Brain anatomy
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms

Letter F in Image 14 is pointing to:
A. Third ventricle
B. Pituitary gland
C. Hypothalamus
D. Internal carotid artery
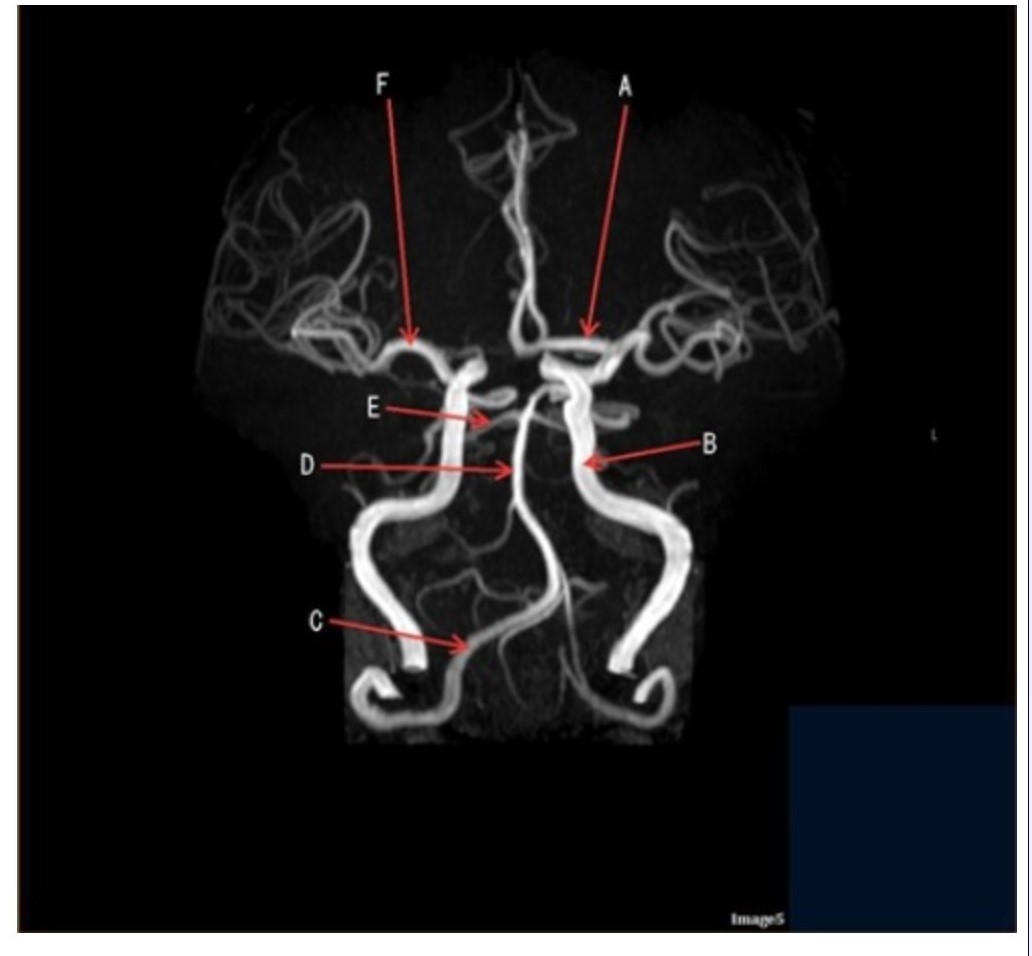
Letter D in Image 5 is pointing to:
A. Anterior cerebral artery
B. Internal carotid artery
C. Basilar artery
D. Posterior cerebral artery
E. Middle cerebral artery
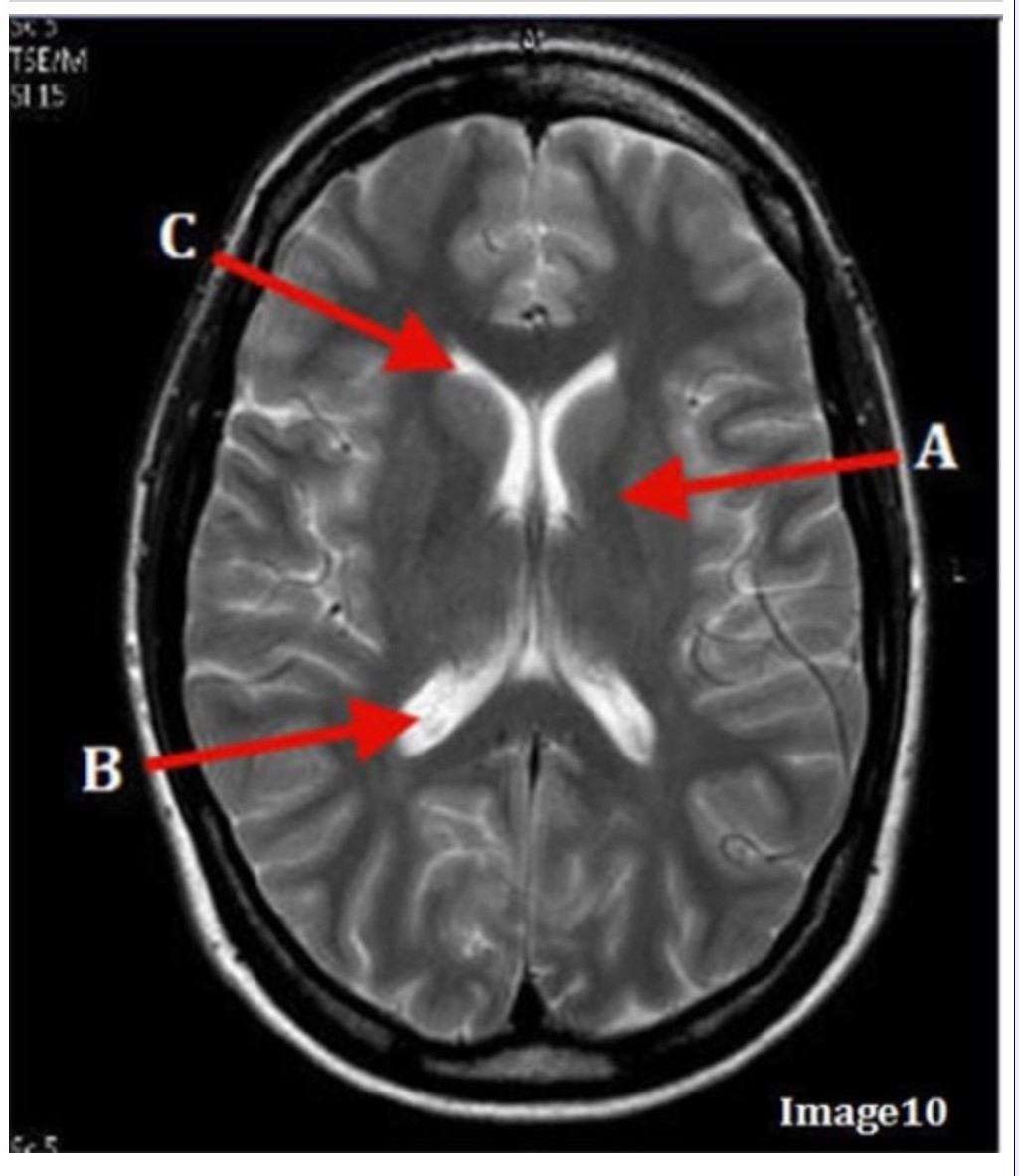
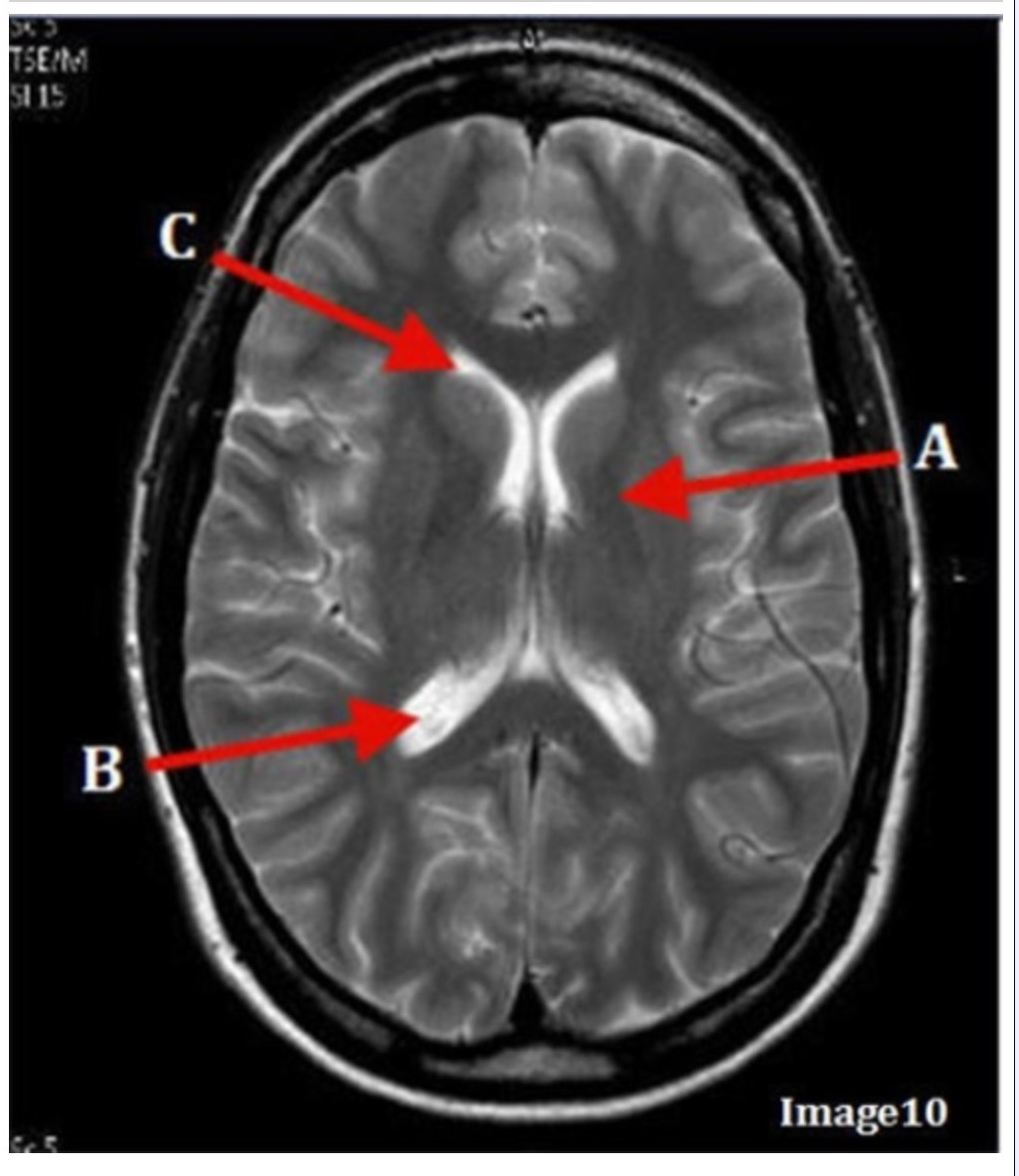
Letter B in Image 10 is pointing to:
A. Third ventricle
B. Basal ganglia
C. Anterior horn lateral ventricle
D. Posterior horn lateral ventricle
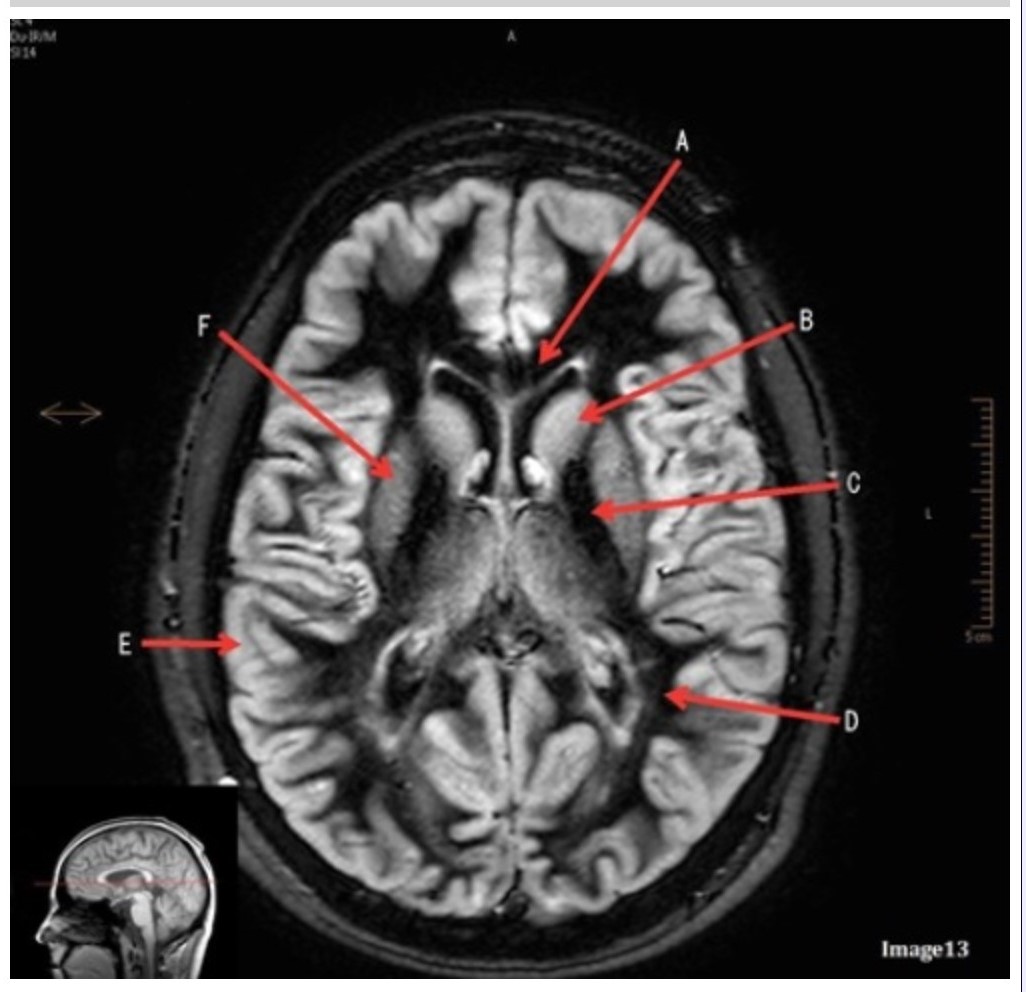
Letter E in Image 13 is pointing to:
A. Grey matter
B. White matter
C. Lentiform nucleus
D. Caudate nucleus
E. Internal capsule
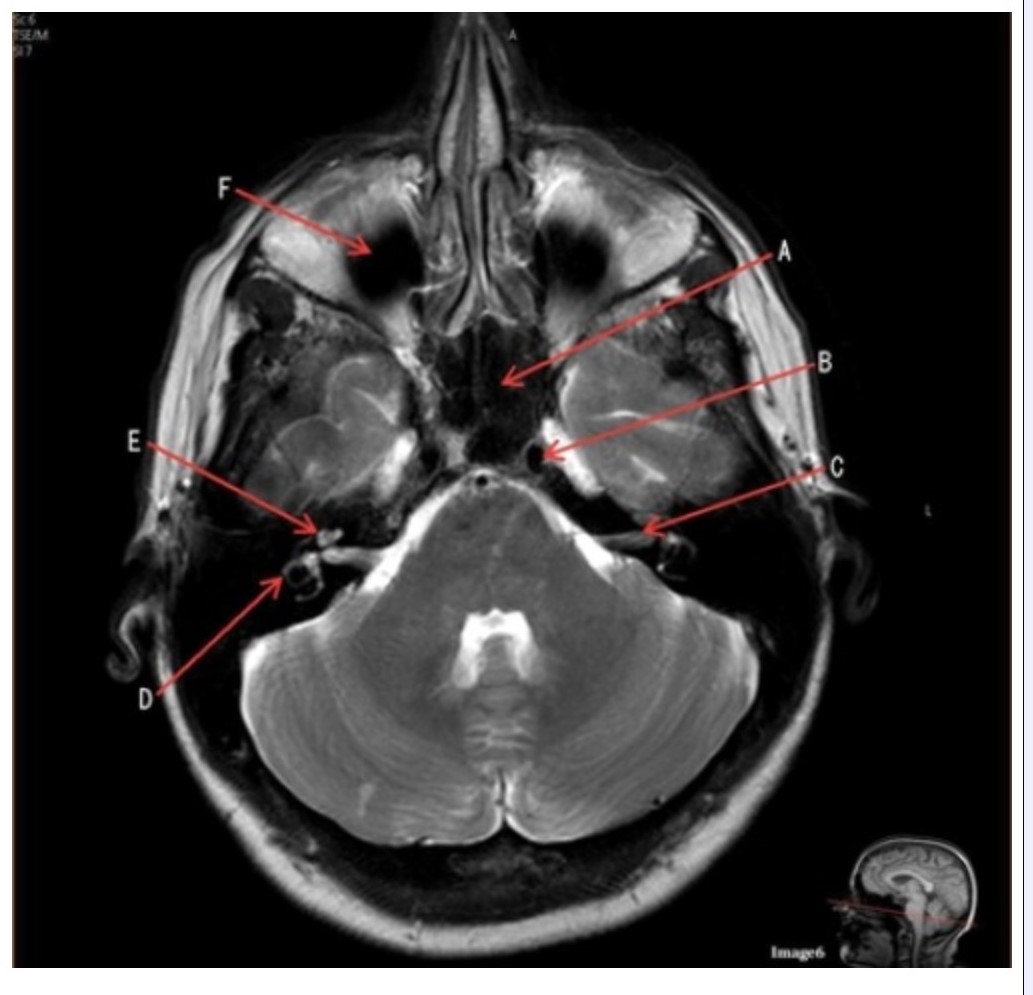
Letter A in Image 6 is pointing to:
A. Maxillary sinus
B. Sphenoid sinus
C. Frontal sinus
D. Internal carotid artery
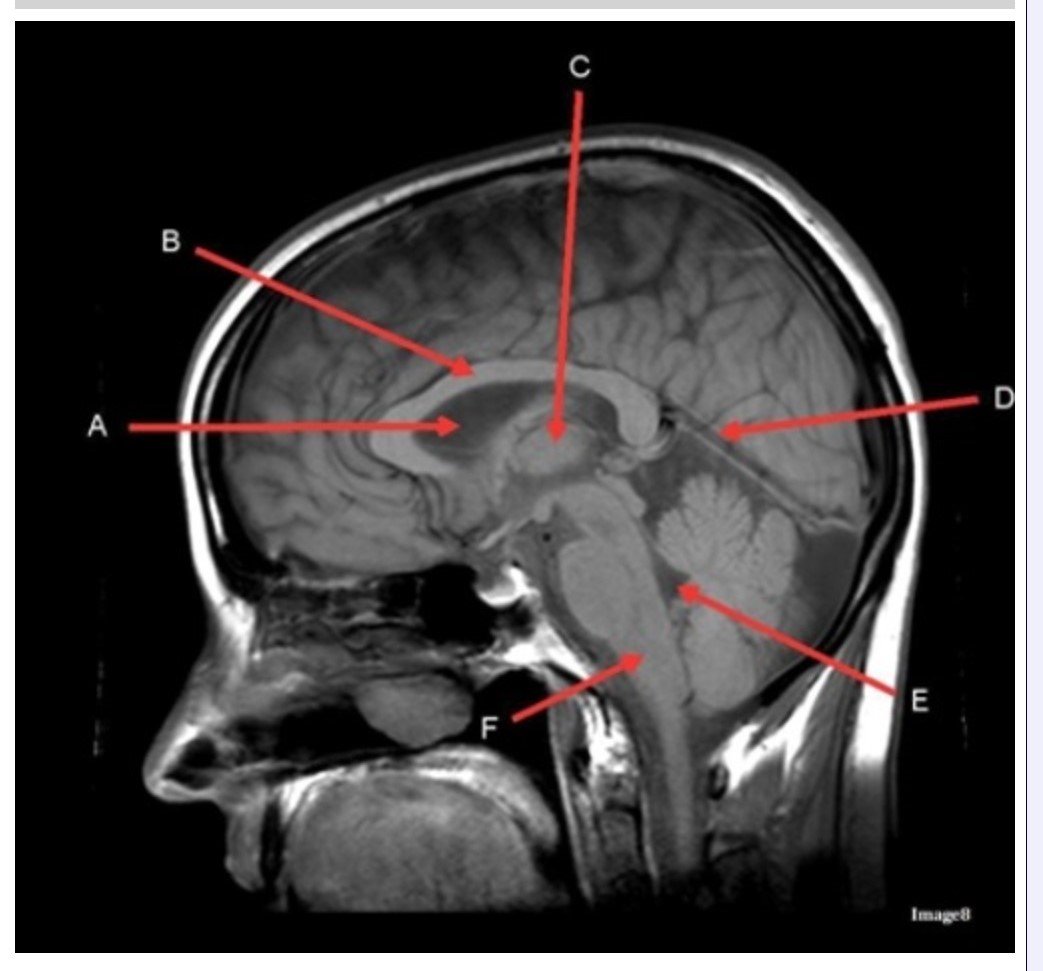
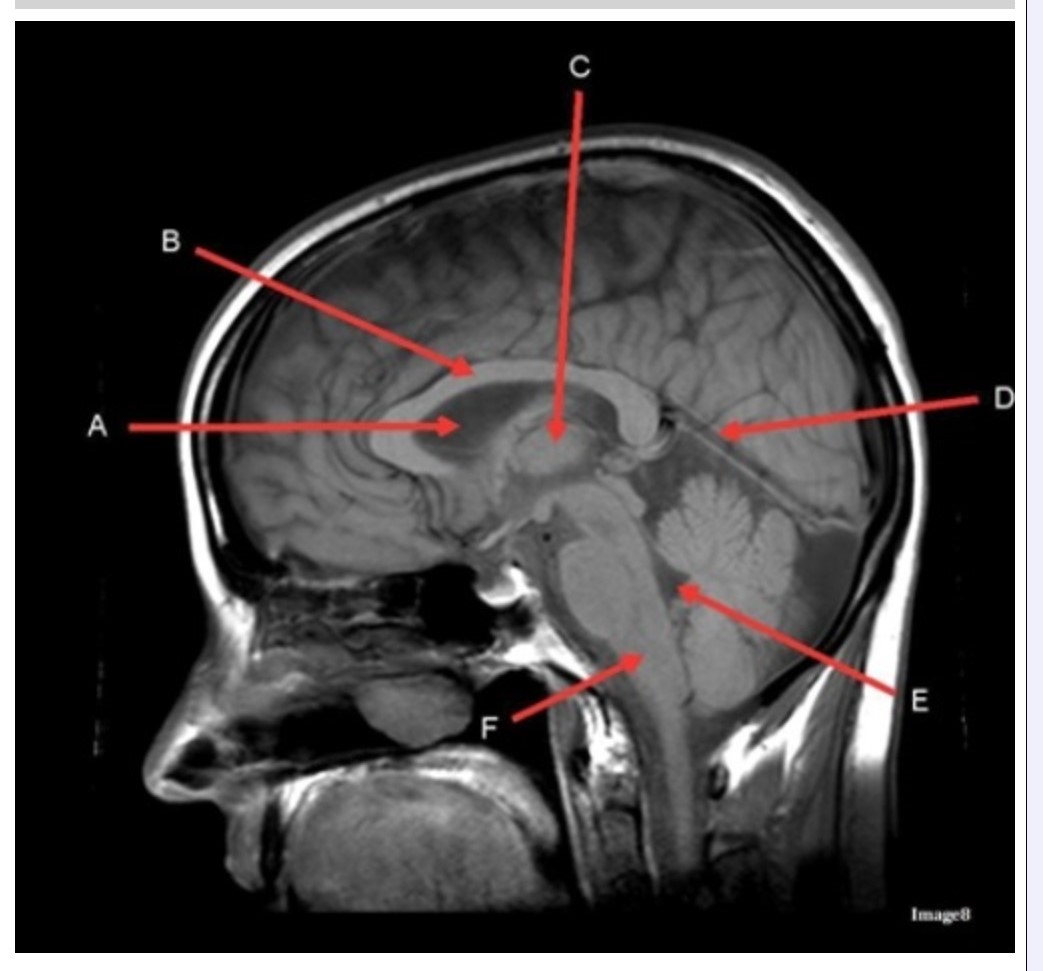
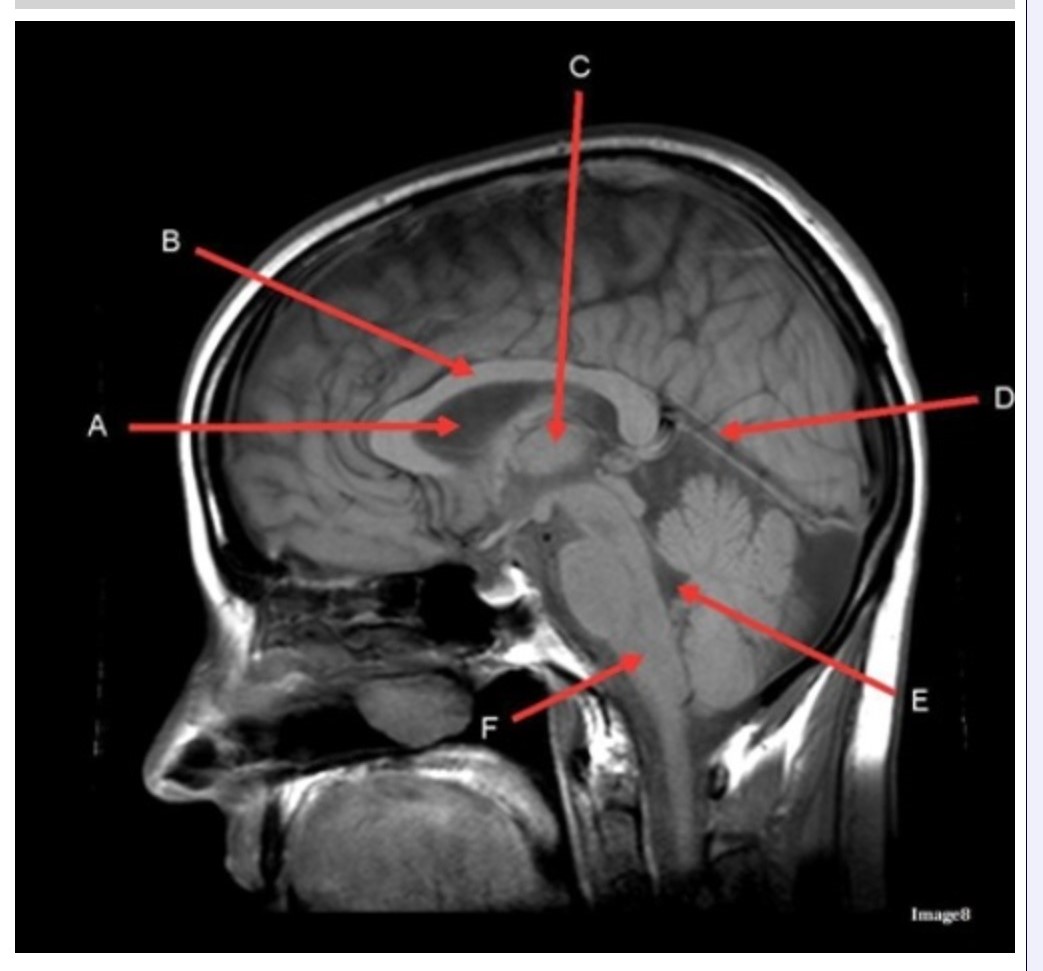
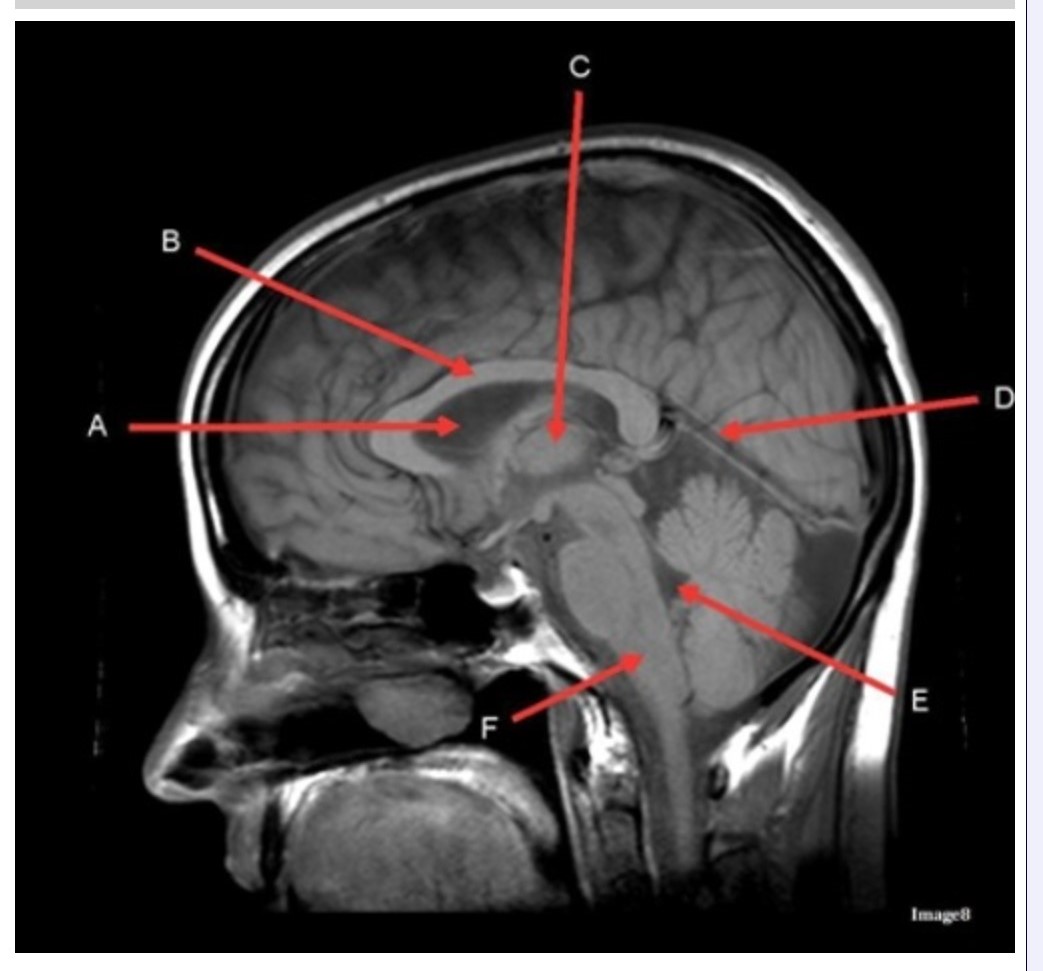
Letter C in Image 8 is pointing to:
A. Tentorium
B. Corpus callosum
C. Thalamus
D. Fourth ventricle
E. Medulla oblongata
Letter F in Image 8 is pointing to:
A. Tentorium
B. Cerebellum
C. Thalamus
D. Fourth ventricle
E. Medulla oblongata
Letter H in Image 12 is pointing to:
A. Lens
