership
Relationship Focused Care/Service CIHC Framework
All members of team will collaborate, create purposeful relationship among & between care/service partners & persons participating in or receiving care/services
Reflect on value & diversity of thoughts, beliefs, talents, literacy & experiences into designing, implementing & evaluating care/services
Develop & continuously cultivate trusting relationships
Team Communication CIHC Framework
All members of a team will communicate w/ each other in cooperative, responsive & respectful manner while paying attention to context & relational elements of communications
Foster open & authentic communication and address potential communication barriers
Role Clarification & Negotiation CIHC Framework
All members of team understand & negotiate their own role & roles of all while using their knowledge & skills appropriately to achieve collaborative relationship-focused care
Seek to understand knowledge, skills and values of team members & including person participating in or receiving care service
Team Functioning CIHC Framework
All members of team understand nature of interprofessional teams
Team members work interdependent & bring shared perspectives to cooperate, coordinate & collab towards shared goal
Optimize efficiency & effectiveness of all members time, expertise & contributions
Team Differences/Disagreement Processing CIHC Framework
Establish a safe enviro. to express opinions & develop level of consensus among different views
All members must actively engage constructively in addressing disagreements
Acknowledge, recognize & value potential positive nature of differences in team
Collaborative Leadership CIHC Framework
All members of team value each other ‘s knowledge, skills & expertise
Acknowledge eveyone contributes different strengths & perspectives
Value & support each other in sharing decision-making, accountability, & responsibilities to achieve common goals
Synergy
phenomenon where an effective team works together to produce results & achieve a common goal that couldn’t be achieved by any one individual
To create synergy team requires
Clear purpose
Active listening
Compassion
Telling the truth
Flexible
Committing to resolution
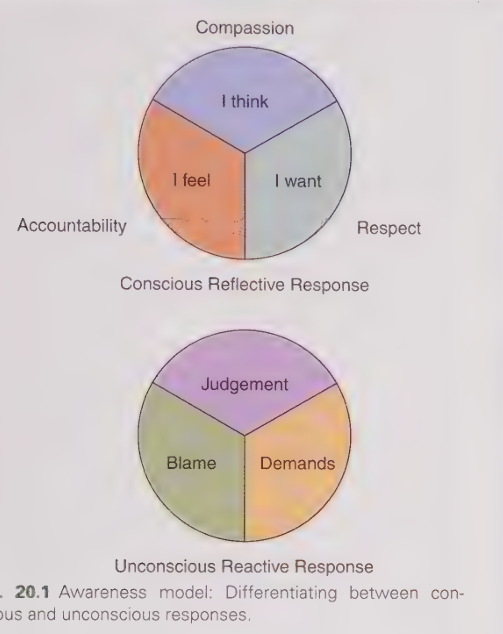
Positive Communication Model
When humans are distressed, disengaged or have emotional reactions to situation or blame they respond with blame judgement or demand
Reacting at feeling level = unconsciously; blame so by taking accountability for these feeling you move out of blame & focus on “I feel”
Trapped in distress or reaction = judgement; so by being compassionate you can respond with “I think”
Distress = make unreasonable demands; so by calming oneself we can find respect & make a request “I want”
Communicating During Conflict 4 Steps
Stop: considering the situation can prevent regretful interaction, collect/organize thoughts & time to think how response
Think: analyze situation; how do you want to change the other person, situation, or yourself
Listen:
Communicate
Linear: focus on goals, purpose & intention of message
Transactional: focus on process of communication; allows conflict to not be one-sided
STOP5: Critical Event Debrief
Stop for 5 minutes
Start w/ intro
Is everyone okay?
explain purpose
participation not compulsory
confidential
S:summary of the case
T:things that went well
O: Opportunities to improve
P:points to action and responsibilities
TAKE STOCK: Hot debrief Tools
Take an instruction sheet
Ask if everyone is okay
Know if anyone needs a break
Equipment issues?
Summaries the event
Things that went well
Opportunities to learn
Cold debrief necessary?
Know who is present
Hot/clinical debriefs
Structured interactive team discussion that occur immediately after a clinical event
Addresses immediate concerns, calm emotions & make sense of event
Facilities reflection identifies strengths & areas improvement, and promotes learning
Why do a Clinical Debrief?
Improves healthcare performance
Leads to better patient outcomes & safer healthcare
Opportunity to discuss, experience & learn for each other & better collaborate
Manage stress, emotions, & strengthen resilience from challenging events
Identify system issues & implement change
Active Listening Guideliness
Be compassionate
Tell the truth
Be flexible
Manage emotions
Communication Pitfalls
Give advice
Make the other feel wrong
being defensive
judging
patronizing
false assurances
asking why
blaming others
Resonant Leadership
Relationship focused leadership
High emotional intelligence
Effective in conflict resolution
Collab & solution focused
Encourages team to work at highest potential
Example: actively seeks & incorporates feedback from nurses acknowledges staff burnouts & implements flexible work arrangements.
