Practicum V - Lab 2
1/216
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
217 Terms
When did the first mammals appear? Modern animals? Found where?
early Mesozoic era; Paleogene/Neogene periods of Cenozoic era; worldwide
What is hair composed of? Complete coat of fur called?
Keratin; pelage
Functions of hair?
Heat insulation and cooling, protection from UV radiation
Name of three ossicles in middle ear?
Malleus, Incus, Stapes
What is the function of new bones in middle ear?
Amplify sounds and allow for more acute hearing
What two bones form the jaw?
Mandible and Maxilla
What two bones form the jaw joint?
Dentary and squamosal
How long did it take for the synapsid skull to evolve?
100 millionyears of evolutionary changes.
How have vertebrate teeth changed?
Modified peg-like teeth into specialized structures for certain tasks
What type of gland is a mammary gland? What is its function?
(Female mammals) produce milk to feed young offspring
What type of gland is the mammary gland modified from?
Sweat/sebaceous gland
What does the word neocortex mean?
New bark
What does the neocortex consist of? How does it differ from rodents to larger mammals?
Grey matter surrounding deeper white matter of cerebrum; other mammals have smooth neocortex
What is the name of the grooves and wrinkles? What do they allow for?
Sulci (grooves), and wrinkles (gyri); increases surface area of neocortex
What are the three major types of mammals and their characteristics?
Protheria [monotremes (egg layers)], Metatheria [Marsupials (pouch animals)], Eutheria (placental (nourished before birth)]
What does the word Protheria mean? When did they split from other mammals? Where were they probably found?
First beast; Mesozoic (Cretaceous per); landmass of Gondwana
What does Monotremata mean? What makes them different than other mammals?
Sewer; lack teeth as adults
How is milk delivery different in monotremes than other mammals?
Milk secreted onto skin within the pouch (lack nipples)
What do monotremes use to locate prey? Where are they found today?
Electroreception; Australia and New Guinea
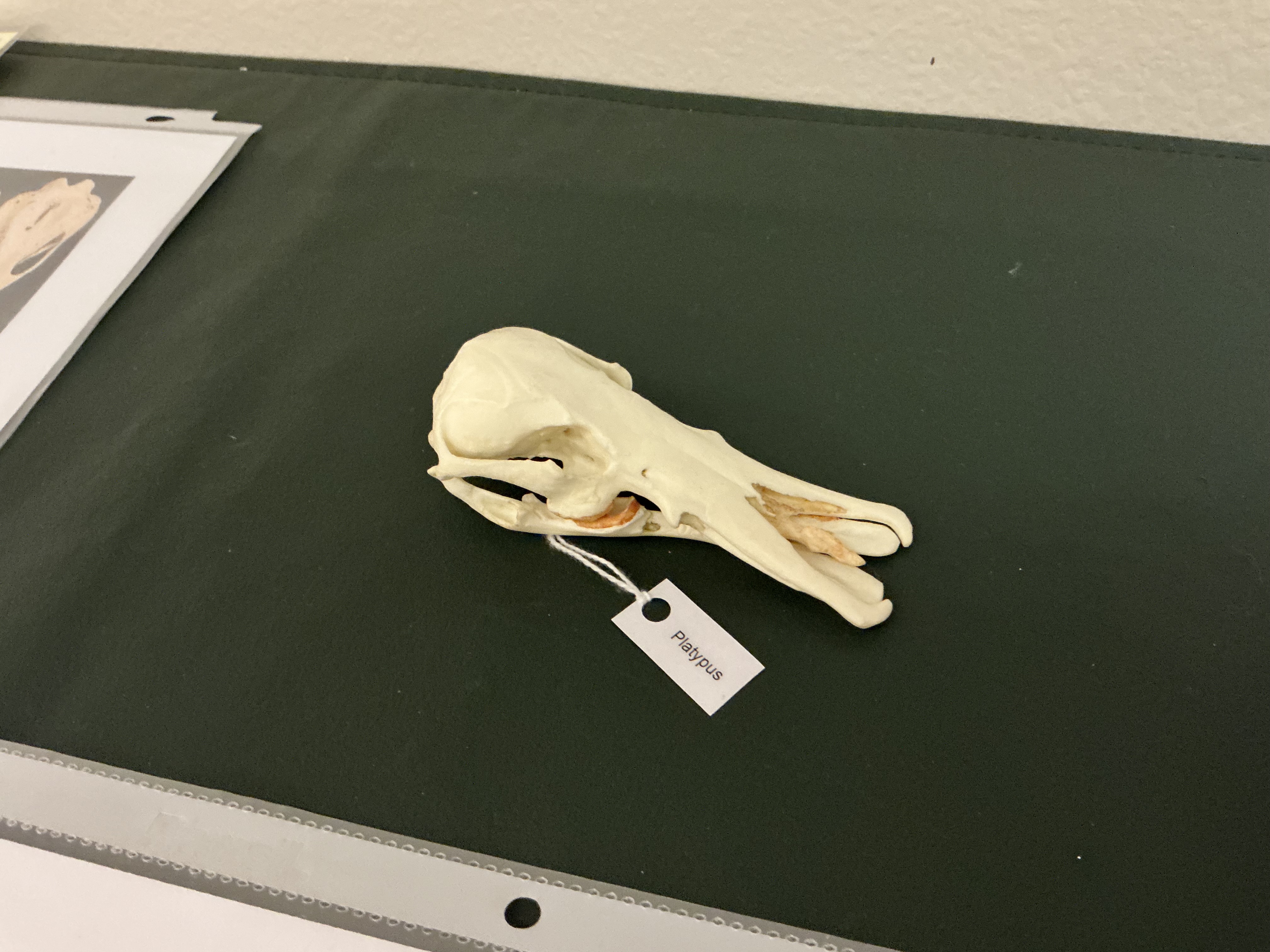

