Module 6 -Labour and Delivery
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Regular, patterned uterine fundal contractions, progressive effacement and dilation of cervical, loss of mucus plug, rupture of membranes
Define labour
Bloody show
What is another term for the loss of the mucus plug
Water broke
What is another term for the rupture of membranes
Not effaced or dilated
Describe the cervix in this image
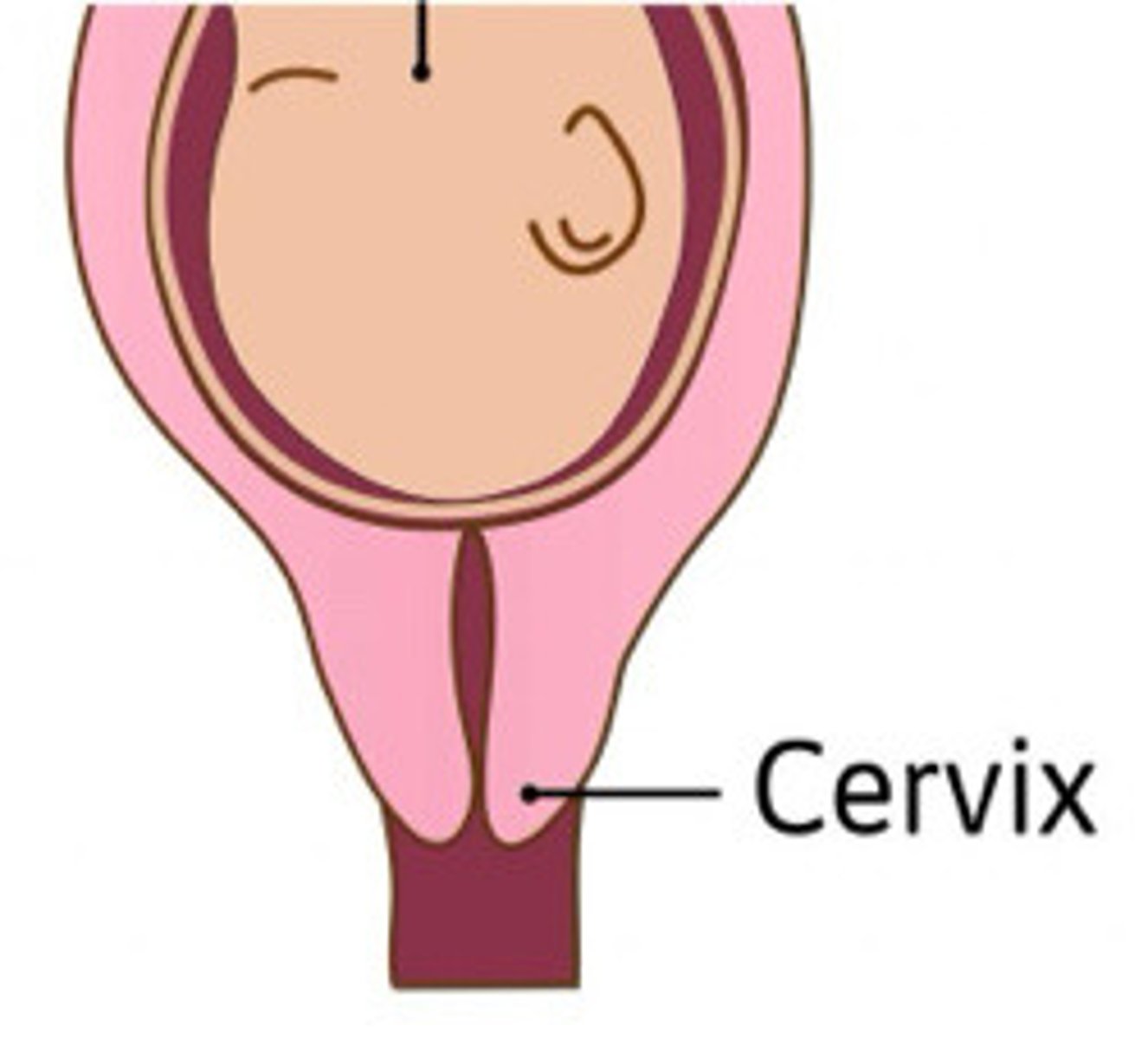
Cervix effaced and not dilated
Describe the cervix in this image
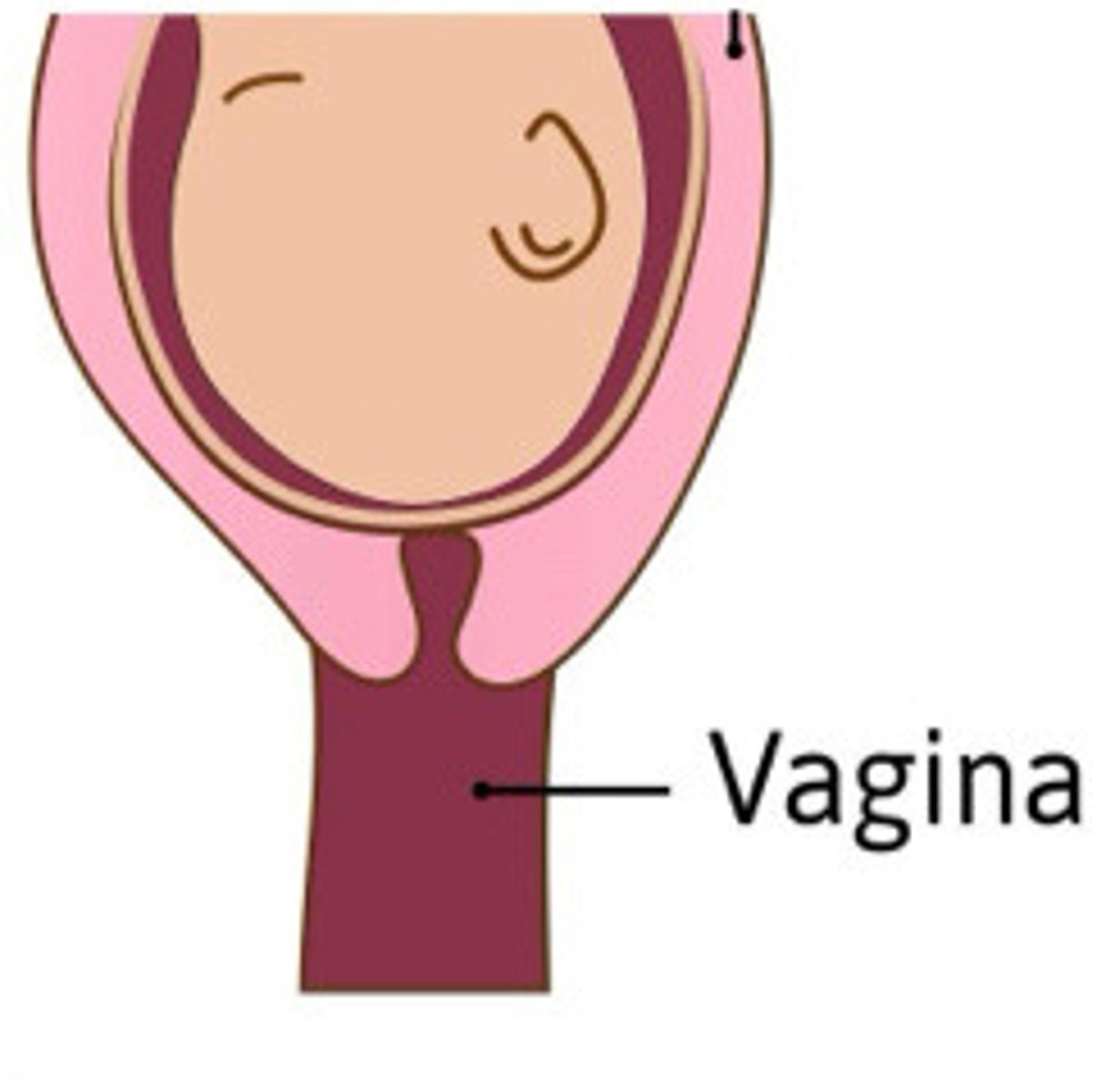
Cervix fully effaced and starting to dilate
Describe the cervix in this image
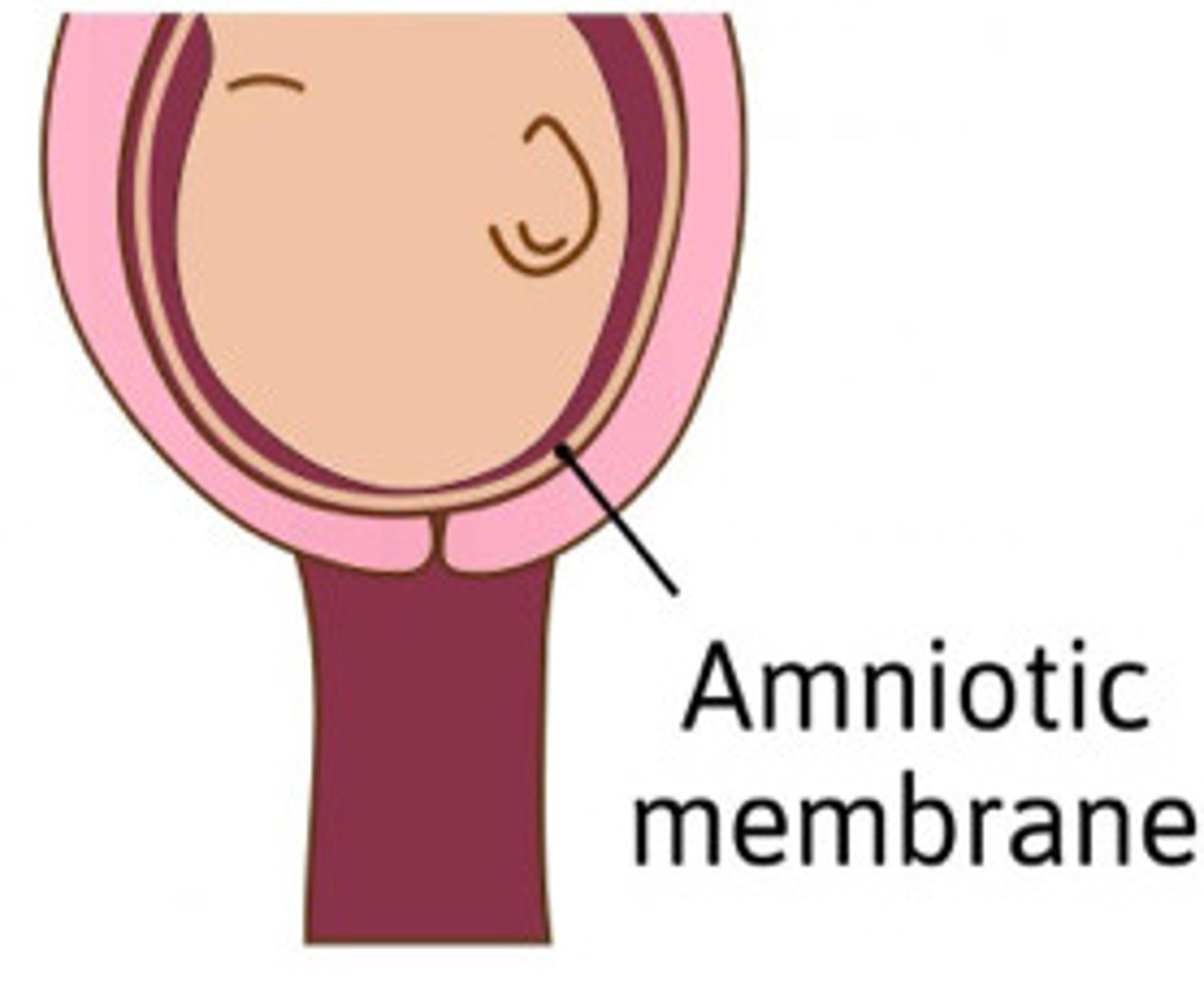
3
How many stages of labour are there
Progressive cervical effacement and dilatation, descent of fetus, regular contractions
What is the first stage of labour
12-24 hours
How long does the first stage of labour usually last
1cm/hr
What is the normal progression of cervical dilatation
2nd stage
What stage of labour does delivery occur in
True
T/F: the cervix is fully dilated in stage 2 of labour
50mins
What is the average duration in the second stage of labour in the primigravida patient
20mins
What is the average duration in the second stage of labour in the multiparous patient
