Chapter 25: Structure and Function of the Cardiovascular System PrepU
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
The electrical activity of the heart is recorded on the ECG. What does the T wave on the ECG represent?
Depolarization of the sinoatrial node
Depolarization of the ventricular conduction system
Repolarization of the atrium
Repolarization of the ventricles
4
Which factor has a powerful vasodilatory effect on arterioles and increases capillary permeability?
histamine
norepinephrine
prostaglandins
serotonin
1
A client with a history of heart failure has the following echocardiogram results: heart rate 80 beats/minute; end-diastolic volume 120 mL; and end-systolic volume 60 mL. What is this client's ejection fraction (EF)?
50%
2 mL
180 mL
0.80
1
Which blood vessel layer is made primarily of muscle?
Tunica intima
Tunica adventitia
Tunica externa
Tunica media
4
There are three main atrial pressure waves that occur during the cardiac cycle. What are the three main atrial pressure waves? Select all that apply.
b
a
v
c
2,3,4
The heart consists of four valves. Which are the semilunar valves? Select all that apply.
Pulmonary
Mitral
Tricuspid
Aortic
1,4
Which enzyme has a powerful vasodilator effect on arterioles and increases capillary permeability?
Serotonin
Histamine
Prostaglandins
Arachidonic acid
2
The nurse is reviewing the anatomy and physiology of the heart. What is the function of the right atrium?
Pumps blood to the lungs
Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs
Pumps blood into the systemic circulation
Receives blood returning to the heart from the systemic circulation
4
The nurse identifies the blood vessel layer that constricts to regulate and control diameter as:
Tunica externa
Tunica media
Tunica intima
Tunica adventitia
2
Which of the following is true regarding pulmonary circulation?
It is the larger of the two circulatory systems.
It consists of the left side of the heart, the aorta, and its branches.
It is a low-pressure system that allows for improved gas exchange.
The system functions with an increased arterial pressure to circulate through the distal parts of the body.
3
A client took a weight loss drug that activated the alpha-adrenergic receptors in the sympathetic nervous system. Which manifestations would the nurse expect to occur? Select all that apply.
Increased cardiac cycle speed
Decreased myocardial contraction
Increased blood pressure of cardiac contraction
Decrease in respiration rate
1,3
A nurse is assessing a client who lost consciousness during a wrestling match when their opponent applied a neck hold. The client likely lost consciousness because:
the client experienced temporary cardiac ischemia.
a baroreceptor was stimulated.
cardiac output suddenly dropped.
the position caused bradycardia.
2
The heart consists of four valves. Which are the heart's atrioventricular valves? Select all that apply.
Aortic
Pulmonary
Mitral
Tricuspid
3,4
The nurse is caring for a client with a deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which is occluding the client's left posterior tibial vein. For which potential complications would the nurse monitor the client? Select all that apply.
Infarction of left lower leg
Thrombotic stroke
Pulmonary embolism
Left lower leg edema
Myocardial infarction
3,4
The heart controls the direction of blood flow. What is the role of the aortic valve?
Controls the direction of blood flow from the ventricles to the atria
Controls the direction of blood flow from the atria to the ventricles
Controls the direction of blood flow from the left side of the heart to the systemic circulation
Controls the direction of blood flow from the left side of the heart to the lungs
3
A client has prominent jugular veins. What type of medical problem is associated with prominent jugular veins?
Right-sided heart failure
Shock
Cerebrovascular accident (stroke)
Left-sided heart failure
1
Which is the correct sequence of blood return to the heart?
capillaries, arterioles, arteries, right atrium
capillaries, arterioles, veins, left atrium
capillaries, venules, veins, left atrium
capillaries, venules, veins, right atrium
4
If a client experiences sympathetic nervous stimulation of the heart, the nurse will observe which changes in manifestations?
Decreased contractility and decreased heart rate
Decreased rate and force of contraction
Increased heart rate and increased contractility
Increased heart rate and decreased contractility
3
Which related circulatory complication can result from surgical treatment for metastatic breast cancer?
Hypotension upon standing
Lymphedema in the affected arm
Irregular heart rate
Tachycardia when at rest
2
A client has just experienced stimulation of the vagus nerve. Which sign would the nurse anticipate the client to manifest?
