CHAPTER 1: PHYSIOLOGY EXAM 1
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key terms from the Chapter 01 notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Physiology
Study of biological function; how the body works; emphasizes mechanisms and cause–effect sequences in normal cell function.
Pathophysiology
Study of how disease or injury alters physiological processes; helps understanding of normal processes.
Comparative physiology
Study of differences and similarities in function across species; has aided drug development.
Scientific Method
Systematic process of making observations
Asking questions, forming testable hypotheses,
Predicting outcomes,
Conducting experiments,
Analyzing data
Replicating results
Hypothesis
A testable educated guess about a phenomenon.
In vitro
Experiments performed outside living organisms, typically in a culture dish.
In vivo
Experiments performed in living organisms.
Phase I clinical trials
Drug tested in healthy volunteers to assess safety, metabolism, dosage, and side effects.
Phase II clinical trials
Trials to assess drug effectiveness in patients with the disease.
Phase III clinical trials
Large-scale trials to evaluate safety and efficacy across diverse populations before FDA approval.
Phase IV clinical trials
Post-marketing studies to explore additional applications of the drug.
Homeostasis
Constancy of the internal environment; maintained by physiological mechanisms; deviation indicates disease; often achieved by negative feedback.
Negative feedback loop
Regulatory pathway that moves a variable in the opposite direction of a change to restore the set point.
Sensor
Receptor that detects changes and sends information to the integrating center.
Integrating center
Control center (often the brain) that interprets signals and directs responses.
Effector
Organ or tissue that carries out the response to counteract the change.
Set point
Target value around which a physiologic variable is maintained.
Antagonistic effectors
Pairs of effectors that move conditions in opposite directions to maintain normal range.
Positive feedback
End product amplifies the process; increases changes and is usually part of a larger regulatory system that ends with a negative feedback.
Example: Child Labor & Growth
Intrinsic regulation
Regulation within an organ by its own cells sensing and responding to changes.
Extrinsic regulation
Regulation of an organ by signals from brain or other organs through endocrine or nervous systems.
Neural regulation
Regulation of organs via the nervous system with nerve fibers.
Endocrine regulation
Regulation via hormones released into the blood by endocrine glands.
Dendrites
Branched extensions of a neuron that receive signals.
Axon
Long projection of a neuron that transmits signals away from the cell body.
Neuron
Nerve cell that conducts impulses; composed of dendrites, an axon, and a cell body.
Neuroglia
Supporting cells in the nervous system essential for neuron function.
Epithelial tissue
Tissue that forms membranes covering body surfaces, lining hollow organs, and glands; classified by layers and cell shapes.
Simple epithelium
Single layer of epithelial cells; functions vary with type (transport, secretion, absorption).
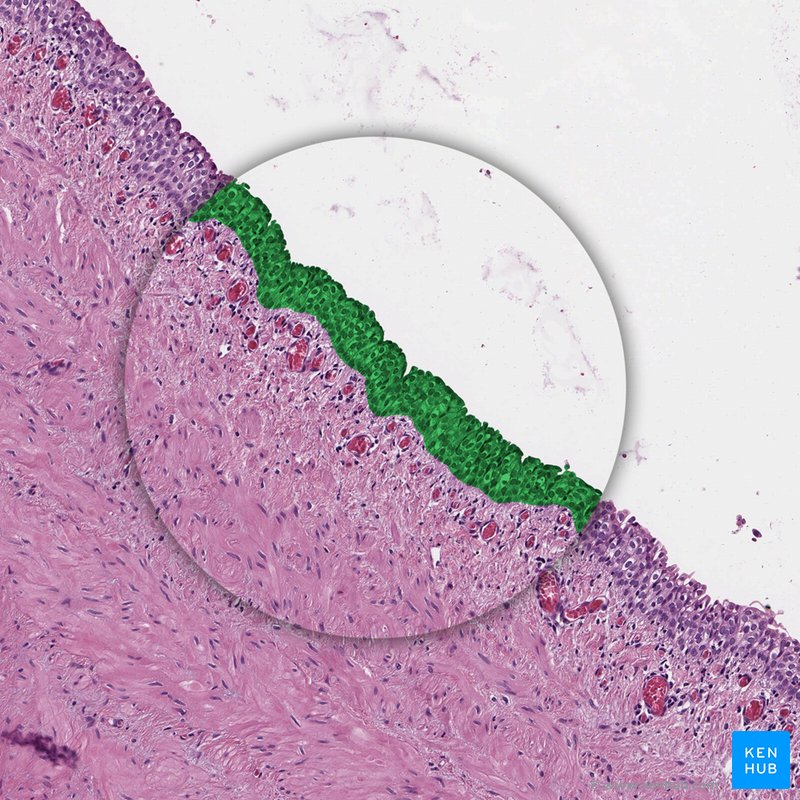
Stratified epithelium
Two or more layers of epithelial cells; mainly provides protection.