Birth to expulsion of placenta
What is the third stage of labour
10 mins
What is the usual duration of the third stage of labour
Oxytocin
What hormone is released in the third stage of labour
Cephalic/vertex
what is the most common position of a fetus?
4%
What is the percentage of babies in the breech presentation
Small baby, can move around easier
What may increase the risk of the baby being in the breech position
Difficult birth
Define dystocia
Failure to progress, cervix not changing with contractions
Describe dystocia
Oxytocin through IV
How are patient with dystocia treated
Disproportion of the fetal head to the maternal pelvis, mass obstructing way, abnormal position
What are some things that may cause dystocia
Fetal head too big or maternal pelvis too small
Explain an examples of the fetal head being disproportional
Fibroids in canal
Give an example of a mass causing dystocia
Painless bleeding
What is placenta previa
Painful bleeding
What is abruption of the placenta
Induced labour
What is PROM
Placenta previa is painless and abruption is painful
What is the difference between placenta previa and the abruption of the placenta
Mild placenta abruption, IUGR, post dates, amnionitis, PROM, maternal disease, fetal death, hx of quick delivery but great distance from hospital
List 8 reasons for the induction of labour
After 40 week gestation
What post date may indicate induction of labour
Pre-eclampsia, diabetes
What are two maternal disease that may indicate the induction of labour
Black tarry substance in the neonate's first bowel movement
What is meconium
After birth
When should the meconium occur
If meconium occurs in utero
When can meconium aspiration occur
Distress
What may cause a fetus to have the meconium in utero
Lung infection
What is the main concern when aspiration of the meconium occurs
Footling/incomplete breech, prolonged membrane rupture and not uterine contractions, fetal distress, dystocia, >4kg weight, small maternal pelvic, social reasons
What are 7 reasons for a cesarean section
L/S ratio, non stress test, fetal scalp blood gases
What are some diagnostic test associated with labour and deliver
2:1
What L/S ratio indicates that fetal lungs are mature
If the fetus is monitored with contractions
When does a non stress test become a stress test
Fetal monitor
What is a non stress test
Done during labour to determine if fetus is getting enough oxygen, and determine is c-section is needed
What is a fetal scan blood gases test