B. Lateral rectus muscle
C. Medial rectus muscle
D. Internal carotid artery
E. Globe
The medial and lateral rectus muscles are located in the:
A. Ears
B. Gluteus maximus
C. Eyes
D. Outer neck regions
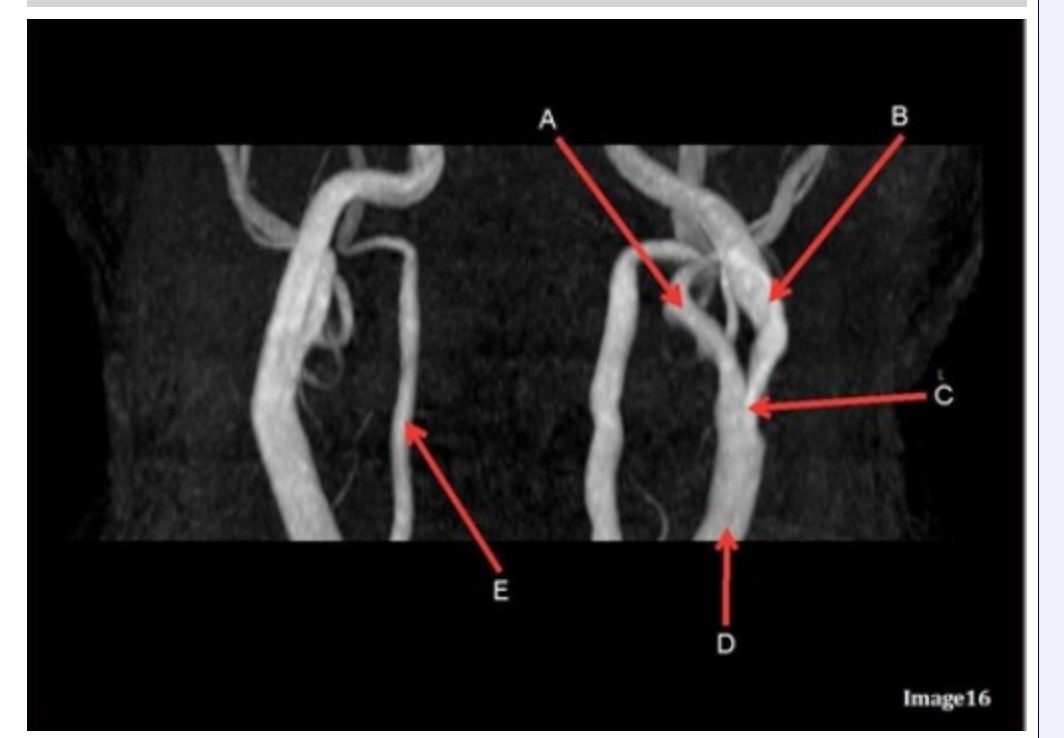
Letter B in Image 16 is pointing to:
A. Internal carotid artery
B. External carotid artery
C. Vertebral artery
D. Common carotid artery
E. Common carotid bifurcation
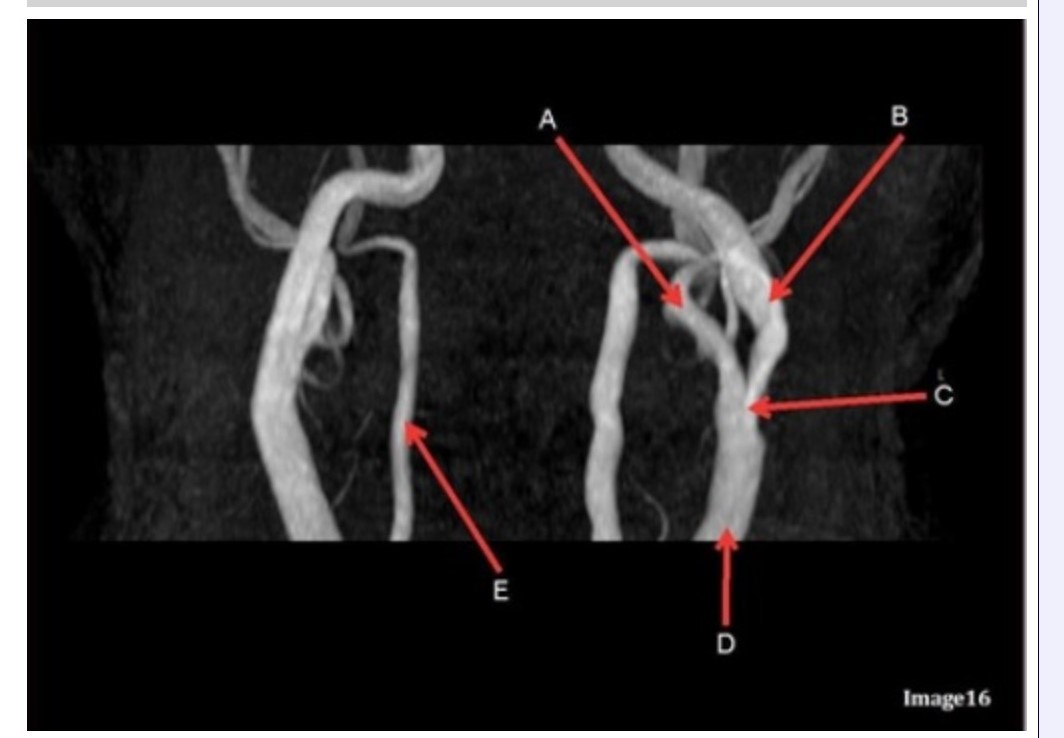
Letter E in Image 16 is responsible for blood supply to the:
A. Anterior brain
B. Posterior brain
C. Face
D. Upper extremities
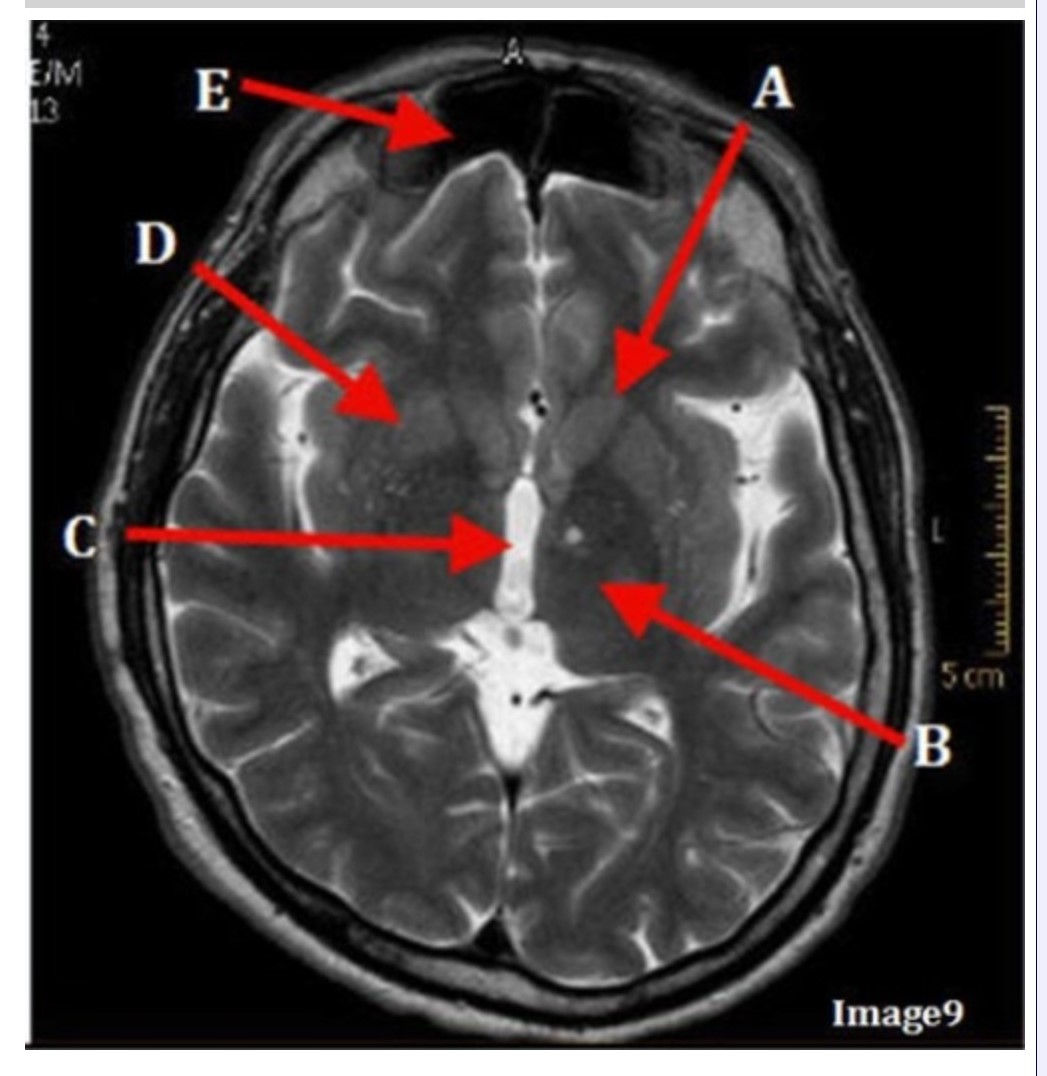
Letter C in Image 9 is pointing to:
A. Third ventricle
B. Thalamus
C. Lentiform nucleus
D. Caudate nucleus
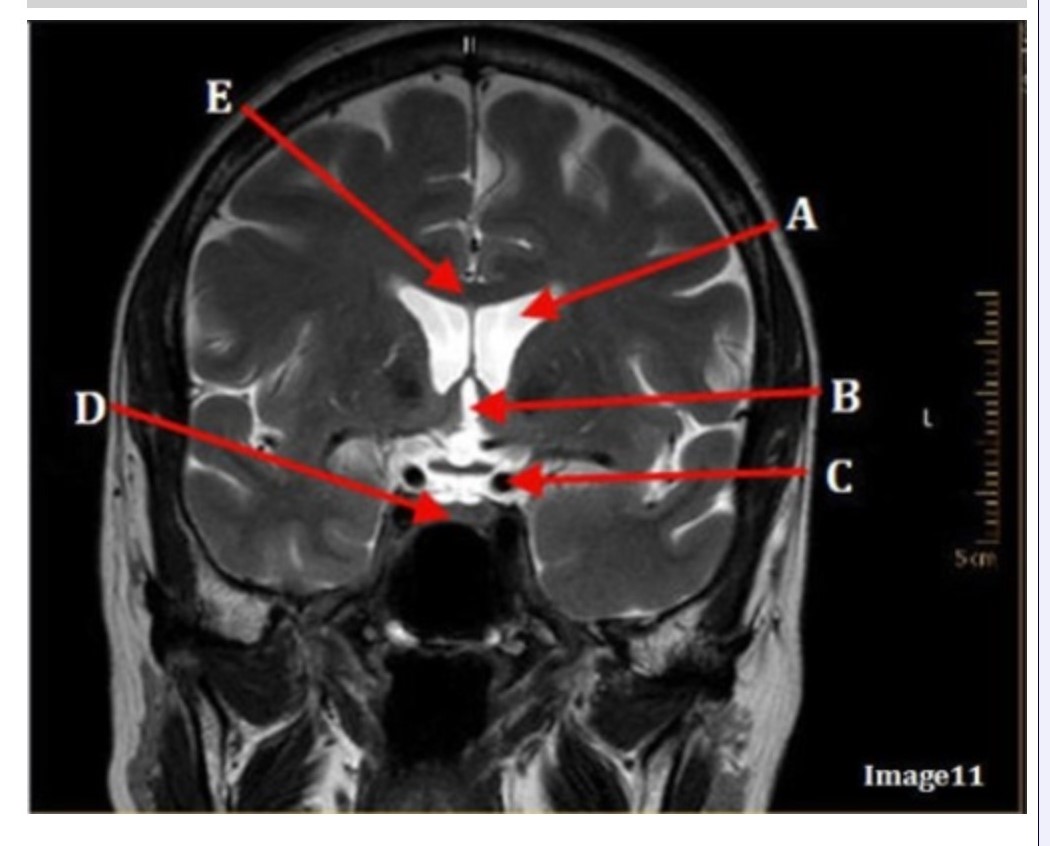
Image 11 is an example of a _______ weighted sequence acquired in the _________ scan plane.
A. T1; Axial
B. T1; Coronal
C. T2; Axial
D. T2; Coronal
E. STIR; Axial
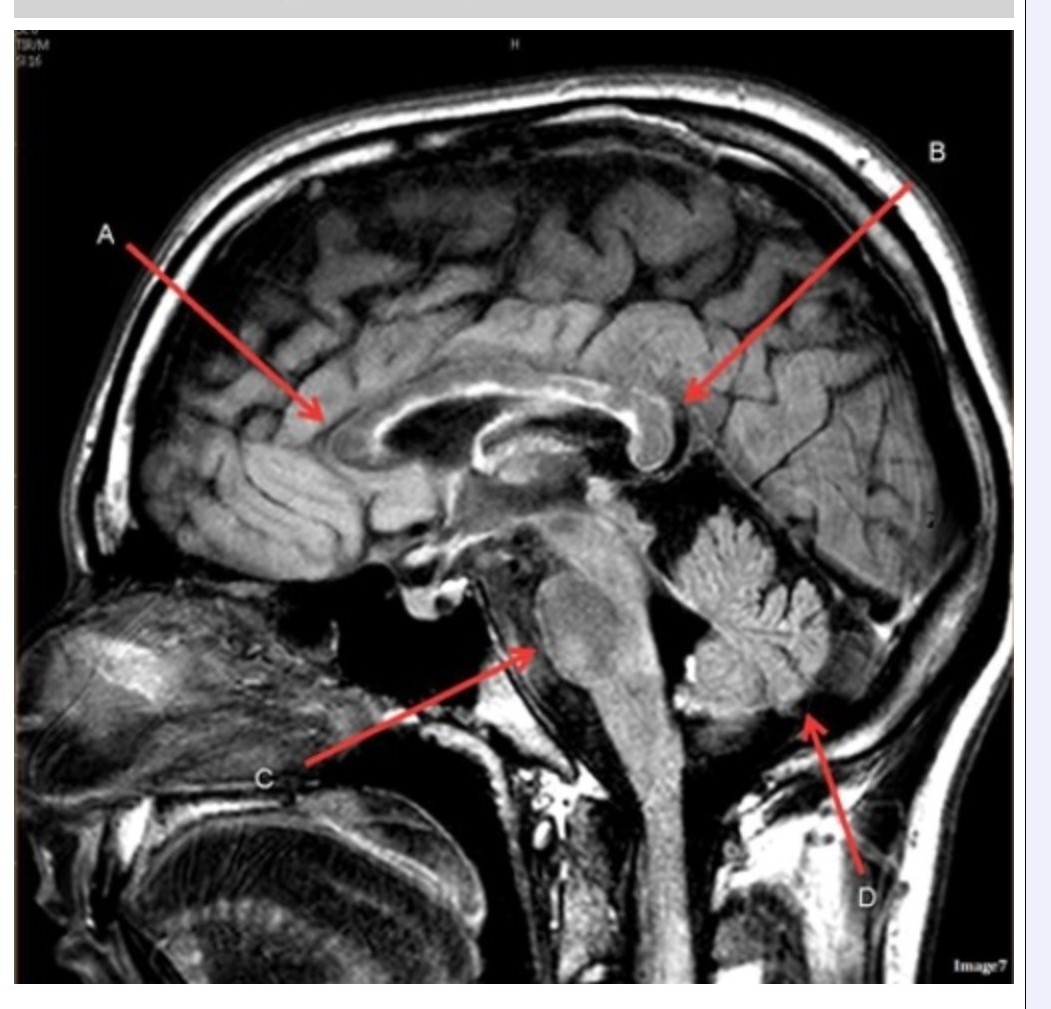
Letter C in Image 7 is pointing to:
A. Pons
B. Cerebellum
C. Hypothalamus
D. Genu of the corpus callosum
E. Splenium of the corpus callosum
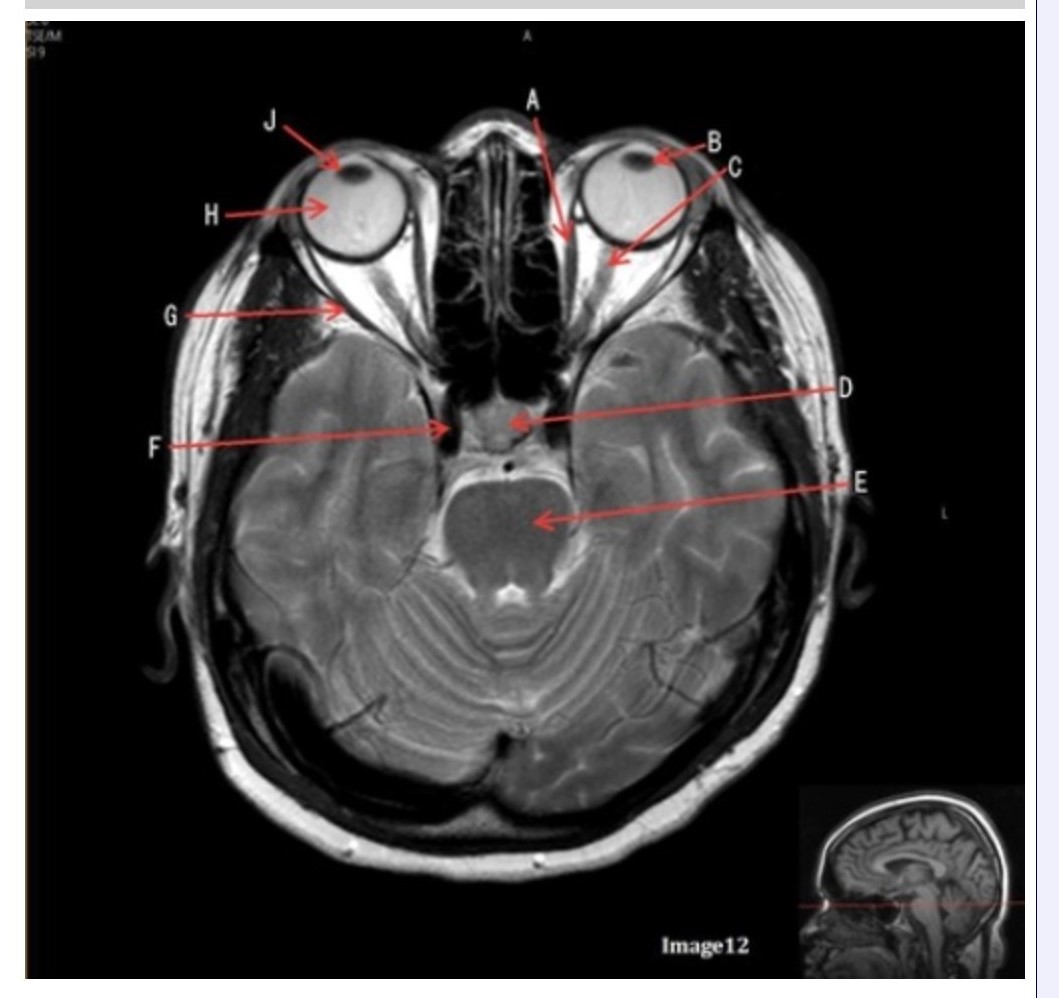
Letter B in Image 12 is pointing to:
A. Left optic nerve
B. Lateral rectus muscle
C. Medial rectus muscle
D. Lens
E. Midbrain
The pituitary stalk is also known as:
A. Hypothalmus
B. Internal capsule
C. Lentiform nucleus
D. Infundibulum
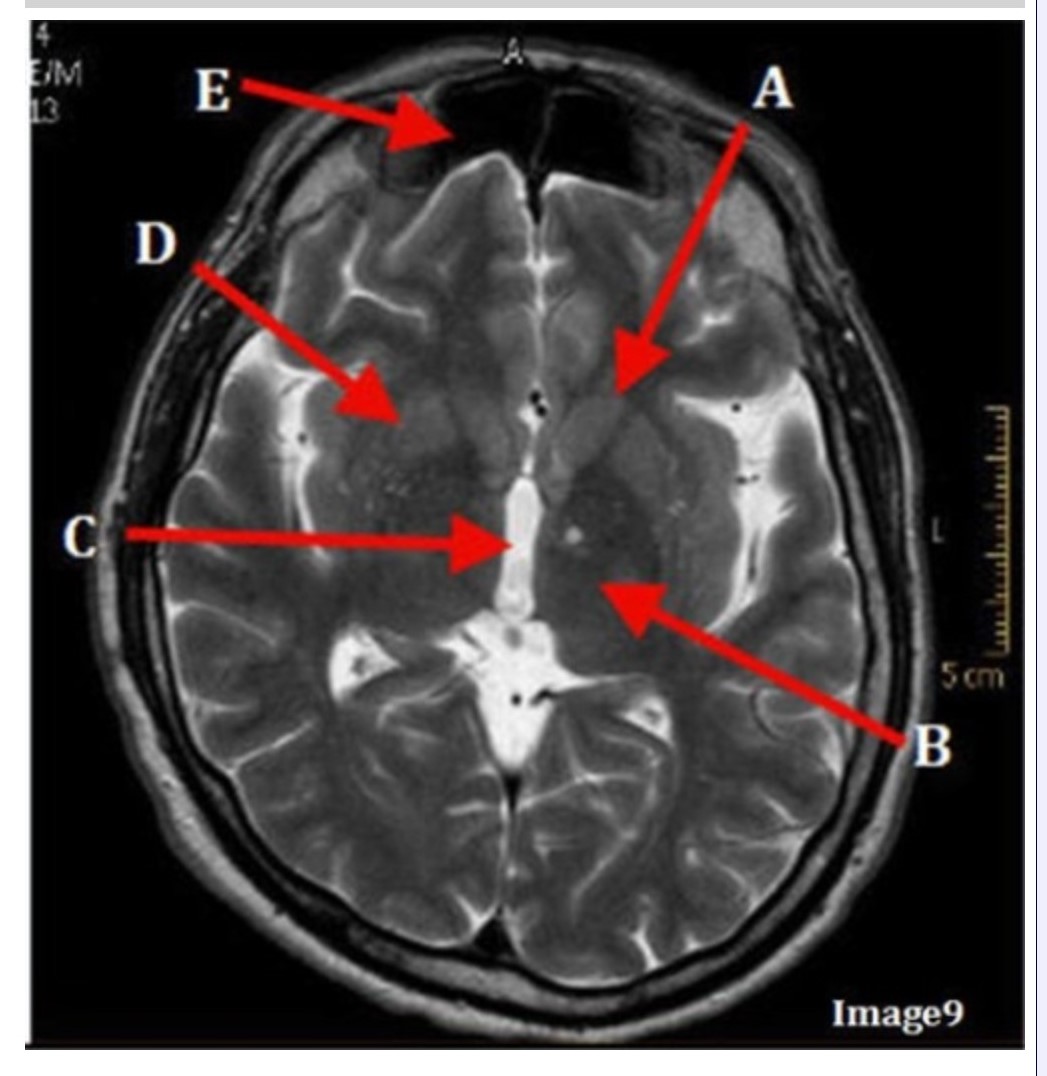
