Cognitive Approaches to Personality and Self-Concept
1/176
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
177 Terms
Cognition
Awareness and thinking processes in personality.
Information Processing
Transformation of sensory input into mental representations.
Perception
Imposing order on sensory information received.
Interpretation
Making sense of or explaining events.
Conscious Goals
Standards for evaluating oneself and others.
Personalizing Cognition
Recalling personal experiences related to new events.
Objectifying Cognition
Recalling objective facts in response to events.
Field Dependence
Reliance on external visual cues for perception.
Field Independence
Using internal sensations to interpret visual information.
Rod and Frame Test
Measures field dependence through visual adjustments.
Herman Witkin
Developed the Rod and Frame Test in 1948.
Solomon Asch
Collaborated on the Rod and Frame Test.
Information Age
Era of rapid growth in cognitive study (1970s-1980s).
Mental Behaviors
Includes perceiving, interpreting, and remembering.
World View
Personal lens through which events are interpreted.
Attitudes
Personal beliefs influencing perception and interpretation.
Values
Core principles guiding individual judgments and actions.
Beliefs
Convictions that shape how reality is interpreted.
Expectations
Anticipated outcomes influencing perception of events.
Visual Field
External cues affecting perception and cognition.
Cognitive Styles
Different strategies for problem-solving and thinking.
Mental Representations
Internal images or concepts formed from sensory input.
Field Dependence
Difficulty in locating figures within complex backgrounds.
Field Independence
Ability to find hidden figures quickly and efficiently.
Embedded Figures Test (EFT)
Test measuring field dependence-independence using geometric figures.
Field-independent students
Favor natural sciences, math, and engineering fields.
Field-dependent students
Prefer social sciences and education disciplines.
Social orientation
Field-dependent individuals rely on social information.
Autonomy
Field-independent individuals function with greater independence.
Impersonal orientation
Field-independent people display detachment in social contexts.
Distraction filtering
Field-independent individuals excel at ignoring irrelevant information.
Hypermedia learning
Field-independent students learn better in multimedia environments.
Facial expression decoding
Ability to interpret emotional cues from facial expressions.
Emotion recognition study
Research showing field-independent subjects excel in difficult tasks.
Sensory stimulation response
Field-independent people better manage distractions in tasks.
Pain tolerance
Variation in pain perception among individuals.
Reducer-augmenter theory
