all ceramic restoration
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
what is the most common dental ceramic used in dentistry
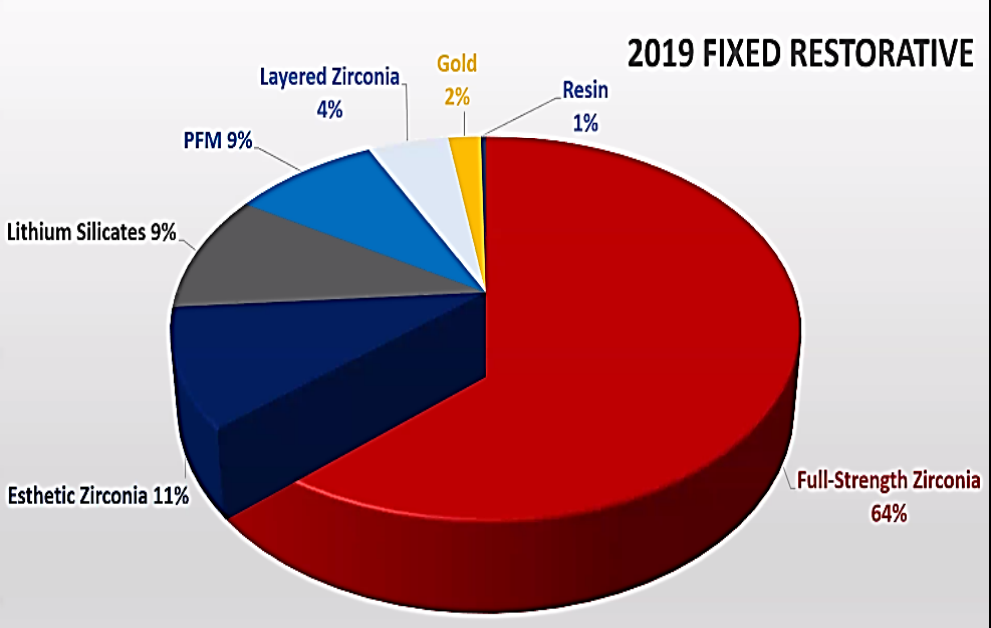
full-strength zirconia
two types of all-ceramic systems
silicate ceramics- glass/crystalline phase
oxide ceramics- metal oxides; no/or reduced glass phase
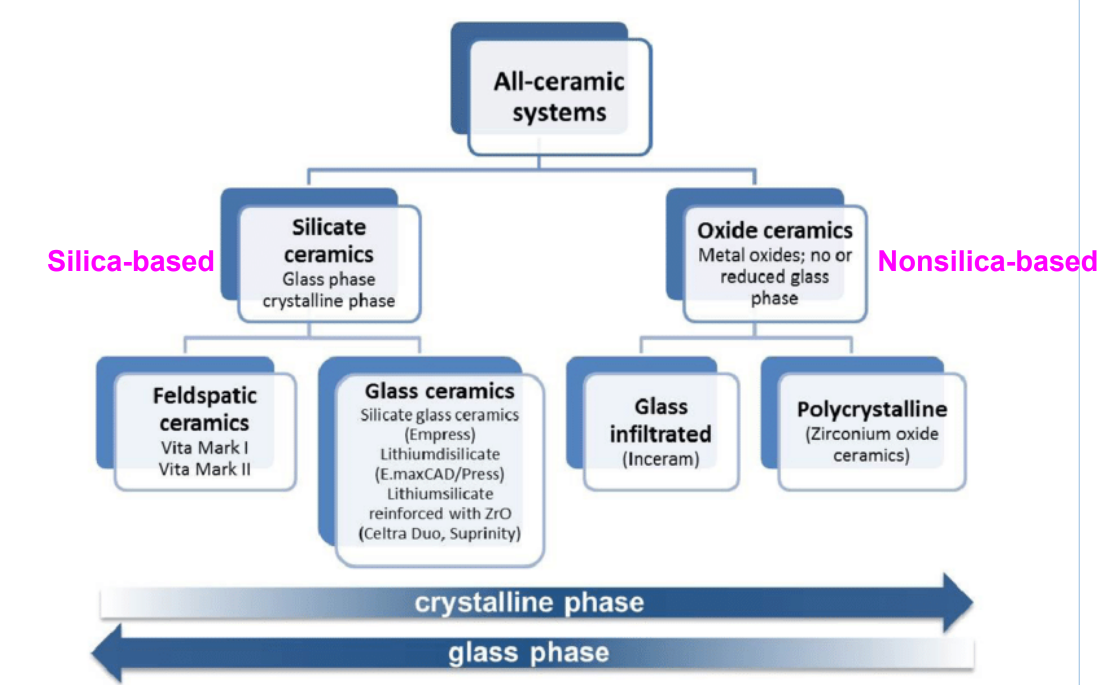
two types of silicate ceramics
feldspathic ceramics
glass ceramics
two types of oxide ceramics
glass infiltrated
polycrystalline: zirconium oxide ceramics
what is the most important property of all-ceramic materials
mechanical properties
castable ceramic crowns are composed of…
dicor
pyroceram
biocor

