Chemistry S1
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Proton
nucleus
+1
1.6726 × 10-27 kg
1 amu
Neutron
nucleus
0
1.6749 × 10-27kg
1 amu
Electron
energy levels
-1
9.109 × 10-27kg
negligible amu
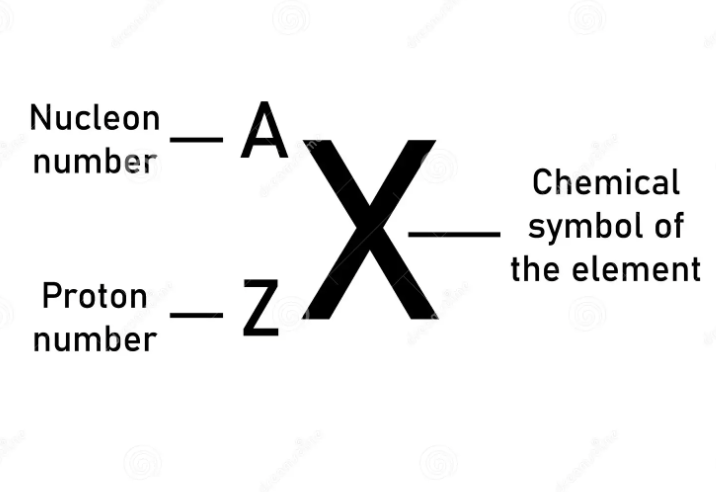
Atomic Number (Z)
identity of an element
# of p+
Mass Number (A)
# of p+ + # of n0
always a whole #
Element Symbol
Isotopes
Atoms of the same atomic number but different mass number
Same chemical properties (same behavior in reactions), different physical properties (e.g. BP, MP, etc)
Radioisotopes
Isotopes with an unstable nuclei.
Emits ALPHA, BETA and GAMMA as they change to become more stable.
Relative Atomic Mass
The weighted average of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element relative to carbon-12.
The Mass Spectrometer
An analytical instrument used to measure the masses of the isotopes of an element and their abundances.
It determines the composition of an unknown molecular substances.
Solid Sphere Model
John Dalton 1803
indivisible
unqiue elements
Plum Pudding
J. J. Thompson 1904
exsitence of electrons
atoms are a positive cloud
Nuclear Model
Ernest Rutherford 1911
positive charge in the center
electrons in orbits
gold foil experiment
Planetery Model
Niels Bohr 1913
electrons in fixed orbits and E levels
no E emittence
Quantum Model
Erwin Schrodinger 1926
clouds of possibility
uncertain positions, movement in waves
Gold Foil Experiment Results
electrons mostly pass right through → atom are mostly empty space
electrons are bounced at small angles → there is a dense center
electrons are deflected from the center → the center is positively charged and repels the positive charge of the alpha particles
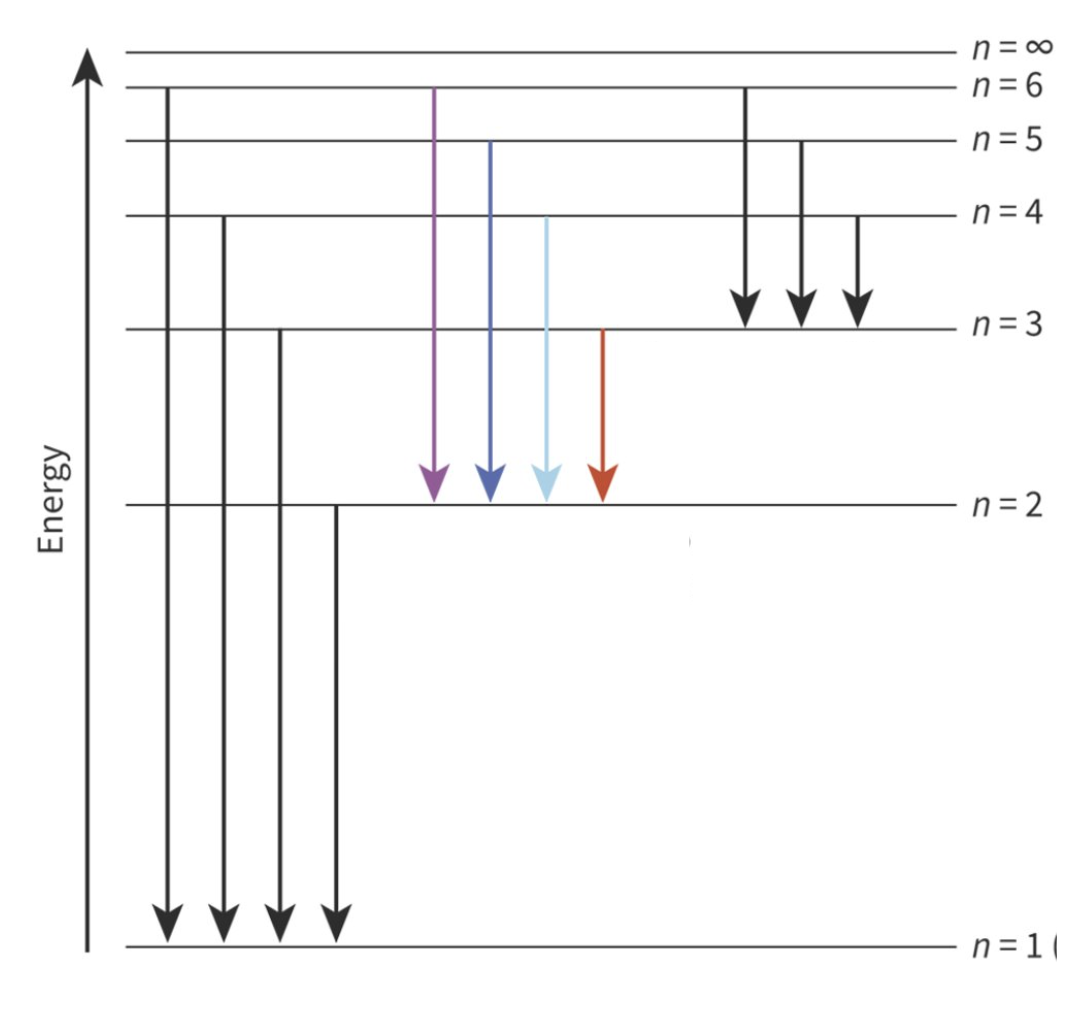
Electron Transition
The distance of travel when an electron emits radiation and falls down to a lower E level
3 characterisitcs of light
wavelength
frequency
energy in J
Electromagnetic spectrum
Gamma rays - x rays - UV - Visible light - infared - microwave - radio waves
Visible light spectrum
(400nm) VIBGYOR (700nm)
Emission Spectrum
breaks down light
shows colors produced on a black background
Continuous Spectrum
Shows the whole spectrum of visible light
Discontinuous/ Line Spectrum
Shows certain discrete colors of visible light produced
Formation of Electron Spectrum
electron absorbs energy while it is at ground state
electron jumps to a higher corresponding E level at an excited state, unstable status
electron falls to a lower E level while emitting the proportional value of energy
Bohr Model proposes that
electrons occupy around the nucleus
electrons can exist at E levels, but not in between them
only certain defined energy values are possible for each E level
Higher E levels…
converge at n = ∞. When an electrons goes there, it is lost to that atom.
Hydrogen Emission Spectrum

Hydrogen Line Emission Spectrum
UV → falls to n=1 (highest E)
VL → falls to n=2
IR → falls to n=3 (lowest E)