Antebellum America & Slavery (Chapter 16)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
West Africa Squadron
(established 1808) British Royal Navy force formed to enforce the abolition of the slave trade in 1807. It intercepted hundreds of slave ships and freed thousands of Africans.
Breakers
Slave drivers who employed the lash to brutally "break" the souls of strong-willed slaves.
Black Belt
Region of the Deep South with the highest concentration of slaves. The "Black belt" emerged in the nineteenth century as cotton production became more profitable and slavery expanded south and west.
Responsorial
Call and response style of preaching that melded Christian and African traditions. Practiced by African slaves in the South.
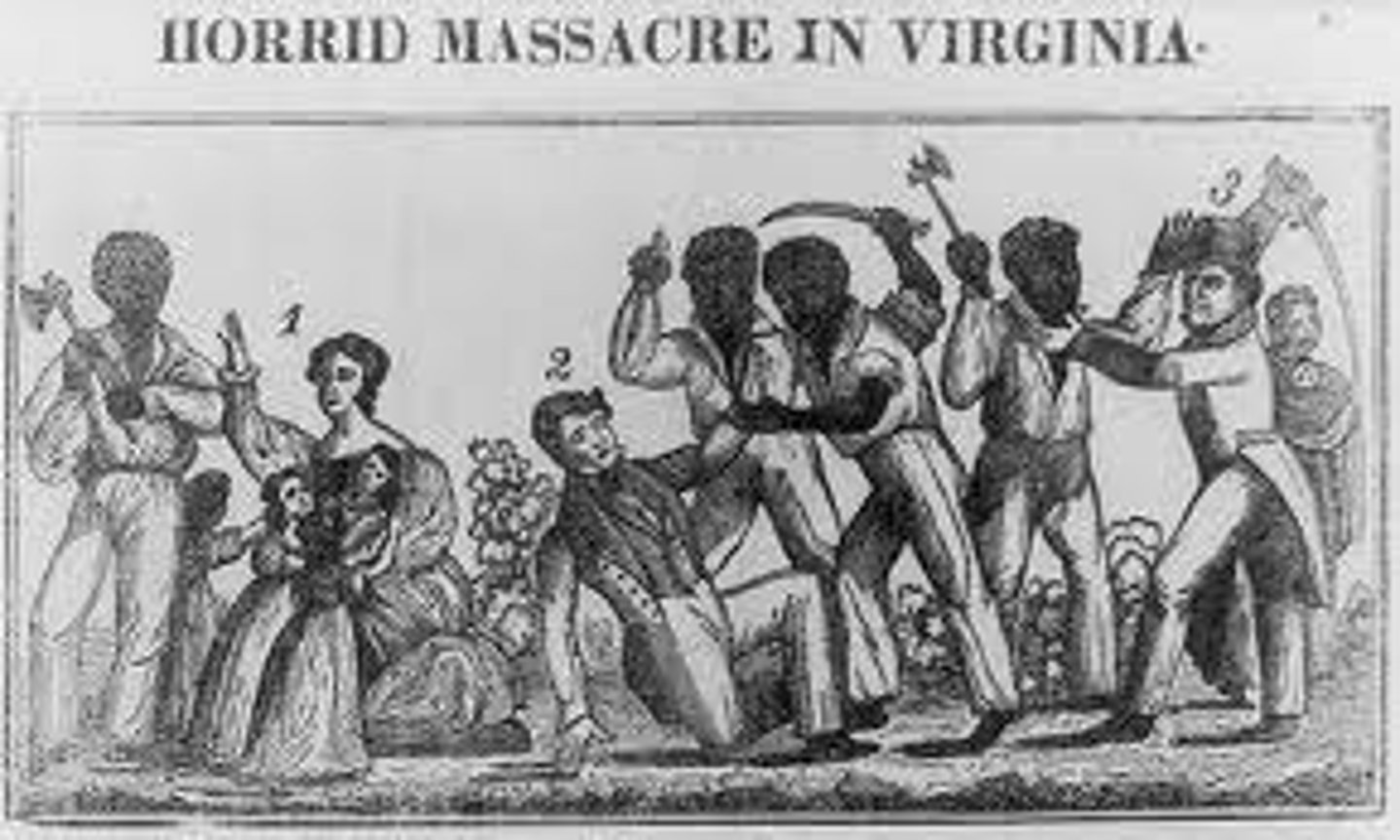
Nat Turner's Rebellion
a slave rebellion led by enslaved man Nat Turner that took place in Virginia in 1831