the material tetrasilicic mica requires a two-step tx w…
separate holds for nucleation and crystal growth
purpose of castable glass-ceramic crown
to improve esthetics
problems w castable glass-ceramic crown
strength
marginal adaptation
what is the overall error that could be “clinically acceptable”
0.5%

CAD/CAM stands for
Computer Aided Design/ Computer Aided Manufacturing
CEREC stands for
CEramic REConstruction
Chairside Economical Restoration of Esthetic Ceramics
characteristics of CEREC
quick
esthetic
strong
preserve tooth structure

if there is no impression needed, what is taken instead for CEREC
photo taken in mouth

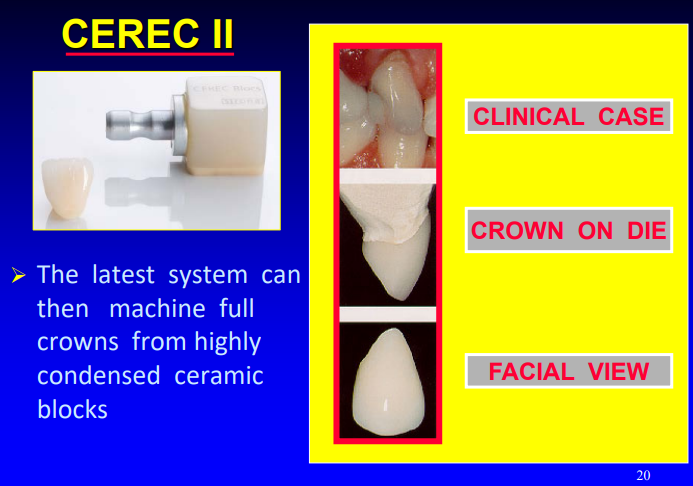
what is the latest system that can machine full crowns from highly condensed ceramic blocks
CEREC II
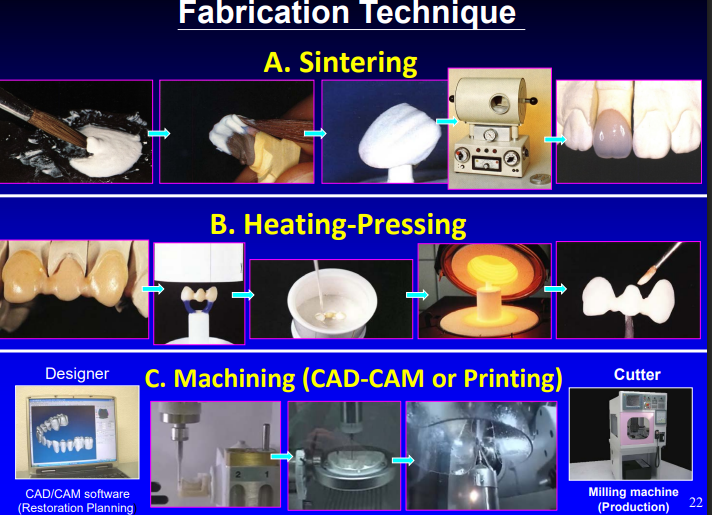
history of all ceramic restoration of fabrication techniques

three types of fabrication techniques
sintering
heating-pressing
machining (CAD-CAM or Printing)
pressable ceramics
ceramic material is leucite-reinforced glass-ceramic and prefabricated in pre-cerammed cylinders in various shades

what two things are needed for fabrication of IPS Empress 2 restoration
ceramic plunger
ceramic ingot

