Biology chapter 1 - cell biology
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Includes: Cells, microscopy, cell differentiation and specialisation, chromosomes and mitosis, binary fission, culturing microorganisms, stem cells, diffusion, osmosis, active transport, exchange surfaces, exchanging substances
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
differences of prokaryotic vs eukaryotic cells
Prokaryotic:
small and simple
genetic material isn’t enclosed in a nucleus
very few organelles
unicellular
Eukaryotic cells:
large and complex
genetic material is enclosed in a nucleus
many organelles
multicelluar
similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
They both have a cell membrane
They both have ribosomes
They both contain DNA
Explain each function of the organelles from an animal cell:
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Cell membrane
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
Nucleus - contains genetic material that controls the activities of the cell
Cytoplasm - gel-like substance where most of the chemical reactions happen. It also contains enzymes that control the chemical reactions
Cell membrane - holds the cell together and controls the molecules which go in and out of the cell
Mitochondria - these are where most of the reactions for aerobic respiration take place.
Ribosomes - site of protein synthesis
Explain the function of the organelles from a plant cell:
Cell wall
Vacuoles
Chloroplasts
Cell wall - made of cellulose. It supports the cell and strengthens it
Vacuole - contains cell sap, a weak solution of sugar and salts. It also helps give the plant cell its shape
Chloroplasts - where photosynthesis occurs, which makes food for the plant as it contains chlorophyll which absorbs light needed for photosynthesis.
Differences between a light microscope and an electron microscope
Light microscopes use light and lenses to form an image while electron microscopes use electrons.
Electron microscopes use a higher resolution which gives a sharper image
Electron microscopes have a higher magnification which allows us to see much smaller things in more detail.
formula for magnification
Magnification = image size/real size
How to prepare a slide to view an onion cell
Using a pipette add a drop of water to the middle of a clean slide
Cut up the onion and separate it out into layers by using forceps to peel off the top epidermal tissue from the bottom of an onion
Place the epidermal tissue into the water on the slide
Add a drop of iodine solution to the epidermal tissue on the slide, this will stain the epidermal tissue to make it easier to see under the microscope
Then place a cover slip over the specimen but at a 45 degree angle so that no air bubbles get trapped in it.
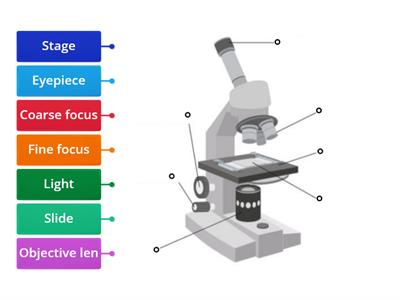
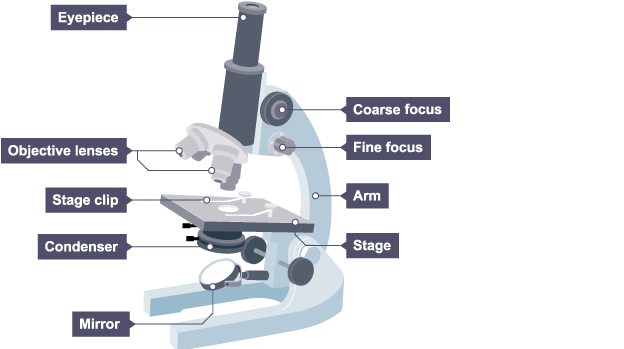
label the microscope
answers:
What is cell differentiation
Is the process by which a cell changes to become specialised for specific function
How is the sperm cell specialised for reproduction?
The function of a sperm is to get the male DNA to the female DNA (ovum). It has a long tail and a streamlined head to help it swim to the egg. There are lots of mitochondria in the cell to provide the energy needed. It also carries enzymes in its head to digest through the egg cell membrane. It contains their genetic information in the nucleus, however it only contains half the genetic information of a normal adult cell.
How is the nerve cell specialised for rapid signalling?
The function of the nerve cell is to carry electrical signals from one part of the body to another. These cells have a long axon so they can cover more distance and carry electrical impulses. The axon is covered in myelin which insulates the axon and speeds up the transmission of nerve impulses. They also have synapses at their ends which allow impulses to pass from one nerve cell to another. Dendrites increase the surface area so that other nerve cells can connect more easily.
How is the muscle cell specialised for contraction
The function of a muscle cell is to contract quickly, they contain protein fibres which can change their length allowing them to contract. These cells are long so they have space to contract and contain many mitochondria to generate the energy needed for contraction. They work together to form muscle tissue.
How is the root hair cell specialised for absorbing water and minerals?
Root hair cell are cells on the surface of plant roots which grow into hairs. This gives the plant a big surface area for absorbing water and mineral ions from the soil. They also don’t contain chloroplasts because they are underground, meaning that they don’t photosynthesise.
