2.3 Aggregate Supply
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
short run
time period where at least one factor of production is fixed
what causes a movement along SRAS
change in the price level
what causes a shift in SRAS
change in conditions of supply:
-changes in cost of raw materials and energy
-changes in exchange rates
-changes in tax rates
acronym for exchange rates effect
SPICEE
strong pound imports cheap exports expensive
long run
productive capacity has the ability to increase
what is productive capacity influenced by
changes in quantity or quality of factors of production
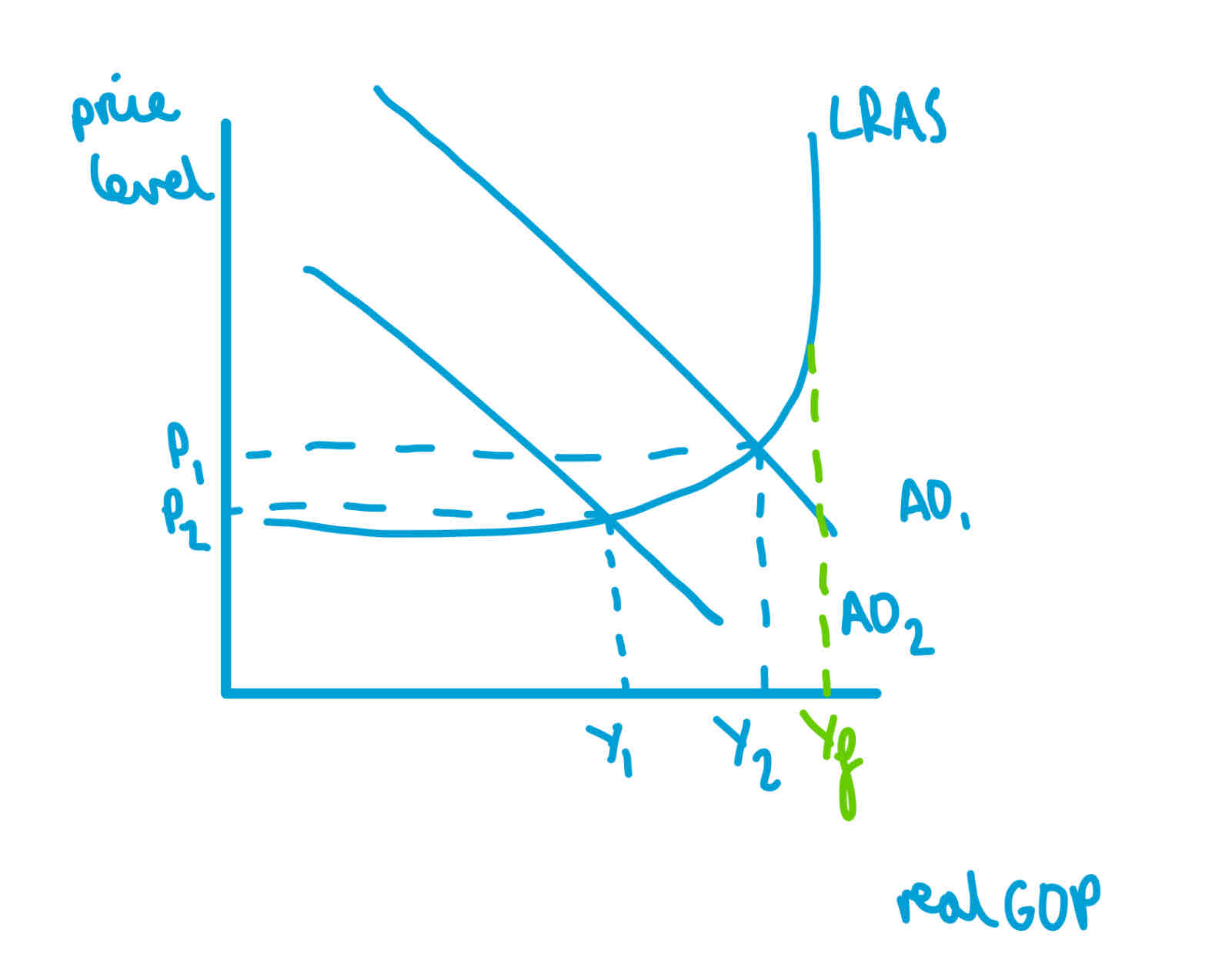
Keynesian LRAS
at Yf all factors of production are employed
supply is elastic at lower levels of output as there is high spare production capacity
supply is inelastic at full output as there is no spare production capacity