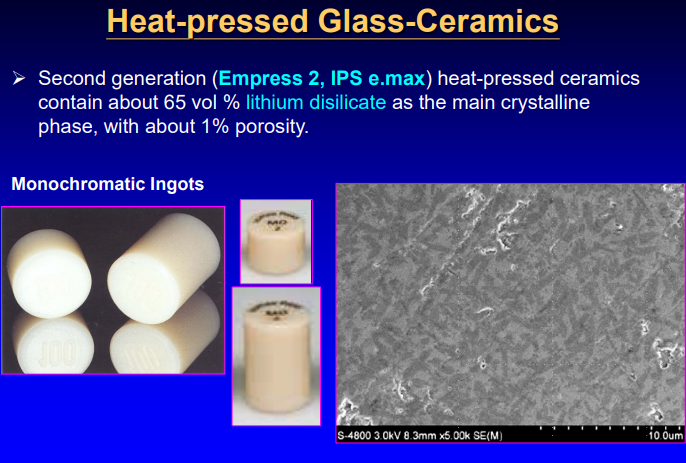
heat-pressed glass ceramics
second generation heat-pressed ceramics contain about 65% lithium disilicate as the main crystalline phase, w about 1% porosity
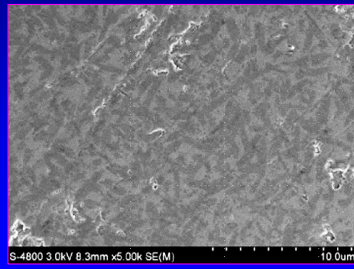
the gray and black spots represent
black has low molecular weight- due to lithium
gray- glass; silica (higher molecular weight)
the XRD patterns shown in heat-pressed glass ceramics…
the lithium disilicate phase, lithium metasilicate phase and lithium ortho-phosphate phase; crystalline structure > 65% volume
the final microstructure of heat-pressed glass ceramics consists of…
highly interlocked lithium disilicate crystals, 5 microns in length and .8 microns in diameter

what specific technique is used for fabrication of the IPS Empress 2 restoration
layering technique
advantages of pressable ceramics
esthetics
less shrinkage after pressing
no ceramming
disadvantages of pressable ceramics
strength
marginal adaptation
as opposed to metal-ceramics, all-ceramic contains a significantly greater amount of…
crystalline phase from 35% to 95 vol %
the higher level of crystallinity is responsible for an improvement in…
mechanical properties and higher opacity
CAD/CAM uses a _____________________ and ______________ to produce physical instances from 3D models (STL file formate)
uses a subtractive process (like computer numerical control milling) and additive process (3D printing)
Sielmens, CEREC systems: CAD/CAM dental restorations are milled from..
a solid block of ceramic or composite resin that closely matches the basic shade of the restored tooth; metal alloys may also be milled or digitally produced
what is subtractive manufacturing
making objects by removing of material from a bulk solid to leave a desired shape

what is zirconia
polymorphe w different atom arrangement states; monoclinic, tetragonal, cubic
zirconium dioxide can undergo phase transformation toughening from…
tetragonal → monoclinic
you want to stabilize zirconia in ___ or ____ at room temp
tetragonal or monoclinic
zirconia will undergo what arrangement at high temps (2370 C)
cubic
zirconia will undergo what arrangement at medium temperatures (1170)
tetragonal
zirconia will undergo what arrangement at room temperature
monoclinic
pure zirconium dioxide is a _____________ material that occurs in 3 forms
polymorphic
several different oxides are added to zirconia to stabilize the tetragonal and/or cubic phases such as…
magnesium oxide, yttrium oxide, calcium oxide, and cerium III oxide
what is the difference between the arrangement states of zirconia at various temperatures
size; cubic < tetragonal < monoclinic if at room temp