How is the phloem and xylem cells specialised for transporting substances?
Phloem:
Tubes carry dissolved sugars up and down the plant
Contains phloem vessel cells which have no nucleus and only limited cytoplasm. End walls of the vessel cells have pores called sieve plates. These two features allow dissolved sugars to move through the cell interior
Each phloem vessel cell has a companion cell connected by pores. The mitochondria in the companion cell provide energy to the phloem vessel cell
Xylem:
They are found in the plant stem and form long tubes which carries water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the leaves
Have very thick walls containing lignin which provides support to the plant. This also causes the xylem to die.
The end walls between the cells have broken down so the cells have now formed a long tube
No nucleus, cytoplasm, vacuole, or chloroplasts.
Have no internal structure at all making it easier for water and minerals to flow
What is mitosis and how is it used?
Mitosis is the stage of the cell cycle when the cell divides. Multicellular organisms use mitosis to grow or replace cells that have been damaged.
Growth and DNA replication of the cell cycle
In a cell that’s not dividing the DNA is all spread out in long strings
Before it divides, the cell has to grow and increase the amount of subcellular structures such as mitochondria and ribosomes
It then duplicates its DNA so there is one copy for each cell.
Stages of the cell cycle (summary)
Stage 1 - the longest stage, building cell mass and replicating DNA
Stage 2 - Mitosis: nuclear division, nucleus divides into two
Stage 3 - Cytokinesis: cell splits into two, producing two daughter cells
Stages of mitosis
The chromosomes line up at the centre of the cell and cell fibres pull them apart. The two arms of each chromosome go to opposite ends of the cell
Membranes form around each of the sets of chromosomes. These become the nuclei of the two new cells - the nucleus has divided.
Lastly the cytoplasm and cell membrane divide.
The cell has now produced two new daughter cells. The daughter cells contain exactly the same DNA - they’re identical to each other and to the parent cell.
How is a cell controlled by genes?
Inside a cell there is a chromosome in a nucleus with a DNA. The chromosome never leaves the nucleus. mRNA go into the nucleus and receive directions from one section of the DNA. mRNA take the directions to parts of the cell. These directions tell the ribosomes in the cell to make certain proteins. Each part of the organelle makes something different. A different cell has a different DNA, and so it makes different end proteins.
Difference between a plant and animal cell
Plant:
Have a regular shape
have a cell wall
contain chloroplasts which contain chlorophyll for photosynthesis
Animal:
irregular shape
Don’t have a cell wall
don’t have a large permanent vauole
How to use a light microscope to view a prepared slide
Place the slide onto the stage using the clips to hold the slide in place
Select the lowest power objective lens which is usually 4x
Position the objective lens so it almost touches the microscope slide. To do that slowly turn the coarse focussing dial
Look at the microscope from the side while adjusting the position of the objective lens. When the objective lens almost touches the slide stop turning the dial.
Then look down through the eyepiece
Slowly turn the coarse focussing dial, to increase the distance between the objective lens and the slide until the cells come into focus
Then use the fine focussing dial to make the cells clearer
How to calculate total magnification
Magnification of the eyepiece lens * magnification of the objective lens
How do bacteria multiply?
Simple cell division.
One bacterial cell splits into two bacterial cells - binary fission
How can binary fission occur in bacteria?
Bacteria can carry out binary fission once every twenty minutes as long as they have enough nutrients and the temperature is suitable
Formula for number of bacteria present after a given time
2n
n = number of rounds of division
e.g. a type of bacterium divides every twenty minutes. Calculate the number of bacteria present after three hours.
