Virtual avatars & Immersive education
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
seminar 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Immersive education & VR
VR provides realistic scenarios allowing learning of abstract or inaccessible topics
many studies found immersive learning beneficial
however needs to be further explored
Immersive education
not a single pedagogy or specific practice
wide range of approaches to teaching & learning
interdisciplinary & collaborative framework
commonly associated w/VR & active learning
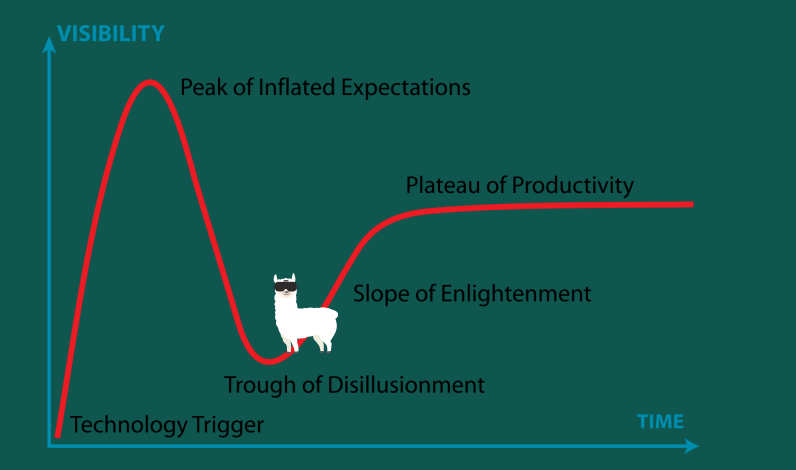
Gardner cycle
Each new technology goes through a cycle
technology trigger
peak inflated expectations
excited about research
trough of disillusionment
realising the actual effect
slope of enlightenment
platuea of productivity
edify teacher
interact & set up lesson & broadcast
teacher is 3d presenting it to the students
students access and interact remotely
moslty during covid
multi user VR
when you are all in the same VR place but across the world
like frame VR
bay stations/play area
are in which an individual can use VR to play & track
hard to space out
requires limited things on the floor
Exemplar apps
Virtual printing press
students learning the history of printed by doing in VR
Preliminary user testing of project mobius
some apps were explored more than others e.g disease diagnosis
instructions were followed easily w/minor errors
controllers were used w/minor errors
good feedback
Data collection (Savickaite et al 202?)
The initial unique data which is available is the student’s position in physical and virtual space
The following examples were collected in the Disease Diagnostics lesson
User interaction data from the Mobius apps can be exported as a .json file and converted to .csv format for further analysis.
Since the initial mobius study
VR became more mainstream
no longer need for controllers
Challenges with VR & immersive learning
clarity of instructions
expertise
experience of controls was hard
Accessibility Considerations in XR
Customizable Experience
different filters for colourblindness
Selective Simulation
can be good for empathy, but danger of stereotyping disorders
Haptics
spatial audio
Neurodivergence
consider how much info is given at time
Co-Design
making sure accessiblilty is throughout not just at the end
Uncanny Valley (UV)
First proposed in 1970s by Mori
describes/observes negative reaction to human-looking entities such as avatars
manifest as a cold eerie & repellent feeling
Uncanny valley hypothesis (Mori et al, 2012)
affinity for artificial humans rises with human-likeness up to a point, then drops sharply when the entity is almost - but not quite - human, before rising again as it becomes indistinguishable from a real person
what increases uncanny valley effect
movement
mismatches in timing dynamics or micro expressions
feel eerie
uncanny valley depends on (Diel et al, 2021)
appearance, animation quality, and context
Is not inevitable if appearance–behaviour congruence is high
Research on uncanny valley (2005+)
2/3 of studies found affect still exists
cognitive & neural basis is still unclear
facial expressions in human like avatars affect behavioural realism
Virtual avatar
digital representation of a user
vary in visual fidelity (abstract/human) to behavioural (canned animations to facial capture)
bridges gap between the digital & physical world providing sense of presence
what makes avatars effective
realistic movement
facial expressions
ability to interact w/objects in a natural way
Avatar design (Latoschik et al, 2017)
Choices of visual fidelity to behavioural fidelity influence the presence, embodiment, social copresence, and emotional recognition during interaction
Avatar realism
impact both aesthetic & functional characteristics of an avatar
Increased realism ≠ increased approval of avatar
may intensify the sensitivity to cues highlighting falsehood
what does increasing realism do for experience of avatar (Higgins et al, 2021)
improve ownership & social interaction
may trigger aversion if the appearance is almost human-like
ALIVE project (Savickaite et al)
basic emotions repeated 3 times (anger, disgust, fear, surprise, contempt, happiness and sadness)
avatars 1 (Wolf3D) vs avatars 2 (MetaHuman)
VR (Oculus Quest1)
Measures: Ratings of emotions, Errors, Reaction Times, Demographics (gender, age, VR experience)
mystery study’s results
Meta-humans are perceived as more 'uncanny' than the cartoons → have slightly worse animation quality, but better emotion recognition accuracy
Each of these varied a lot by the specific emotion
it is likely a product of the exaggerated expressions on the meta-humans
more exaggerated expressions = more 'uncanny' perception rating but better recognition
P reported that some expressions were very evident but made the avatar look strange (both cartoon & meta-human)
darker skin tone made avatars seem more realistic
Some emotions were very hard to distinguish (particularly in the cartoon condition).
follow up mystery study results
ND view metahumans as uncannier than NT
experience greater discomfort & UV
ND have a lower mean accuracy than NT
ND are less accurate w/negative emotions the NT
Females have higher accuracy than males
no significance between avatar race
Limitations of ALIVE study
Metahumans
Self-reported questionnaire
Future research
Different VR settings
Exploring different avatars
Looking at diverse populations for between races of avatar and participant
Limitation of VR avatars
Technological difficulties
latency is major issue
scalability
privacy & security
Creation of digital avatars
defining avatar appearance using software for customisation
often employ 3d modelling techniques e.g Blender
rigged w/skeleton structure enabling movement & interaction
can be animated using motion capture technology
limitations of creating avatars
achieving a high level of realism without sacrificing performance
realistic avatars require significant computational power
Metahuman
framework/toolset for creating fully rigged high fidelity digital humans w/controllable face, body hair, clothing & materials