yttrium-oxide is added to pure zirconia to control the….
volume expansion and to stabilize it in the tetragonal phase at room temp
the tetragonal-to-monoclinic phase transformation occurs below ______ C and is accompanied by a ____% volume expansion
below 1170 C; 3-5% volume expansion
if sufficient quantities of the metastable tetragonal phase is present, an applied stress- magnified by the stress concentration at the crack tip, this can cause…
tetragonal phase to convert to monoclinic w the associated volume expansion
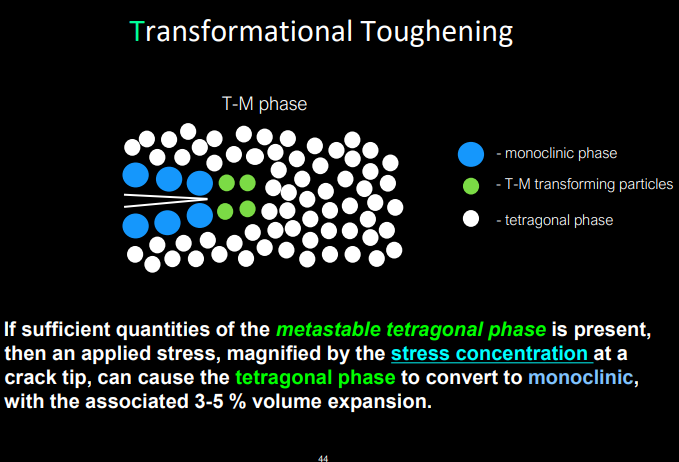
the phase transformation of tetragonal to monoclinic cause put the crack into compression, retarding its growth, and enhancing the…
fracture toughness
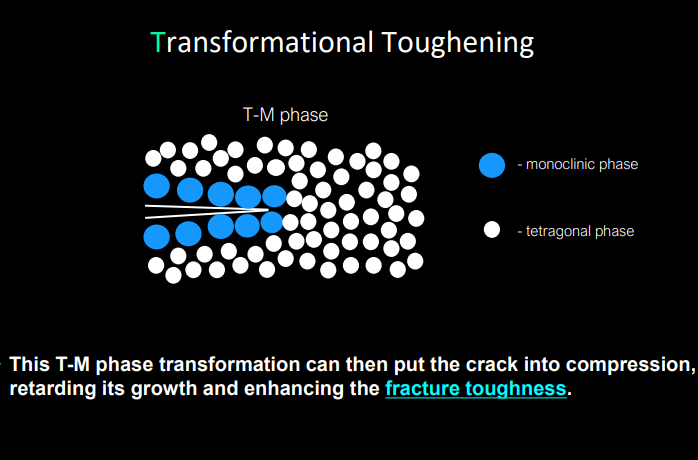
what is the mechanism called that zirconia can undergo when transitioning between tetragonal to monoclinic phase
transformation toughening
transformation toughening can significantly extend the reliability and lifetime of products made w…
yttrium-oxide stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystalline
the larger particles exert a crack-closing force in the _________ zone behind the crack tip, effectively resisting propagation of the crack
process zone
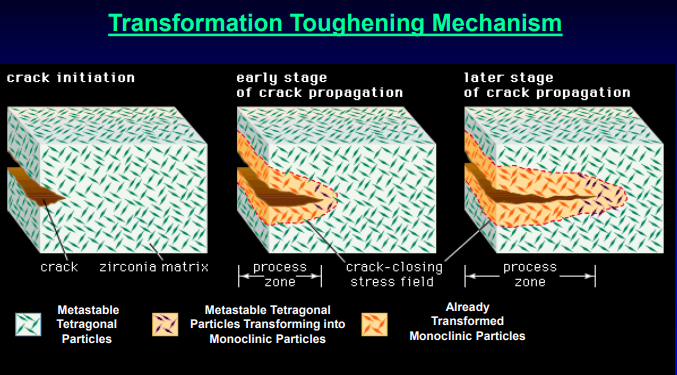
the energy required for the transformation of partially stabilized zirconia (PSZ) is taken from the enery, allowing the…
crack to propagate
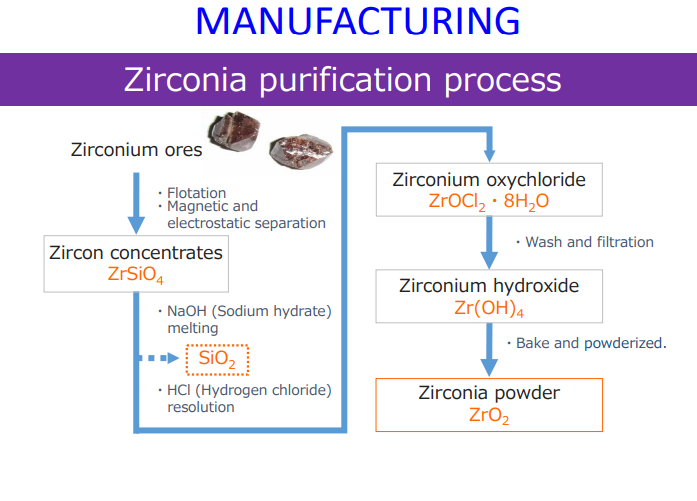
manufacturing of zirconia purification process
in order to produce translucent monolithic zirconia restorations, company has altered the amount of…
alumina and yttria
_______________ is used to stabilize monoclinic-tetragonal transformation to form homogenous solid solutions
hafnium dioxide
what are the pressure techniques for manufacturing ceramic materials
uni-axial
bi-axial
isostatic