Transactional (Autocratic) Leadership
Task completion leader
Sets standards for performance & task
Seeks obedience, loyalty & strict adherence to rules
Effective in high pressure or crisis situation where clear directives are needed
Bring structure & clarity to team roles & responsibilities
Rewards staff w/ recognition or bonuses for achieving targets
Can lead to low team morale, frustration, stifles creativity & creates dependence
Example: during a code decisions must be made quickly, the nurse takes control of decision-making due to limited time to collab & discuss.
Laissez-Faire Leadership
Task completion leadership
Hands-off approach
Autonomy for highly-skilled & self-motivated teams
Team members work independently w/ minimal supervision or guidance
Works well in creative environments
May lack sense of direction or accountability
May lead to difficulties if team members lack initative or need more guidance, supervision or structure
Example: allow a team of experienced nurses to manage daily task & pt care w/ minimal direction
Democratic Leadership
Encourages collab, diverse input, & shared discission making
Works to reach consensus
Time consuming
Conflicts & disagreements can arise
Ineffective in emergencies or w/ inexperienced teams
Example: staff meet, a nurse manager invited input from team on how to improve shift handover processes. After reviewing everyone suggestions, they collectively decide on a new & efficient protocol.
Servant leadership
Fosters culture of care, empathy & community
High level of team satisfaction & patient trust
Strong sense of selflessness
Prioritize needs & well-being of others, emphasizes service & development of team members
Less likely to work well where strict protocols, timeliness & accuracy are required
Example: prioritizes the well-being of the team by ensuring adequate breaks during long shifts & mentoring junior staff to help grow professionally
Indigenous Leadership
Not hierarchal or linear
Holistic, shared & determined by community
Address issues that affect the collective
4-inter-related lenses
Individual leader: skills used to contribute to community well-being
Leadership through culture: actions driven by communities cultural values
Leadership through processes: distributed leadership & collective desicion making involving the community
Leadership through integration: leadership as a communal activity
Key Points in Nursing Leadership
Understand personal leadership style & how you will use in nursing practice
Consider how you engage w/ your team from a lens of leadership
Use a blend of different leadership styles depending upon the situation
As you grown & gain experience & confidence as RN you might adjust your leadership approach over time
LEADS in a Caring Environment Framework
Approach to developing Leadership ability
Lead self
Engage others
Achieve results
Develop coalitions
Systems transformation
Strengths-based nursing & health leadership
Approach to developing Leadership ability
6 core values
Healing & Health: restoring wholeness
Uniqueness: everyone has different strengths
Holism & embodiment: all aspects are interconnected & interrelated
Subjective reality & created meaning: understanding/interpretations affect reactions/responses
Self-determination: take charge, making choices, feelin in control
Person environment: goodness-of-fit between environment demands & values, needs, goals, strengths
Horizontal/lateral violence
hostile and aggressive behavior among colleagues
workplace bullying, relational aggression or exclusion
Vertical violence
hostile and aggressive behaviors between individuals at different levels of hierarchical system
Beneficence
Actions and intentions are aimed at doing “good”
Provide high-quality, holistic & responsive nursing care based on competent and ethical practices
Nurses should be educated in accredited nursing programs and maintains competencies in active practice & continuing professional education
Nursing manages have the obligation to support staff to continue professional education & grow & maintain own clinical competencies.
Autonomy
Freedom & right to choose what will happen to one’s own person
Informed consent gives the patient the ability & infomration about options to make decisions
Patients have the right to be involved in decisions to the extent they are able
Nurses have obligation to consider the unique needs, opinions and preferences for care.
Respect for autonomy of one individuals should not come at the expense of another’s
Veracity
truthfulness
Ethnocentrism
Form of cultural bias
Individual applies one’s own culture or ethnicity as a frame of reference to judge other cultures, practices or beliefs.
