B4.1 Adaptations
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What is a habitat?
The place in which an organism lives. Includes geographical and physical location as well as the type of ecosystem
Biotic vs abiotic factors
Biotic factors are living and abiotic factors are non-living. Biotic factors dominate ecosystems where there are dense communities of organisms. Abiotic factors dominate in extreme habitats where populations are low.
Challenges faced in sand dune habitats?
Sand retains little water. Beaches are windy and so water lost through transpiration. High salt concentrations in sea spray which reduces osmosis and water uptake.
Marram Grass adaptations
Thick waxy cuticle to reduce water loss through transpiration. Rolled leaves to create a humid chamber and reduce wind exposure. Hairs on the inside to trap water vapour and reduce transpiration. Tough sclerenchyma tissue to prevent wilting during droughts. Rhizomes (underground stems) that grow upwards as sand accumulates and also extend deep into the dune.
Challenges for trees in mangrove swamps?
Waterlogged and anaerobic soil. Tidal variation. High salt content.
Adaptations of trees to mangrove swamps?
Cable roots growing close to soil surface to access more oxygen. Stilt roots to give tree support in the mud. Large buoyant seeds. Accumulation of minerals to increase osmotic potential in roots thus allowing more water absorption from sea water. Roots covered in suberin which reduces salt permeability thus preventing absorption.
Range of tolerance?
The range of tolerance of a species is the range of environmental conditions within which it can survive. The adaptations of a species determine the range of environmental conditions that it can tolerate.
What is a limiting factor in the context of a species’ range of tolerance?
A limiting factor is any biotic or abiotic factor that restricts the growth of organisms. Plays a role in determining a species’ range of tolerance.
What abiotic factors usually affect plant distribution?
Temperature, Light intensity, Water availability, Soil pH, Salinity, Concentration of minerals.
Population size in zone of intolerance?
Population absent
Population size in stress zones?
Few individuals
Population size in optimum tolerance range?
Abundance of individuals
How to correlate the distribution of a species with an abiotic variable?
A transect can be used to collect data and determine correlation between species distribution and abiotic variables. Sensors can be use to measure abiotic variables.
Examples of sensors to measure abiotic variables?
Thermometer to measure temperature. Electronic light metre to measure light intensity. Indicator solution to measure soil pH.
What is a transect?
A line laid out across a habitat, usually along an environmental gradient, along which abundance and distribution can be measured.
What is a semi-natural habitat?
A habitat that has been influenced by human activities but that is still dominated by wild species rather than cultivated species.
What are corals?
Corals are structures that form due to the mutualistic relationship between coral polyp (animal) and zooxanthellae (algae).
What is the primary building material of coral reefs?
Calcium carbonate which is secreted by some species of coral polyps
Relationship between polyps and zooxanthellae?
Polyps have a mutualistic relationship with photosynthetic zooxanthellae.
Diet of polyps?
They are mixotrophs. Have a diet of plankton which they supplement with the products of photosynthesis from the zooxanthellae.
Conditions for coral reef formation?
Less than 50m deep water. pH above 7.8. Salinity between 32 and 42 parts per 1000 dissolved ions. Clear water. Temperature between 23-29ºC
Water depth limiting effect on coral reef formation?
Light only penetrates to relatively shallow depths. Zooxanthellae are photosynthetic and require adequate light levels.
Water temperature limiting effect for coral reef formation?
Global warming means water temperature is too warm for corals to tolerate. They become stressed and expel symbiotic zooxanthellae living in their tissues. Results in bleached coral.
Water clarity as a limiting effect for coral reef formation?
Needs to be clear enough for light to pass through for the photosynthetic zooxanthellae.
Water pH as the limiting effect for coral reef formation?
Increased carbon dioxide from fossil fuel emissions results in lower pH. PH affects coral reef formation by influencing the availability of carbonate ions needed for calcium carbonate formation; lower pH means more H+ ions which react with the carbonate ions instead of the calcium. Reduces coral growth.
Features of hot deserts?
Very high daytime temperatures and cold nights. Very low annual rainfall. Soil development is very limited.
Example of plant adapted to hot deserts?
Saguaro is a species of cactus adapted to life in hot deserts
Saguaro adaptations?