what crystalline phase corresponds w the soft machining, sintering and heat-pressing fabrication technique
zirconia/fluorapatite- leucite glass ceramic
what crystalline phase corresponds w the heat pressing fabrication technique
leucite, lithium disilicate
what crystalline phase corresponds w the sintering fabrication tecnique
leucite
what was CAD/CAM technology originally intended for
fully sintered ceramic blocks→ it has now been expanded to partially sintered ceramic (soft machining), that are later fully tx to ensure adequate sintering
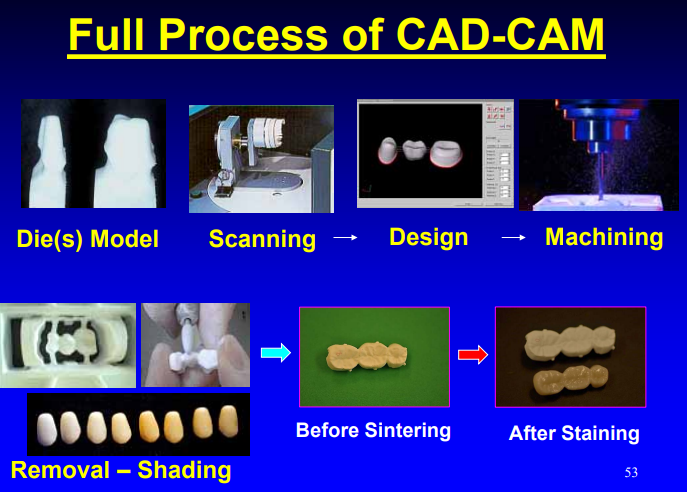
full process of CAD/CAM
dies/models → scanning → design → machining → removal/shading → sintering/stain

Y factor
3Y

Y factor and translucency
4Y ; high translucent
Y factor and translucency
5Y ; super translucent
Y factor and translucency
6Y ; ultra translucent
what arrangement of zirconia is associated w 3Y
tetragonal (>75%)
what arrangement of zirconia is associated w 4Y
hybrid ~75% tetragonal + 25% cubic
what arrangement of zirconia is associated w 5Y
cubic 50% tetragonal + 50% cubic
what is the grain size in conventional 3Y zirconia
less than .5 microns