Amistad (1839)
Spanish slave ship dramatically seized off the coast of Cuba by the enslaved Africans aboard. The ship was driven ashore in Long Island and the slaves were put on trial. Former president John Quincy Adams argued their case before the Supreme Court, securing their eventual release.
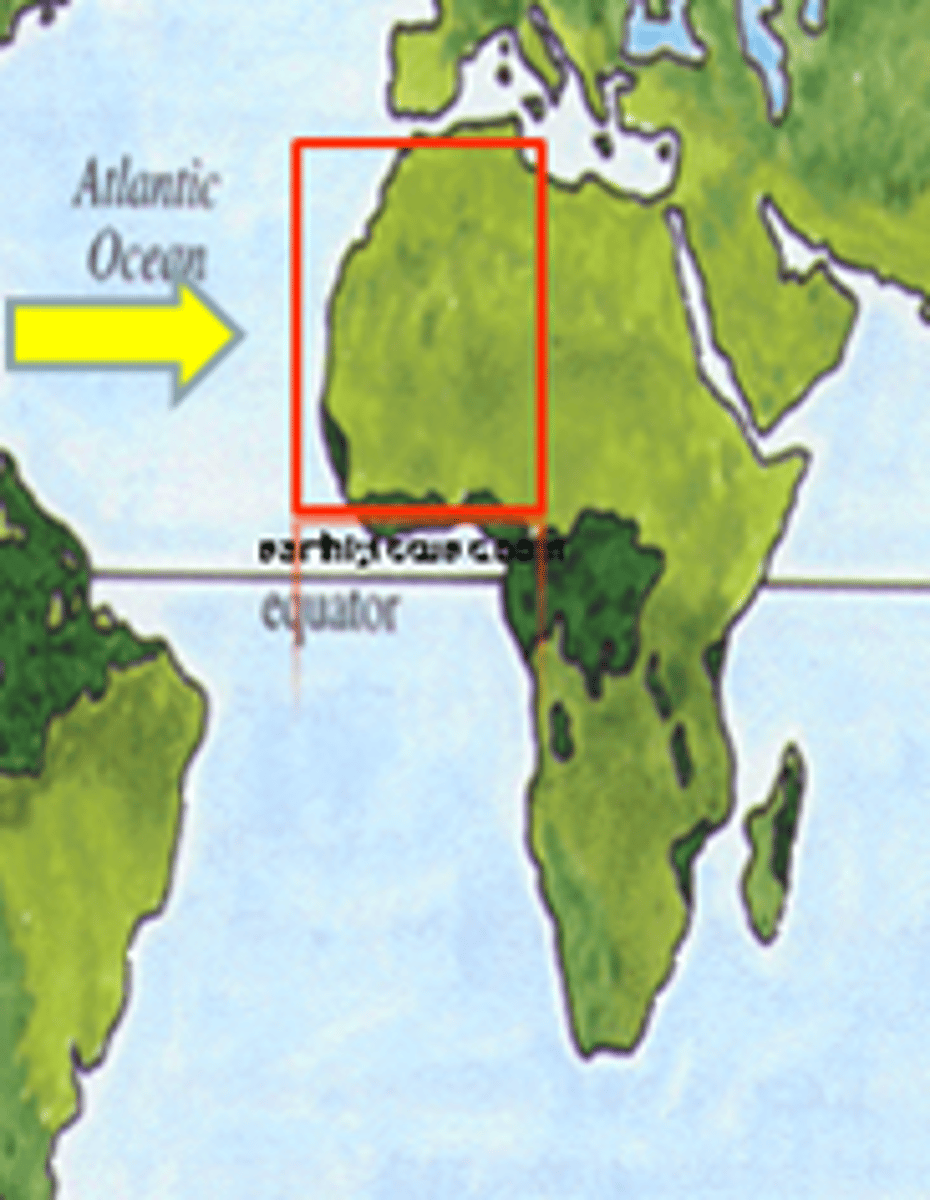
American Colonization Society
Formed in 1817, it purchased a tract of land in Liberia and returned free Blacks to Africa.
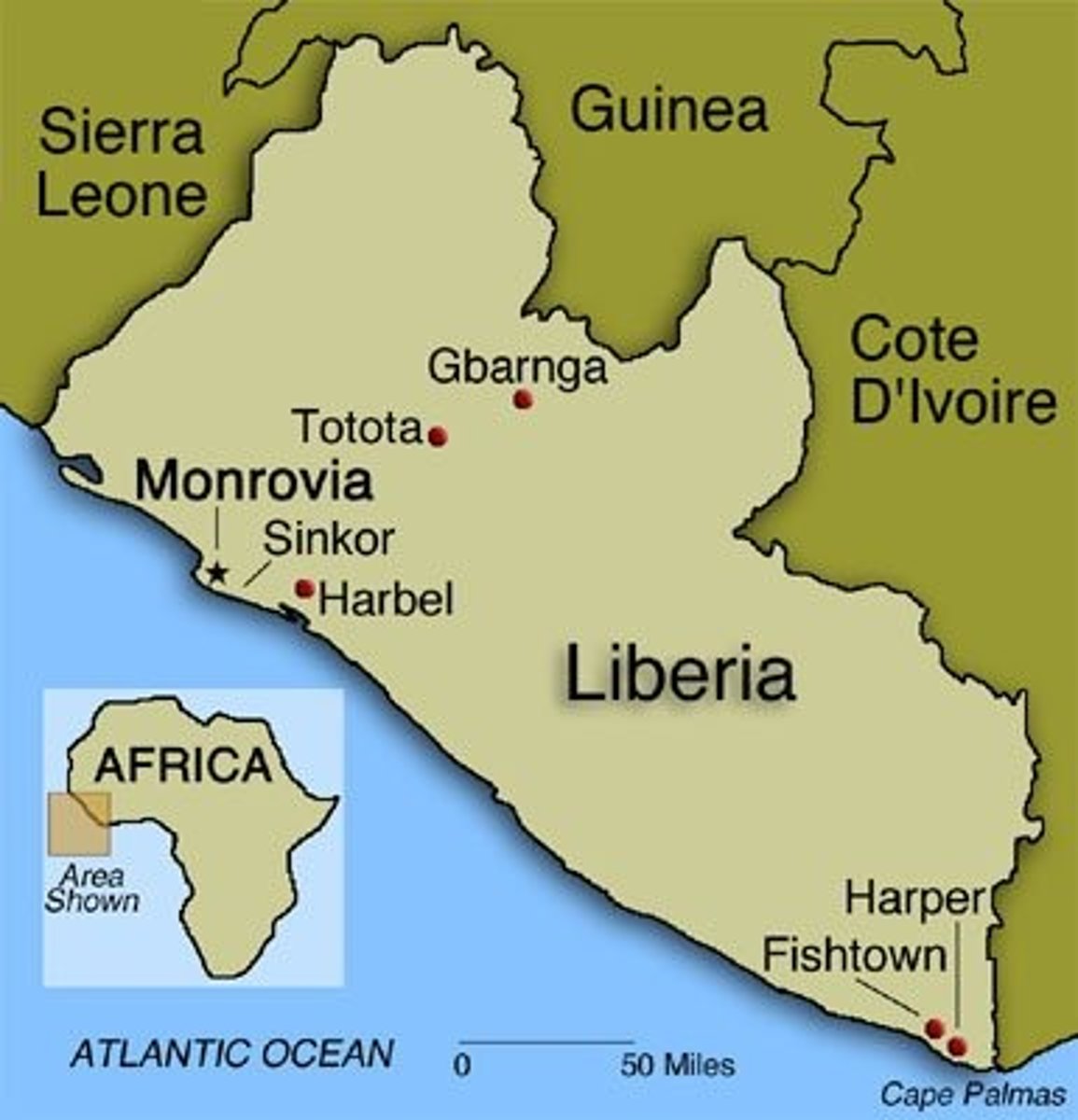
Liberia
In 1820, the American Colonization Society created a colony in West Africa for freed slaves to go. By the 1840s this colony had its own constitution and became an independent nation.
The Liberator
An anti-slavery newspaper written by William Lloyd Garrison. It drew attention to abolition, both positive and negative, causing a war of words between supporters of slavery and those opposed.

American Anti-Slavery Society
Abolitionist society founded by William Lloyd Garrison, who advocated the immediate abolition of slavery. By 1838, the organization had more than 250,000 members across 1,350 chapters.

Appeal to the Colored Citizens of the World (1829)
Incendiary abolitionist track advocating the violent overthrow of slavery. Published by David Walker, a Southern-born free black.

Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass (1845)
Vivid autobiography of the escaped slave and renowned abolitionist Frederick Douglass