Places own culture and ethnicity as #1
Acculturation
Assimilating to a different culture
Confidentiality
ethical obligation to uphold privacy and security of privately held personal information
legal obligation to protect personal information & not release information without patient consent
ethical violations
actions or failures to act that breach fundamental duties to the person receiving care or to colleagues & other HCP’s
Due to neglect of moral obligations & breach of duty
justice
Address fairness in regards to how individuals are treated
Subjective, dependent on situations, decisions, views & process
Nurses must go above & beyond to support justice by engaging in good & right actions to ensure justice
Examples
Advocating for vulnerable patients to ensure they receive the best care
Reporting unsafe practice
Nursing managers evenly distributing workloads
3 Types of Justice
Distributive justice: how benefits & burdens are allocated; should be equally distributed in society
Procedural justice: how laws, rules & policies are created & applied
Substantive justice: how decisions are made about fairness of rules
moral distress
Knowing the right things to do but system structures or personal limitations prevent doing the right course of action
Creates feelings of guilt, concerns, frustration, professional dissatisfaction, weakened moral sensitivity, poor mental & physical health, reduced morale, leaving the profession
moral residue
consequence of moral distress
When situations of moral distress are unresolved it creates feeling of powerlessness & compromise of self or personal values which can embed into one’s self conflict
moral resilience
positive result of experiencing moral distress
Individuals are able to find positive guidance and hope after experiencing situations that are morally distressing
moral uncertanity
a situation where there are conflicts between one or more values and there is uncertainty about correct course of action
Resolve through discussion with patient, colleagues, and HC team members
nonmaleficence
all actions and intentions must “do no harm”
Requires competence, awareness of safety concerns & anticipation of potentional risk
Explore what patients believes and perceives as “harm” to respect autonomy
social justice
Fair distribution of society’s benefits, responsibility & consequences
Focuses on the relative position of one social group in relationship to others in society and root causes of disparities and actions to eliminate them
Nurses should explore inequities and address contributing factors, social structures & systems
3 Guides for ethical nursing decisions & actions
Law: criminal laws, protection laws, nursing regulatory acts, natural laws & labour laws
Ethical principles: autonomy, justice, beneficence, nonmaleficence, social justice
Professional accountabilities: code of ethics, standards of care & organizational policies
Ethics
evaluates whether actions and intentions are “right” or “wrong”
3 branches: Meta-ethics, normative ethics & applied ethics
Morality
code of conduct accepted by a society, group or individual
Reflected in individual, cultural & professional values
Based on ideas about right or wrong
Meta-ethics
explores broader theory & meaning of morality
Foundation of moral values words & theories
Normative ethics
focuses on standards most people use to guide behaviors
Ex: murder is wrong, stealing is wrong, helping others is good
Applied Ethics
Involved how to apply ethical principles to resolving real-life ethical challenging situations
Ex: how to provide ethically competent nursing care & how to engage responsible conduct of research involving human participants
Bioethics
Branch of applied ethics focusing on science and human life
Considerer principles such as autonomy, justice, beneficence & nonmaleficence
Relational ethics
Focuses on ethical actions within relationships
What should I do? What should I do for others? How do my actions affect those around me?
Core Elements
Engagement
Mutual respect
Embodied knowledge
Uncertainty
Vulnerability
Interdependent environment
Engagement: Relational Ethics
Participating in engaging interactions that promote interprofessional and patient-nurse relationship
Nursing leaders have the role as communicator, counsellor, teacher and decision maker.
Examples of Actions & Behaviors
Participate in team meetings
Foster/facilitate nurse-patient therapeutic relationships
Identifies need for additional supports
Provides ongoing professional development opportunities for staff and patients
Engaged w/ ethics or advisory committees
Mutual Respect: Relational Ethics
Nursing leaders have the role as negotiator, team builder and patient advocate
Examples of actions & behaviors
Participate in patient rounds
Facilitates IP team meetings
Addresses challenges in the team & provides support to work through issues
Participates in care discussions w/ patients and families
Establishing & maintaining therapeutic relationships
Internal & External factors for Supporting Ethical Relationships
Internal: fatigue, moral residue, moral distress or values conflict
External: high rates of turnover, casual nursing staff, staff shortages, high workloads, unhealthy or hostile work environments and poor staff morale.
Conscientious objection
an instance where a nurse has a personal objection to practicing in certain types of situations or certain procedures due to personal values do not align permitting the nurse to step back.
Example: medical assistance dying, blood transfusions or situations which accessible care is being refused
Embodies knowledge: Relational Ethics Framework
Nurses roles:
Researcher
Coordinator of care
Professional development supporter
Policy and procedure administrator
Expert clinician
Examples of Actions & behaviors
Participates in scholarship and engages in research
Takes time to understand unique needs of patients and families
Remains current by attending conferences and engaging in the literature
Engages with institutional policy and procedure committees
Vulnerability
Roles as nursing leaders
Advocate
consultant
Risk Manager
Examples of Actions & behaviors
Engages in the literature and with multidisciplinary expert clinicians
Helps develop policy and procedures
Consults appropriately with allied health care team members, and local experts Advocates for quality care for all
Interdependent environment: Relational Ethics Approach
Roles as nursing leaders
Team leader
advocate for social justice
Examples of Actions & behaviors
Applies code of ethics, values, and principles to practice
Actively participates in professional associations
Actively participates in policy development
CNA Code of Ethics: Nursing Values & Ethical Responsibilities
Providing safe, compassionate, competent & ethical care
Promoting health & well-being
Promoting and respecting informed decision making
Honoring dignity
Maintaining privacy and confidentiality
Promoting justice
Being accountable
Steps in Ethical Decision Making
Clarify the need
Identify all involved
Arrange a meeting
Select a facilitator or chair: must be impartial
Identify areas of agreement
Identify areas of disagreement
Offer resources
Seek outside advice if necessary
Make a decision
Implement the decision