Theory explaining differences in pain tolerance levels.
Low pain tolerance
Nervous system amplifies sensory information effects.
High pain tolerance
Nervous system reduces sensory input effects.
Asenath Petrie
Researcher who studied individuality in pain perception.
Pattern recognition
Field-independent individuals excel at finding and interpreting patterns.
Complex information analysis
Field-independent individuals analyze intricate emotional expressions better.
Multimedia learning effectiveness
Field-independent students switch between media faster.
Social information reliance
Field-dependent individuals often seek others' opinions.
Asenath Petrie
A notable figure referenced in personality studies.
Pain Tolerance
Ability to withstand discomfort without excessive reaction.
Reducing Subjects
Individuals seeking strong stimulation due to low sensory reactivity.
Augmenting Subjects
Individuals with high sensory reactivity, seeking less stimulation.
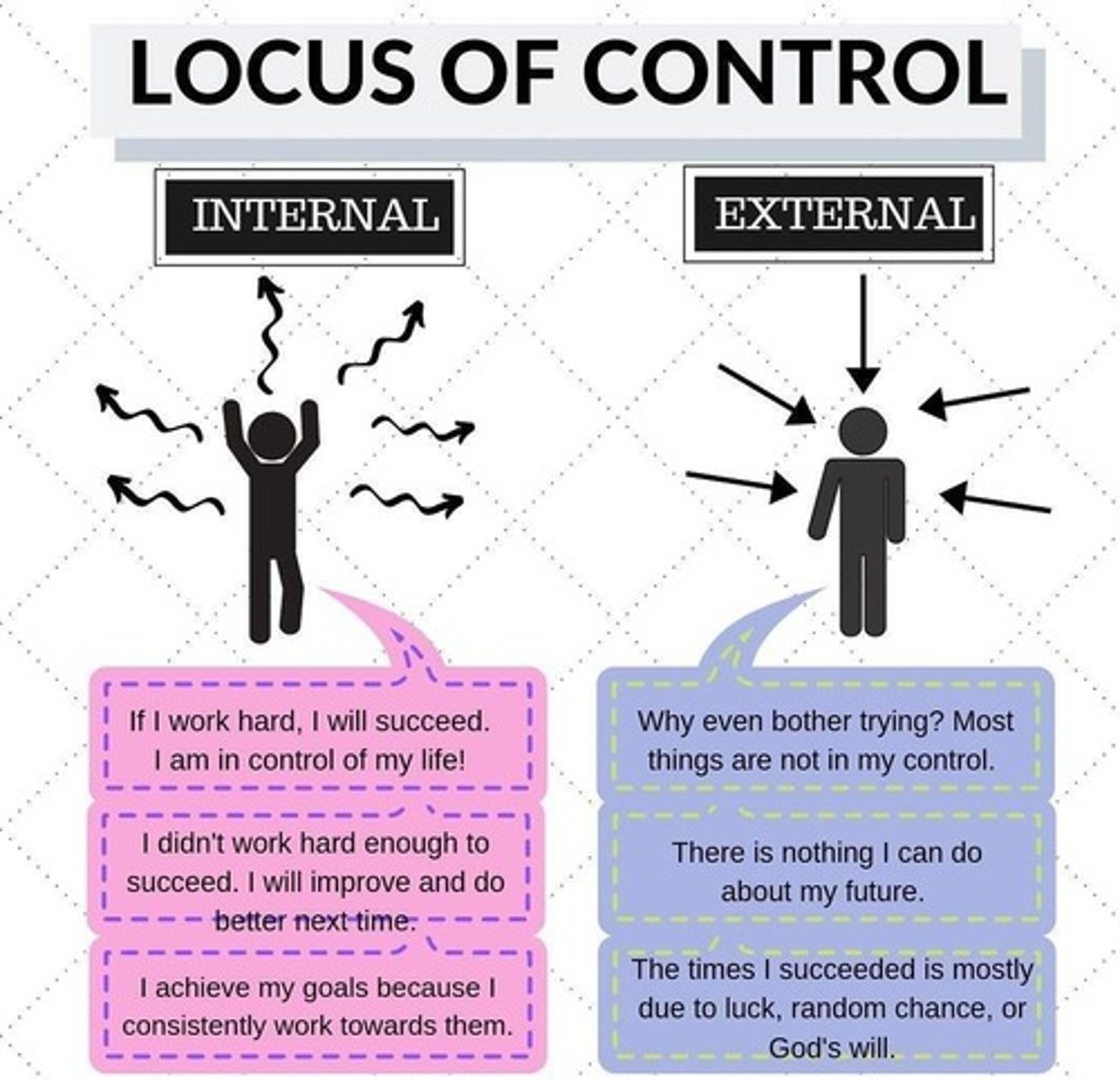
Locus of Control
Belief about control over life events and outcomes.
Learned Helplessness
Condition where individuals feel powerless to change outcomes.
Kelly's Personal Construct Theory
Theory viewing humans as scientists interpreting life events.
Personal Constructs
Mental frameworks used to interpret and predict events.
Fundamental Postulate
Anticipation of events channels psychological processes.
Transparent Templates
Mental models created to fit over real-world experiences.
Construct Revision
Updating mental frameworks based on new experiences.
Julian Rotter
Psychologist known for Social Learning Theory.
Social Learning Theory
Behavior determined by expectancy of outcomes and their value.
Internals
Individuals who believe they control events in their lives.
Externals
Individuals who view events as beyond their control.
External Locus of Control
Belief that outcomes are determined by external factors.
Internal Locus of Control
Belief that individuals control their life outcomes.
Walter Mischel
Psychologist known for Cognitive-Affective Personality System.
Cognitive-Affective Personality System (CAPS)
Theory emphasizing individual differences in cognitive and emotional processes.
Behavior Correlation
Relationship between personality traits and observed behaviors.
Trait Scores
Numerical values representing personality traits measured in assessments.
Accessibility of Processes
Ease of access to cognitive and affective responses.
Verbal Aggression
Aggressive speech influenced by specific situations.
Impulse Control Problems
Difficulty managing immediate reactions or urges.
Cognitive-Affective Personality System
Mischel's theory linking cognition, emotion, and behavior.
Psychological Situation
Individual's interpretation of a situation's meaning.