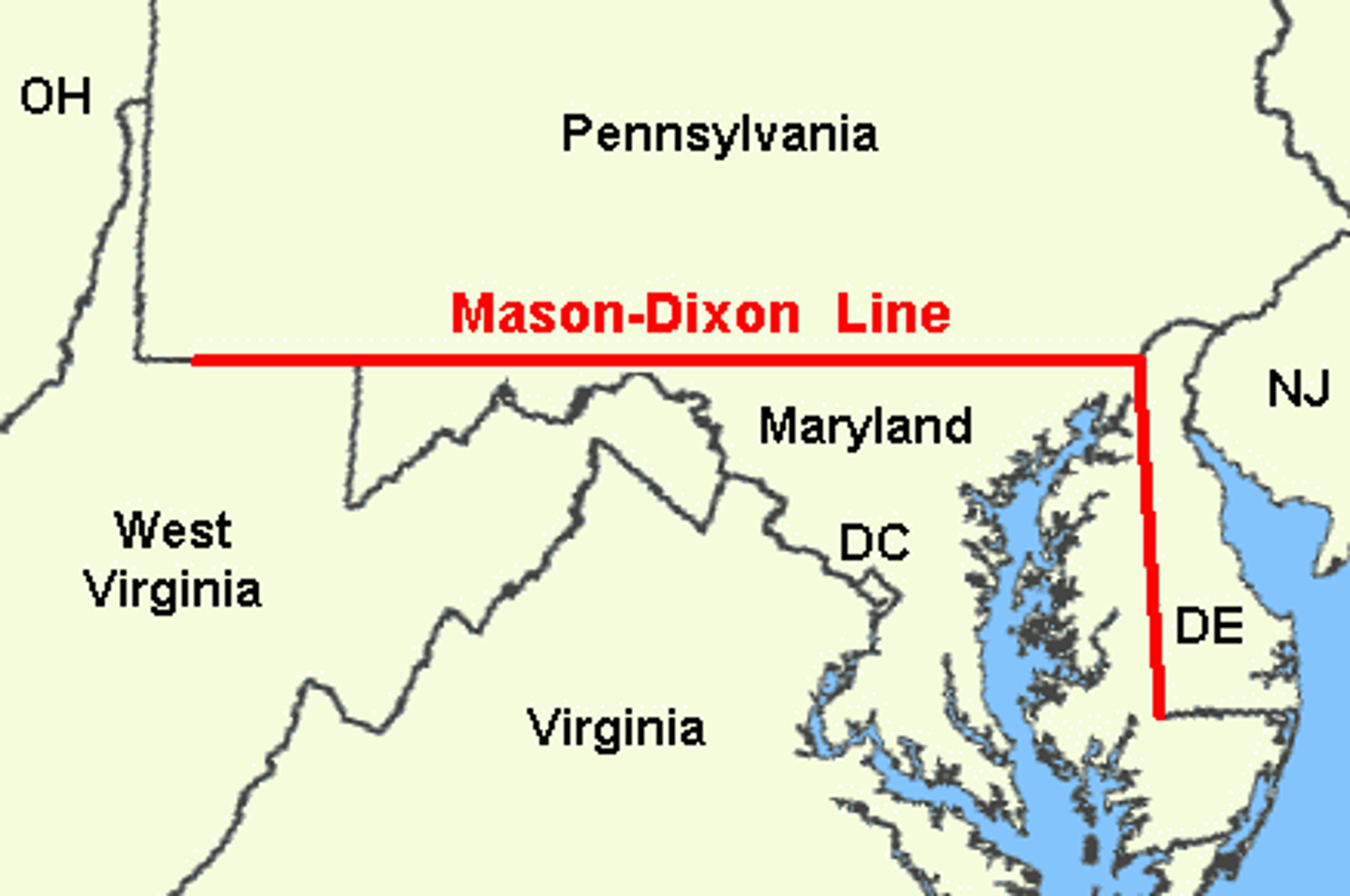
Mason-Dixon line
Boundary between Pennsylvania and Maryland that divided the Middle Colonies from the Southern Colonies
Gag Resolution
Strict rule passed by prosouthern Congressmen in 1836 to prohibit all discussion of slavery in the House of Representatives
William T. Johnson
A free Black American man who owned slaves himself; known as the "Barber of Natchez"
Nat Turner
Leader of a slave rebellion in 1831 in Virginia. Revolt led to the deaths of 20 whites and 40 blacks and led to the "gag rule' outlawing any discussion of slavery in the House of Representatives.

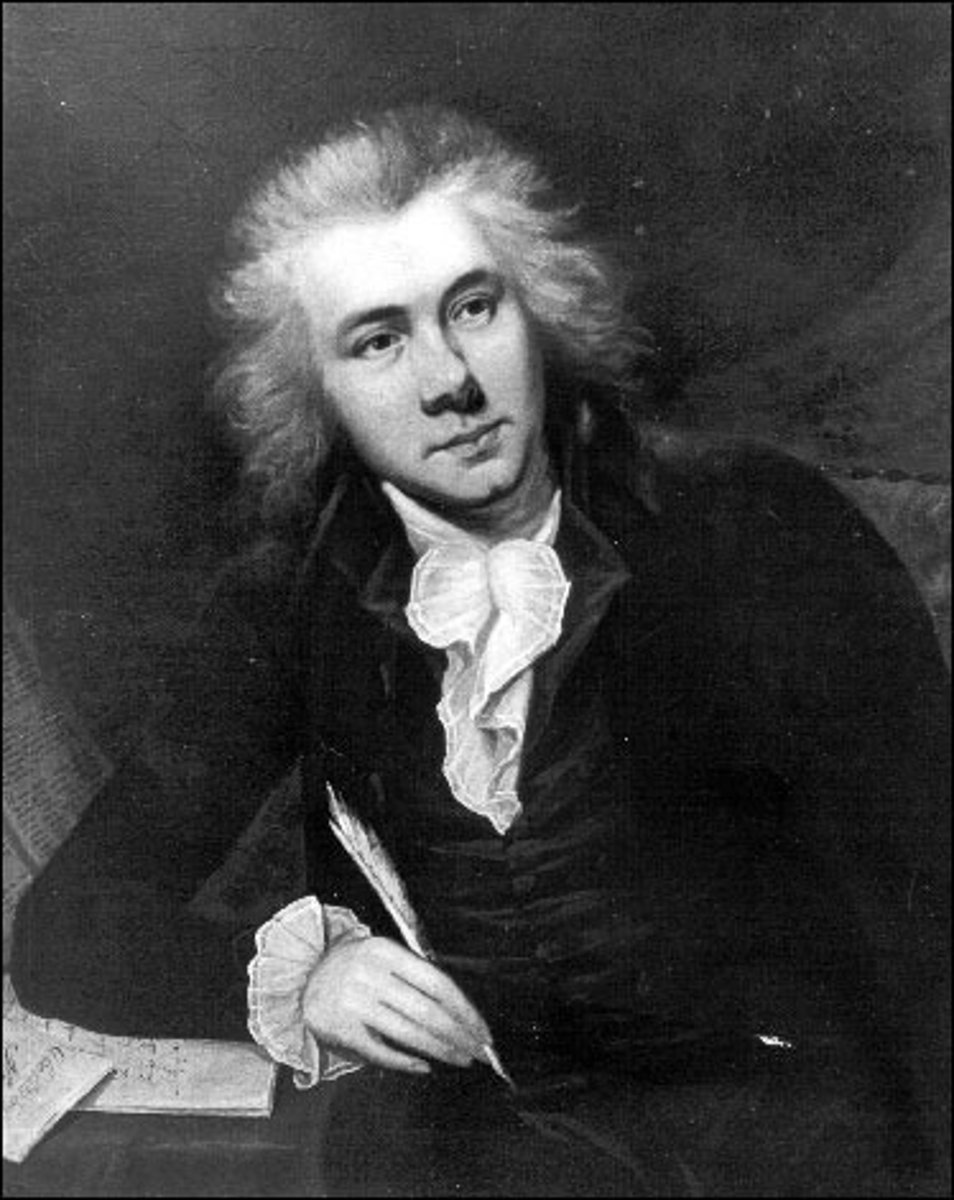
William Wilberforce
British statesman and reformer; leader of abolitionist movement in English parliament that led to end of English slave trade in 1807.