3 hours = 180
180/20 = 9 rounds of division
number of bacteria = 29 = 512
How to avoid contamination when using a petri dish
Sterilise all petri dishes, bacterial nutrient broth and agar to kill any unwanted bacteria or microorganisms and prevent contamination
Sterilise the inoculating loop by passing it through a Bunsen burner flame
Attach the lid of the petri dish using adhesive tape to top the lid from falling off and unwanted microorganisms entering
Place the agar plate upside down into an incubator to stop moisture from dripping down onto the bacteria and disrupting the colonies
How to choose the right temperature of culturing bacteria on agar jelly
In school labs, we incubate bacteria at 25oC to reduce the chances that harmful bacteria will grow
Required practical:
Effect of antibiotics on bacterial growth
Clean the bench with disinfectant solution which kills microorganisms that could contaminate our culture
Sterilise an inoculating loop by passing it through a Bunsen burner flame
Open a sterile agar gel plate near a Bunsen burner flame which kills bacteria in the air
Use the loop to spread the chosen bacteria evenly over the plate
Place sterile filter paper disc containing antibiotic onto the plate
Incubate the plate at 25oC
What is around the antibiotic discs
Around the antibiotic discs we have a region where the bacteria have not grown which is called the zone of inhibition
formula for the area of the zone of inhibition
area of zone of inhibition = pi x r2
What is a stem cell
An undifferentiated cell which can give rise to more cells of the same type and can differentiate to form other types of cells
Bone marrow transplant steps
Leukaemia is a cancer of the bone marrow
To treat this the patient’s existing bone marrow is destroyed using radiation
The patient then receives a transplant of bone marrow from a donor
The stem cells in the bone marrow now divide and form new bone marrow. They also differentiate and form blood cells
Problems with bone marrow transplant
The donor has to be compatible with the patient otherwise the white blood cells produced by the donated bone marrow could attack the patient’s body
There is a risk that viruses can be passed from the donor to the patient
Therapeutic cloning steps
In therapeutic cloning an embryo is produced with the same genes as the patient. So, stem cells from the embryo can be transplanted into the patient without being rejected by the patients immune system
Once inside the patient, the stem cells can then differentiate to replace cells which have stopped working correctly
Benefits and issues with therapeutic cloning
Can be useful for a range of medical conditions such as diabetes or paralysis
Some people have ethical or religious objections to the procedure
What is meant by diffusion
Diffusion is the spreading out of particles resulting in a net movement from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Factors that effect rate of diffusion
Difference in concentrations - The difference in concentration is also called the concentration gradient. The greater to concentration gradient, the faster diffusion takes place.
Temperature - The higher the temperature the greater the rate of diffusion because the particles have more kinetic energy and are moving faster.
Surface area of the membrane - The larger the surface area of the cell membrane, the greater the rate of diffusion
What is surface area to volume ratio
When something has a large surface area for their volume
How to calculate surface area to volume ratio
Find the total surface area
Find the total volume
Put the values into a ratio
Simplify the ratio
Trend in the surface area to volume ratio + their problems
As organisms get larger the surface area to volume ratio falls sharply. This presents a huge problem for multicellular organisms because their surface area is not large enough for their volume.
How do fish get their oxygen?
The oxygen-rich water passes into the mouth. It then flows over gills, where the oxygen is transported into the blood stream. The gills are covered in a very large number of fine filaments where gases pass in and out of the blood. Deoxygenated blood passes into the filament. Oxygen diffuses from the water into the blood. Oxygenated blood returns to body.
Three adaptations of filaments
Massive surface area
thin membrane to provide a short diffusion pathway
efficient blood supply to take the oxygenated blood away. This ensures that the concentration gradient is always high
These adaptations make diffusion efficient as possible
What is meant by osmosis
Osmosis the the diffusion of water from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution through a partially permeable membrane.
What is meant by a high or low concentration of water
Dilute solutions contain a high concentration of water (high water potential)
Concentrated solutions contain a low concentration of water
What does a partially permeable membrane mean
Membranes that allow some molecules to pass through but not all molecules
effects of osmosis on animal cells
The water will diffuse into the animal cell and cause it to expand or even burst
If an animal cell is placed in a very concentrated solution, the water will move out of the cell by osmosis and the cell with shrink.
effect of osmosis on plant cells
If a plant cell is placed in water, then water will move into the cell via osmosis and expand. The cell wall prevents the plant cell from bursting. Instead the cell becomes swollen also known as turgid.
If a plant cell is placed in a concentrated solution the water moves out of the plant cell causing it to shrink which is also known as flaccid.
Potato experiment - osmosis
Peel the potato because the skin can affect osmosis
Use a cork borer to produce 3 cylinders of potato. Using the cork borer makes all the cylinders the same diameter
Use a scalpel to trim the cylinders to the same length around 3cm
Measure the length of each cylinder using a ruler and the mass of each cylinder to balance
Place each cylinder into a test tube. Add 10cm3 to a 0.5 molar sugar solution to the first test tube
Then add a 10cm3 of 0.25 molar sugar solution to the second test tube and 10cm3 of distilled water to the third test tube
Leave the potato cylinders overnight to allow osmosis to take place
Remove the potato cylinders and gentry roll them on paper towel to remove any surface moisture
Measure the length and mass of the cylinders again
The calculate the percentage change.
How to calculate percentage change
(change in value/original value) x 100
Results of the potato osmosis experiment
In water, the potato cylinder gains mass as water moves into it by osmosis
In concentrated sugar solution, the cylinder loses mass as water moves out by osmosis
Where the line on the graph crosses the x-axis there is no change in mass because the concentration outside the cell is the same as the concentration inside the cell so no overall osmosis takes place.
What is meant by active transport?
Active transport moves substances from a more dilute solution to a more concentrated solution (against the concentration gradient). This requires energy from respiration
Examples of active transport in animal and plant cells
plant cells - ions in root hair cell
animal cells - lumen of small intestines (sugars to the blood stream)