Letter B in Image 9 is pointing to:
A. Third ventricle
B. Thalamus
C. Lentiform nucleus
D. Caudate nucleus
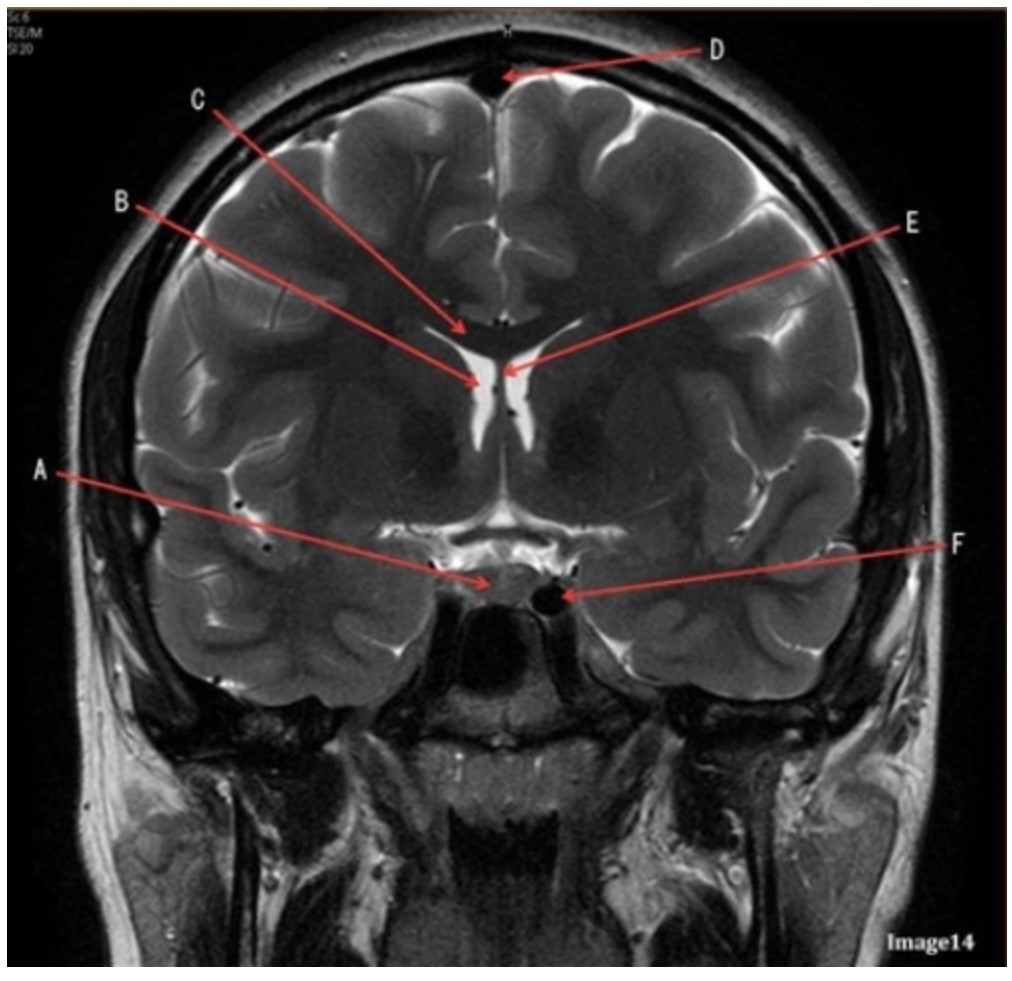
Letter C in Image 14 is pointing to:
A. Corpus callosum
B. Third ventricle
C. Lateral ventricle
D. Pituitary gland
E. Fornix
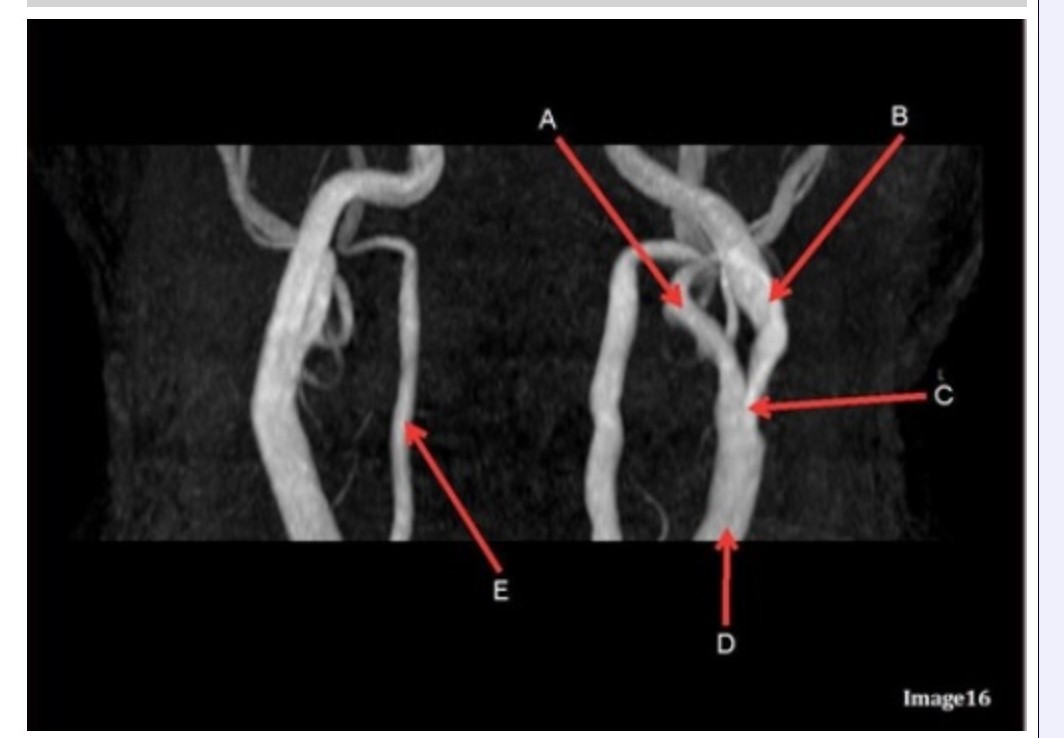
Letter D in Image 16 is pointing to:
A. Internal carotid artery
B. External carotid artery
C. Vertebral artery
D. Common carotid artery
E. Common carotid bifurcation
The right and left optic nerve join at the:
A. Optic chiasm
B. Foramen magnum
C. Transverse sinus
D. Internal optic canals
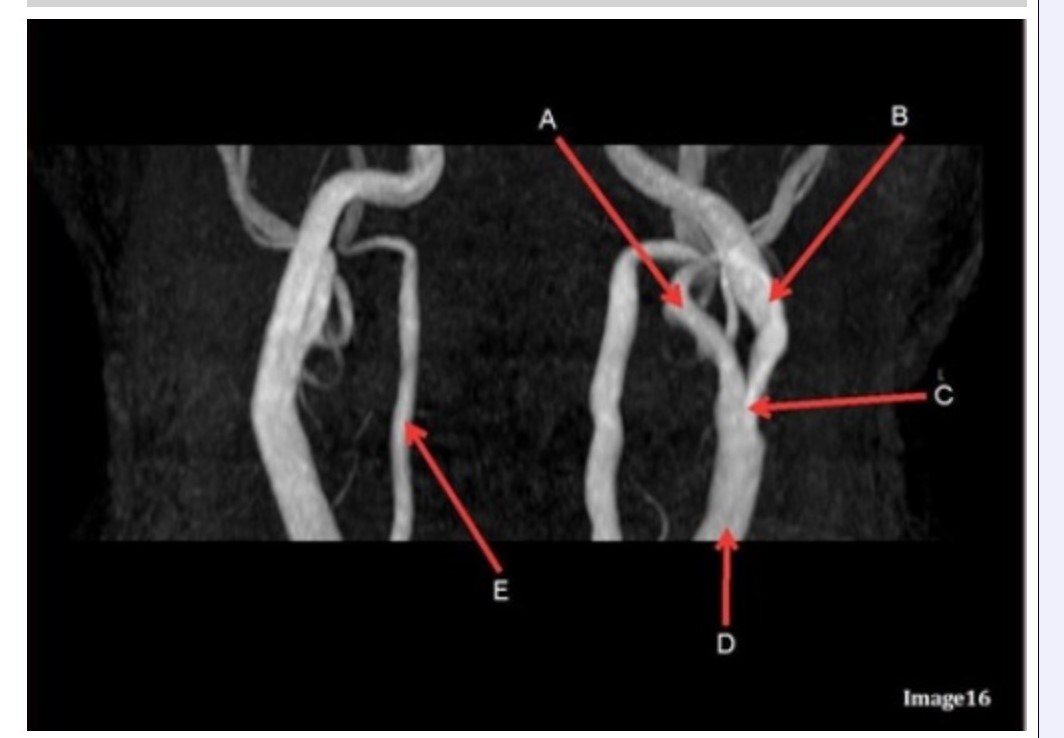
Image 16 is an example of what type of MR image?
A. MR spectroscopy
B. MRA Circle of Willis
C. MRV intracranial circulation
D. MRA extracranial circulation
E. MRA intracranial circulation
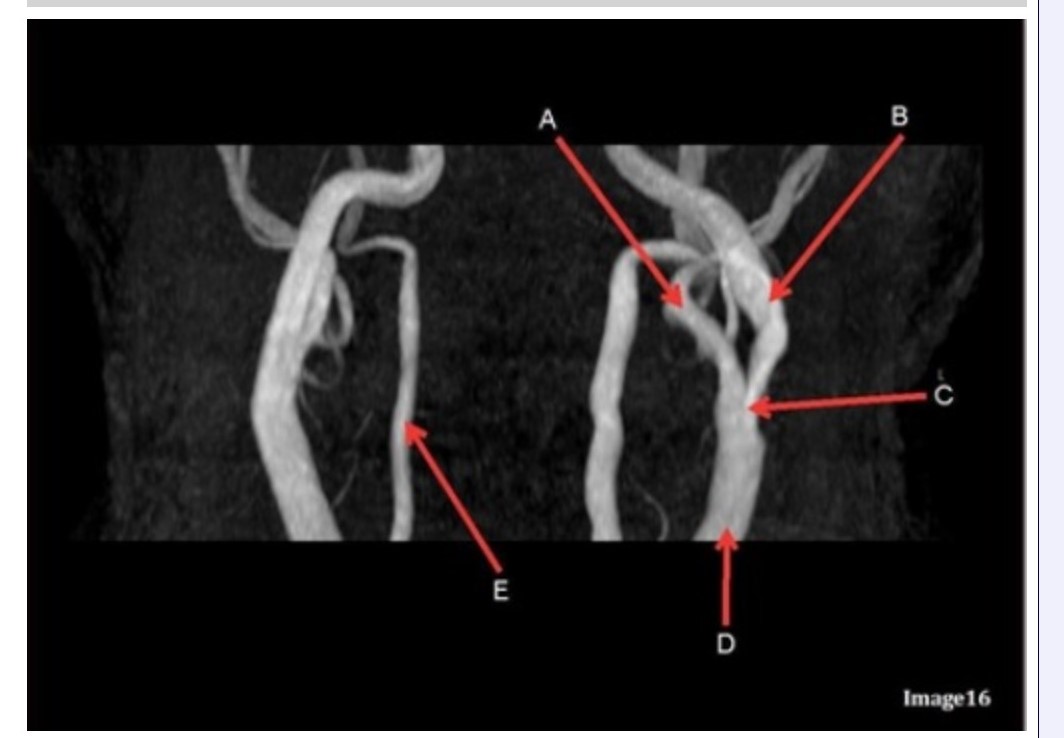
Letter B in Image 16 is responsible for blood supply to the:
A. Anterior brain
B. Posterior brain
C. Face
D. Upper extremities
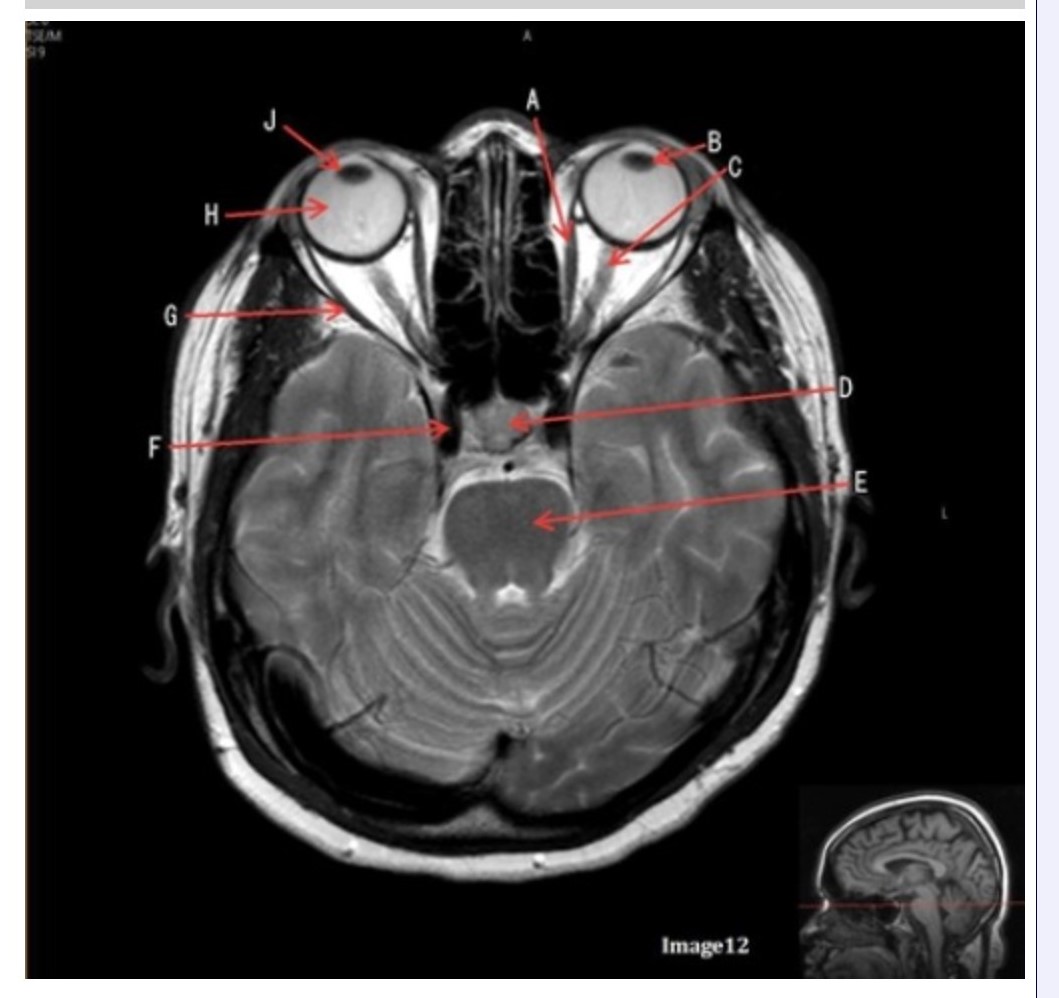
Letter J in Image 12 is pointing to:
A. Globe
B. Lateral rectus muscle
C. Medial rectus muscle
D. Right lens
E. Left lens
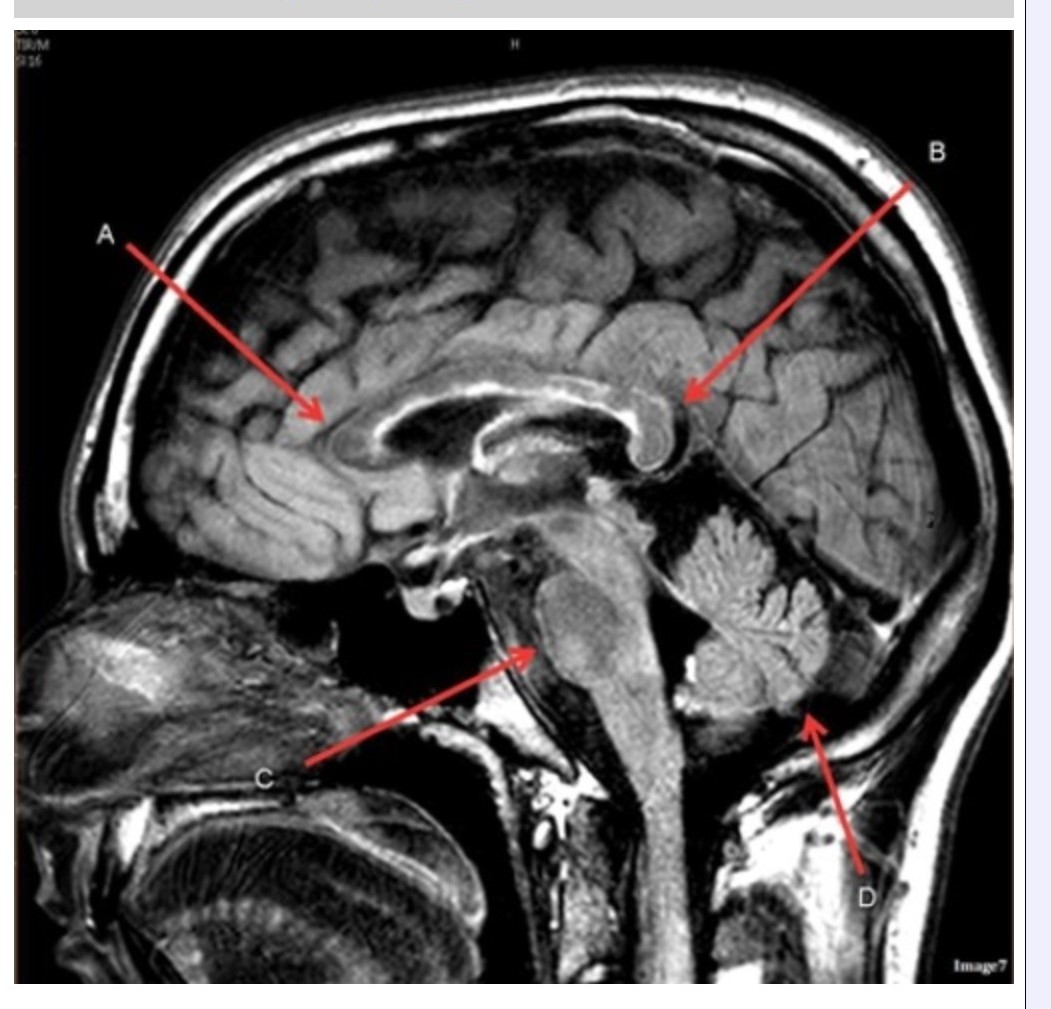
Letter B in Image 7 is pointing to:
A. Pons
B. Cerebellum
C. Hypothalamus
D. Genu of the corpus callosum
E. Splenium of the corpus callosum
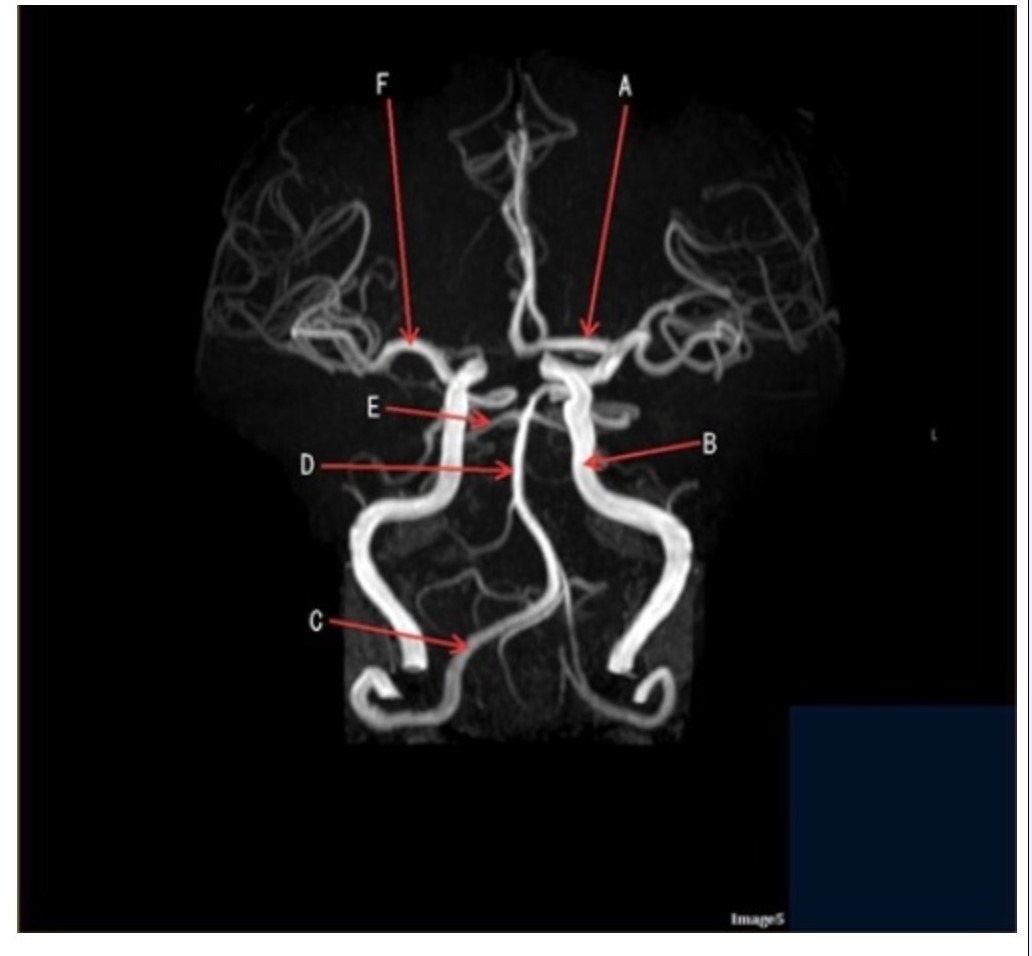