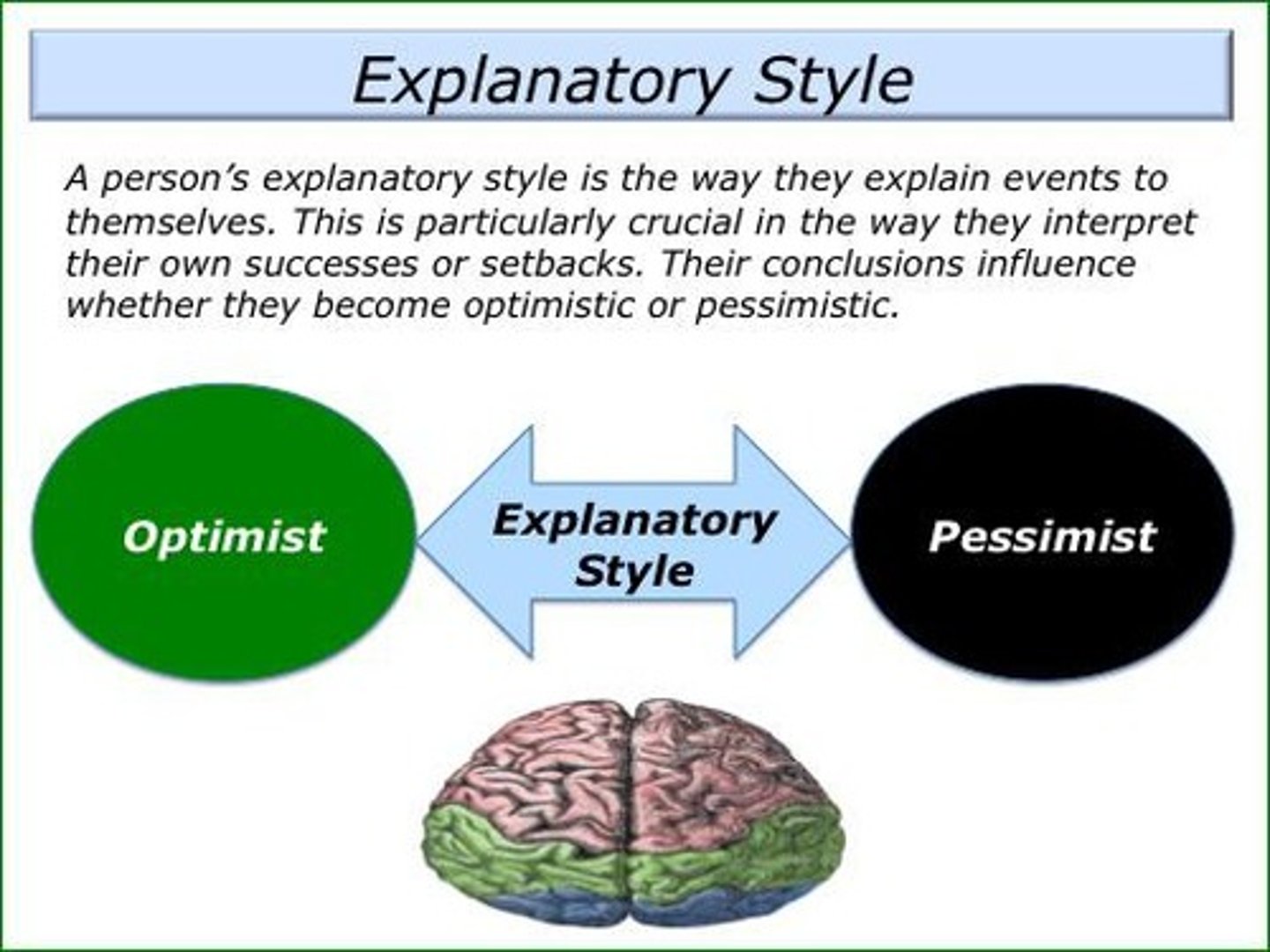
Pessimistic Explanatory Style
Attributing negative events to internal, stable, global causes.
Optimistic Explanatory Style
Attributing positive events to internal, stable, global causes.
Attributional Style
Tendency to explain events in specific ways.
Learned Helplessness
Feeling unable to control outcomes after repeated failures.
Causal Attribution
Explanation for the cause of an event.
Profiles of Aggression
Distinct patterns of aggression based on situations.
Situational Characteristics
Specific context influencing behavior and reactions.
Internal Causes
Factors within a person influencing their behavior.
Stable Causes
Consistent factors that do not change over time.
Global Causes
Broad factors affecting multiple areas of life.
External Causes
Factors outside a person influencing their behavior.
Temporary Causes
Factors that change and are not permanent.
Specific Causes
Narrow factors affecting particular events or situations.
Aggression After Warning
Children aggressive when warned by an adult.
Aggression After Teasing
Children aggressive when teased by peers.
Health Prediction
Pessimistic style linked to poorer health outcomes.
Stress Recovery
Pessimists struggle more with recovering from stress.
Positive Well-Being
Optimists experience better health and less stress.
Personal Project
Set of actions aimed at achieving a selected goal.
Brian Little
Psychologist who studies personal projects and personality.
Neuroticism
Personality trait linked to stress and negative project ratings.
Self-Efficacy
Belief in one's ability to achieve specific goals.
Cognitive Social Learning Theory
Emphasizes cognitive and social processes in goal pursuit.
Bandura's Theory
Highlights intention, reflection, and behavior monitoring.
Growth Mindset
Belief that intelligence can improve with effort.
Achievement View of Intelligence
Knowledge acquired relative to peers of the same age.
Aptitude View of Intelligence
Ability to learn and become educated.
Emotional Intelligence
Awareness and regulation of one's own emotions.
Cultural Context of Intelligence
Intelligence defined by culturally valued skills.
Mastery-Oriented Behaviors
Behaviors focused on learning and persistence.