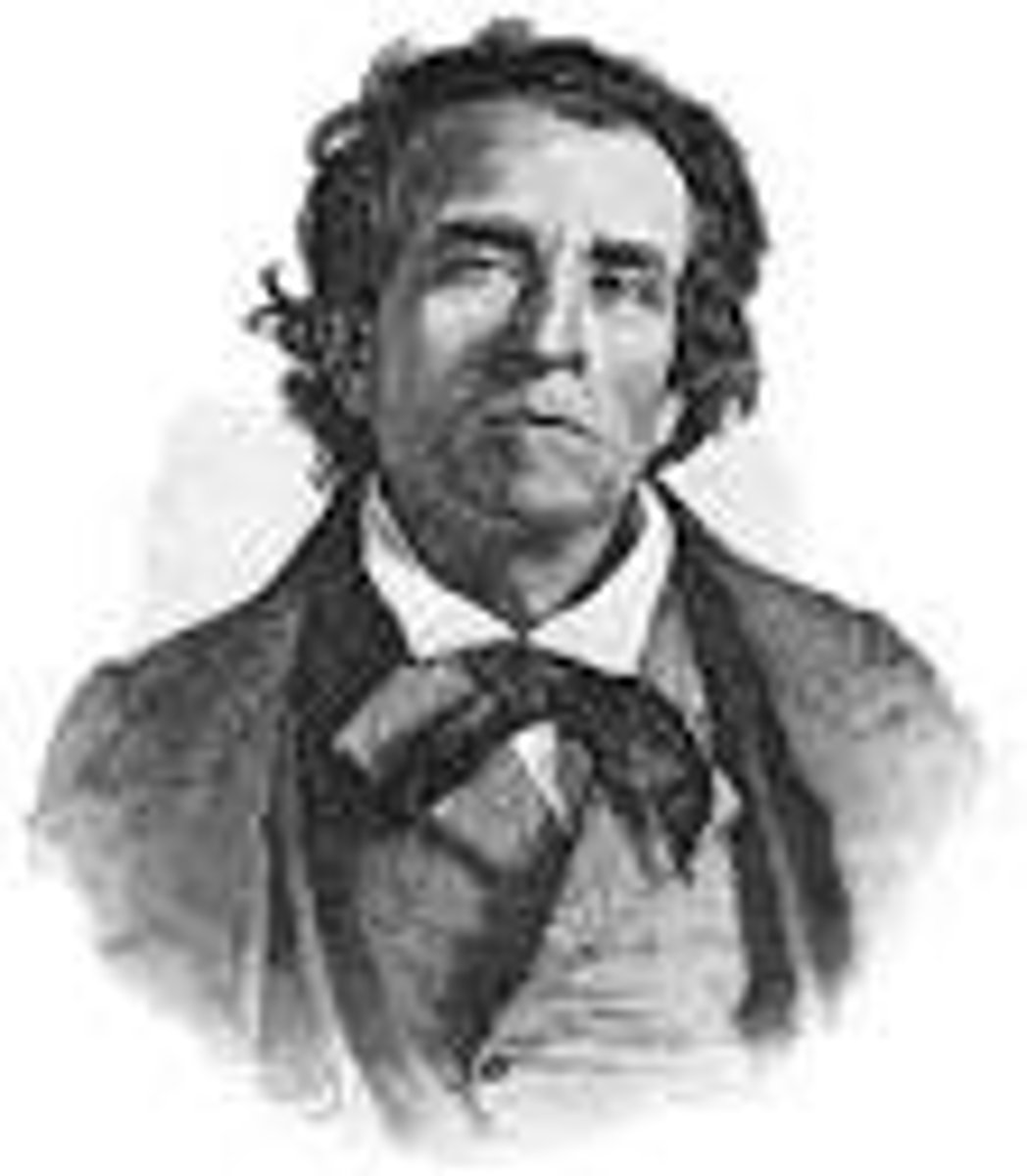
Theodore Dwight Weld
American abolitionist whose pamphlet "American Slavery As It Is" (1839) inspired Harriet Beecher Stowe's novel Uncle Tom's Cabin.

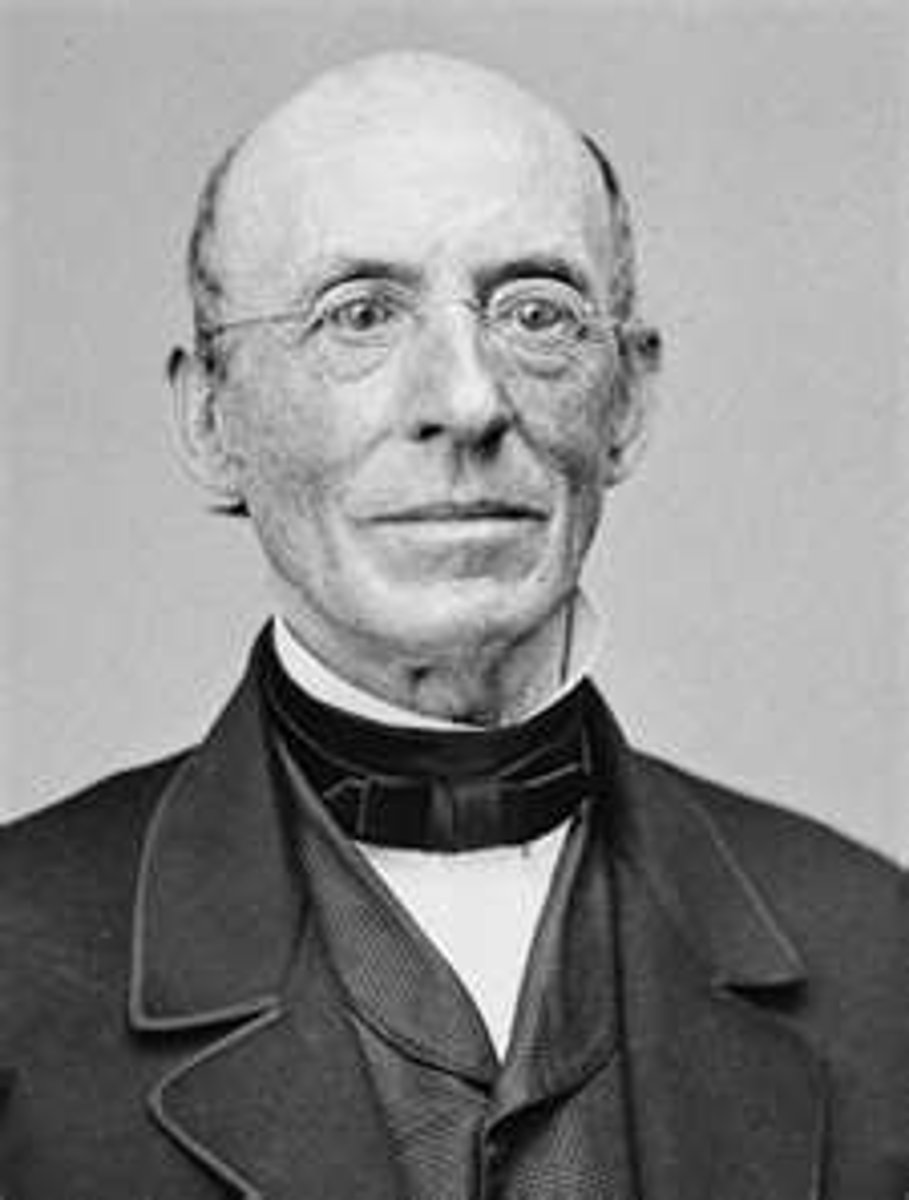
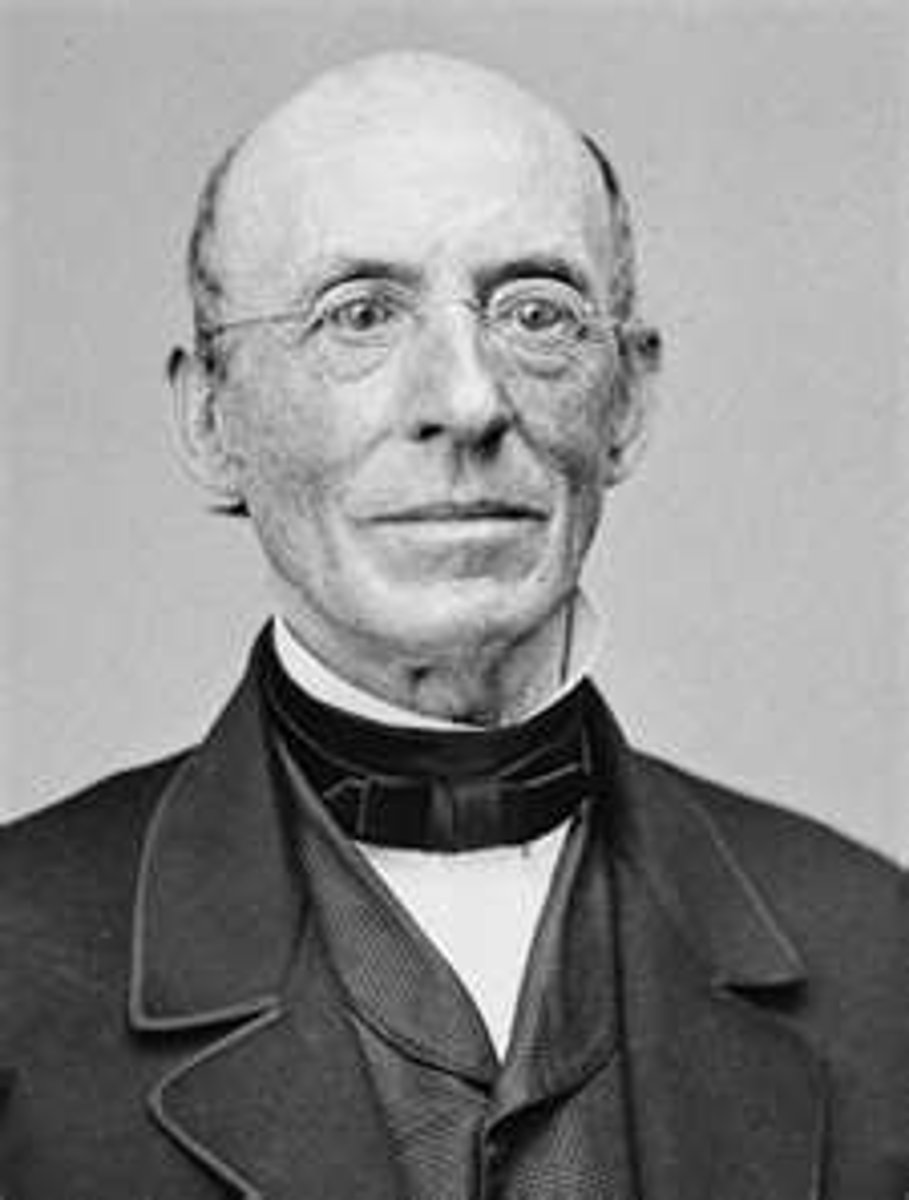
William Lloyd Garrison
1805-1879. Prominent American abolitionist, journalist and social reformer. Editor of radical abolitionist newspaper "The Liberator", and one of the founders of the American Anti-Slavery Society.