Letter F in Image 5 is pointing to:
A. Anterior cerebral artery
B. Internal carotid artery
C. Basilar artery
D. Posterior cerebral artery
E. Middle cerebral artery
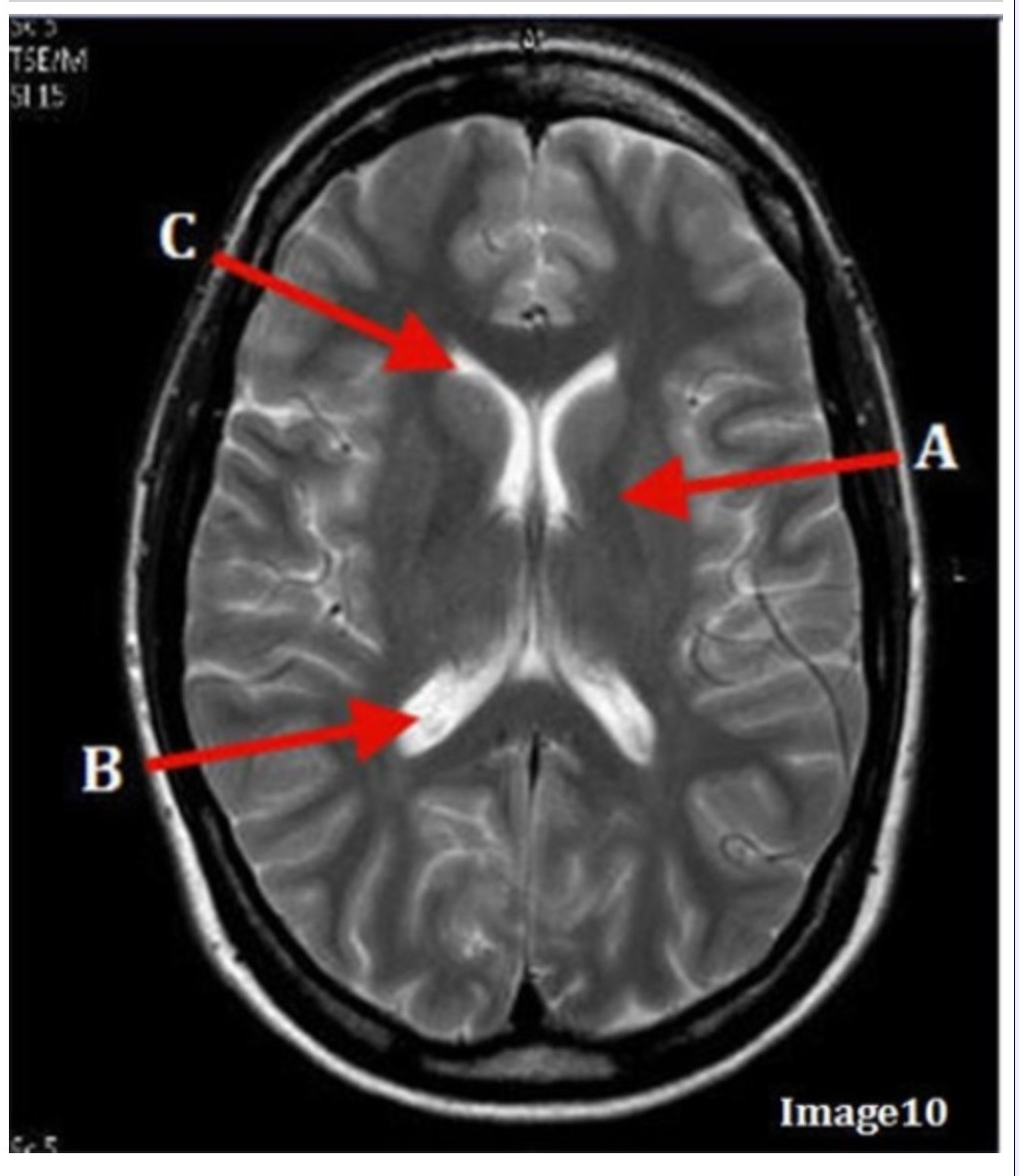
Letter C in Image 10 is pointing to:
A. Third ventricle
B. Basal ganglia
C. Anterior horn lateral ventricle
D. Posterior horn lateral ventricle
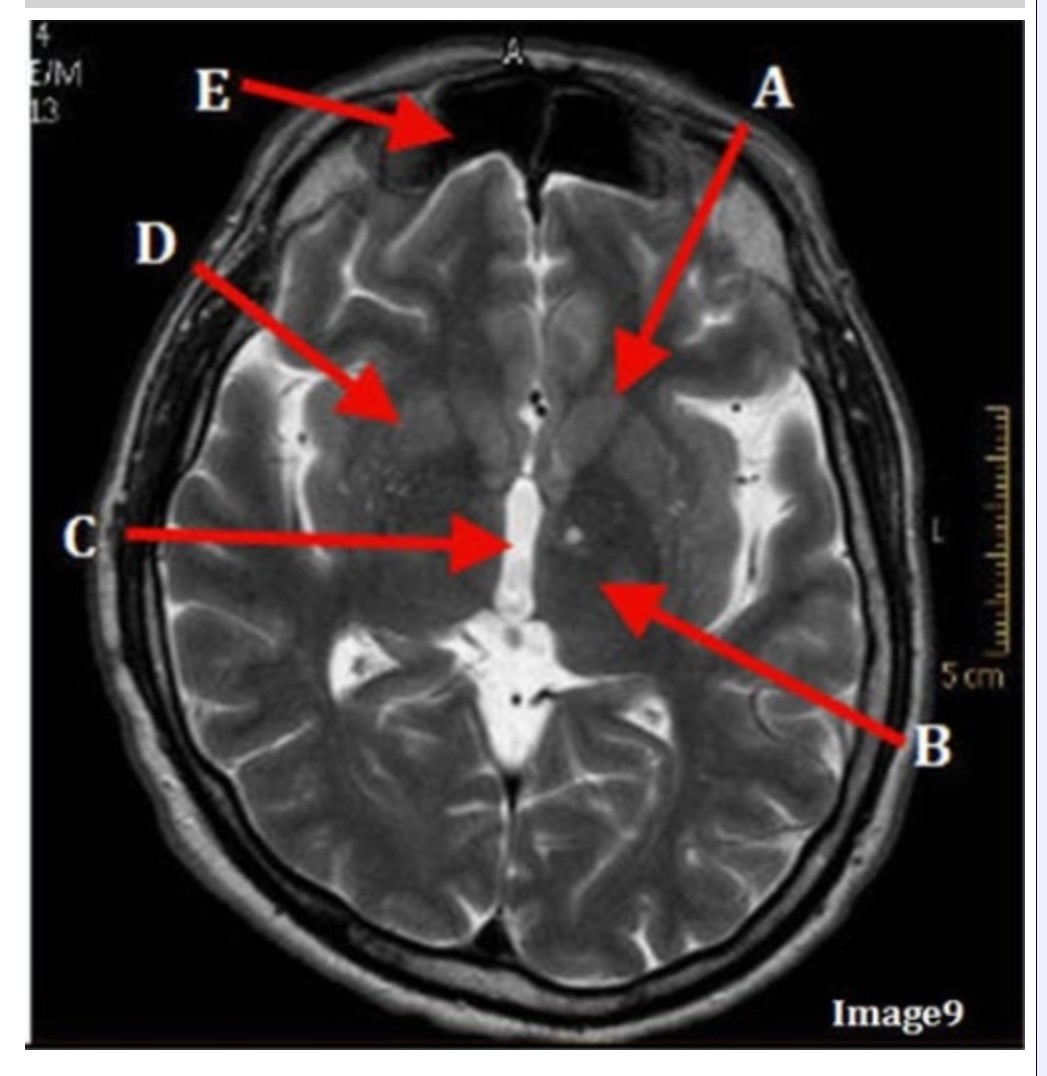
Letter D in Image 9 is pointing to:
A. Third ventricle
B. Thalamus
C. Lentiform nucleus
D. Caudate nucleus
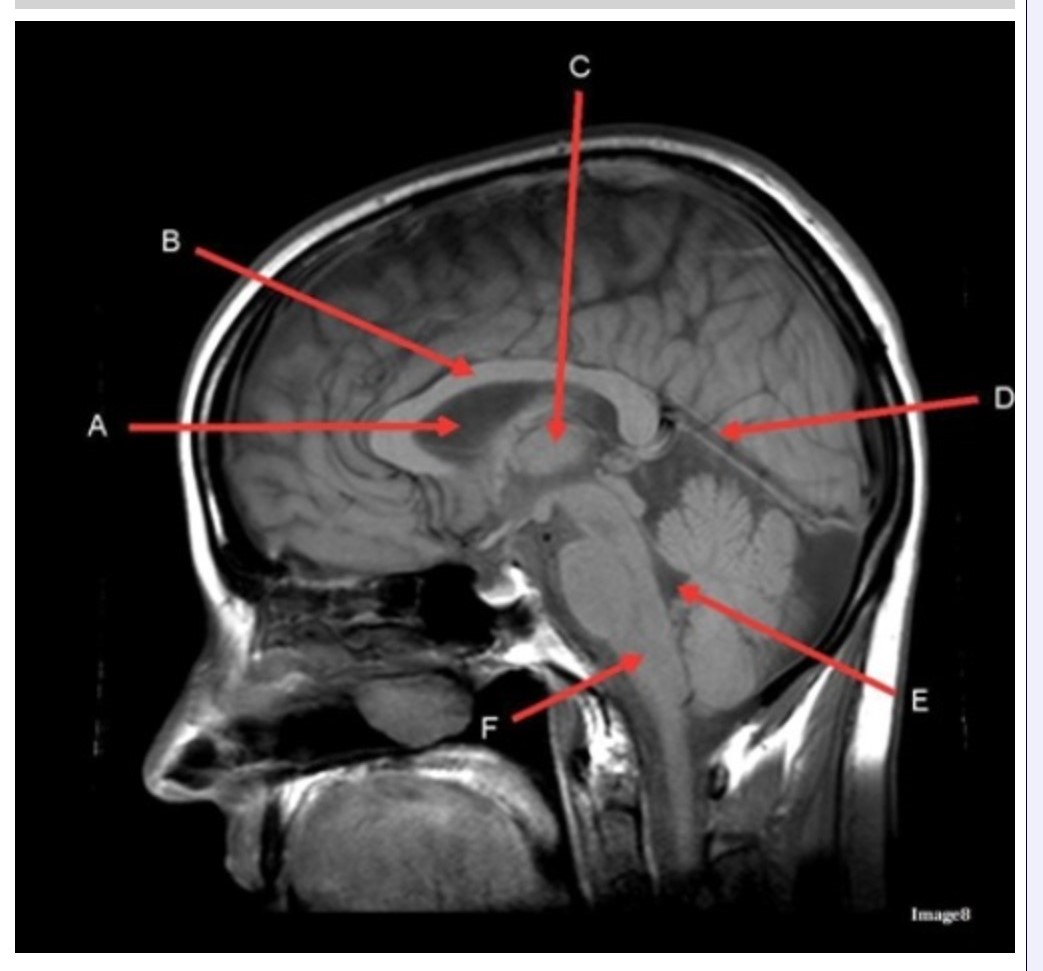
Letter A in Image 8 is pointing to:
A. Tentorium
B. Corpus callosum
C. Hypothalamus
D. Fourth ventricle
E. Lateral Ventricle
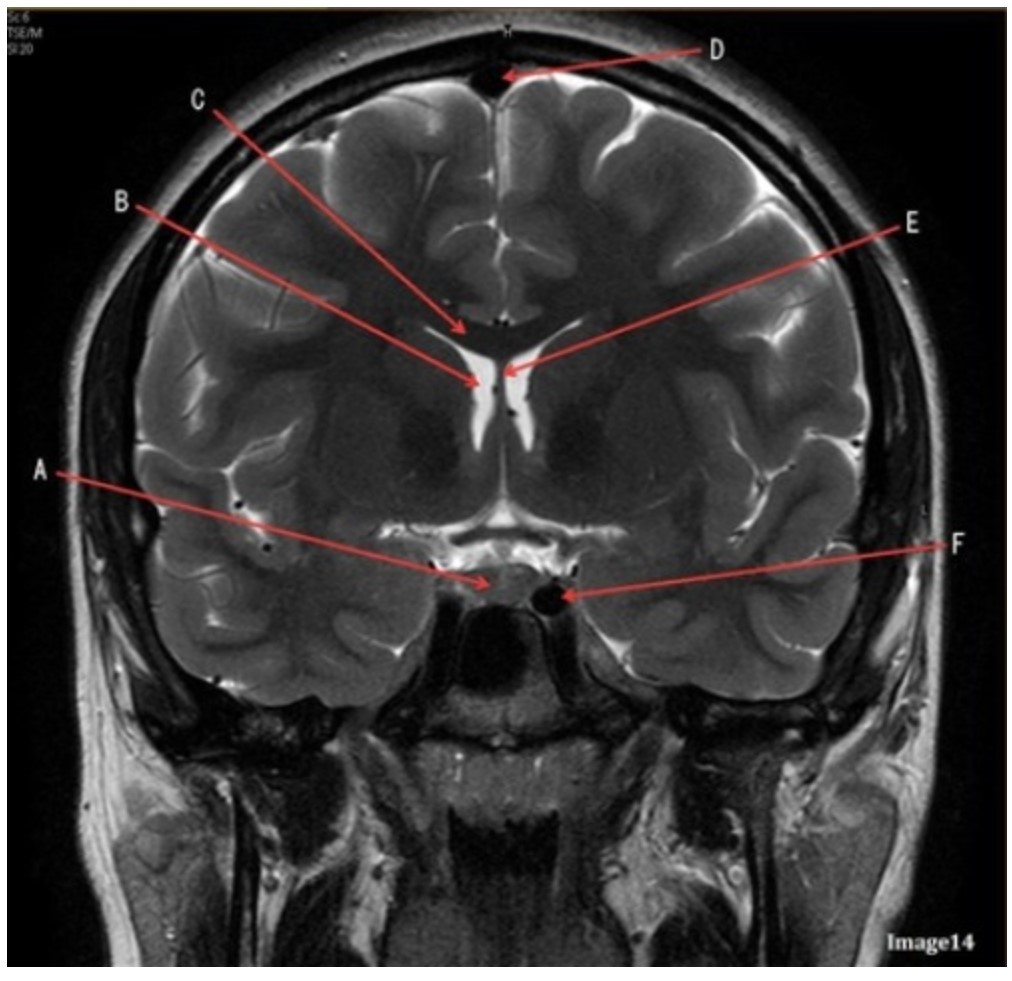
Letter D in Image 14 is pointing to:
A. Tentorium
B. Sphenoid sinus
C. Frontal sinus
D. Sagittal sinus
E. Fornix
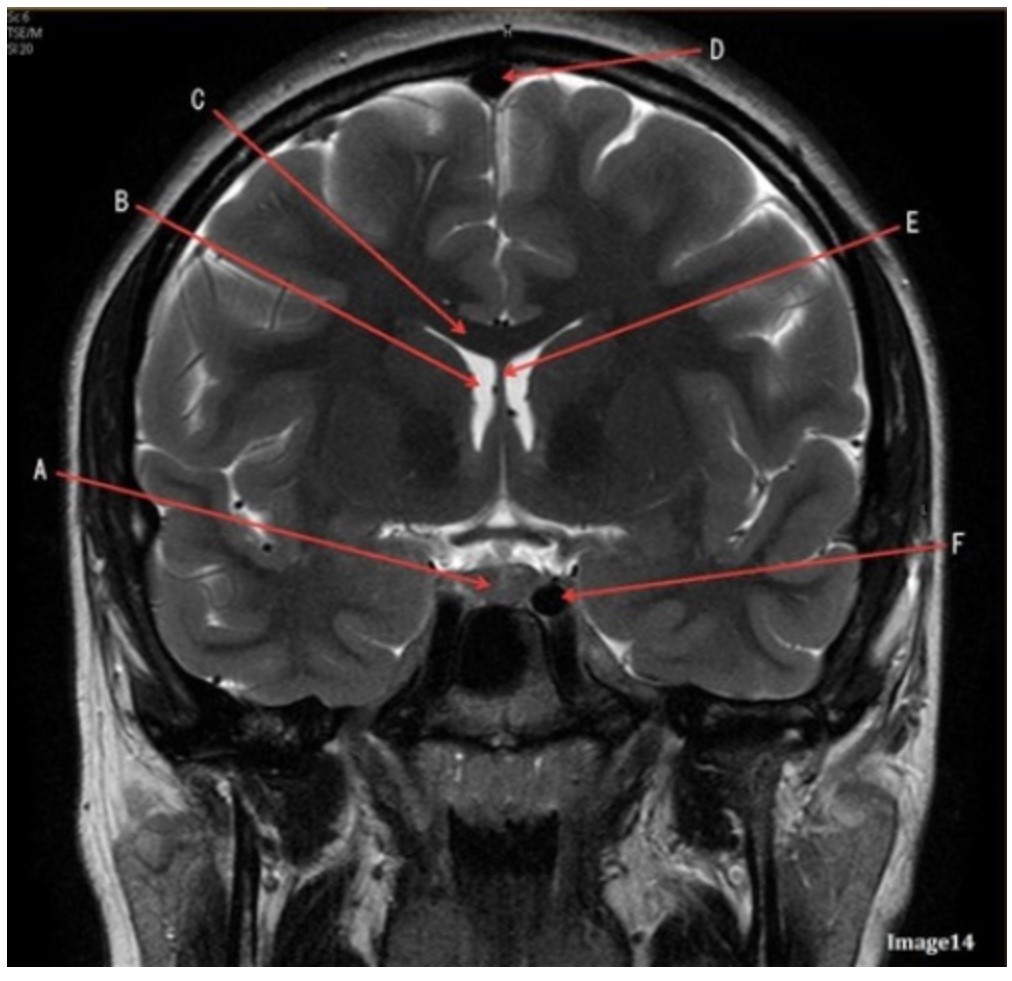
Letter B in Image 14 is pointing to:
A. Corpus callosum
B. Third ventricle
C. Lateral ventricle
D. Pituitary gland
E. Fornix
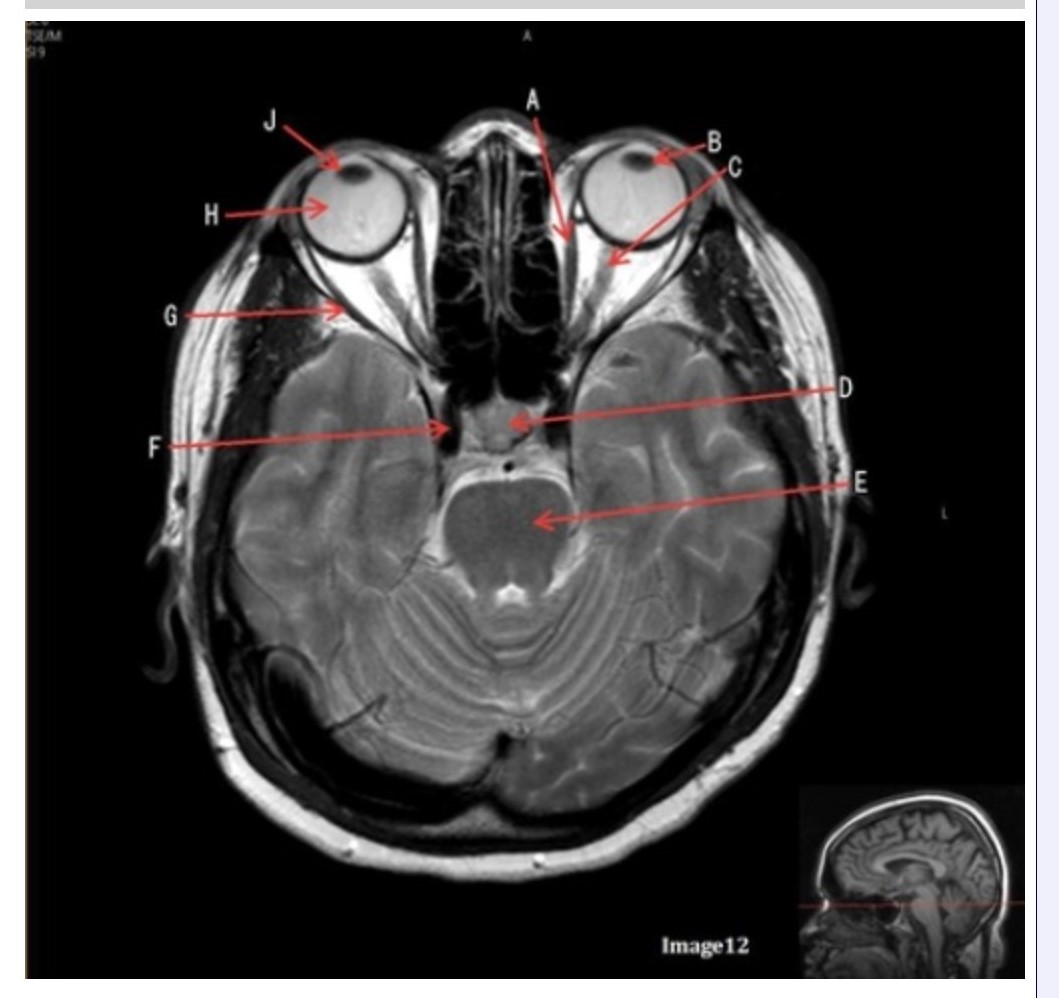
Letter F in Image 12 is pointing to:
A. Lens
B. Lateral rectus muscle
C. Medial rectus muscle
D. Internal carotid artery
E. Globe

Letter D in Image 6 is pointing to:
A. 7th cranial nerve
B. Cochlea
C. Trigeminal nerve
D. Semicircular canal
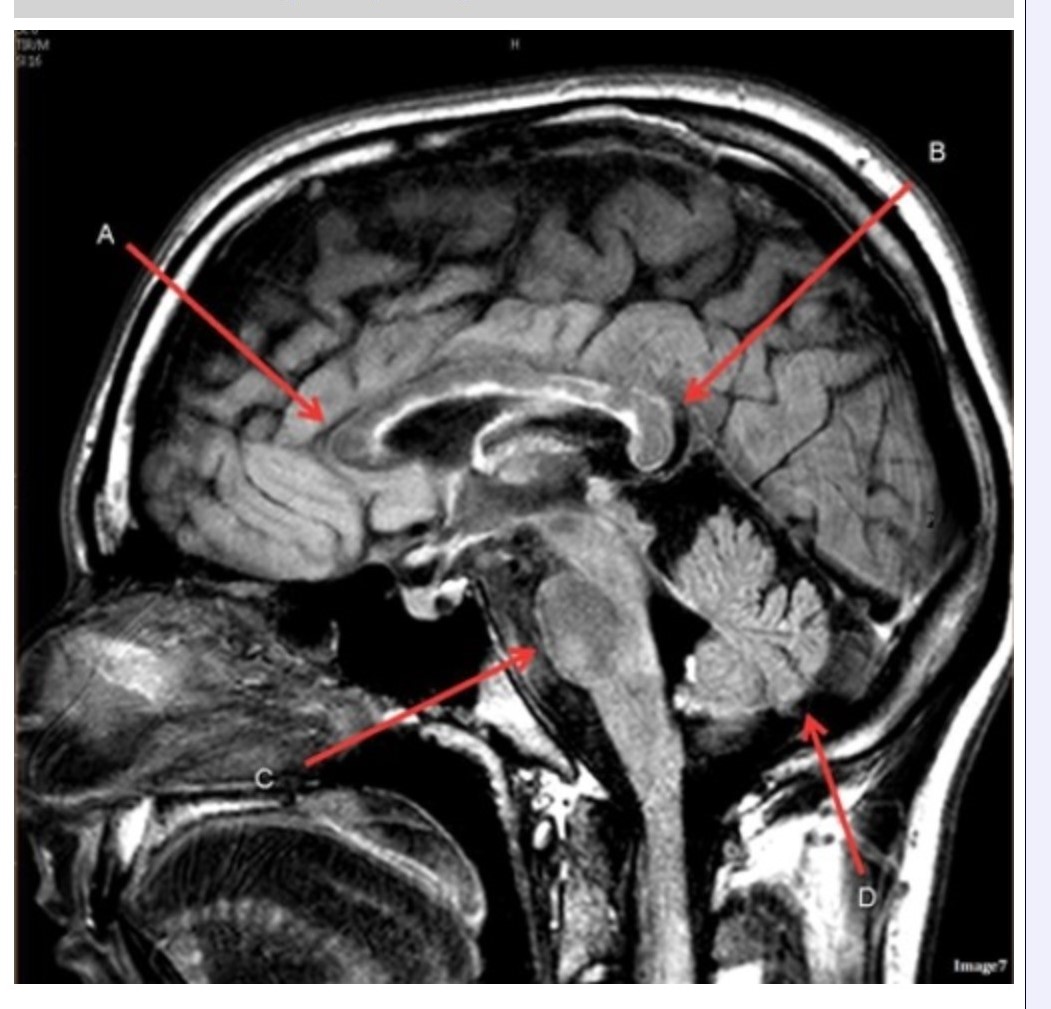
Image 7 is an example of a ______ weighted sequence acquired in the __________ scan plane.