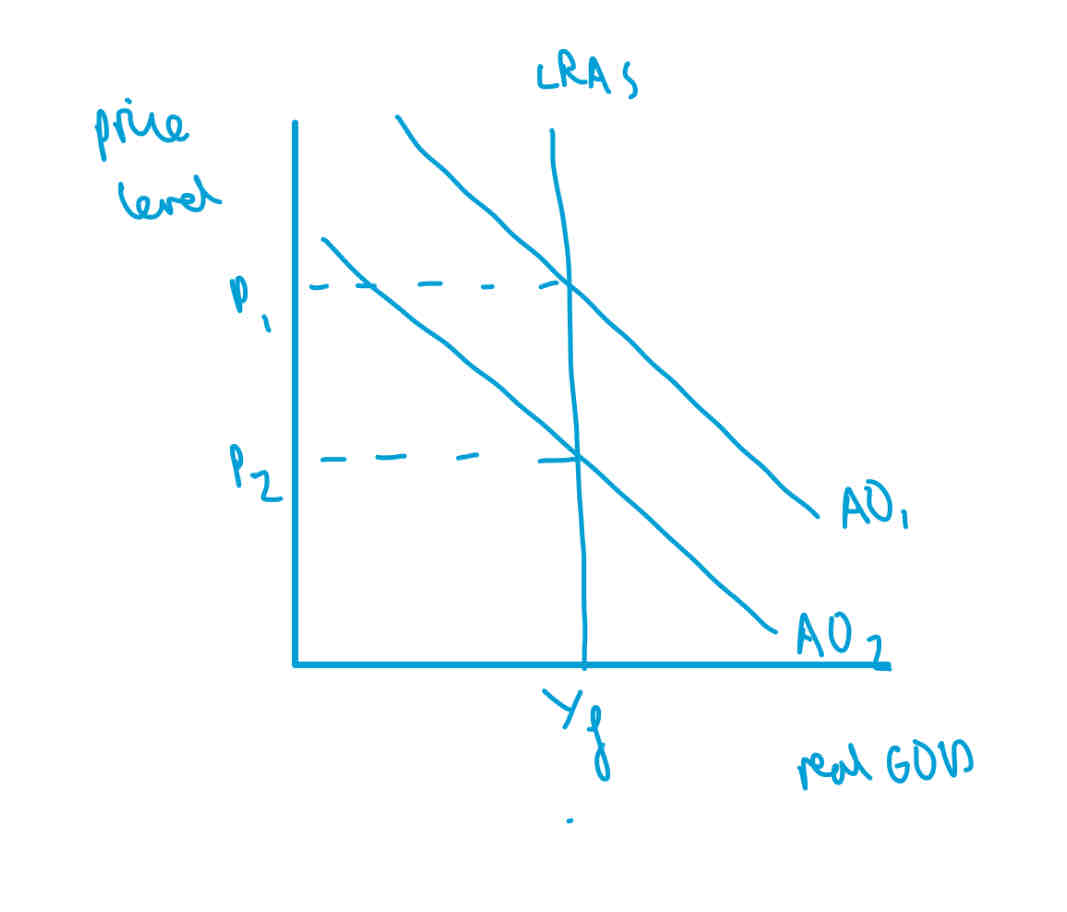
Classical LRAS
LRAS is perfectly inelastic at full employment
in the long run an economy will always return to full employment
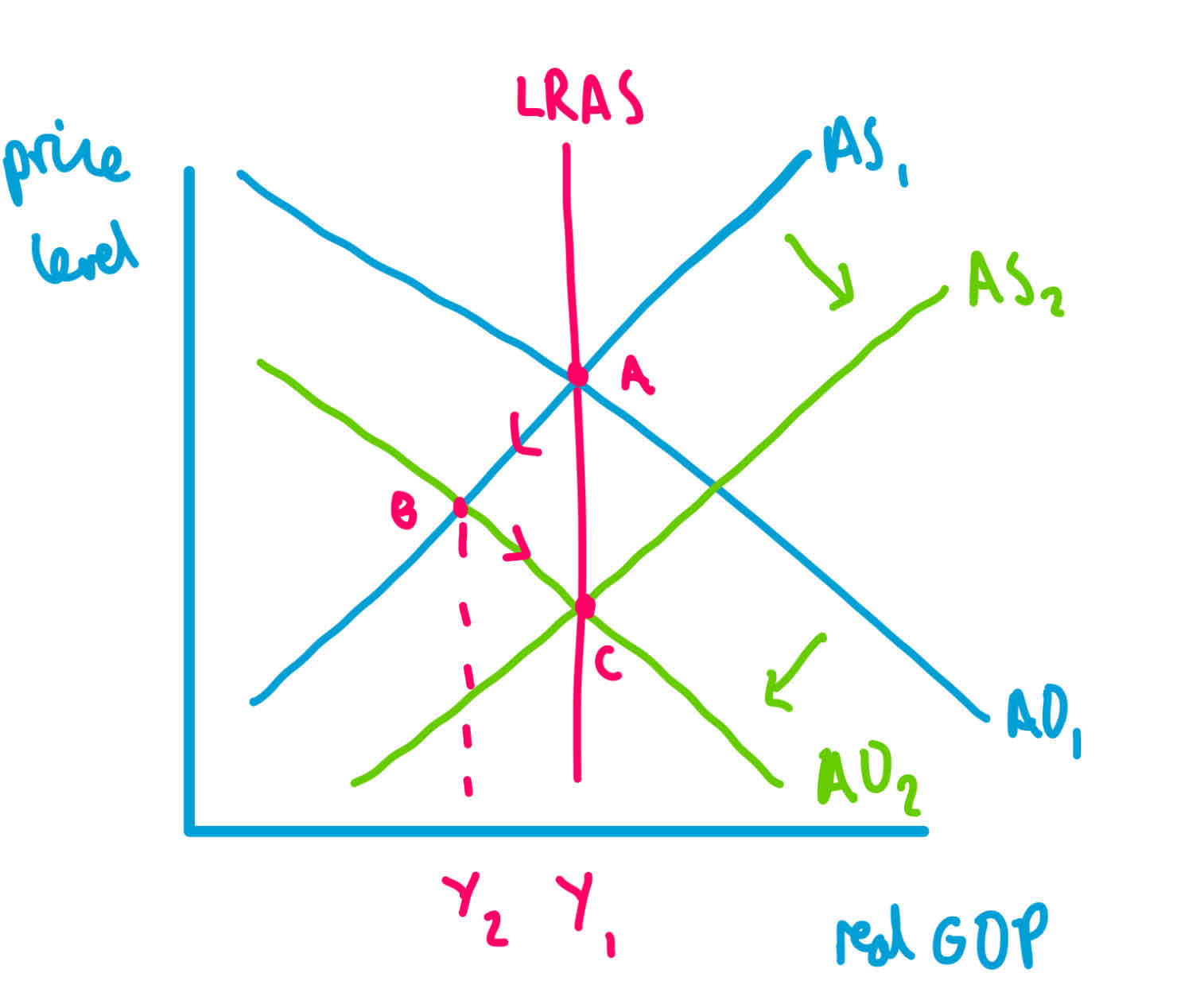
Classical LRAS exogenous shock
a to b: exogenous shock
b to c: recovery due to reducing wages, high unemployment gives firms wage bargaining power, wages fall lowering prices, demand increases ( movement along) real GDP recovers