David Walker
Black abolitionist who called for the immediate emancipation of slaves; wrote the "Appeal to the Colored Citizens of the World."- called for a bloody end to white supremacy; believed that the only way to end slavery was for slaves to physically revolt.
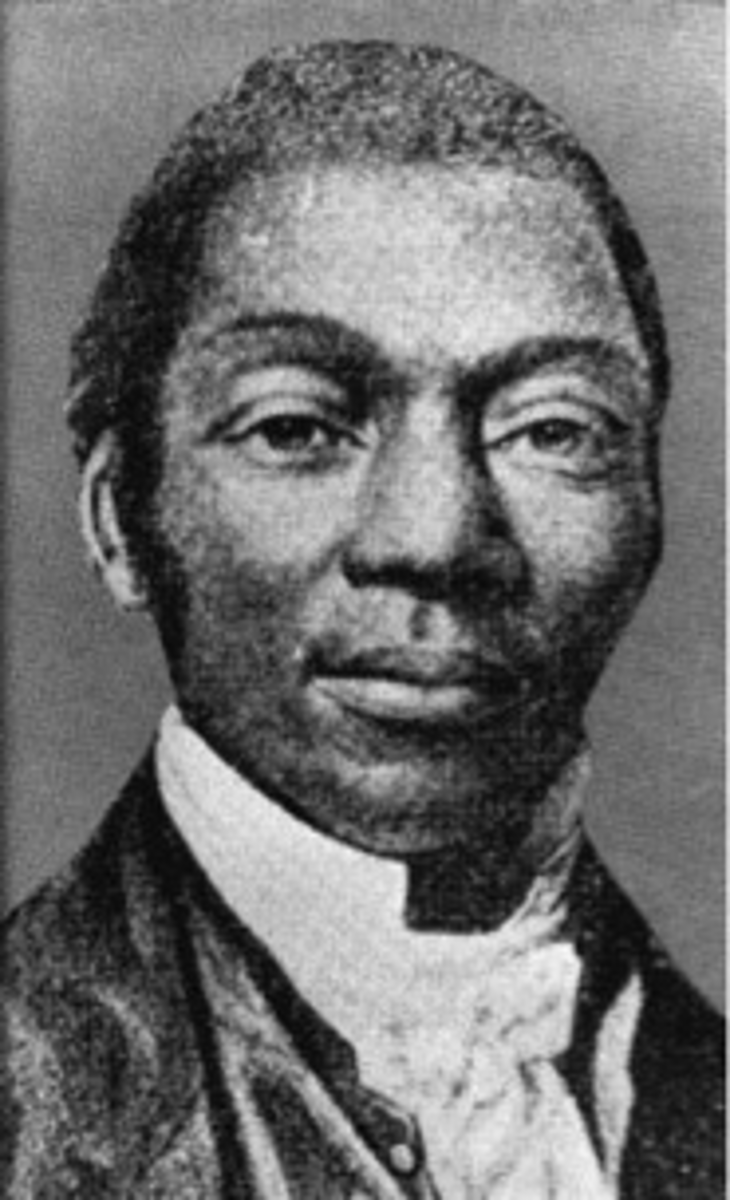