Increased cardiac contractility
Decreased heart rate
Decreased blood coagulation
Increased heart rate
2
The health care provider states that a client has adequate collateral circulation. The nurse interprets this as:
long-term compensatory regulation of blood flow.
anastomosis of the arterial and venous circulation.
development of increased collagen.
establishment of compensatory lymphatic drainage.
1
Which blood vessels function without the benefit of having walls comprised of three muscular layers?
Arteries
Capillaries
Arterioles
Veins
2
If the parasympathetic neurotransmitter releases acetylcholine, the nurse should anticipate observing what changes in the ECG pattern?
Slowing of heart rate to below 60 beats/minute
Disorganized ventricular fibrillation
Heart rate 150 beats/minute, labeled as supraventricular tachycardia
Complete cardiac standstill
1
The school nurse is doing a health class on the functional organization of the circulatory system. What is the function of the capillaries in the circulatory system?
Collect deoxygenated blood from the tissues
Exchange gases, nutrients, and wastes
Distribute oxygenated blood to the tissues
Pump blood
2
Downstream peripheral pulses have a higher pulse pressure because the pressure wave travels faster than the blood itself. What occurs in peripheral arterial disease?
The reflected wave is transmitted more rapidly through the aorta.
Downstream peripheral pulses are increased even more than normal.
Downstream peripheral pulses are greater than upstream pulses.
The pulse decreases, rather than increases, in amplitude.
4
Nitroglycerin is the drug of choice in treating angina. What does nitroglycerin release into the vascular smooth muscle of the target tissues?
Calcium channel blocker
Antithrombin factor
Nitric oxide
Platelet-aggregating factor
3
Release of which humoral factors will result in vasodilation?
Angiotensin II
Histamine
Serotonin
Norepinephrine
2
A client says that when the hospital checked their blood pressure after they lost a lot of blood in a work-related accident, the top number (systolic pressure) was lower than usual but the bottom number (diastolic pressure) was about the same. Why is this?
Systemic vasodilation maintained the diastolic pressure.
Systemic vasoconstriction maintained the diastolic pressure.
The stroke volume increased with blood loss.
The heart rate increased with blood loss.
2
A client’s echocardiogram identified a narrowed valve that has resulted in a decreased blood flow between the left atria and left ventricle. The nurse would interpret this as the:
Pulmonic valve
Tricuspid valve
Bicuspid valve
Aortic valve
3
The circulatory system can be divided into two parts. What does the systemic circulation include? Select all that apply.
Right heart
Aorta
Pulmonary artery
Capillaries
2,4
During a physical examination of a client, the nurse palpates the point of maximal impulse (PMI) in the seventh intercostal space lateral to the left midclavicular line. What is the most appropriate action for the nurse to take?
Notify the health care provider.
Assess the client for symptoms of left ventricular hypertrophy.
Auscultate both of the carotid arteries for the presence of a bruit.
Document that the PMI is in the normal anatomic location.
2
A nurse working with a client in heart failure is explaining why the symptoms of the heart failure were not evident for a long period of time. When describing the Frank–Starling mechanism, the nurse will explain:
the molecular structure of actin and myosin and their effect on contraction.
the relationship between venous return and stroke volume.
the physiologic function of chemoreceptors and baroreceptors.
the high oxygenation needs of cardiac muscle and the role of coronary circulation.
2
A nurse is reviewing an echocardiogram for a client with a congenital defect in the papillary muscles of the heart. Based on this result, which assessment should the nurse complete?
Auscultate for a murmur caused by the backward expulsion of blood through the atrioventricular valves.
Monitor the blood pressure.
Auscultate for an extra heart sound due to incomplete semilunar valve closure.
Palpate the pericardium for a heave or thrill.
1
During an assessment of a client with ankle swelling, the nurse observes jugular venous pulsations 5 cm above the sternal angle when the head of their bed is elevated 45 degrees. What is the correct interpretation of this finding?
The client has increased pressure related to right-sided heart failure.
The client has stenosis of the jugular veins.
The client has decreased fluid volume.
The client has an increased cardiac output.
1
A client is diagnosed with an abdominal aortic aneurysm that the health care provider just wants to “watch” for now. When teaching the client about signs/symptoms to watch for, the nurse will base the teaching on which physiologic principle?
The primary cause for rupture relates to increase in abdominal pressure, such as straining to have a bowel movement.