what is the output gap
the gap between Yf and Y, the difference in factors employed and total avaliable factors
causes of Keynesian AS shift
-change in price of FoPs
-change in quantity or quality of FoPs
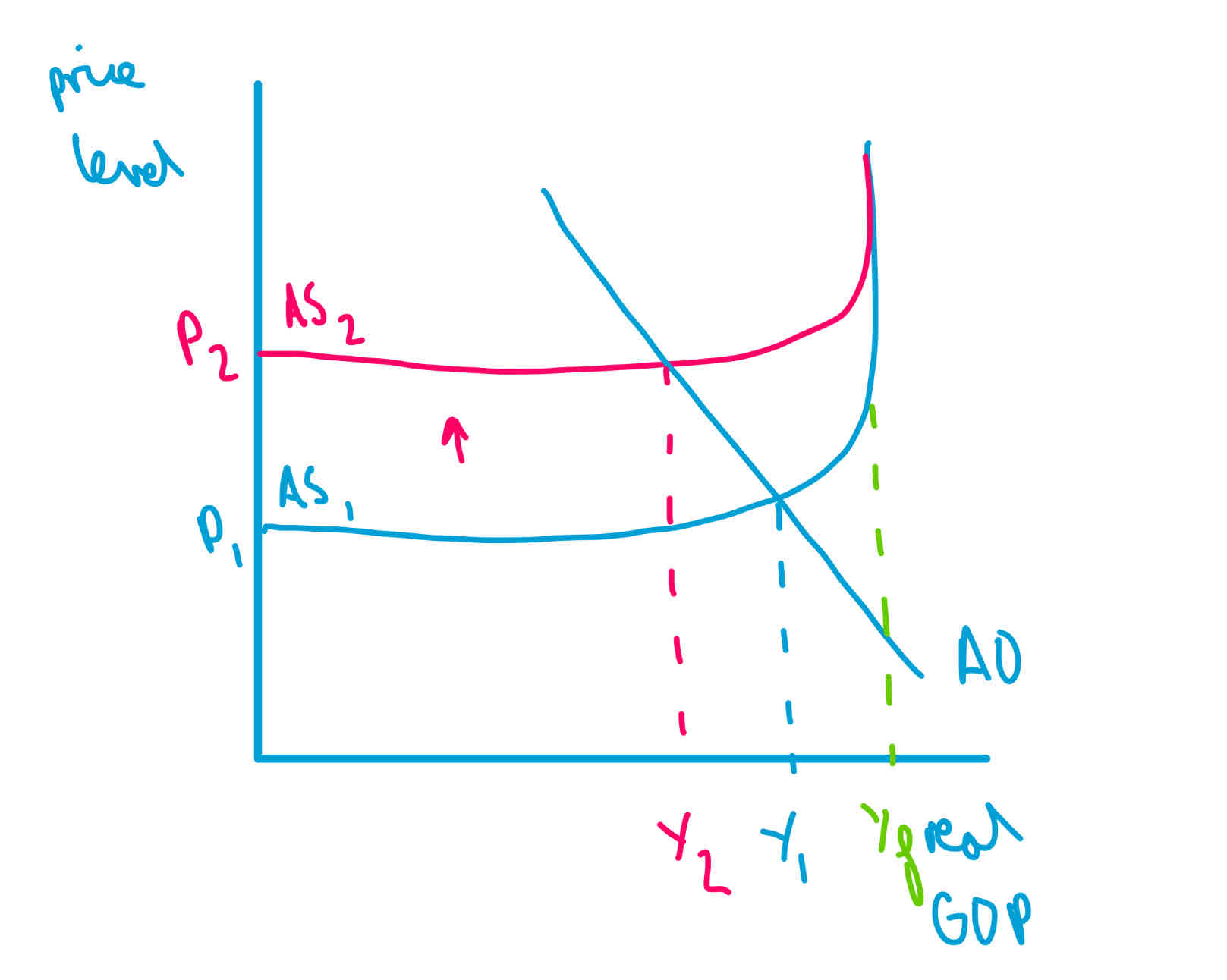
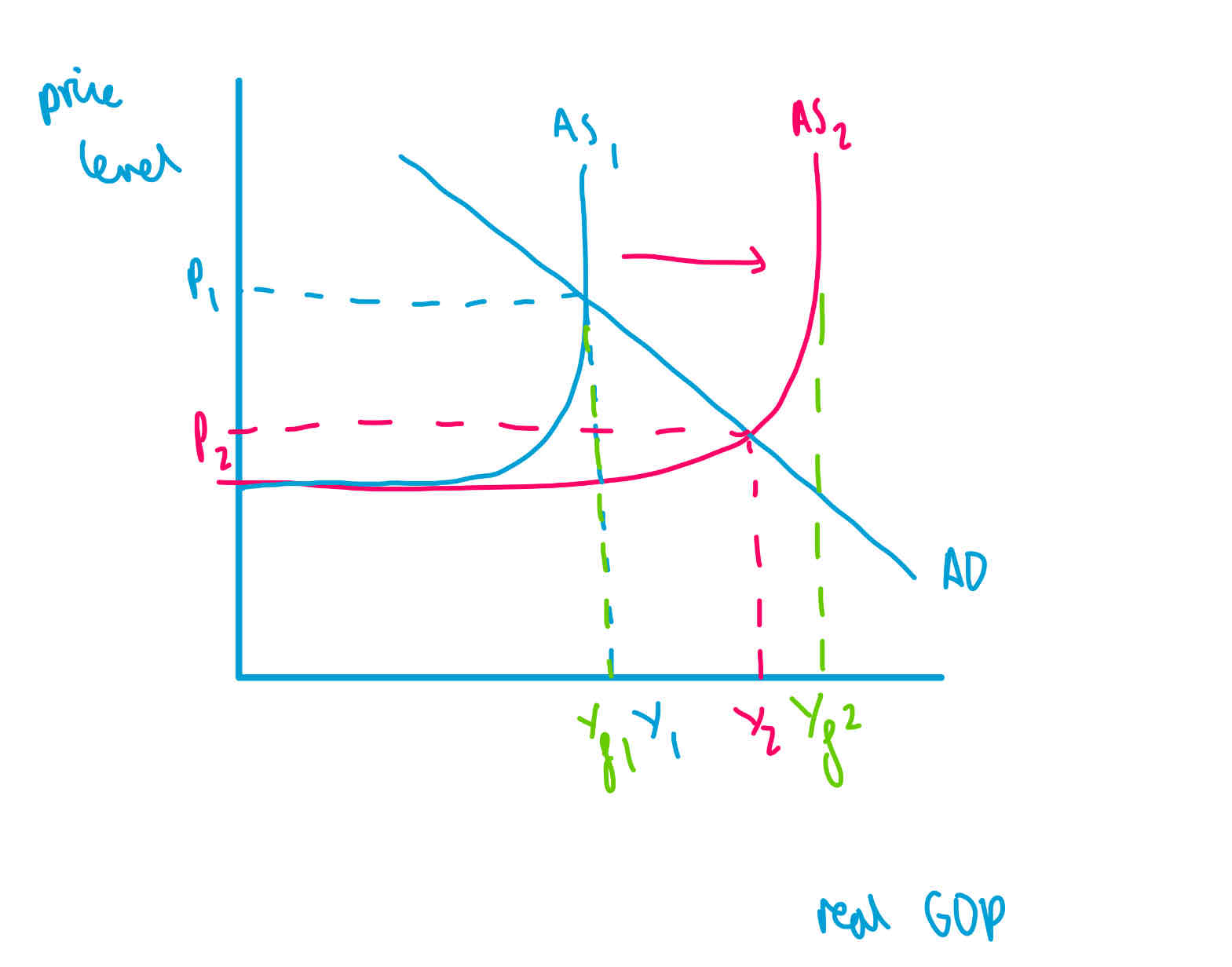
shift in LRAS due to change in price of FoPs
the maximum the economy can produce does not change
the gap between Yf and the actual Y shows unemployment
so unemployment is greater at AS2 than AS1
shift in LRAS due to change in quality or quantity of FoPs
The potential the economy can produce increases
output gap may or may not change
price level decreases
factors influencing LRAS
-technological advances
-changes in productivity
-changes in education and skills
-changes in government regulation
-net migration
-competition policy