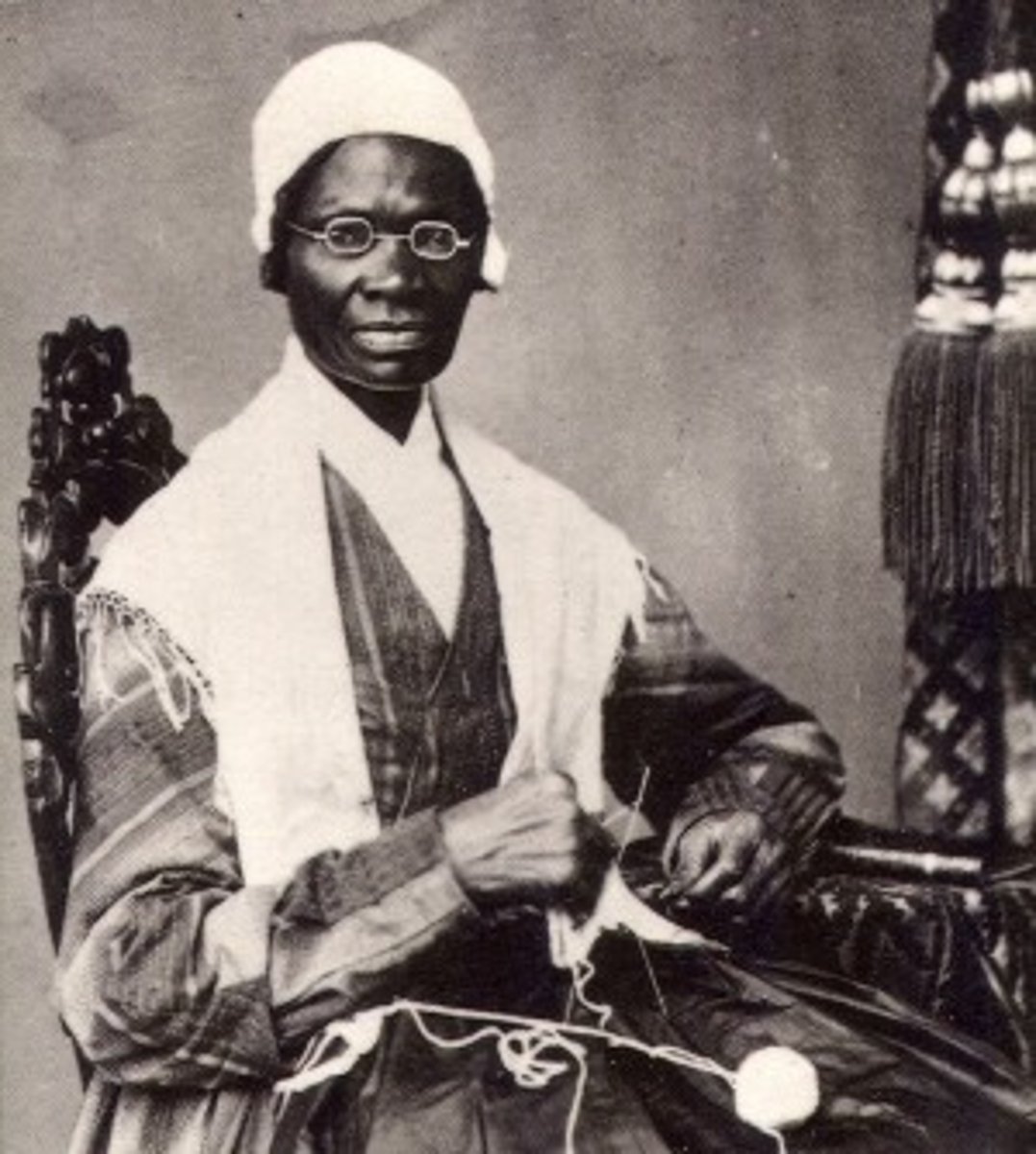
Sojourner Truth
United States abolitionist and feminist who was freed from slavery and became a leading advocate of the abolition of slavery and for the rights of women (1797-1883)

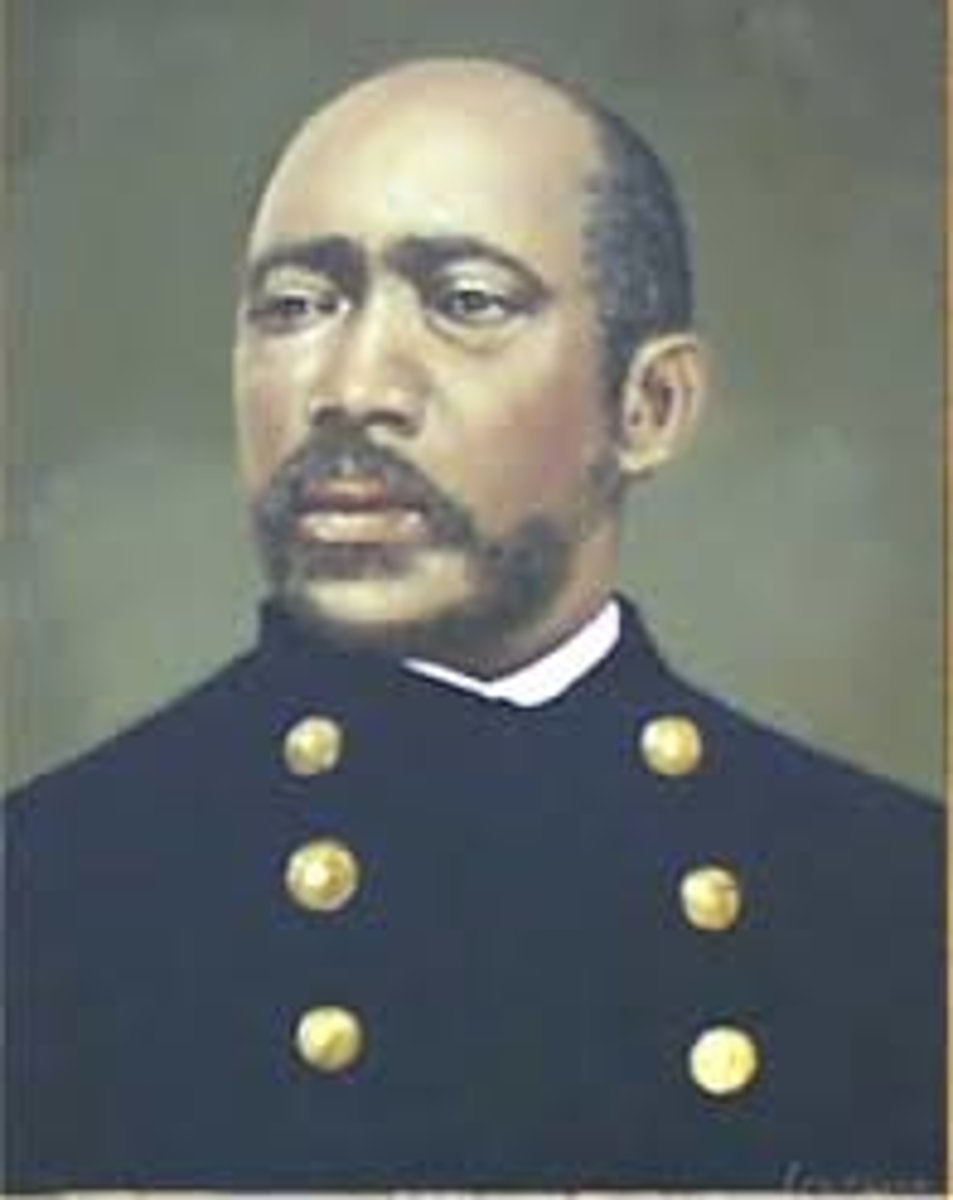
Martin Delany
(1812-1885) Black abolitionist and advocate of relocating freed blacks to Africa, even visiting West Africa's Niger Valley in search of a suitable location in 1859.