Wide-spreading root system to collect water up to 30m from the stem. Thick waxy cuticle on stem epidermis to reduce transpiration. Leaves reduced to spines, to reduce surface area for transpiration and prevent herbivores from eating it. Fat stems with storage tissue to conserve water after infrequent desert rains.
Example of animal adapted to hot deserts?
Fennec fox
Fennec fox adaptations?
Nocturnal to avoid highest temperatures. Builds underground den to stay cool during day. Hairs covering pads of feet to provide insulation when walking on hot sand. Pale coloured coat to reflect sunlight. Large ears to radiate heat and help keep body temperature down.
Abiotic conditions of tropical forest
High temperature, high precipitation, high light intensity, minimal season variation. Nutrient poor soil.
Example of plant adapted to tropical rainforest?
Meranti - species of tree
Adaptaions of meranti?
Can grow to over 100m high avoiding competition for light. Trunk of hard dense wood to provide support against wind stress. Smooth trunk to shed rainwater rapidly. Broad oval leaves with pointed tips that shed rainwater rapidly. Enzymes of photosynthesis adapted to tolerate temperature as high as 35ºC.
Example of animal adapted to tropical rainforest?
Spider monkey
Adaptations of spider monkey?
Long arms and legs for climbing and reaching fruit. Flexible shoulders to allow swinging from tree to tree. Feet act as extra hands for grasping branches or feeding. Long tail that grips branches. Highly developed larynx allowing a wide range of sounds to communicate in dense canopy.
Which two abiotic factors are the principle determinants of biome distribution?
Temperature and rainfall. Represented on a climograph (mean annual rainfall against mean annual temperature).
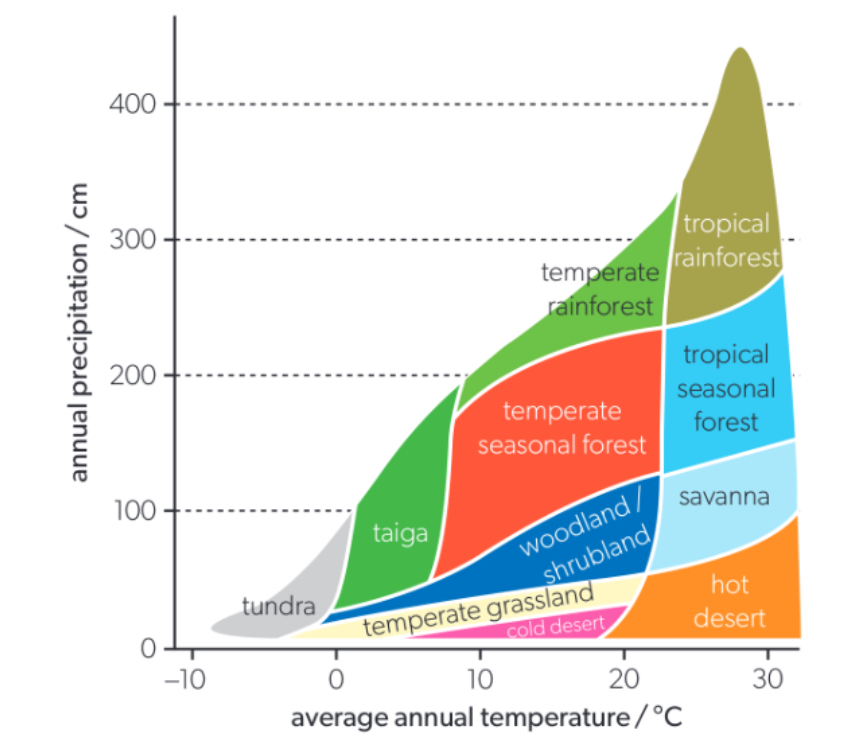
What causes similarities between communities in equivalent biomes?
Due to shared abiotic factors and resultant convergent evolution
Example of convergent evolution due to equivalent biomes?
Plants in deserts develop adaptations for water conservation and storage. Cacti in America and euphorbias in Africa have very similar adaptations despite not being closely related.
Abiotic conditions in temperate forest?
High/medium precipitation. Medium light intensity. Seasonal temperature variation. Fertile soil.
Taiga (boreal) conditions?
Contains coniferous forest with high snowfall and cold temperatures.
Grassland conditions
Medium levels of seasonal rainfall and wide range of seasonal temperatures.
Tundra conditions?
Very low temperatures. Medium/low precipitation. Low light intensity. Very short summers and very cold winters.