what is the grain size in ultra-translucency 5Y zirconia
~1 micron

as you inc in Y factor what happens w grain size
size increases
as you inc in Y factors what happens w strength/toughness
strength/toughness decreases
as you inc in Y factor what happens w translucency
translucency inc
cubic zirconia is a colorless, synthetic gemstone made of…
cubic crystalline form of zirconia dioxide
toughness of dental ceramic materials
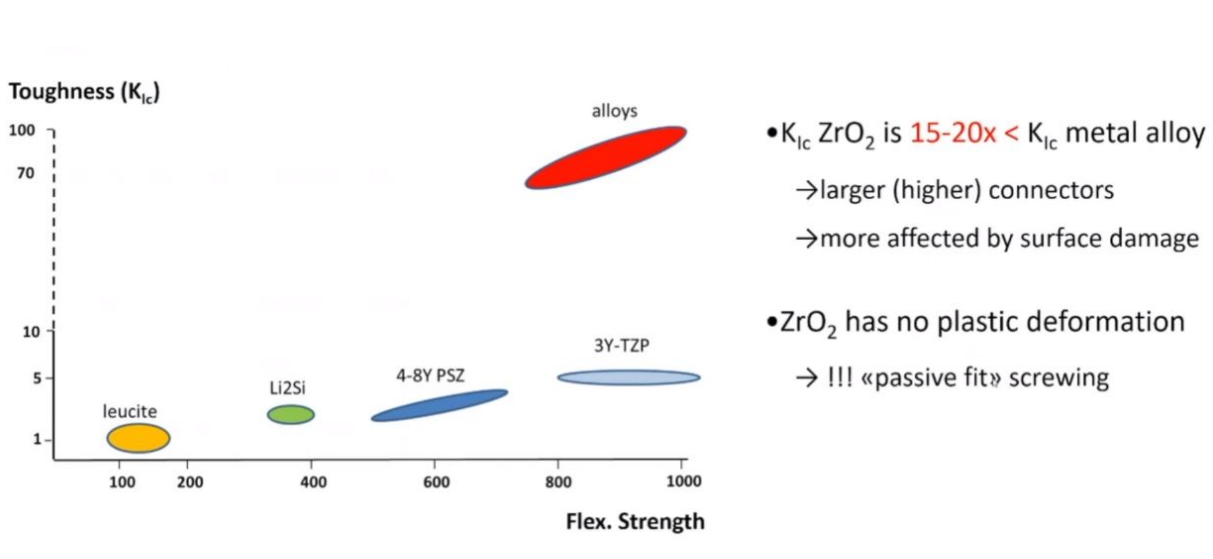
how is translucency related to Yttria content
Low transleucency: 3 mol
intermediate translucency: 4 mol
high/ultra translucency: 5-6 mol
grain boundaries and microporosity induce ____________ resulting in a loss in transmitted light
light scattering
zirconia shading methods