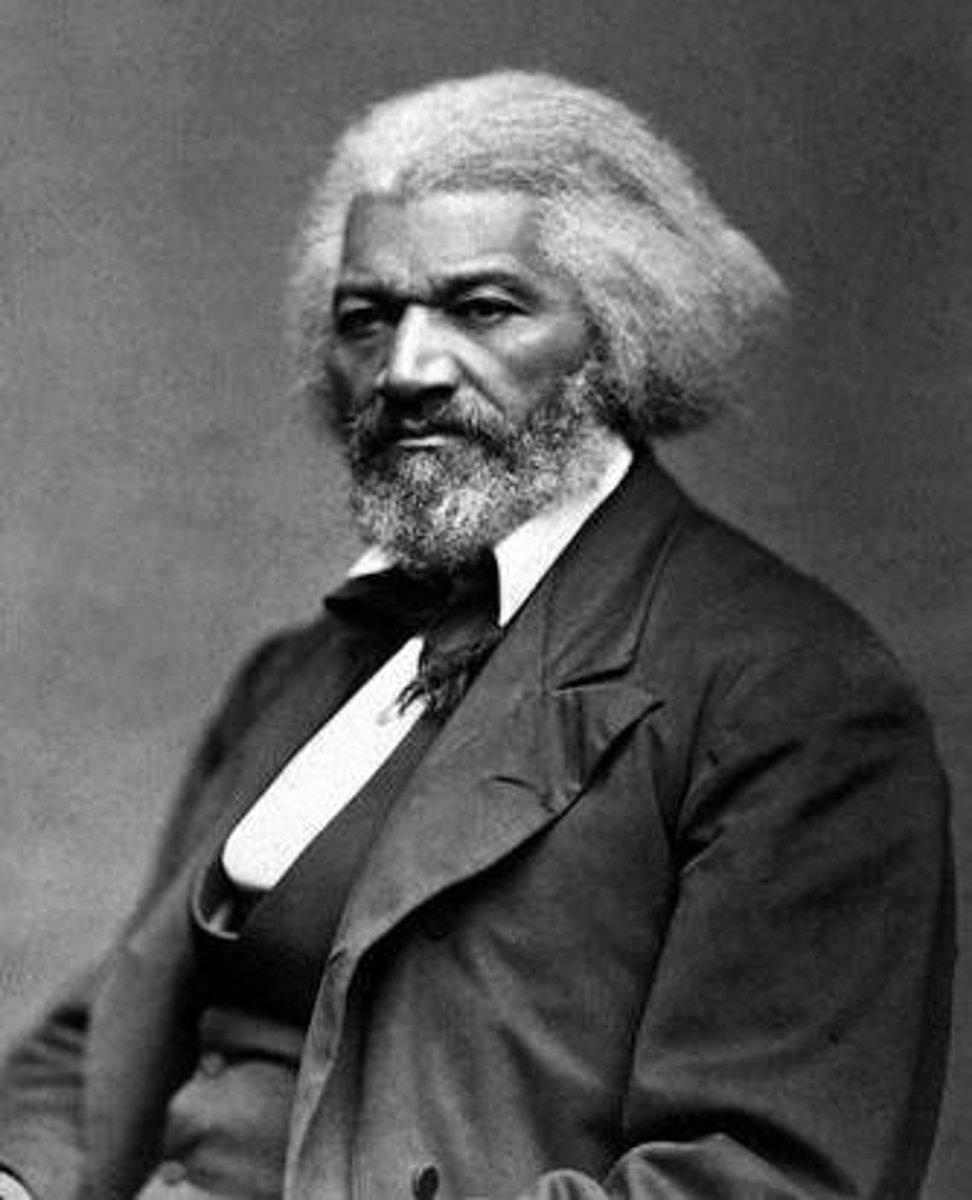
Frederick Douglass
(1817-1895) American abolitionist and writer, he escaped slavery and became a leading African American spokesman and writer. He published his biography, The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, and founded the abolitionist newspaper, the North Star.