As the aneurysm grows, more tension is placed on the vessel wall, which increases the risk for rupture.
The larger the aneurysm, the less tension placed on the vessel.
Small diameter of this vessel will cause it to rupture more readily.
2
Colloidal osmotic pressure acts differently than the osmotic effects of the plasma proteins. What is its action?
Pulls fluid back into the capillary
Pushes fluid into the extracellular spaces
Controls the direction of the fluid flow in the large arteries
Pulls fluid into the interstitial spaces
1
The troponin complex is one of a number of important proteins that regulate actin–myosin binding. Troponin works in striated muscle to help regulate calcium-mediated contraction of the muscle. Which of the troponin complexes is diagnostic of a myocardial infarction?
Troponin T and troponin I
Troponin C and troponin T
Troponin A and troponin C
Troponin A and troponin I
1
The nurse is teaching a client diagnosed with heart failure about preload. Which principle would be most appropriate to provide to the client?
Preload determines the frequency by which the ventricles contract and blood is ejected.
Preload represents the volume work of the heart.
Preload is the ability of the heart to change its force of contraction.
Preload is the pressure or tension work of the heart.
2
The linear velocity of blood flow in the circulatory system varies widely. What is the linear velocity in the aorta?
40 to 45 cm/second
20 to 25 cm/second
50 to 55 cm/second
30 to 35 cm/second
4
A grandparent who works as a cook at a nearby school was recently hospitalized when they lost an extensive amount of blood in a work-related accident. The grandparent tells the nurse that they heard that they would keep feeling faint until the brain made more blood. The nurse knows that when the blood pressure dropped, the pressure in the carotid arteries decreased. This was detected by baroreceptors in the carotid arteries. What did the baroreceptors do?
Increase sympathetic stimulation of the heart and blood vessels
Increase parasympathetic stimulation of the heart and blood vessels
Stimulate the brain to form new red blood cells
Inhibit renin release from the kidneys to promote fluid retention
1
The circulatory system is divided into two parts. What does the pulmonary circulation include? Select all that apply.
Pulmonary veins
Vena cava
Pulmonary artery
Aorta
Right heart
1,3,5
When intracranial pressure (ICP) equals intra-arterial pressure, the central nervous system ischemic response is initiated. This response is directed at raising arterial pressure above ICP, thereby reestablishing blood flow to the vasomotor center of the brain. What is this response called?
Cushing law
Cushing syndrome
Cushing reflex
Cushing response
3
The heart valves control the direction of blood flow. What is the function of the pulmonic valve?
Controls the direction of blood flow from the left side of the heart to the systemic circulation
Controls the direction of blood flow from the right side of the heart to the systemic circulation
Controls the direction of blood flow from the right side of the heart to the lungs
Controls the direction of blood flow from the left side of the heart to the lungs
3
Which of the following factors affect cardiac performance? Select all that apply.
Preload
Myocardial contractility
Heart rhythm
Afterload
1,2,4
A client is experiencing a sudden increase in heart rate resulting in less time in diastole. This can result in which potential complication?
Loss of action potential
Reduced cardiac contractility
Decreased stroke volume
Increased blood viscosity
3
The heart is a four-chambered muscular pump. In one day, how many gallons of blood are pumped throughout the body?
1700
1500
1600
1800
4
Preload, the stretch on the heart before contraction, is largely determined by which factor?
Vascular resistance
Venous blood return
Force of contraction
Ventricular emptying
2
Which factor represents the amount of blood that the heart must pump with each beat and is determined by the stretch of the cardiac muscle fibers and the actions of the heart prior to cardiac contraction?
Afterload
Cardiac contractility
Heart rate
Preload
4
A client with aortic insufficiency is experiencing an increase in afterload. The client will experience fatigue and activity intolerance due to:
resistance to ejection of blood from the heart.
residual blood in heart following contraction.
pressure applied to valves.
slow ventricular filling.
1
When the semilunar valves open it signals the onset of the ejection period. The aortic pressure reflects changes in the ejection of blood from which part of the heart?
Right ventricle
Left atrium
Right atrium
Left ventricle
4
During ventricular systole, closure of the atrioventricular (AV) valves coincides with which physiologic event?