A. T1; Axial
B. T2 FLAIR; Sagittal
C. T2; Axial
D. T2; Sagittal
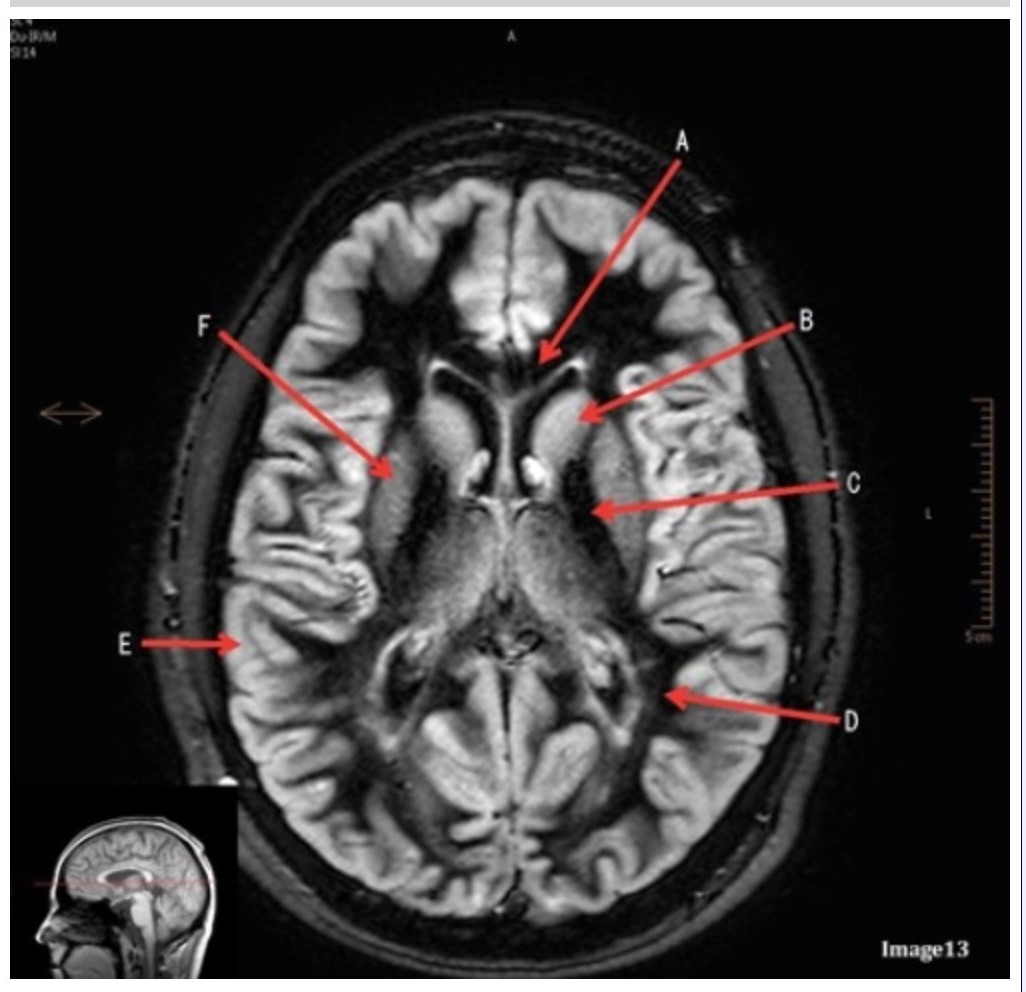
Letter B in Image 13 is pointing to:
A. Splenium of the corpus callosum
B. Genu of the corpus callosum
C. Lentiform nucleus
D. Caudate nucleus
E. Internal capsule
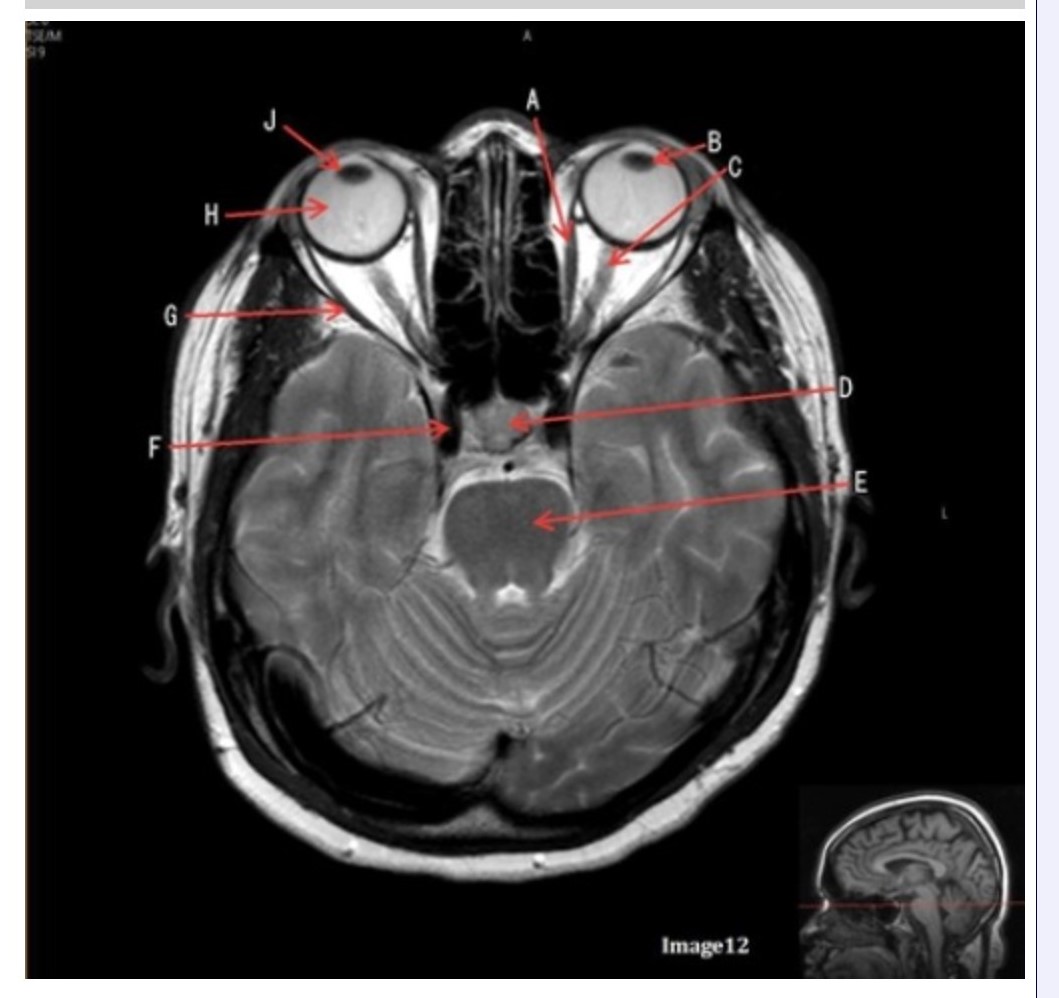
Letter C in Image 12 is pointing to:
A. Left optic nerve
B. Lateral rectus muscle
C. Medial rectus muscle
D. Lens
E. Midbrain
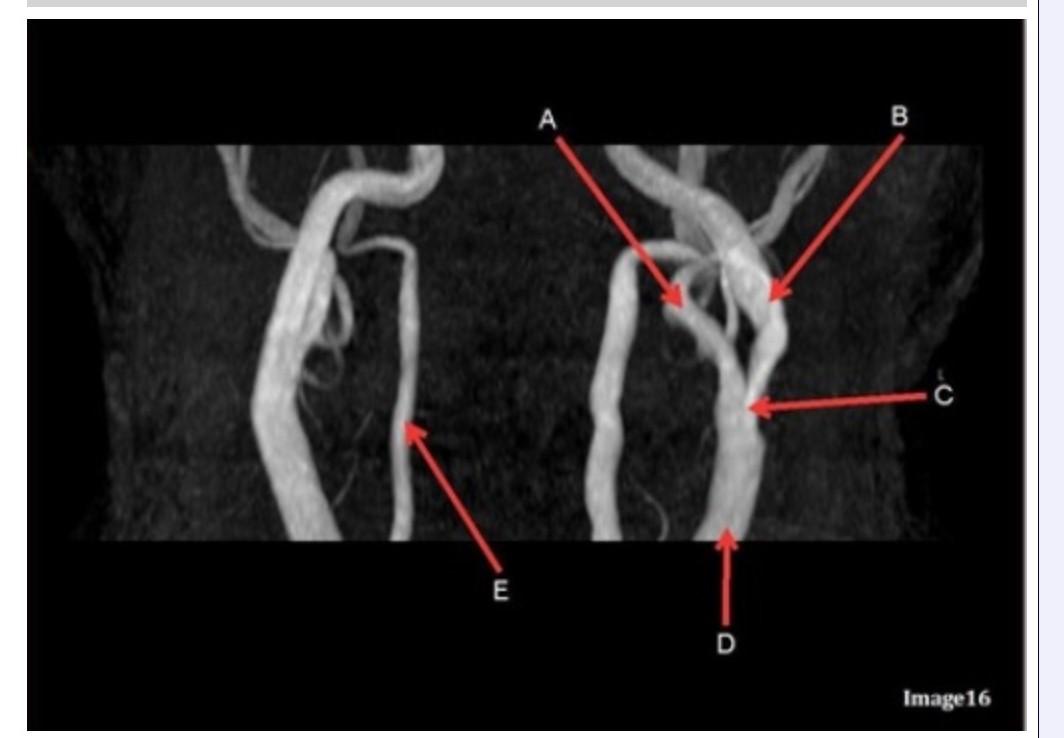
Letter E in Image 16 is pointing to:
A. Internal carotid artery
B. External carotid artery
C. Vertebral artery
D. Common carotid artery
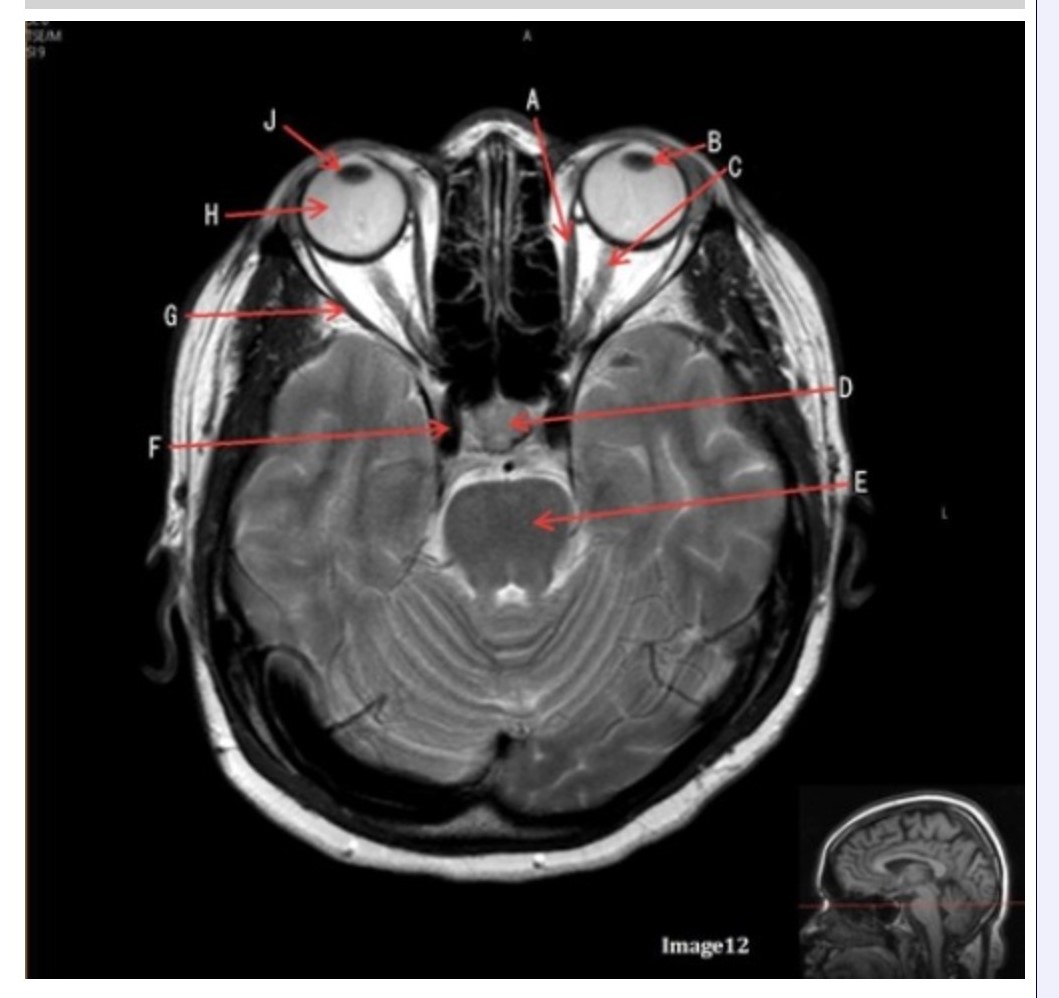
Letter D in Image 12 is pointing to:
A. Optic nerve
B. Pituitary gland
C. Globe
D. Lens
E. Midbrain
Which intracranial artery passes through the sylvian fissure?
A. Basilar
B. Internal carotid
C. External mesenteric
D. Middle cerebral
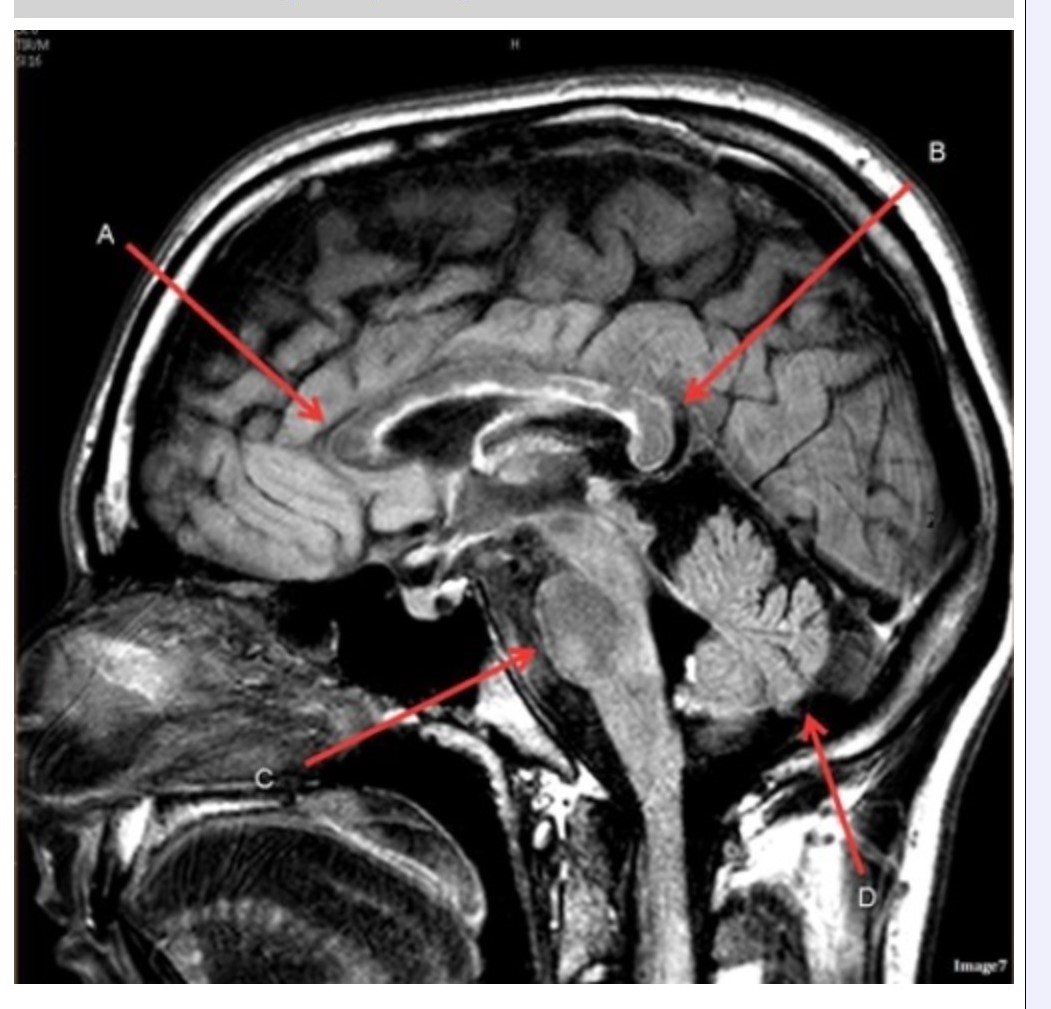
Letter D in Image 7 is pointing to:
A. Pons
B. Cerebellum
C. Hypothalamus
D. Genu of the corpus callosum
E. Splenium of the corpus callosum
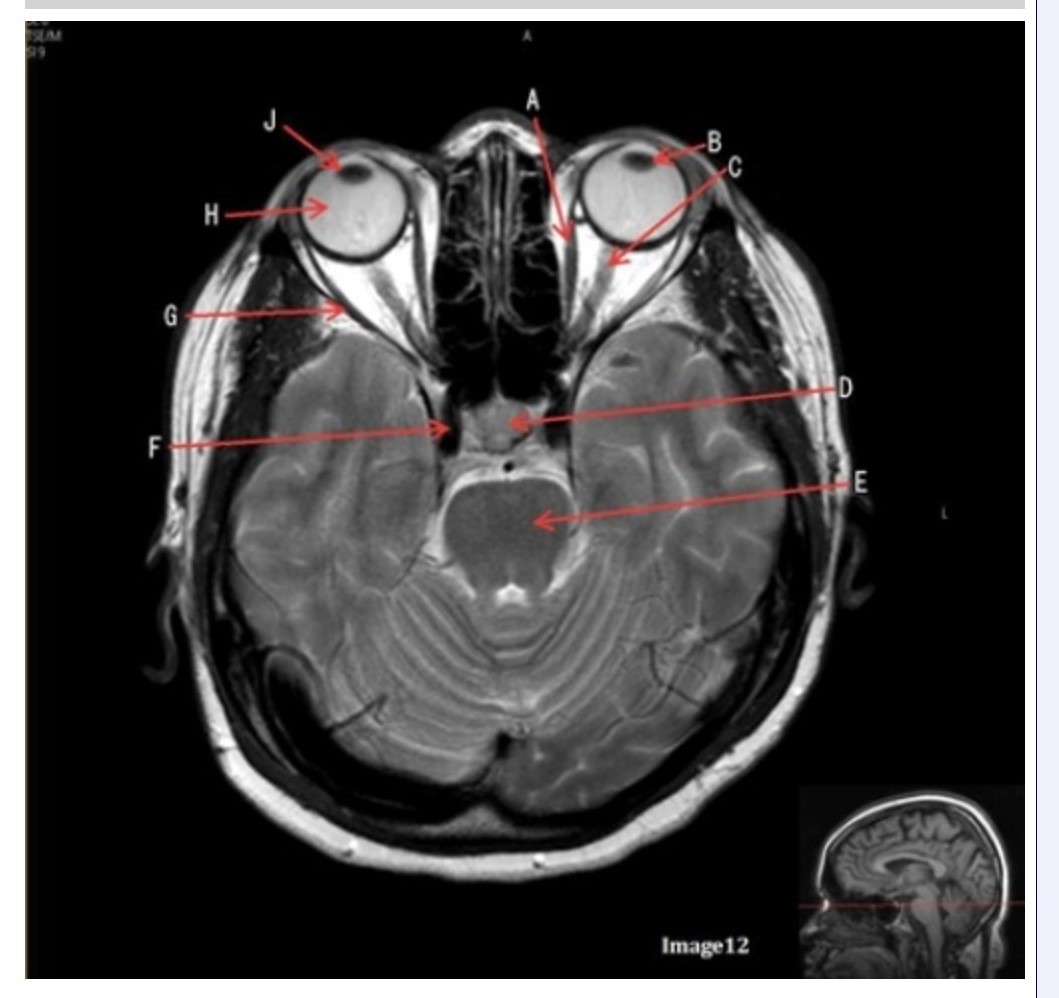
Letter G in Image 12 is pointing to:
A. Lens
B. Lateral rectus muscle
C. Medial rectus muscle
D. Internal carotid artery
E. Globe
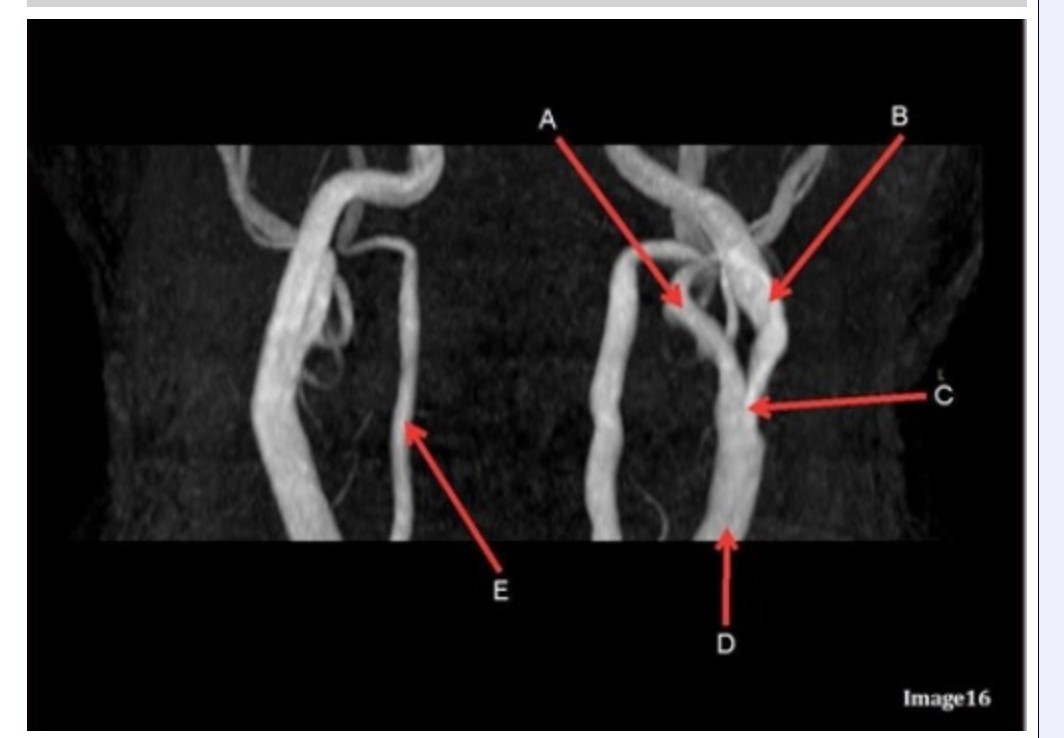
Letter C in Image 16 is pointing to:
A. Internal carotid artery
B. External carotid artery
C. Vertebral artery