Unique about the Duck-Billed Platypus? Habitat?
(male’s spurs) venomous; side-to-side motion of the animals’ head while hunting; small streams and rivers

What do echidnas feed on? How do their electroreceptors compare to the platypus?
Ants and termites; only has 2,000 compared to the 40,000 in platypus
What does the word Metatheria mean? What do these animals give birth to? What must they attach to?
“sort-of beast”; “larval-like” offspring; attach to nip in the pouch
When did Metatheria diverge from the ancestors of placentas? Where are they found today?
Jurassic period; Australasia
What make marsupials different from placental mammals? When and where did they first evolve? When did they reach Australia?
younger are carried in a pouch; North America 80 MYA; appeared in Australia in Ogliocene
What percent of Marsupialia is found in Australia?
70% of the 3344 extant species

What is unique about the Red Kangaroo?
Largest of all kangaroos, largest mammal native to Australia
What do koalas eat and what does this cause them to do?
Eucalyptus leaves; makes them sleep for up to 20 hours a day
What is the only marsupial found in socal? What type of tail do they have?
The Virginia opossum; prehensile tail that aids in climbing

How many teeth do opossums have? What do they eat?
Omnivorous with 50 teeth
What do opossums do when confronted by predator? Why can’t opossums carry rabies?
feigning death; body temp is too low
(meek) How are brush-tailed possums different from other opossums? Where are they from and where are they found today?
Almost fully haired tail; from New Zealand; found in Australia
What does Eutheria mean? How do they differ from non-eutherian mammals and what does this allow them to do?
True beast; lack epipubic bone, cause faster running
What did Eutheria evolve and where are they found?
160 MYA; now worldwide
What order or Aardvarks? What do they eat? What is the term for this type of feeder?
Tubulidentata; Ants and termites; formicivore
How are Tubulidentata teeth different from other mammals?
no enamel coating and are worm away and regrow continuously
What order are Elephants? How do they use their trunk?
Proboscidea; to grab food and water
How much does the skull comprise of an elephant’s body weight? What other changes have occurred to their skull to accommodate their large size?
12-25% of body weight; network of air-cell cavities to reduce its weight
What adaptations are seen in an elephant’s foot?
embedded in a soft cushion
How are African Elephants different from Asian Elephants?
They have larger ears, three nails on hind feet, tusks on both sexes
What order are Hyraxes? What does the word mean?
Hydracoidea; “shrewmouse”
What are Hyrax’s closest living relative?
Elephants
How do Hyrax slive off leaves and grass?
Use molar teeth

What order are Dugongs and Manatees? What is the common name of these animals? What do they eat?
Sirenia; "sea cows"; herbivorous
What modifications do Sirenia have for aquatic lifestyle?
forelimbs → arms for steering, tail used for propulsion
What are Sirenia’s closest relatives?
Elephants

What order are sloths, armadillo, and anteaters? What does it mean? Why do these animals have this name?
Xenarthra; "strange joints"; refers to their unique bone structure.