external staining
coloring by using infiltration liquids
intrinsic color w metal oxides addition
multi-layer chroma
anterior restorations typically use what type of zirconia
monolithic zirconia 3Y
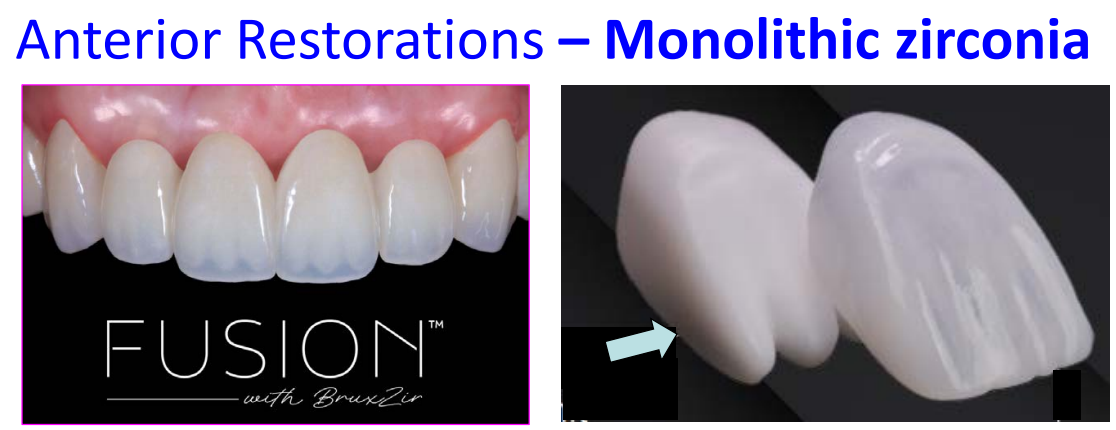
monolithic zirconia characteristics
two zirconias bonded to emulate the dentin-enamel relationship
anatomically shaped core establishes strength, color, and depth
wraparound veneers lets light pass through incisal and interproximal surfaces
flexural strength of all-ceramic restorative material
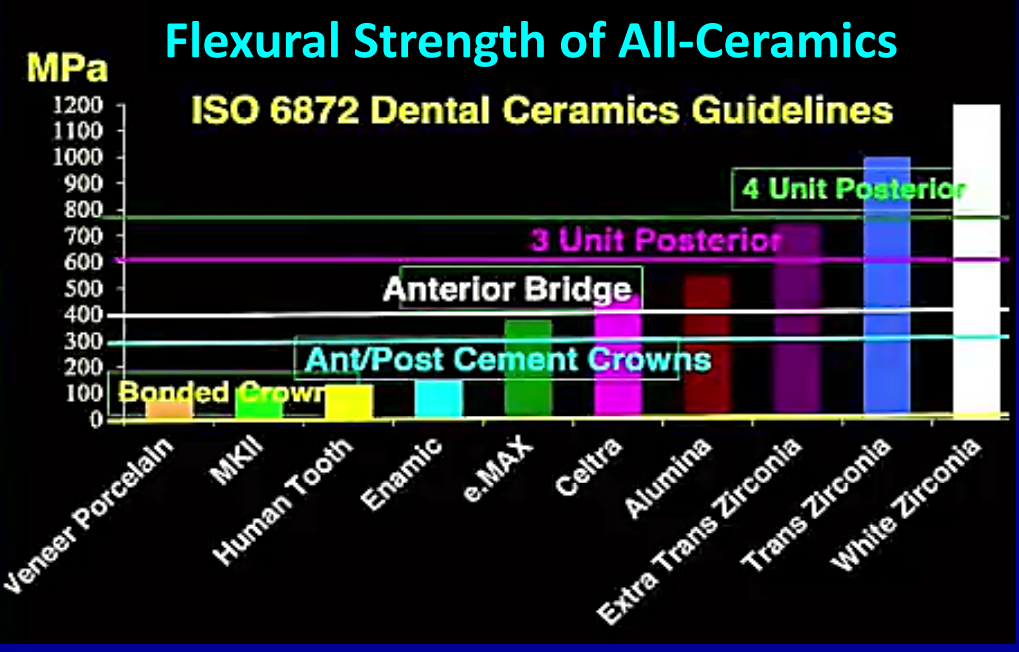
why to use zirconia
highly biocompatible
high compressive strength
versatility- crown, bridge, implants
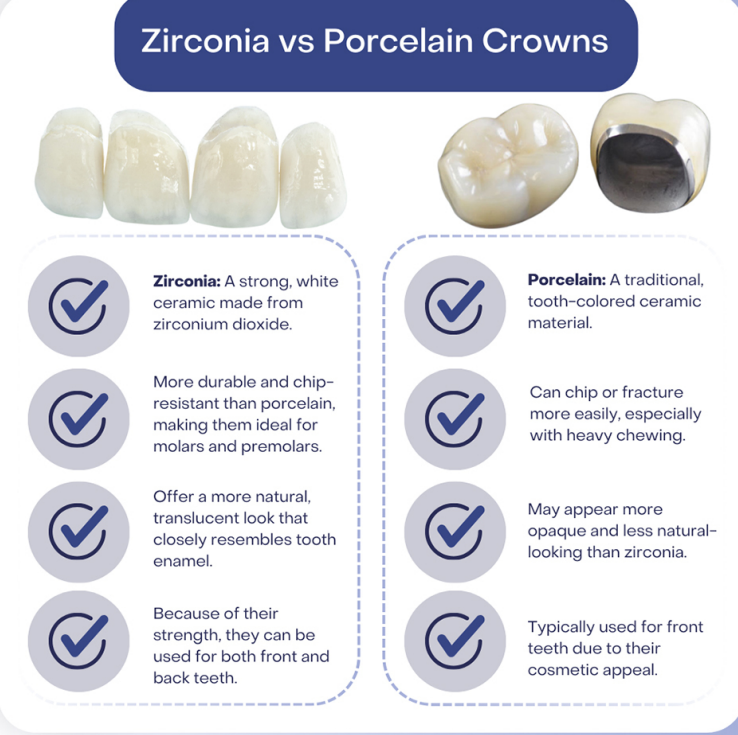
zirconia vs porcelain crowns