D. Common carotid artery
E. Common carotid bifurcation
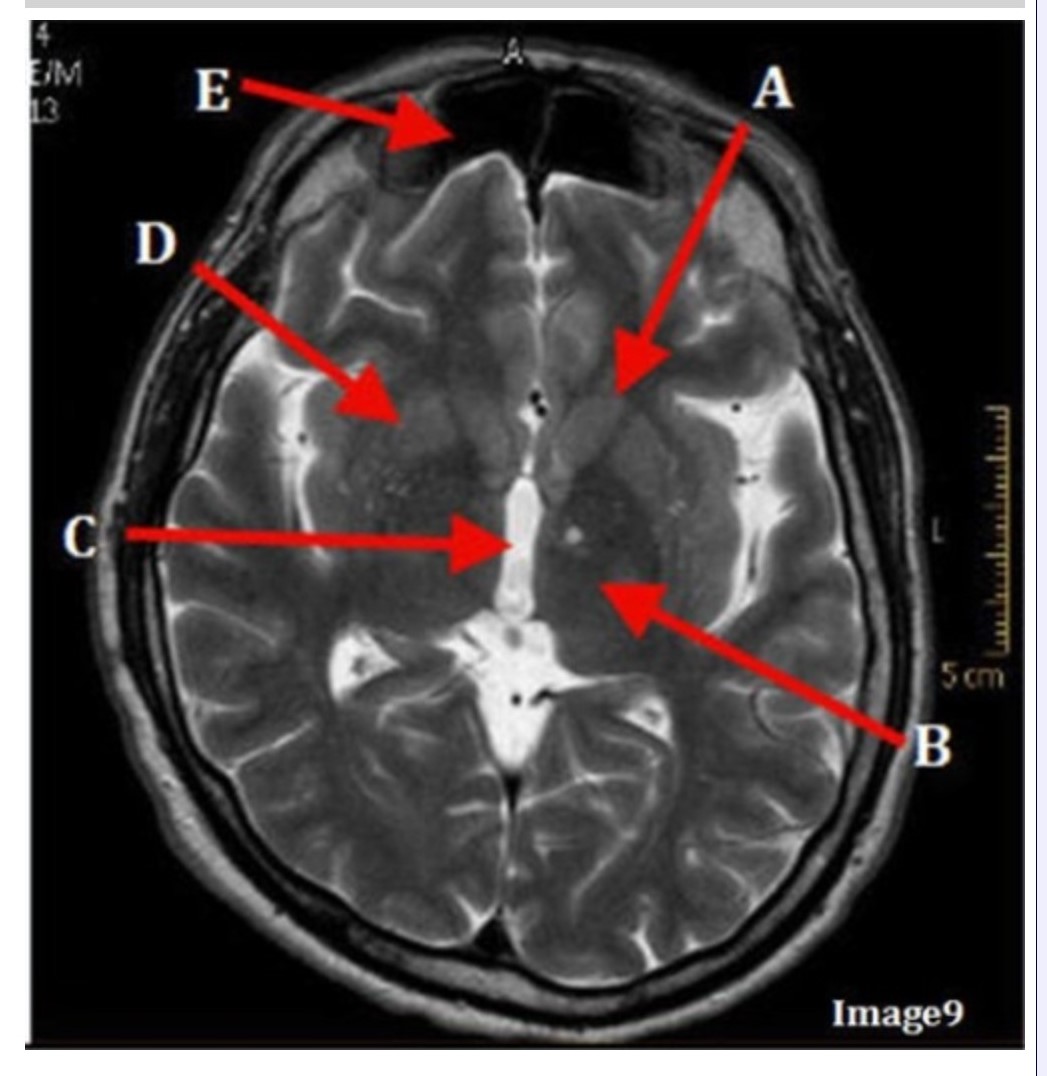
Letter E in Image 9 is pointing to:
A. Maxillary sinus
B. Sphenoid sinus
C. Frontal sinus
D. Ethmoid sinus
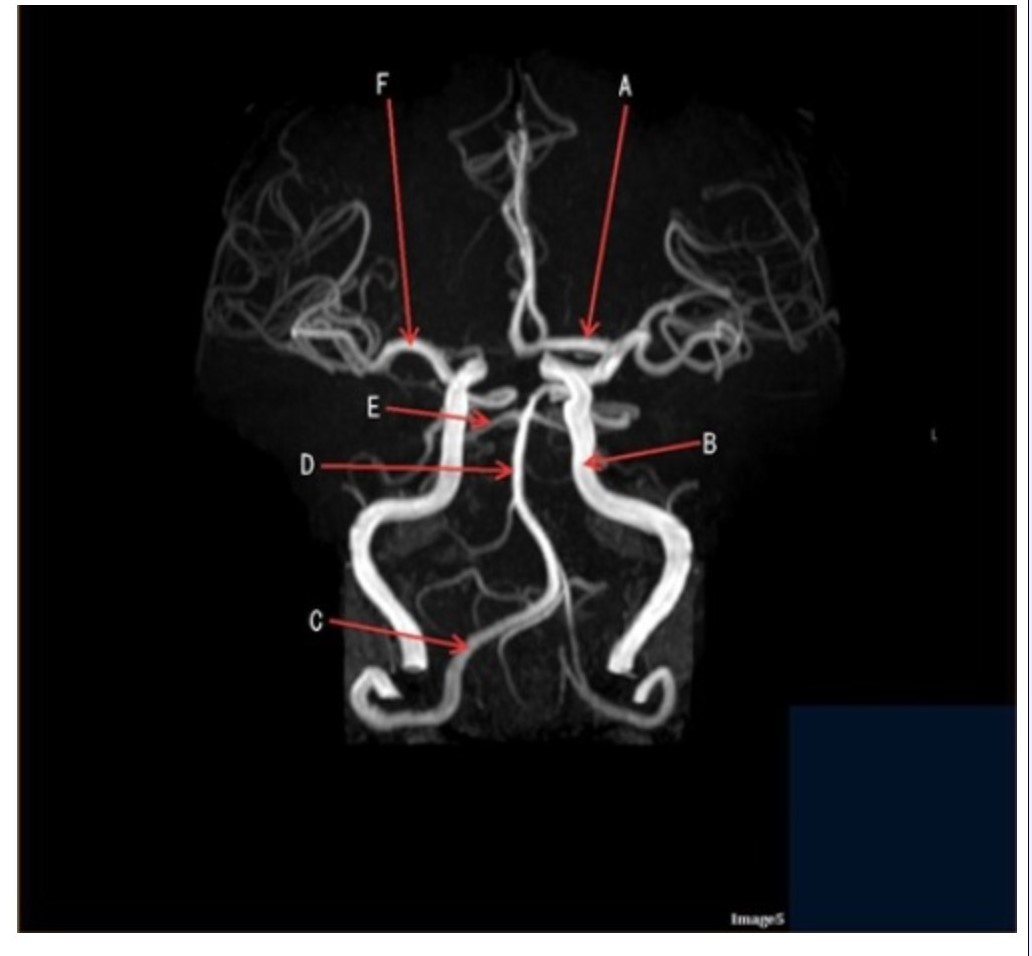
Image 5 is an example of an:
A. MRI brain
B. MRV sagittal sinus
C. MRS single voxel
D. MRA Circle of Willis
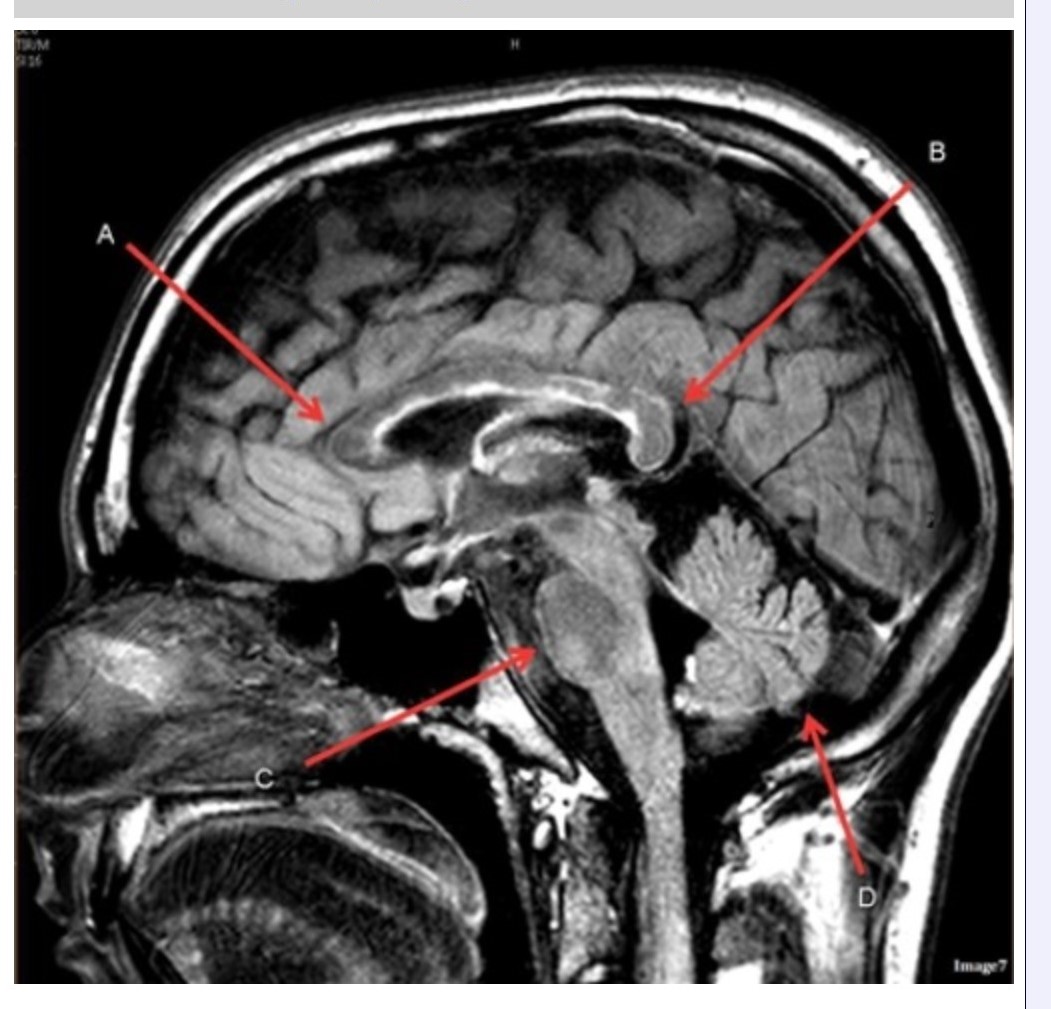
Letter A in Image 7 is pointing to:
A. Pons
B. Cerebellum
C. Hypothalamus
D. Genu of the corpus callosum
E. Splenium of the corpus callosum
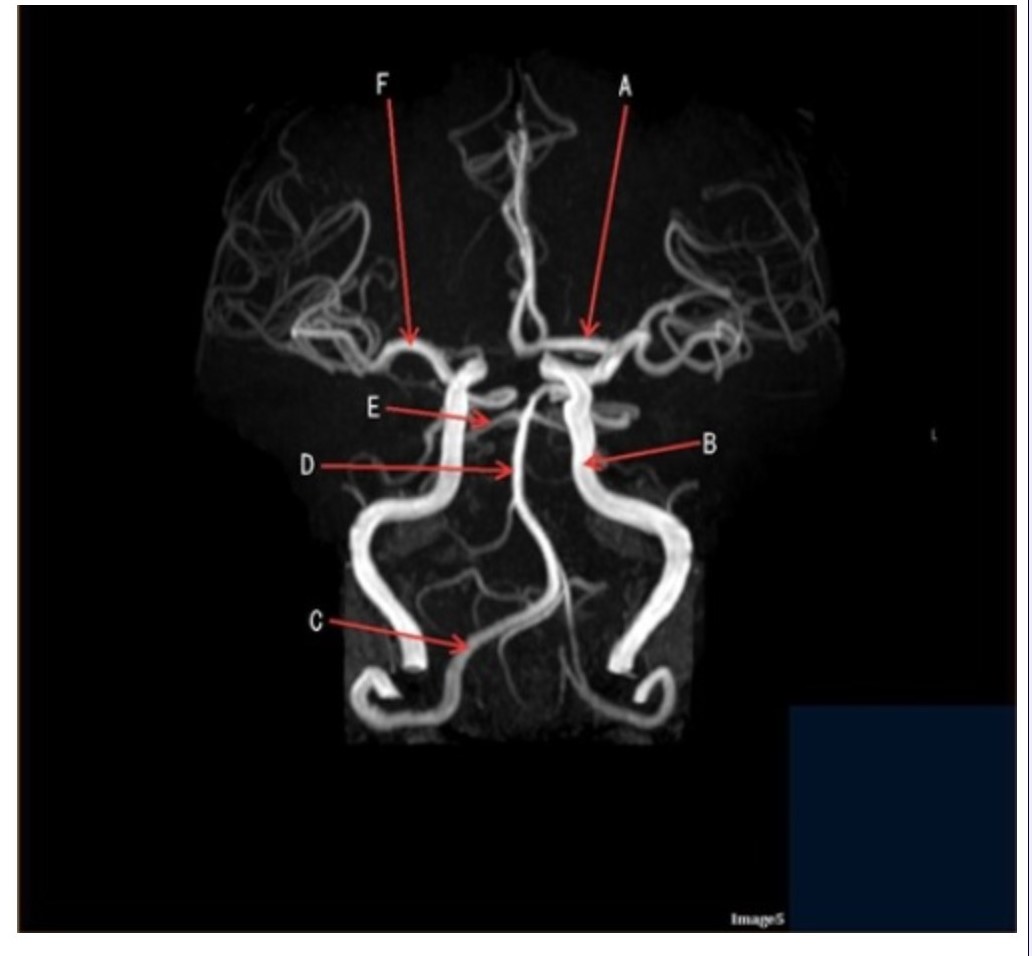
Letter B in Image 5 is pointing to:
A. Anterior cerebral artery
B. Internal carotid artery
C. Basilar artery
D. Posterior cerebral artery
E. Middle cerebral artery
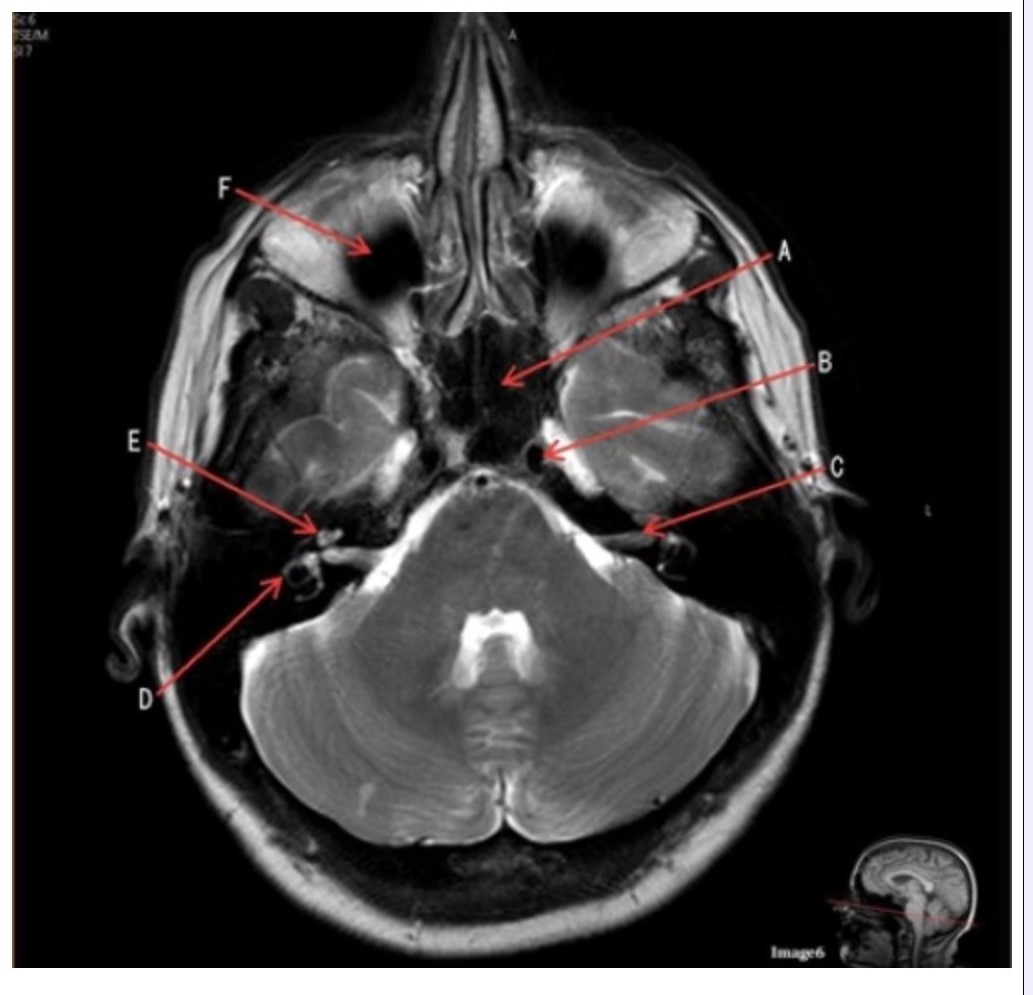
Letter C in Image 6 is pointing to:
A. 7th cranial nerve
B. Cochlea
C. Trigeminal nerve
D. Semicircular canal
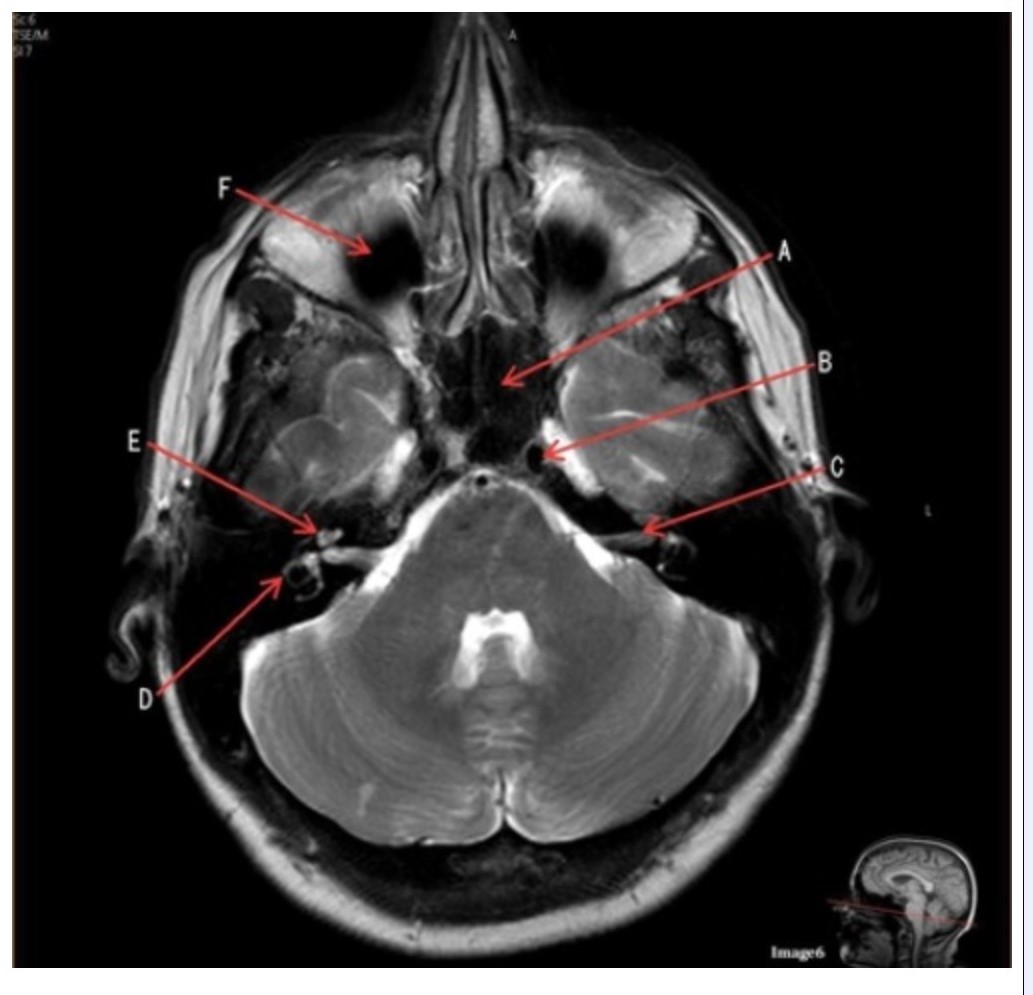
Letter B in Image 6 is pointing to:
A. Maxillary sinus
B. Sphenoid sinus
C. Vertebral artery
D. Internal carotid artery
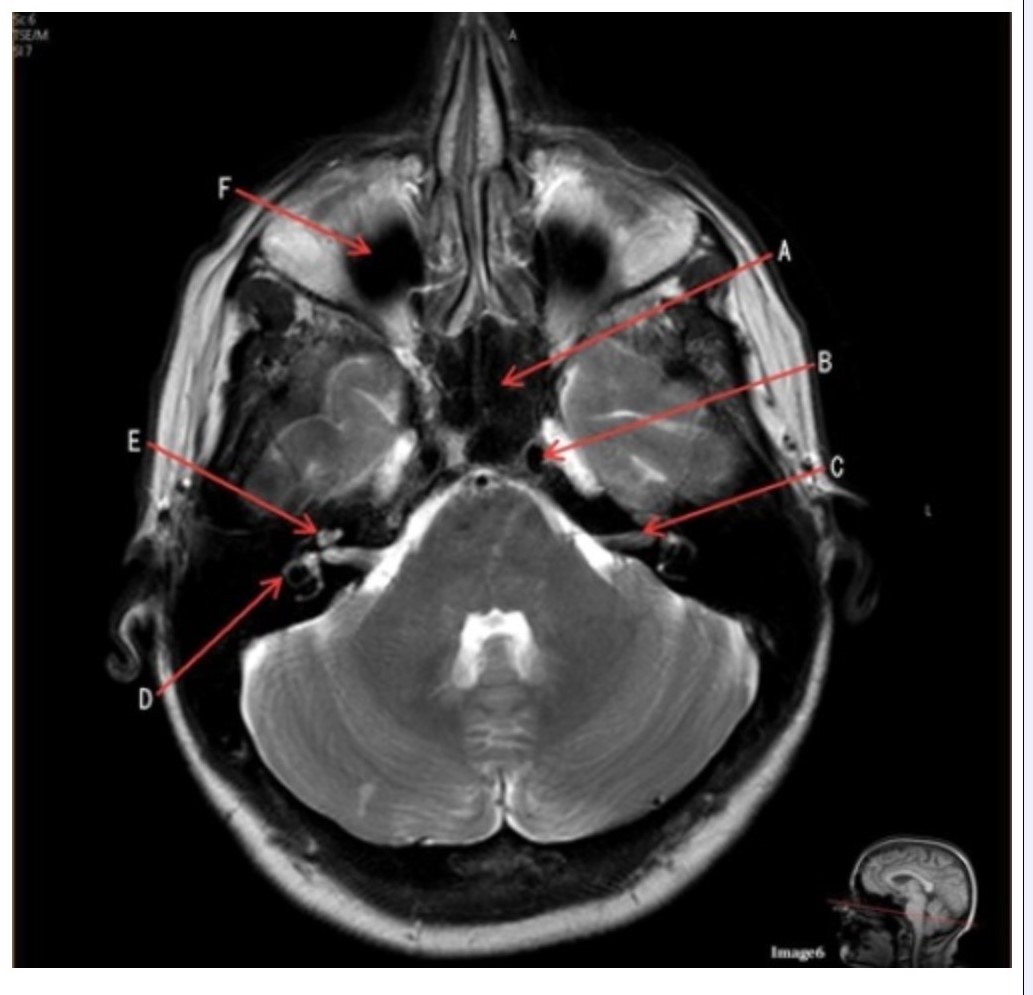
Letter F in Image 6 is pointing to:
A. Maxillary sinus
B. Sphenoid sinus
C. Frontal sinus
D. Optic chiasm
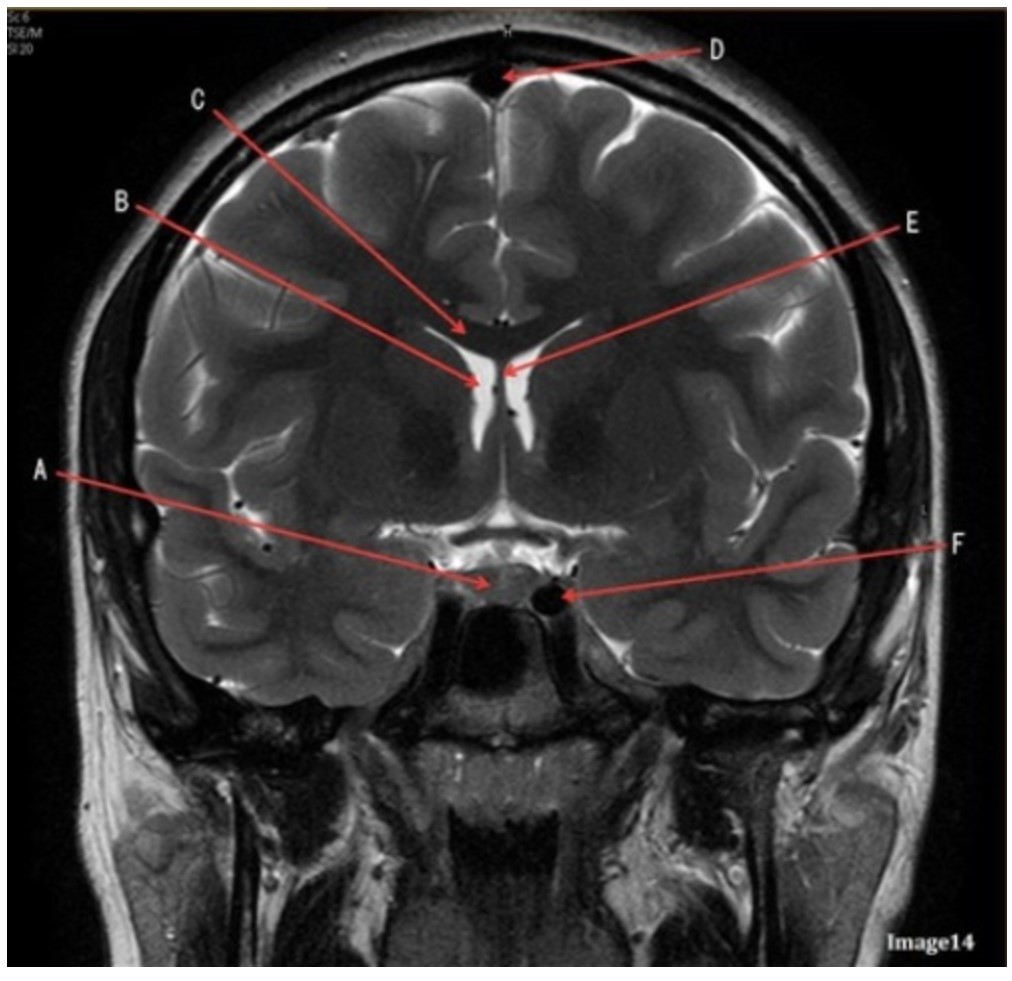
Letter E in Image 14 is pointing to:
A. Corpus callosum
B. Third ventricle
C. Lateral ventricle
D. Internal carotid artery
E. Fornix
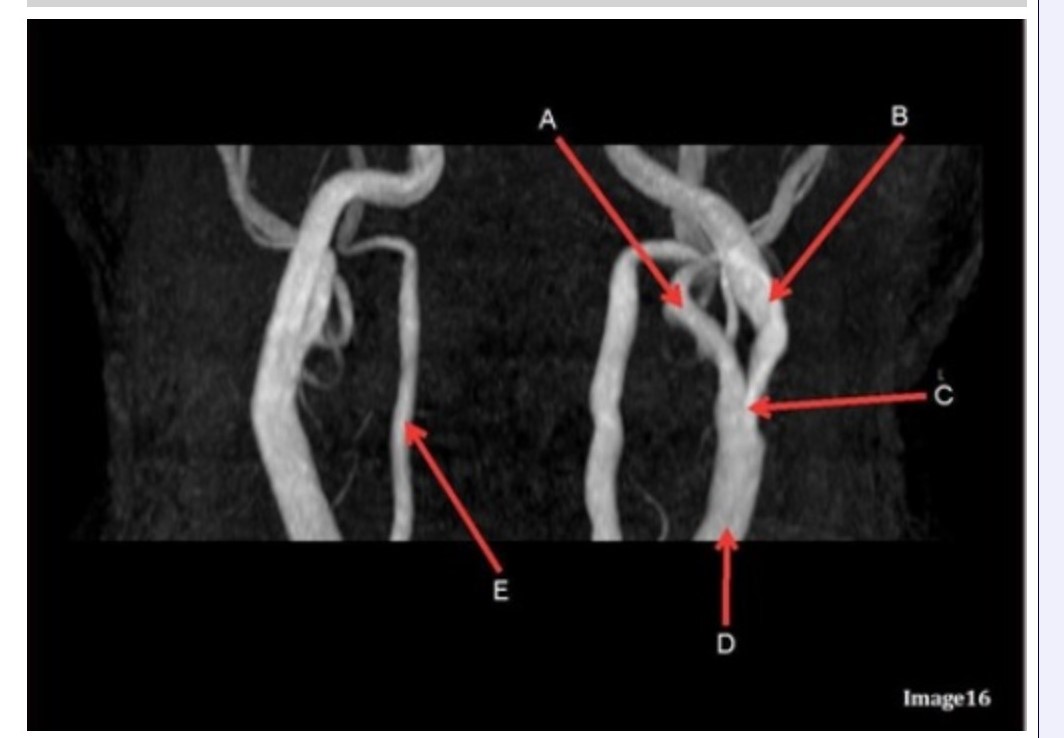