Squamous epithelium
Flattened, scaly epithelial cells.
Cuboidal epithelium
Cube-shaped epithelial cells; typically involved in secretion and absorption.
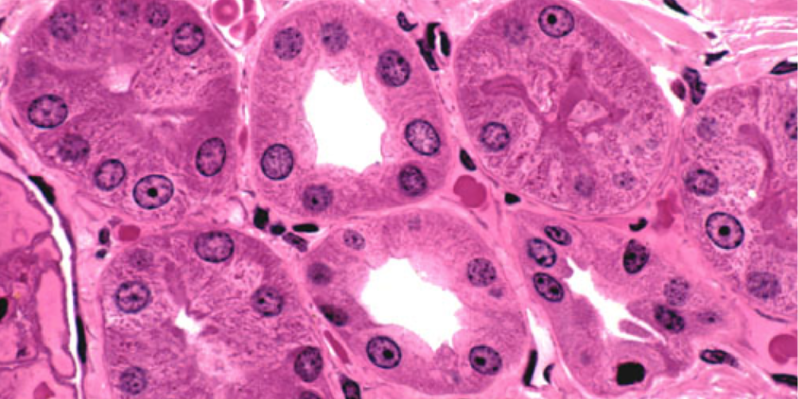
Columnar epithelium
Tall, column-shaped epithelial cells; often absorb and secrete.
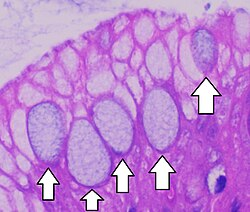
Goblet cell
Mucus-secreting epithelial cell often associated with columnar epithelium.
Cilia
Hair-like projections on epithelial cells that move substances along surfaces.
Simple squamous epithelium
Single layer of flat cells; enables rapid diffusion and filtration.
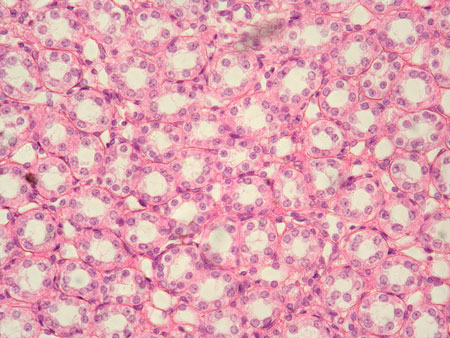
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Single layer of cube-shaped cells; supports secretion/absorption.
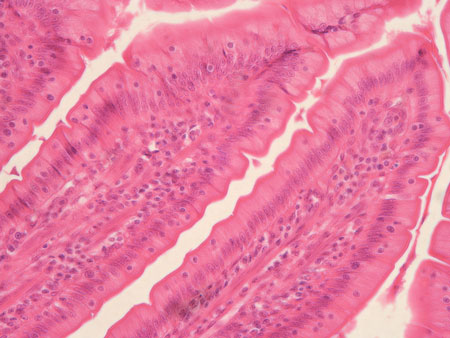
Simple columnar epithelium
Single layer of tall columnar cells; specialized for absorption and secretion.
Connective tissue
Tissue with a matrix of protein fibers and ground substance; supports and binds other tissues.
