HYPOKALEMIA VS HYPERKALEMIA
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
potassium
EXCRETION: normally excreted
FUNCTION:
98% of potassium are in the cells. Low levels in blood
Cardiac
Neuromuscular
Glycogen deposition in muscle and liver cells
*IMPORTANT POTASSIUM REGULATORS
sodium-potassium pump
insulin
ADH: aldosterone or vasopressin
potassium MAINLY comes from where?
diet
hyperkalemia causes
KEY: RENAL FAILURE (CAN’T EXCRETE k+) or high potassium intake
Low aldosterone (adrenal issue)
shift from cell to plasma
salt subsitutes
hyperkalemia
why: salt substitutes are just substituted with potassium
acidosis
hyperkalemia
why: potassium is positively charged. To compensate for acidosis, the cell tries to get rid of positively charged ions inside the cell and that includes potassium (since all of it is inside the cell)
rapid IV potassium infusion
hyperkalemia
potassium containing drugs (potassium pencillin)
hyperkalemia
intense exercise
hyperkalemia
why: pushes potassium out of cell into the blood (since all of potassium resided in the cell)
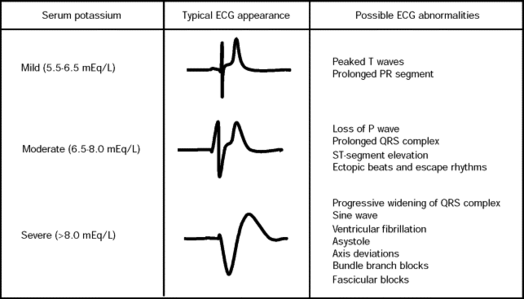
EARLY/MILD hyperkalemia
peaked T waves
SEVERE hyperkalemia ECG
loss of P waves
long PR
depressed ST
wide QRS
paresthesia or numbness/tingling
MILD hyperkalemia
paralysis
SEVERE hyperkalemia
respiratory or cardiac arrest
VERY SEVERE hyperkalemia
abdominal cramping, vomiting, diarrhea
hyperkalemia
why: hyperactivity (nerve impulses) of GI smooth muscles
hyperkalemia treatment: FIRST (stop potassium intake)
stop diet or IV potassium
hyperkalemia treatment: SECOND (potassium excretion)
loop or thiazide diuretics
kayexalate
hemodialysis → IF RENAL FIALURE
hyperkalemia treatment: THIRD (potassium back into cell)
insulin with glucose/dextrose
hyperkalemia d/t metabolic acidosis
sodium bicarbonate
hyperkalemia treatment: FOURTH (cardiac)
IV calcium chloride/gluconate
why: does not LOWER potassium but treats the cardiotoxicity (dysthymias) from hyperkalemia
mild hyperkalemia w. kidney function
stop potassium intake (diet or IV)
increase fluids (pee out potassium)
loop or thiazide diuretics
severe hyperkalemia or symptomatic hyperkalemia
insulin w. glucose
acidosis: sodium bicarbonate (opens up cell for potassium and bicarbonate)
dangerous dysrhythmias
IV calcium IMMEDIATELY
insulin considerations
check glucose
why: because giving insulin can lead to hypoglycemia
IV calcium consideration
check BP
why: giving calcium rapidly can cause hypotension
hypokalemia causes
KEY: loss of potassium (urine)
shift from plasma to cell
diarrhea or vomiting
hypokalemia
ileostomy drainage
hypokalemia
increased urine output or diuretics
hypokalemia
why: potassium is mainly excreted by kidneys
dialysis
hypokalemia
diaphoresis (sweat)
hypokalemia
NG suction
hypokalemia
starvation
hypokalemia
low magnesium levels
hypokalemia
why: low magnesium levels stimulate renin + aldosterone release → potassium is excreted
insulin
hypokalemia
REMEMBER: insulin is a treatment for hyperkalemia, but it can cause hypokalemia
alkalosis
hypokalemia
REMEMBR:
Acidosis = hyperkalemia (why: because during acidosis, the blood is trying to get rid of the acid by exchanging hydrogen with potassium. potassium enters blood)
Alkalosis = hypokalemia (why: because during alkalosis, the blood is trying to get compensate for the lost acid, by exchanging hydrogen with potassium, from the cell. potassium enters cell)
sodium retention
hypokalemia (sodium ↑ = potassium ↓)
low blood volume
hypokalemia
why: low blood volume causes sodium retention as a compensatory response, thus when sodium is retained, potassium is loss
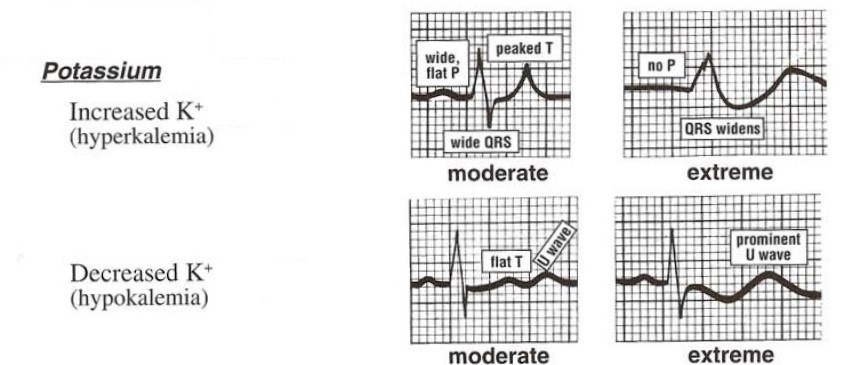
hypokalemia ECG
U wave
flat T
peaked P
depressed ST
wide QRS
paralysis
SEVERE hypokalemia
REMEBER: paralysis may occur with hyperkalemia. Trick: look at serum levels
SOB or respiratory arrest
SEVERE hypokalemia
why: paralyzed muscles
paralytic ileus or constipation
hypokalemia
hyperglycemia
hypokalemia
why: hypokalemia impairs insulin production
oral or IV potassium chloride (KCL)
when blood labs indicate hyperkalemia
potassium-rich foods
for mild hyperkalemia
IV potassium chloride considerations
dilute IV potassium solution
invert (turn upside down) solution
DO NOT HANG potassium to hanging bag (prevent bolus dose)
Infusion Rate: 10 mEq/hr
critical care, continuous ECG monitoring, w. central line access
*may exceed 10 mEq/hr
correct rate of IV potassium chloride
use infusion pump
assess IV sites for phlebitis & infiltration
during IV potassium chloride
why: potassium chloride is irritating to the vein
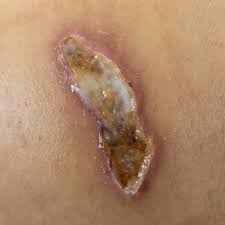
infiltration sign
sloughing & necrosis
critically ill
continuous ECG monitoring
at risk for hypokalemia
continuous ECG monitoring
serum potassium levels monitoring
on digoxin therapy
monitor for digoxin toxicity signs/symptoms (anorexia, n/v, vision issues: blind spots, halo, decreases acuity)