Letter A in Image 16 is pointing to:
A. Internal carotid artery
B. External carotid artery
C. Vertebral artery
D. Common carotid artery
E. Common carotid bifurcation
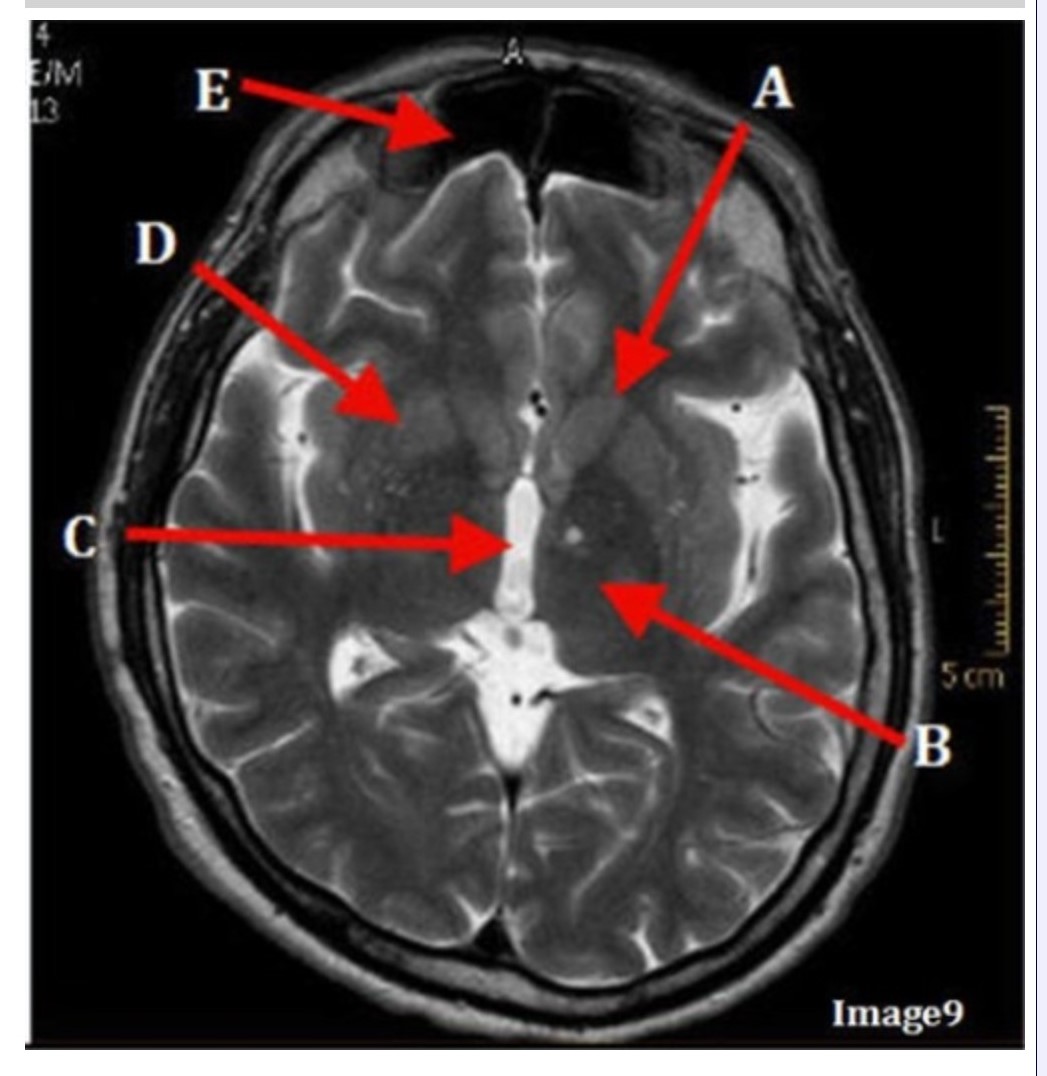
Letter A in Image 9 is pointing to:
A. Third ventricle
B. Thalamus
C. Lentiform nucleus
D. Caudate nucleus
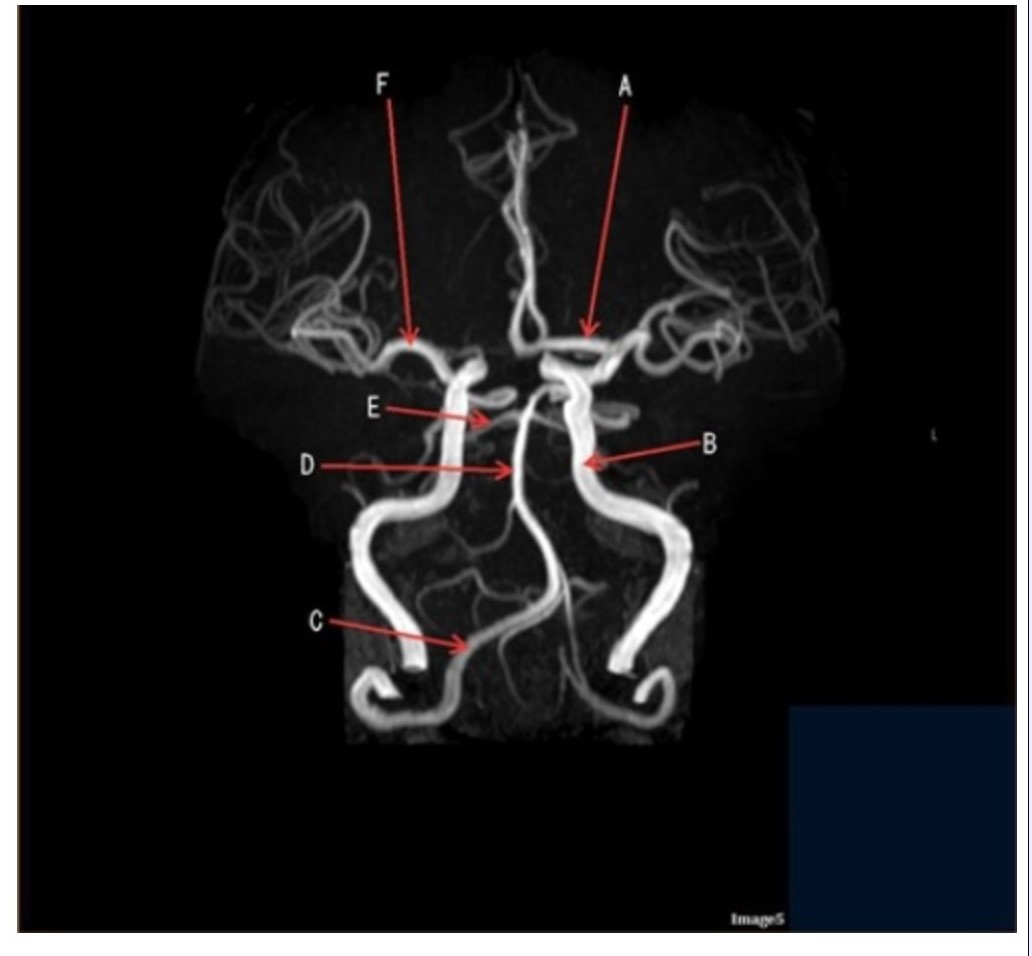
Letter C in Image 5 is pointing to:
A. Vertebral artery
B. Internal carotid artery
C. Basilar artery
D. Posterior cerebral artery
E. Middle cerebral artery
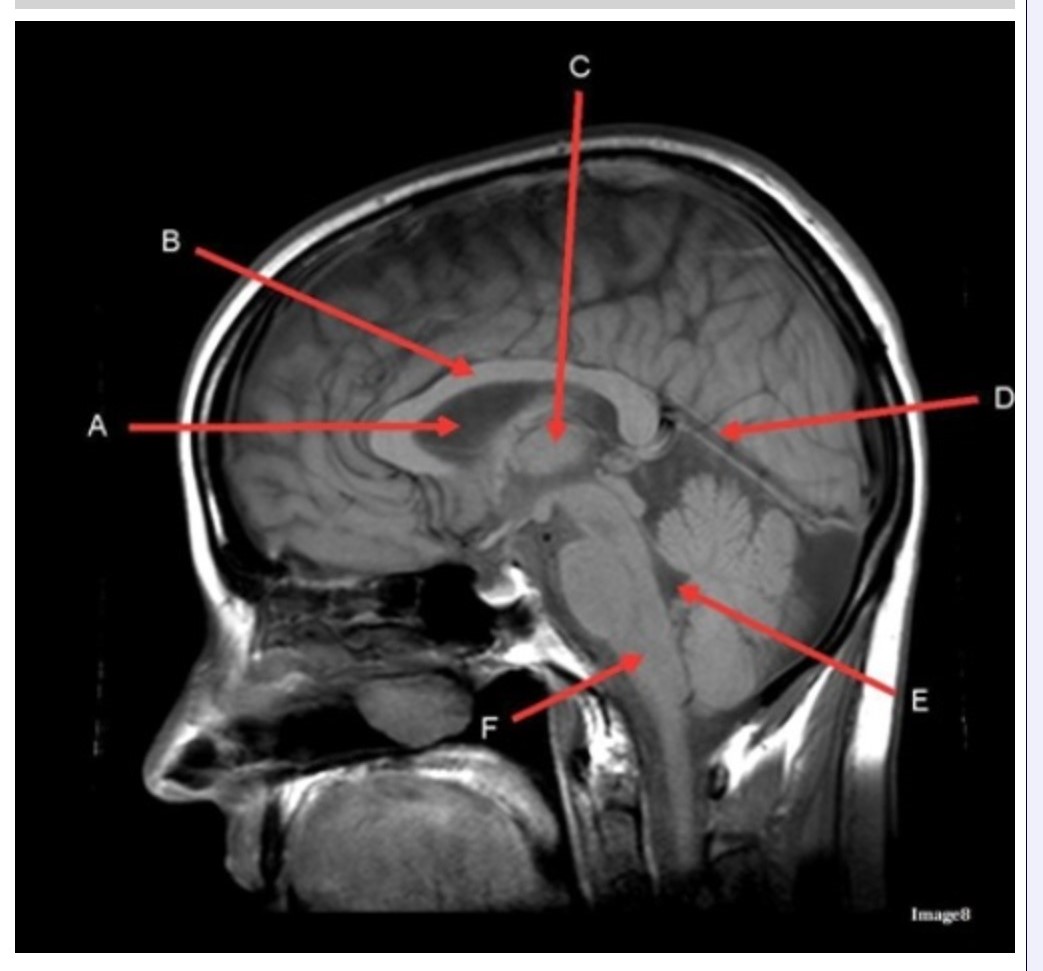
Letter E in Image 8 is pointing to:
A. Tentorium
B. Cerebellum
C. Thalamus
D. Fourth ventricle
E. Medulla oblongata
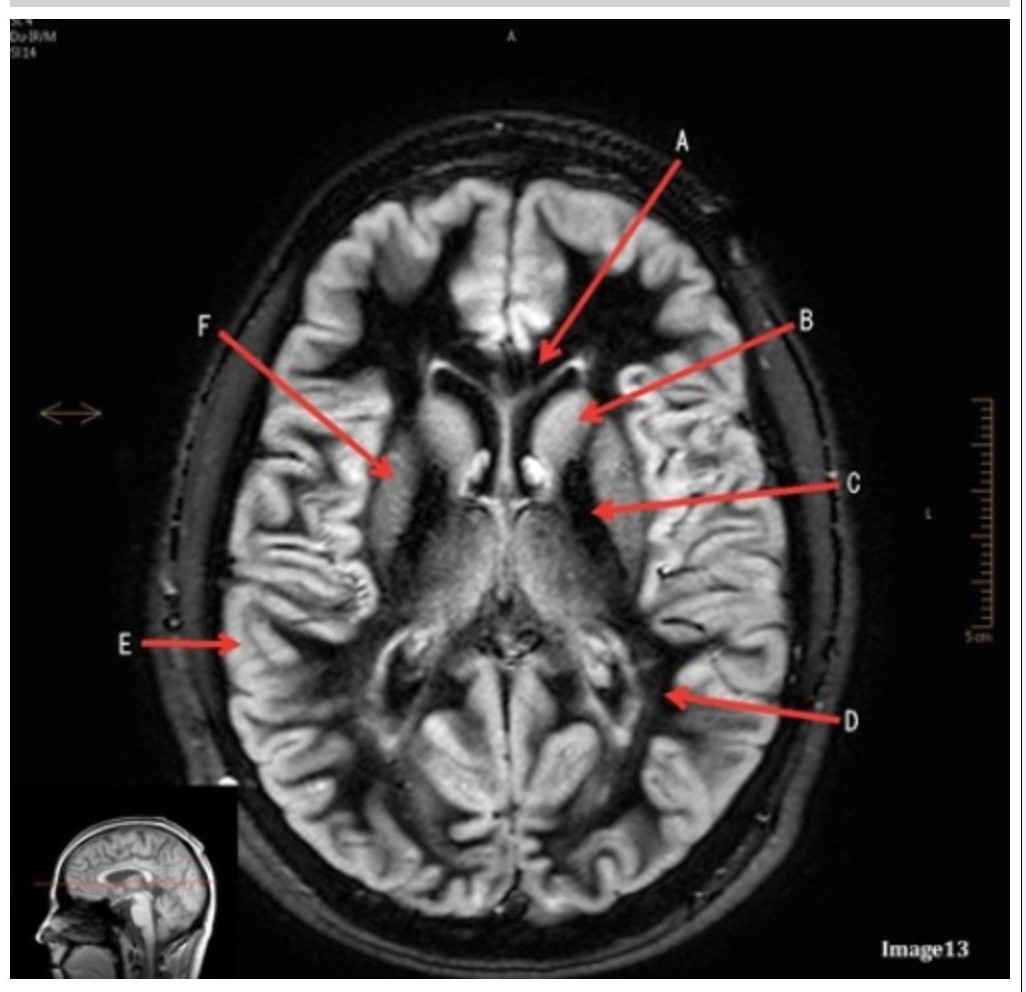
Letter F in Image 13 is pointing to:
A. Grey matter
B. White matter
C. Lentiform nucleus
D. Caudate nucleus
E. Internal capsule

Letter A in Image 14 is pointing to:
A. Corpus callosum
B. Third ventricle
C. Lateral ventricle
D. Pituitary gland
E. Fornix
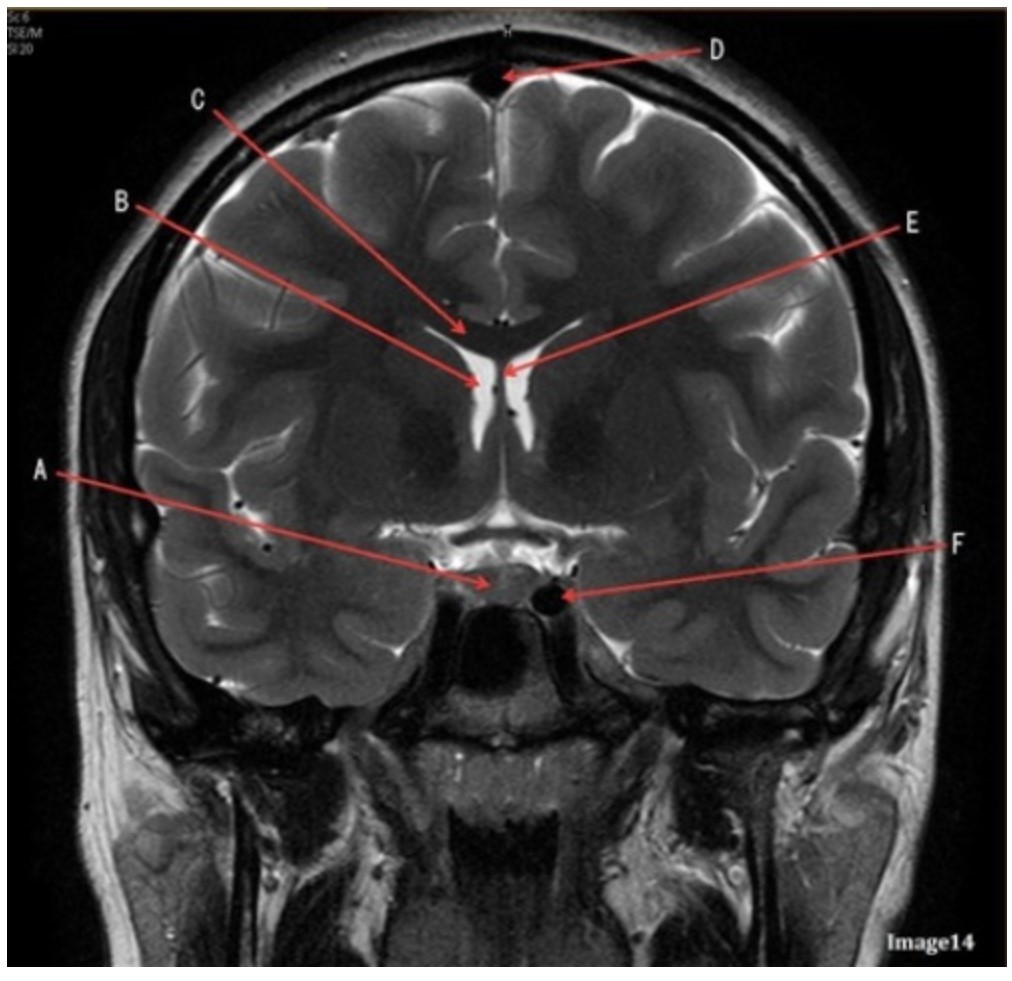
Letter A in Image 14 is pointing to:
A. Corpus callosum
B. Third ventricle
C. Lateral ventricle
D. Pituitary gland
E. Fornix
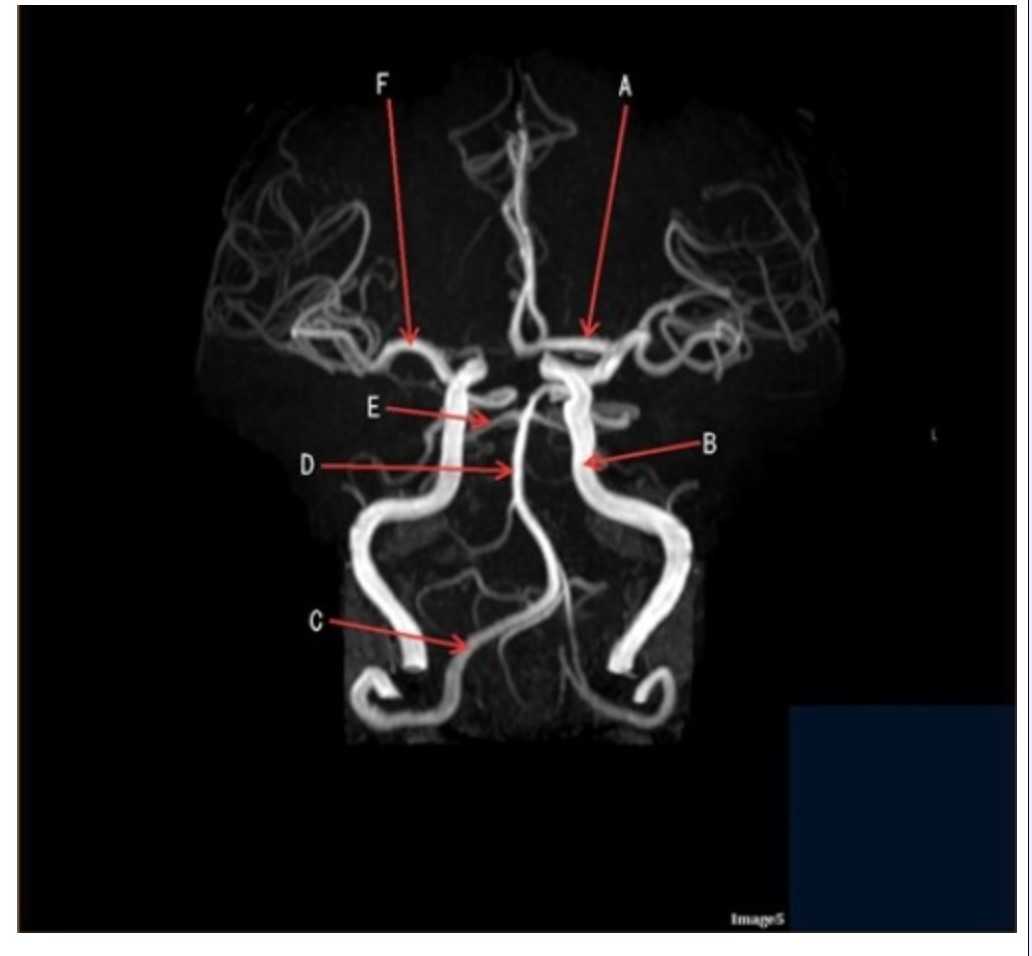
Letter E in Image 5 is pointing to:
A. Anterior cerebral artery
B. Internal carotid artery
C. Basilar artery
D. Posterior cerebral artery
E. Middle cerebral artery
Which arteries join together to form the basilar artery?