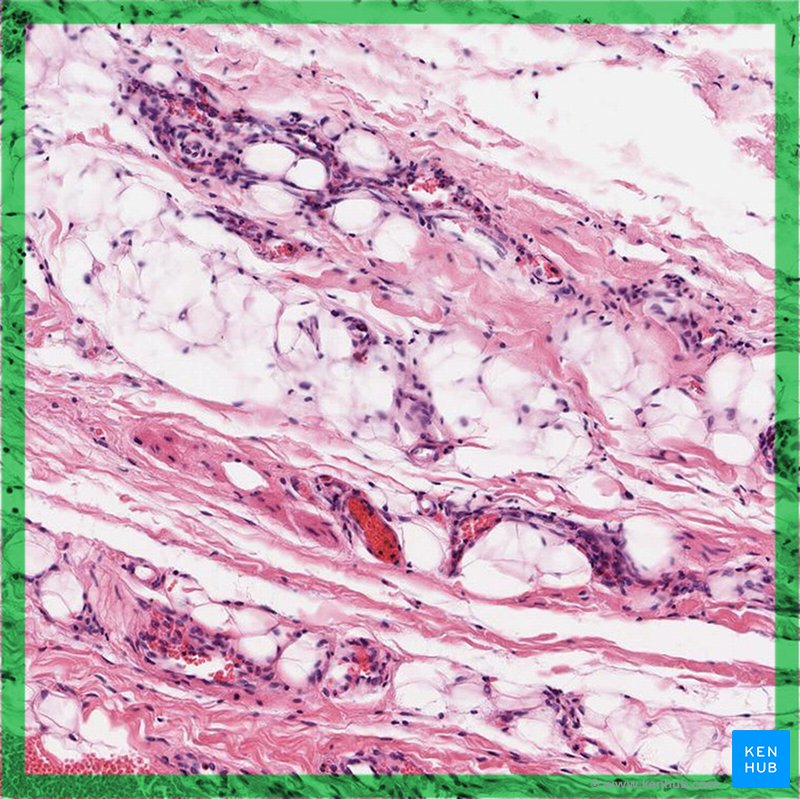
Loose connective tissue
Fibers loosely arranged; more space for blood vessels and nerves.
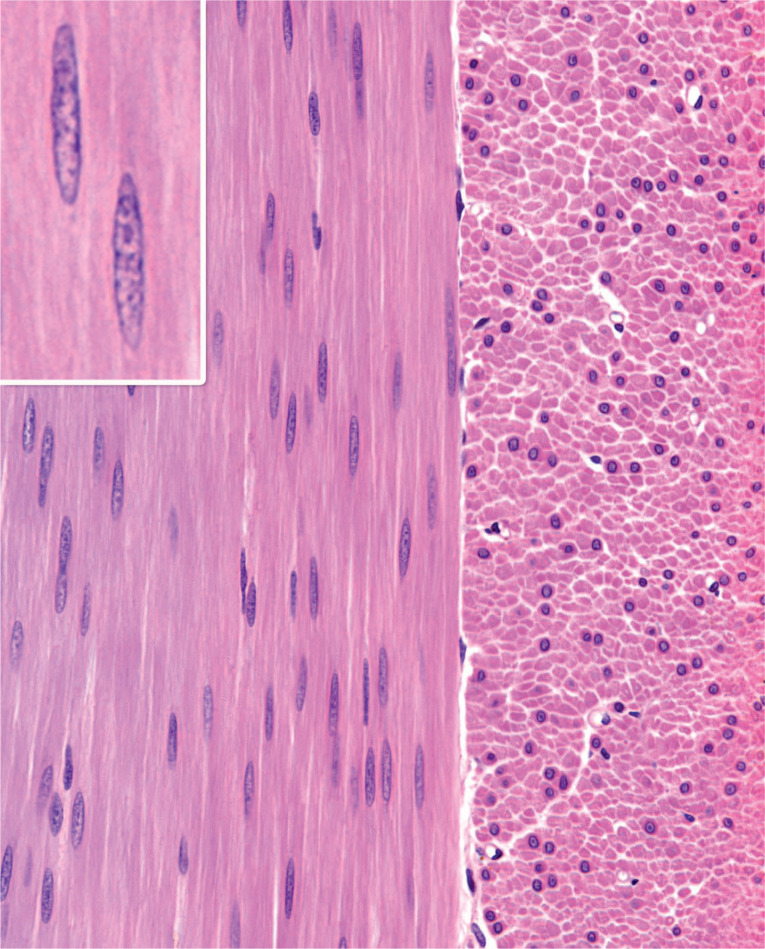
Dense regular connective tissue
Densely packed collagen fibers aligned for unidirectional strength (tendons and ligaments).
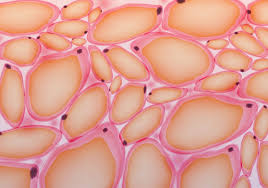
Adipose tissue
Tissue that stores fat; composed of adipocytes.
Cartilage
Semi-solid connective tissue with chondrocytes; cushions joints and provides a developing skeletal template.