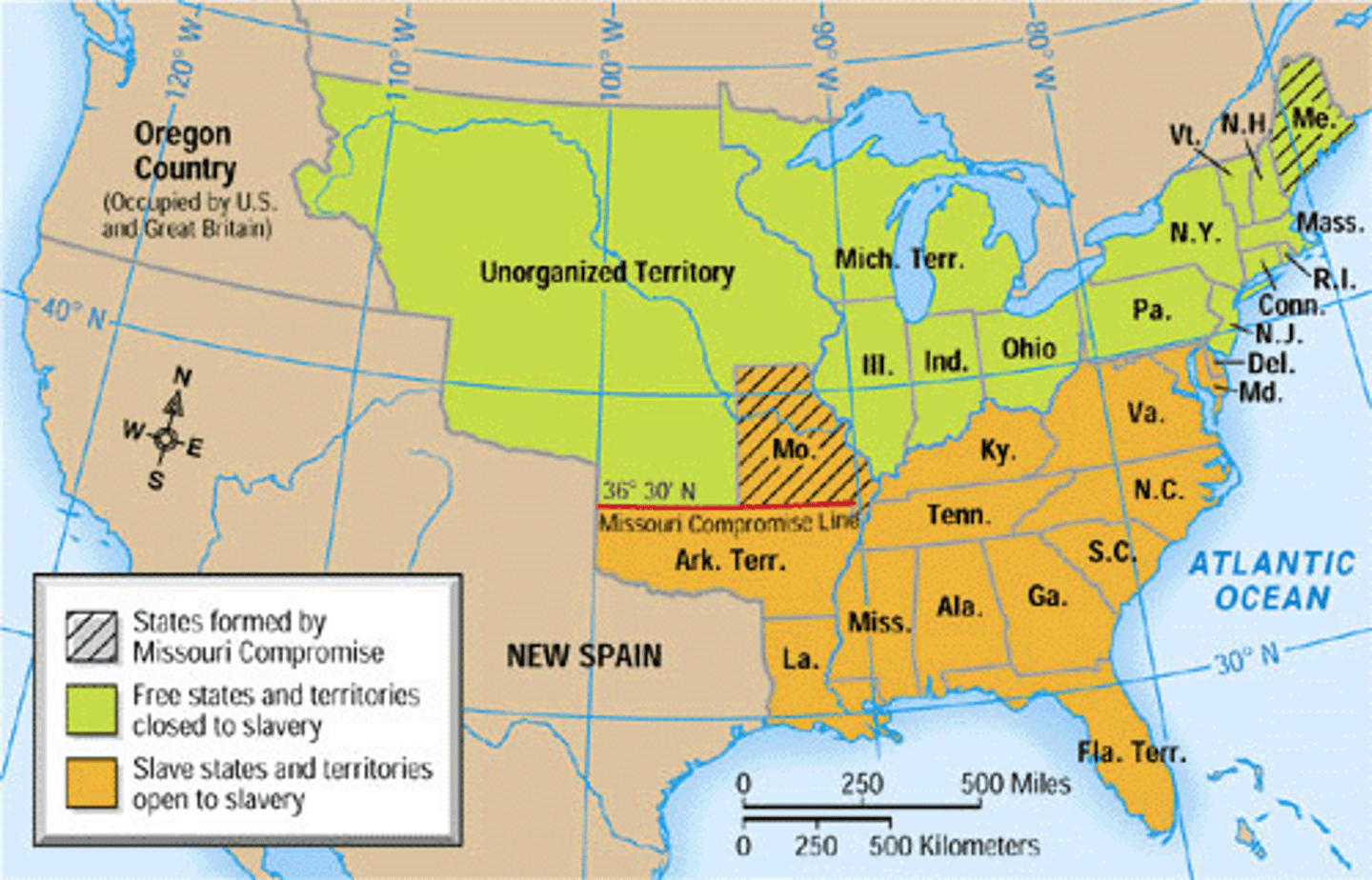
Missouri Compromise of 1820
Allowed Missouri to enter the union as a slave state, Maine to enter the union as a free state, prohibited slavery north of latitude 36˚ 30' within the Louisiana Territory (1820)
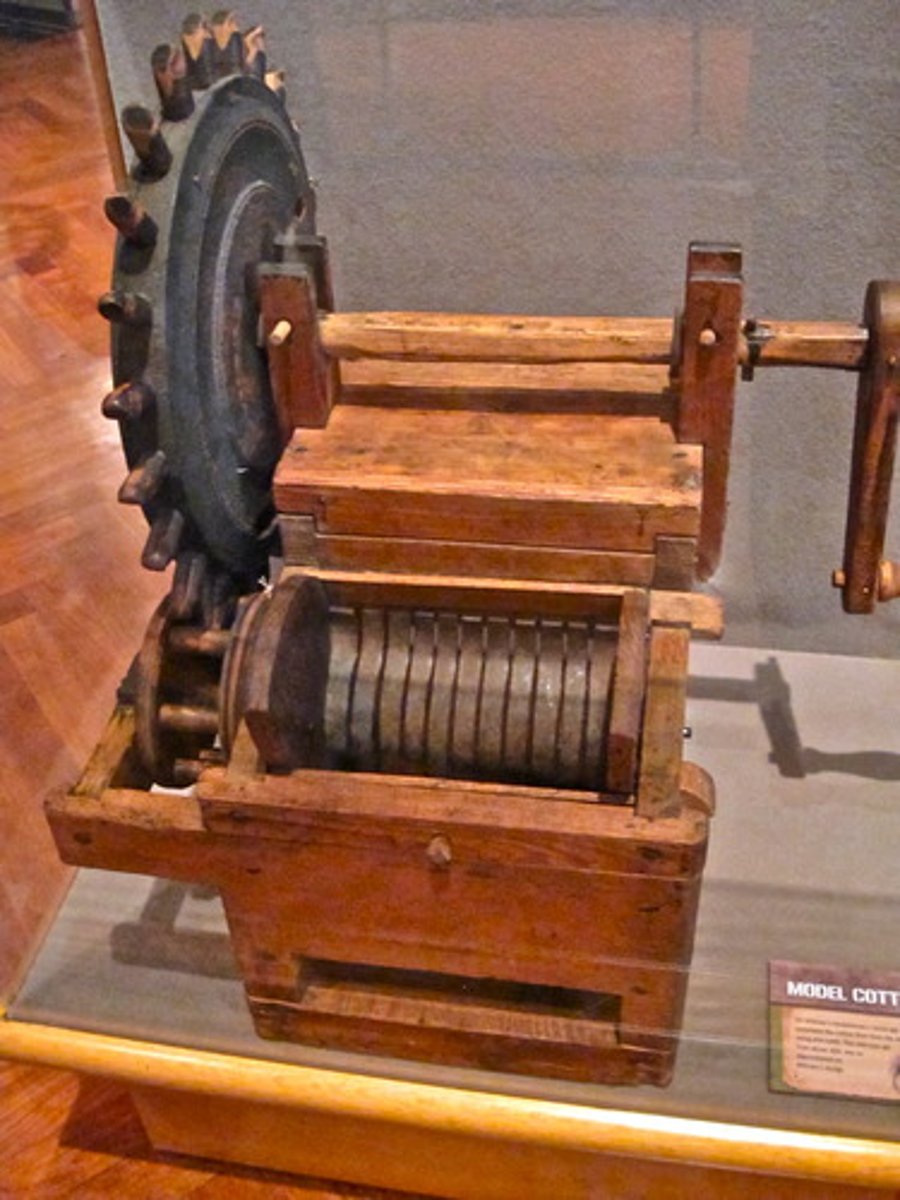
Cotton gin
A machine for cleaning the seeds from cotton fibers, invented by Eli Whitney in 1793
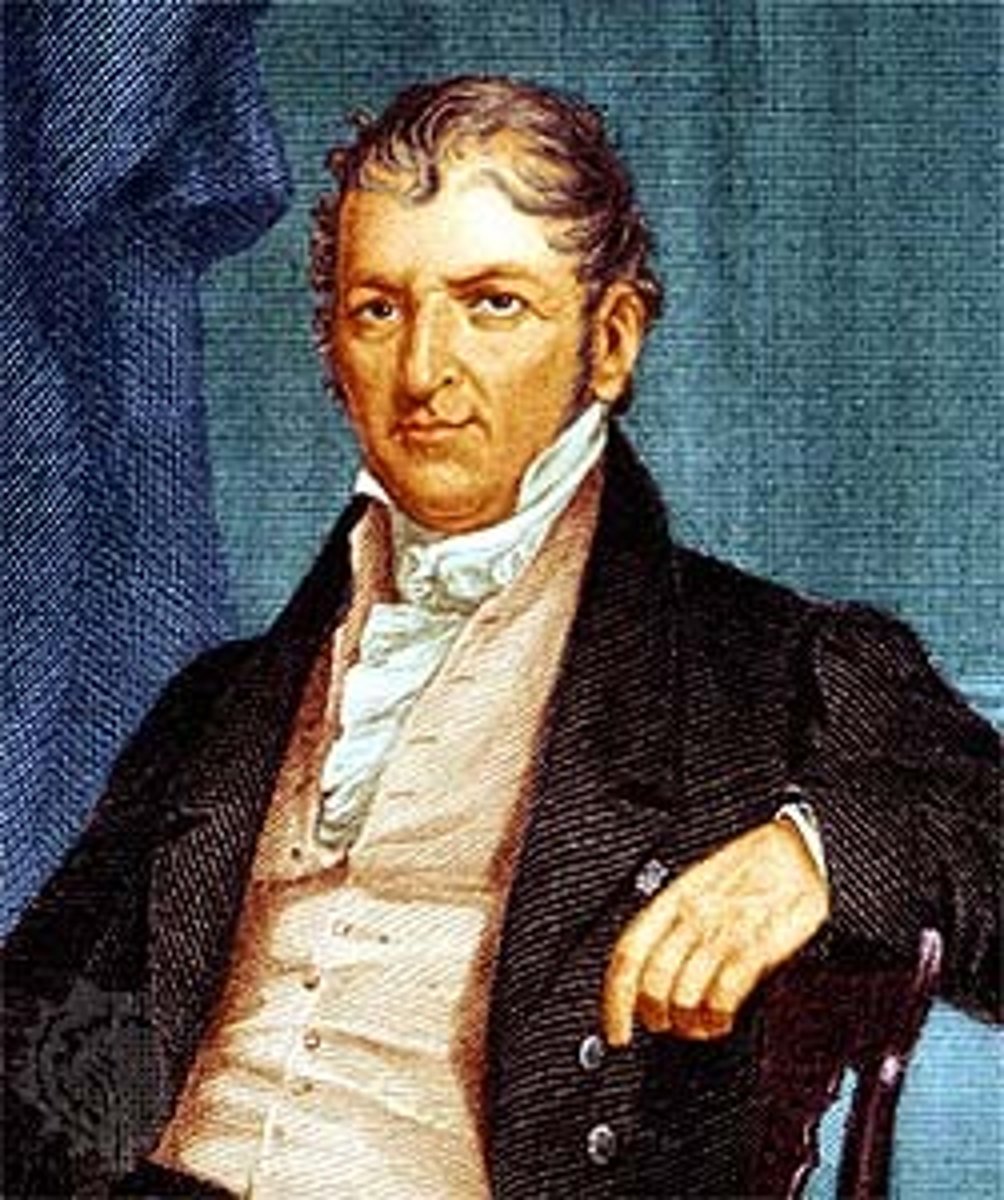
Eli Whitney
United States inventor of the mechanical cotton gin (1765-1825)

Free Soil Party
Formed in 1847 - 1848, dedicated to opposing slavery in newly acquired territories such as Oregon and ceded Mexican territory.

Abolitionist Movement
An international movement that between approximately 1780 and 1890 succeeded in condemning slavery as morally repugnant and abolishing it in much of the world; the movement was especially prominent in Britain and the United States.