A. Vertebral arteries
B. External carotids
C. Internal carotids
D. Iliacs
E. None of the above
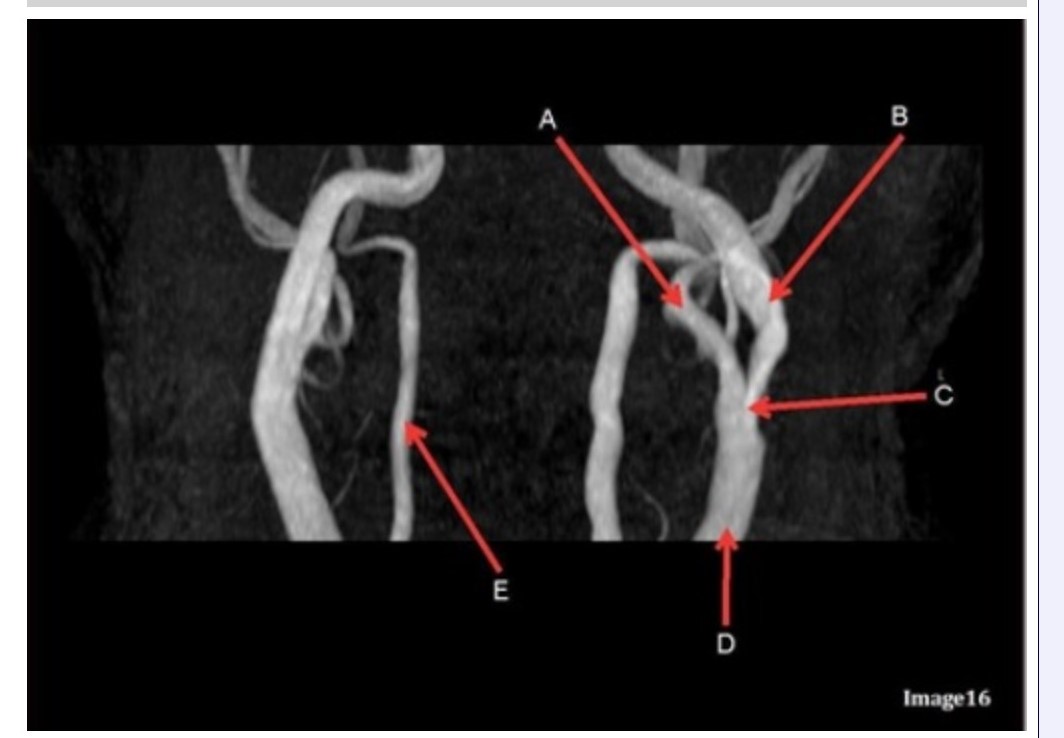
Letter A in Image 16 is responsible for blood supply to the:
A. Anterior brain
B. Posterior brain
C. Face
D. Upper extremities
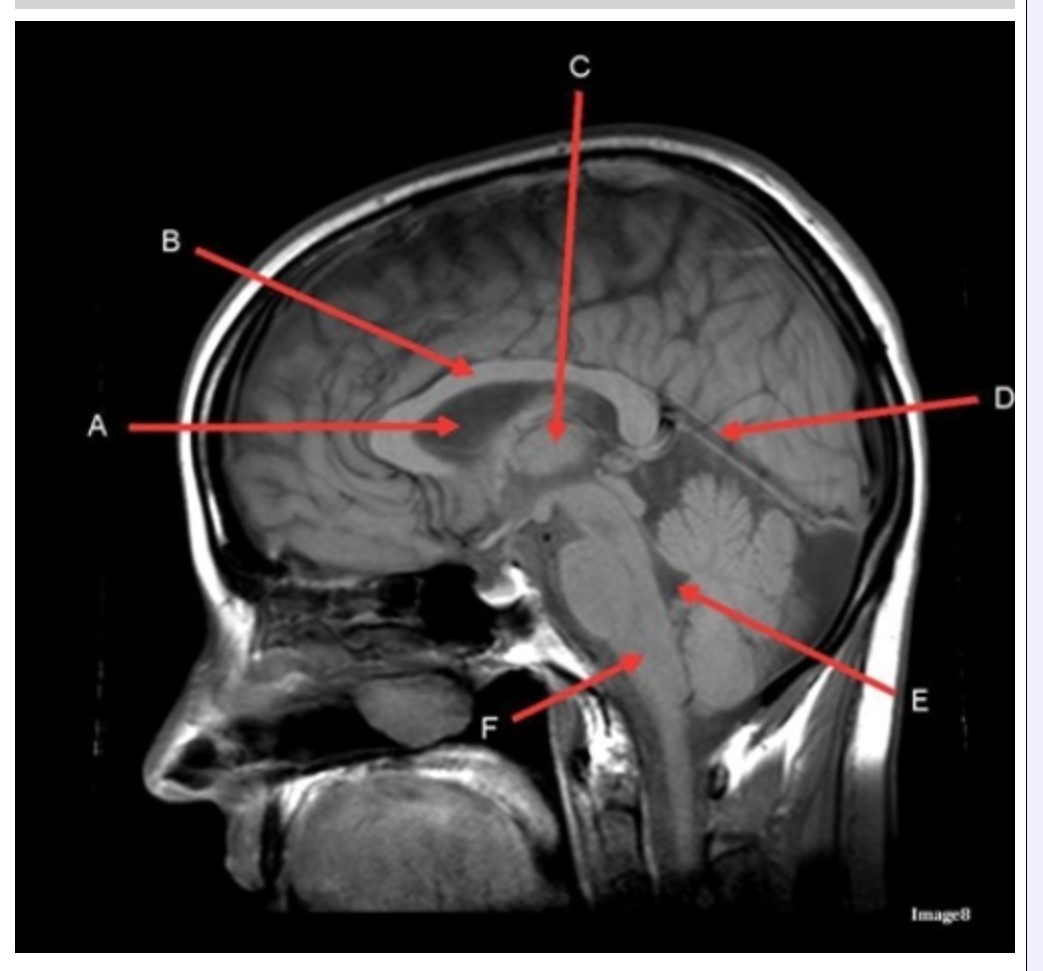
Letter B in Image 8 is pointing to:
A. Tentorium
B. Corpus callosum
C. Hypothalamus
D. Fourth ventricle
E. Medulla oblongata
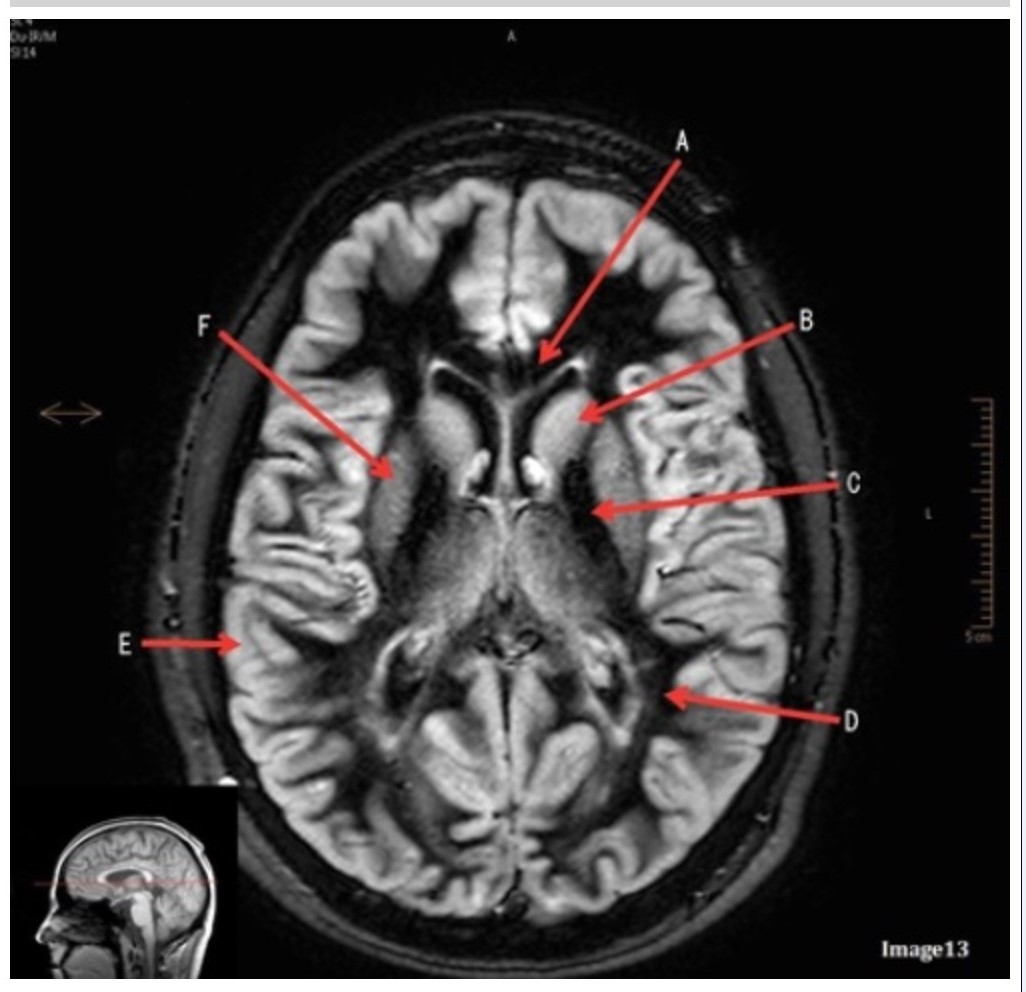
Letter D in Image 13 is pointing to:
A. Grey matter
B. White matter
C. Lentiform nucleus
D. Caudate nucleus
E. Internal capsule
Letter A in Image 10 is pointing to:
A. Third ventricle
B. Basal ganglia
C. Anterior horn lateral ventricle
D. Posterior horn lateral ventricle
Letter D in Image 8 is pointing to:
A. Tentorium
B. Cerebellum
C. Thalamus
D. Fourth ventricle
E. Medulla oblongata
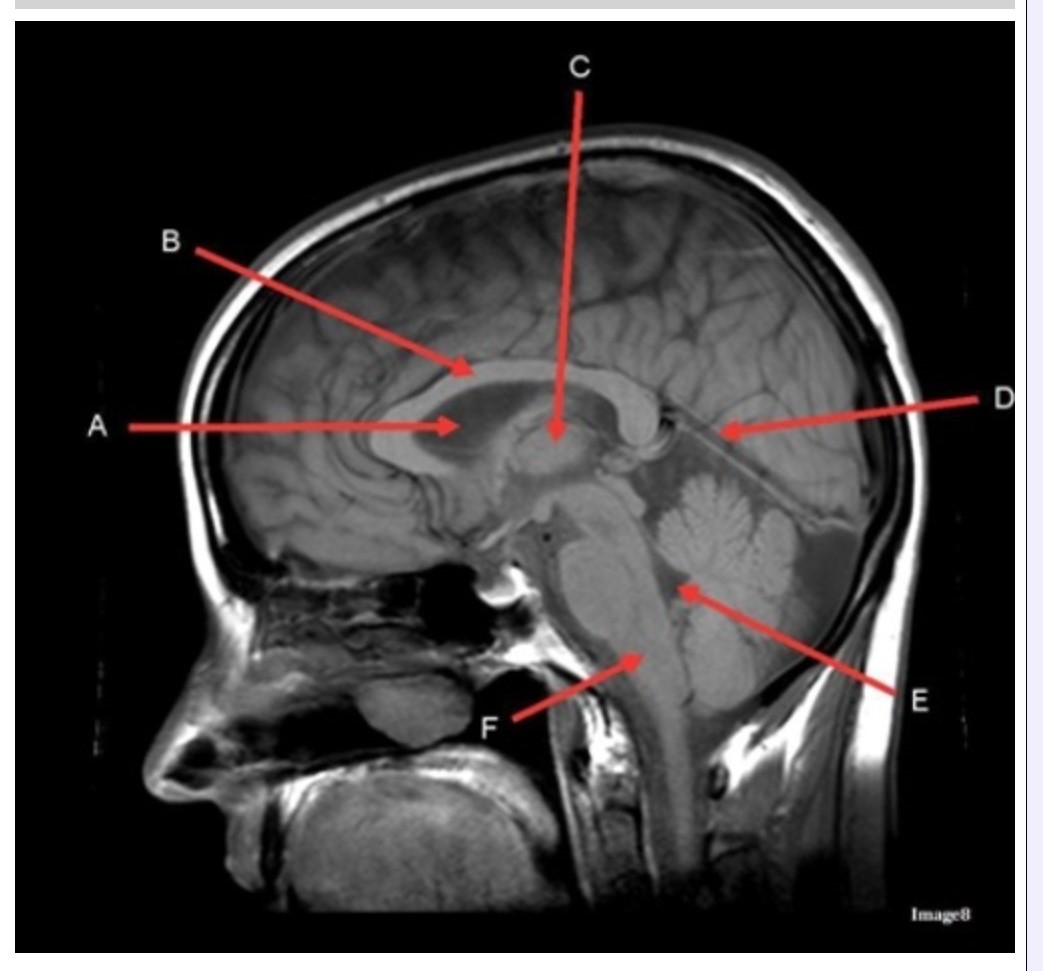
Image 8 is an example of a _______ weighted sequence acquired in the _______ scan plane.
A. T1; Axial
B. T1; Sagittal
C. T2; Axial
D. T2; Sagittal
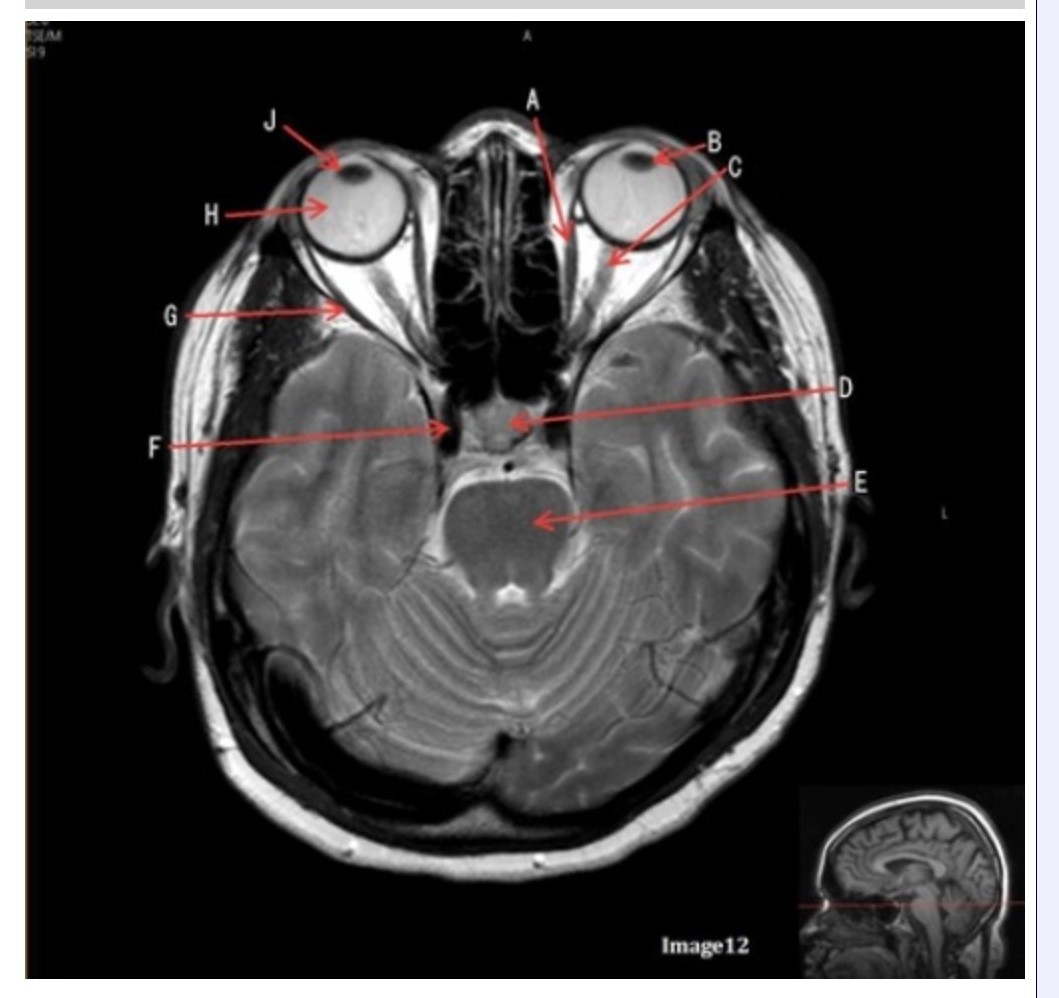
Letter E in Image 12 is pointing to:
A. Optic nerve
B. Pituitary gland
C. Globe
D. Pons
E. Left lens
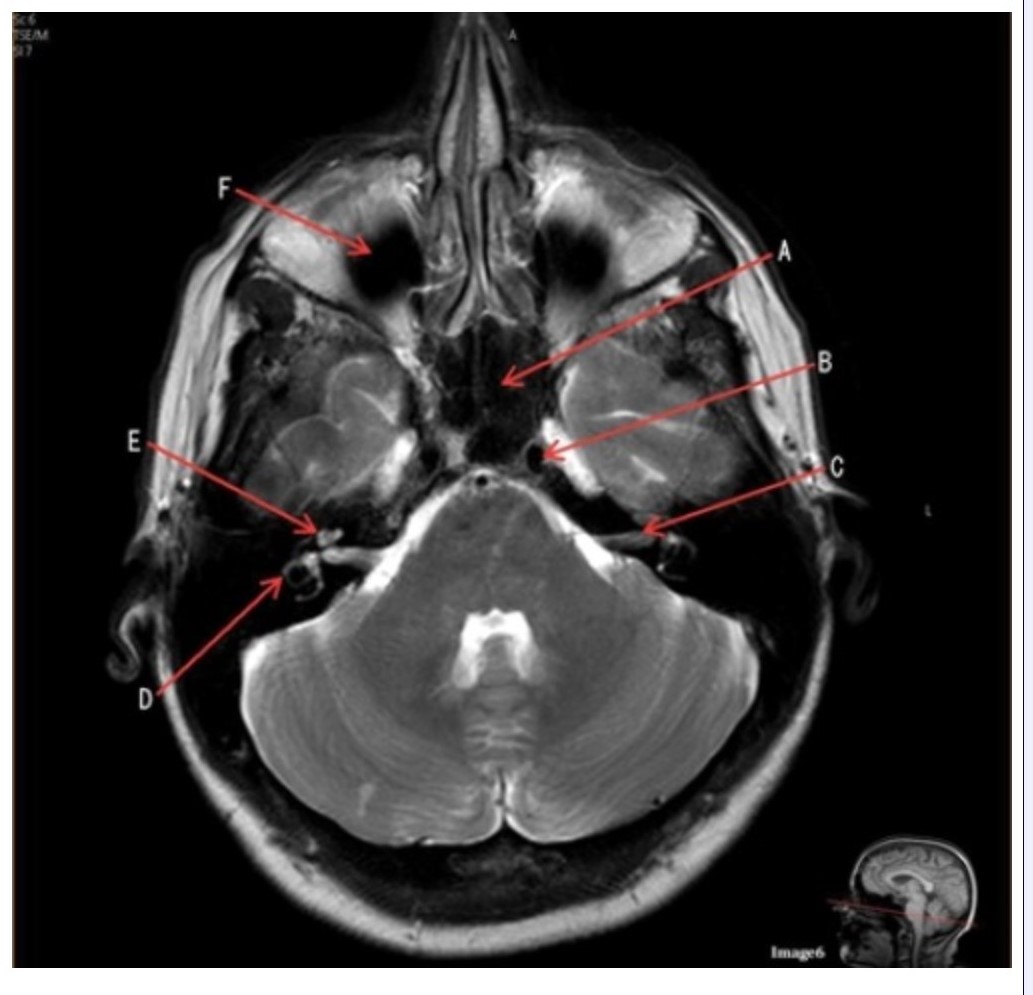
Image 6 is an example of a _____ weighted sequence acquired in the _______ imaging plane.
A. T1; Axial
B. T1; Coronal
C. T2; Axial
D. T2; Coronal
E. STIR; Axial

Letter E in Image 6 is pointing to:
A. 7th cranial nerve
B. Cochlea
C. Trigeminal nerve
D. Semicircular canal
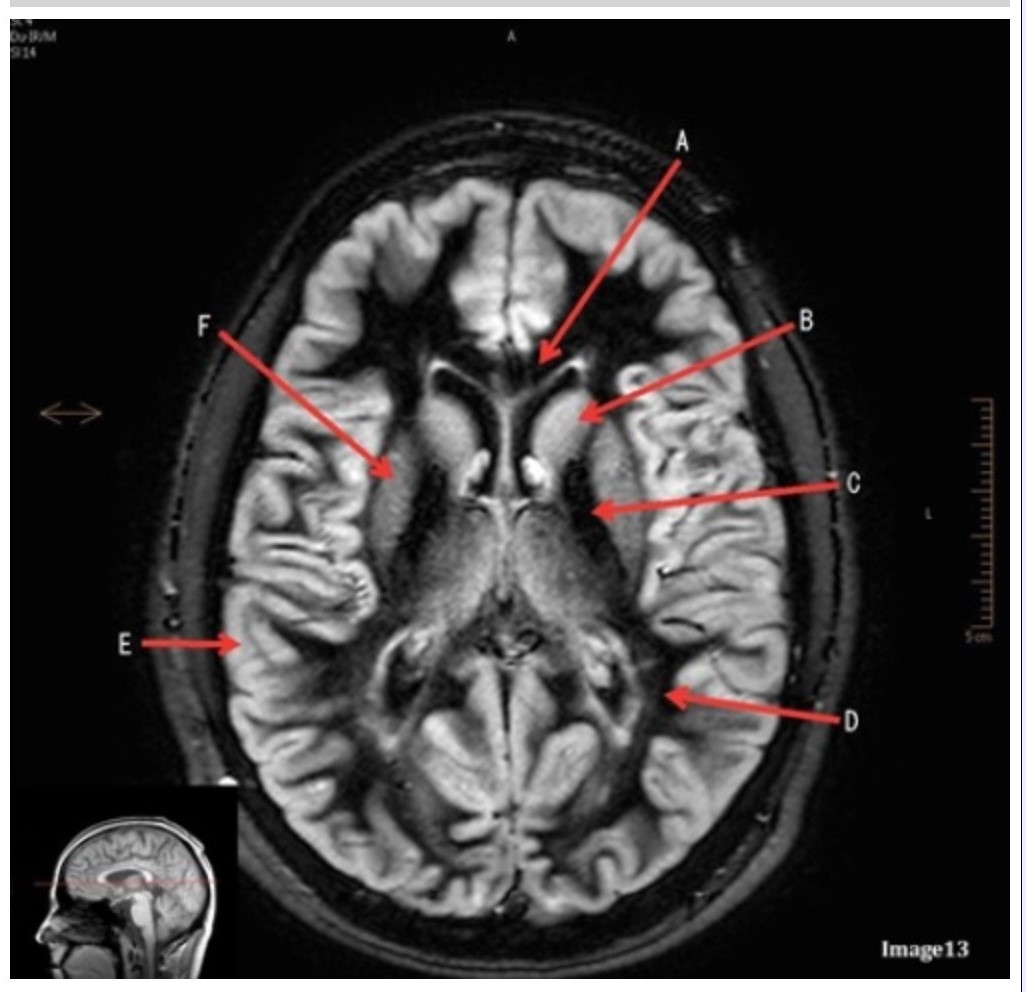
Letter C in Image 13 is pointing to:
A. Splenium of the corpus callosum
B. Genu of the corpus callosum
C. Lentiform nucleus
D. Caudate nucleus
E. Internal capsule
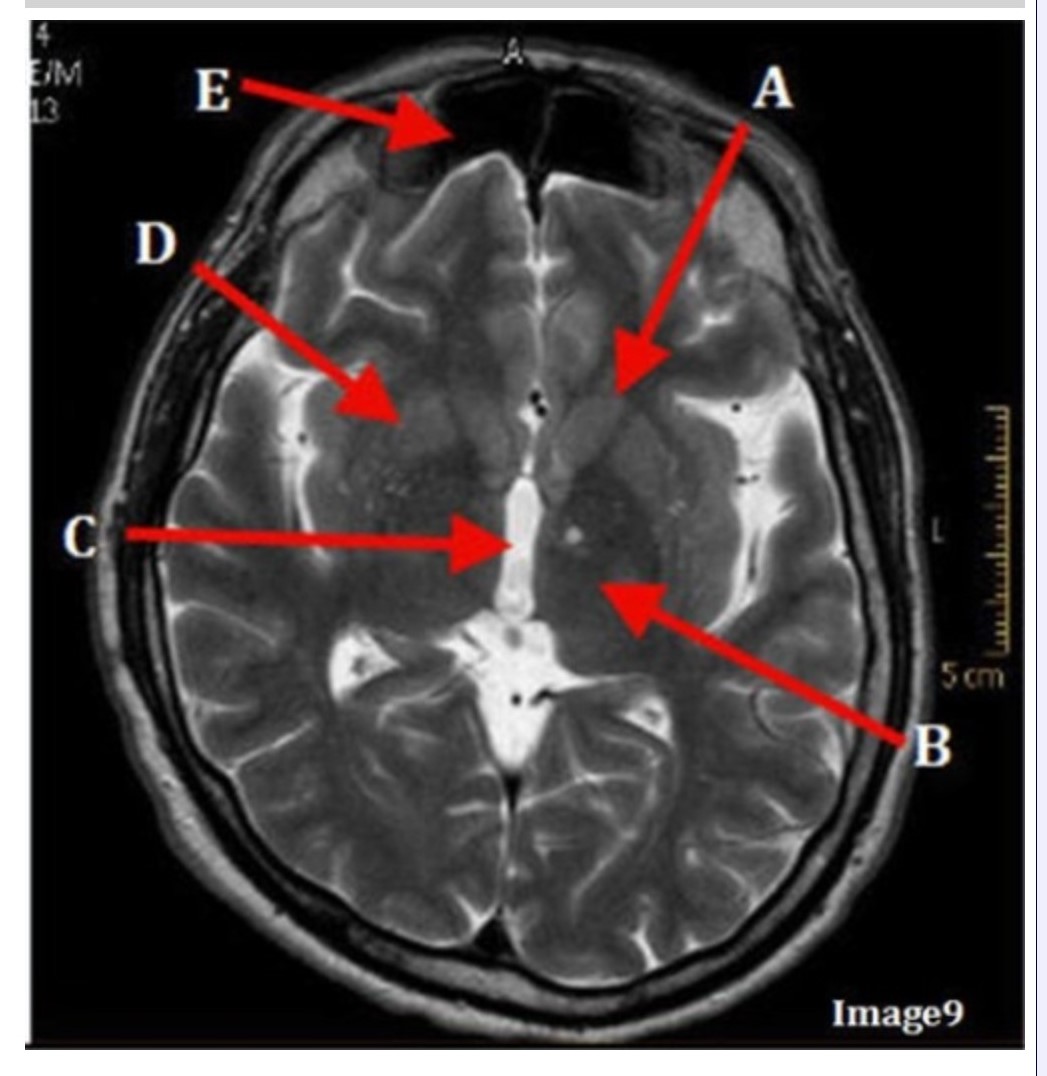
Image 9 is an example of a _____ weighted sequence acquired in the _______ scan plane.
A. T1; Axial
B. T2 FLAIR; Sagittal
C. T2; Axial
D. T2; Coronal
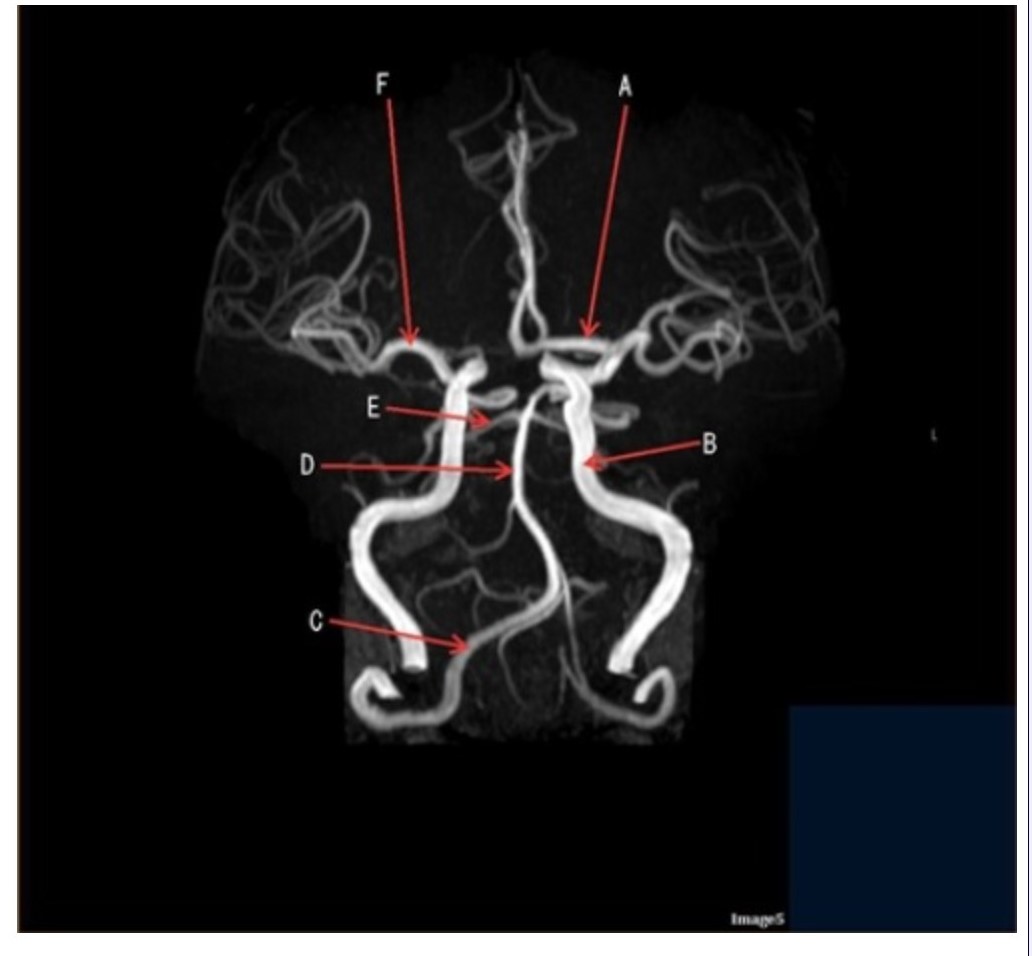
Letter A in Image 5 is pointing to:
A. Anterior cerebral artery
B. Internal carotid artery
C. Basilar artery
D. Posterior cerebral artery
E. Middle cerebral artery