Isovolumetric contraction
Atrial chamber filling
Semilunar valves opening
Aortic valve opening
1
The nurse teaches a client with peripheral edema to elevate their legs above the level of the heart several times a day. The nurse explains this action decreases _______ and increases ________ in order to reduce edema.
A:
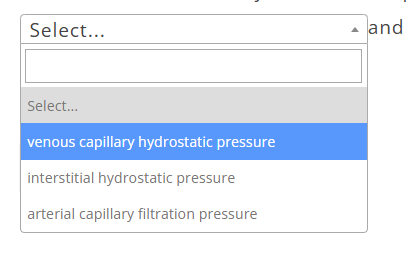
B:
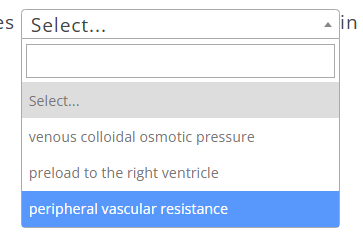
A: venous capillary hydrostatic pressure
B: preload to the right ventricle
A client with heart disease has the left ventricular ejection fraction measured. What is the normal left ventricular ejection when determined by angiocardiography?
55% - 75%
65% - 85%
45% - 65%
35% - 55%
1
A nurse is teaching a client the correct technique for taking an arterial pulse. The nurse explains that the pulsations are:
Turbulence of the blood flow
Blood flow in the veins
Korotkoff sounds
Pressure pulses
4
When reviewing diagnostic test results and physical assessment data for a client with a history of stage II hypertension, which of the following would be of most concern to the nurse?
Blood pressure of 146/80
Point of maximum impulse is located midclavicular at the 5th intercostal space
An ejection fraction of 40%
A heart rate (HR) of 62 beats/minute
3
Which neurotransmitter is associated with the parasympathetic nervous system?
Norepinephrine
Acetylcholine
Epinephrine
Dopamine
2
The ability in the heart to increase output as needs of the body change depends on which physiologic factors? Select all that apply.
Preload
Heart rate
Afterload
Cardiac contractility
Cardiac reserve
1,2,3,4
The difference between the end-diastolic and end-systolic volumes is called what?
Cardiac reserve
Stroke volume
Ejection fraction
Cardiac output
2
The pericardium is a tri-layer sac. Which layer prevents acute dilation of the heart chambers and exerts a restraining effect on the left ventricle?
Outer fibrous layer
Inner serous layer
Parietal layer
Visceral layer
1
Local control of blood flow is regulated by mechanisms that match blood flow to the metabolic needs of the tissue. Which components of the vascular system are involved in the short-term control of blood flow? Select all that apply.
Tissue
Collateral circulation
Smooth muscle
Endothelial cells
1,3,4
Vascular smooth muscle cells produce vasoconstriction or dilation of blood vessels. Which local tissue factors are correlated with smooth muscle contraction and relaxation? Select all that apply.
Increased hydrogen ion concentrations
Decreased hydrogen ion concentrations
Lack of carbon dioxide
Lack of oxygen
1,4
Which statements are true regarding the capillary system? Select all that apply.
Flow into the system is controlled by colloidal osmotic pressure.
Normal function requires that all fluid that leaves the capillary beds be reabsorbed.
Fluid leaves the capillary beds via lymphatic channels.
Flow out of the system is controlled by hydrostatic pressure.
Albumin plays a significant role in maintaining the function of this system.
1,4,5
A client is lying in a recumbent position. In this client, approximately how much total blood volume is in the central circulation?
20% - 25%
25% - 30%
15% - 20%
30% - 35%
2
A nurse is caring for a client with right heart failure caused by pulmonary hypertension. Which hemodynamic parameter is most appropriate for the nurse to monitor?
Central venous pressure (CVP)
Pulmonary arterial pressure (PAP)
Systemic vascular resistance (SVR)
Blood pressure
2
A client comes to the emergency department reporting a “racing” heart and feeling “anxious.” On a heart monitor, the nurse notes a heart rate of 134 and proceeds to monitor for which complications related to tachycardia? Select all that apply.
Decrease in oxygen levels
Risk for angina
Decrease in stroke volume
Decrease in blood pressure
Increase in cardiac output
1,2,3,4
A client is having blood work done. What percentage of red blood cells represents the formed elements of the blood?
60 - 65%
40 - 45%
30 - 35%
50 - 55%
2