What is the Armadillo’s outer shell made of? Why is it quickly spread in the US?
Ossified dermal scutes and keratinized epidermal scales; only has few natural predators within the US

How many times does the anteaters tongue move in and out of their mouths with feeding? What do they use instead of stomach acid?
160 times per second; formic acid

What are sloths classified as? What do they use to camouflage? When are they most vulnerable to predation?
Folivores; they use symbiotic cyanobacteria; the ground to urinate and defecate once a week
What percent of mammals are rodents? Characteristics?
40%; continuously growing incisors in upper and lower jaw
Rodents lack canines, what is the space called?
Diastema
When did rodents first appear?
65 MYA
What makes Naked Mole Rats unique among mammals? What other animals are they similar to and why? What do they lack?
Eusocial behavior; similar to bees and ants; pain sensation in its skin

Where are beavers found? How are they able to fulfill this lifestyle?
Semi-aquatic; large flat paddle-shaped tail
What are beaver homes called? What are they known for?
Lodges; building dams across streams
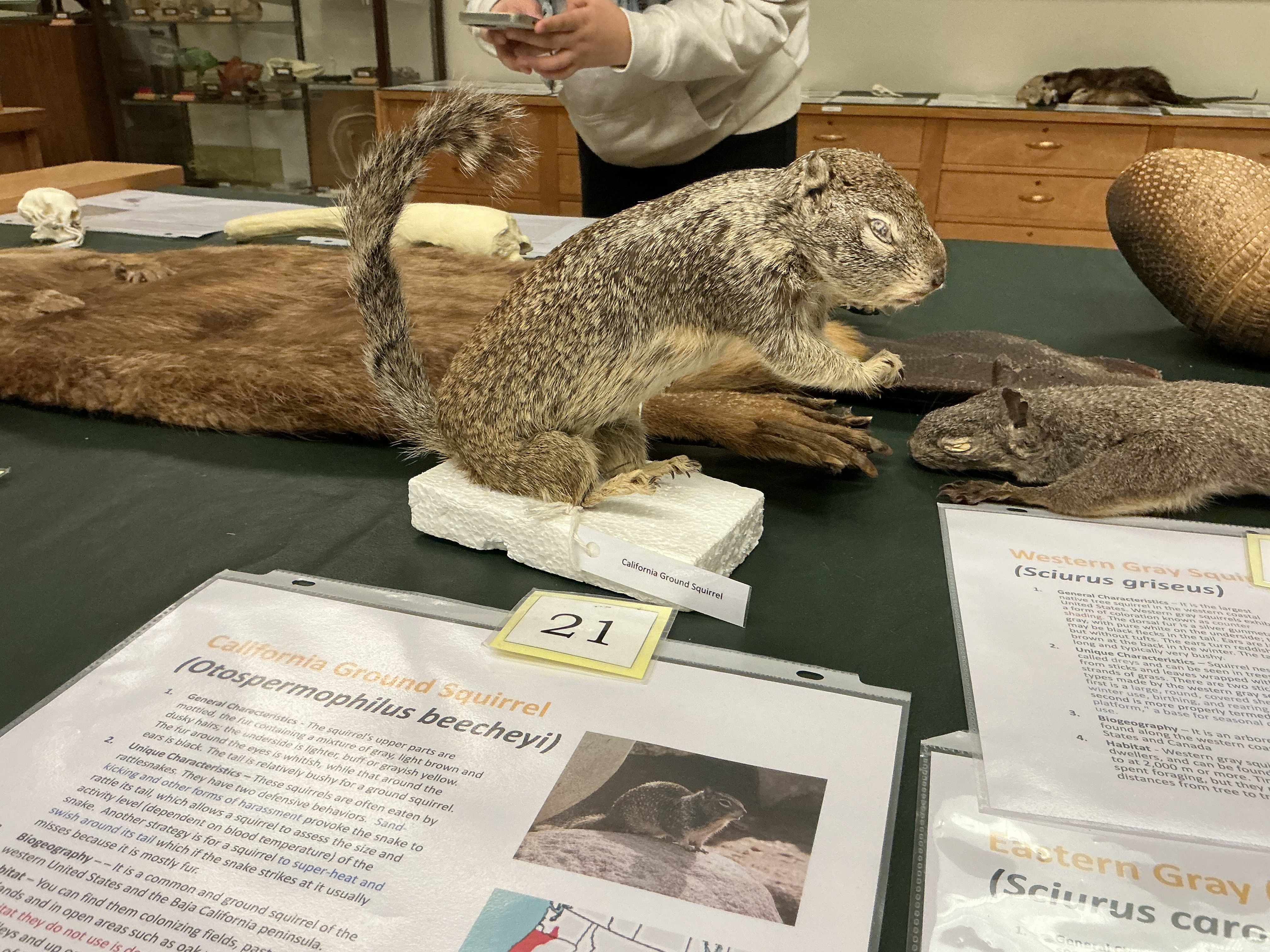

What are the two defensive behaviors seen in CA ground squirrels?
sand-kicking and super-heat and swish around its tail
What is the only habitat in CA that squirrels do not use?
deserts
What is the name of the defensive coloration seen in the Western Gray Squirrel? What is the name of their nests? Types of nests?
Counter shading; dreys; leaf nests and tree cavities

What is the term used for the black morph seen in Eastern Gray Squirrels? Results from?
Abnormal pigment gene; genetic variation in pigmentation
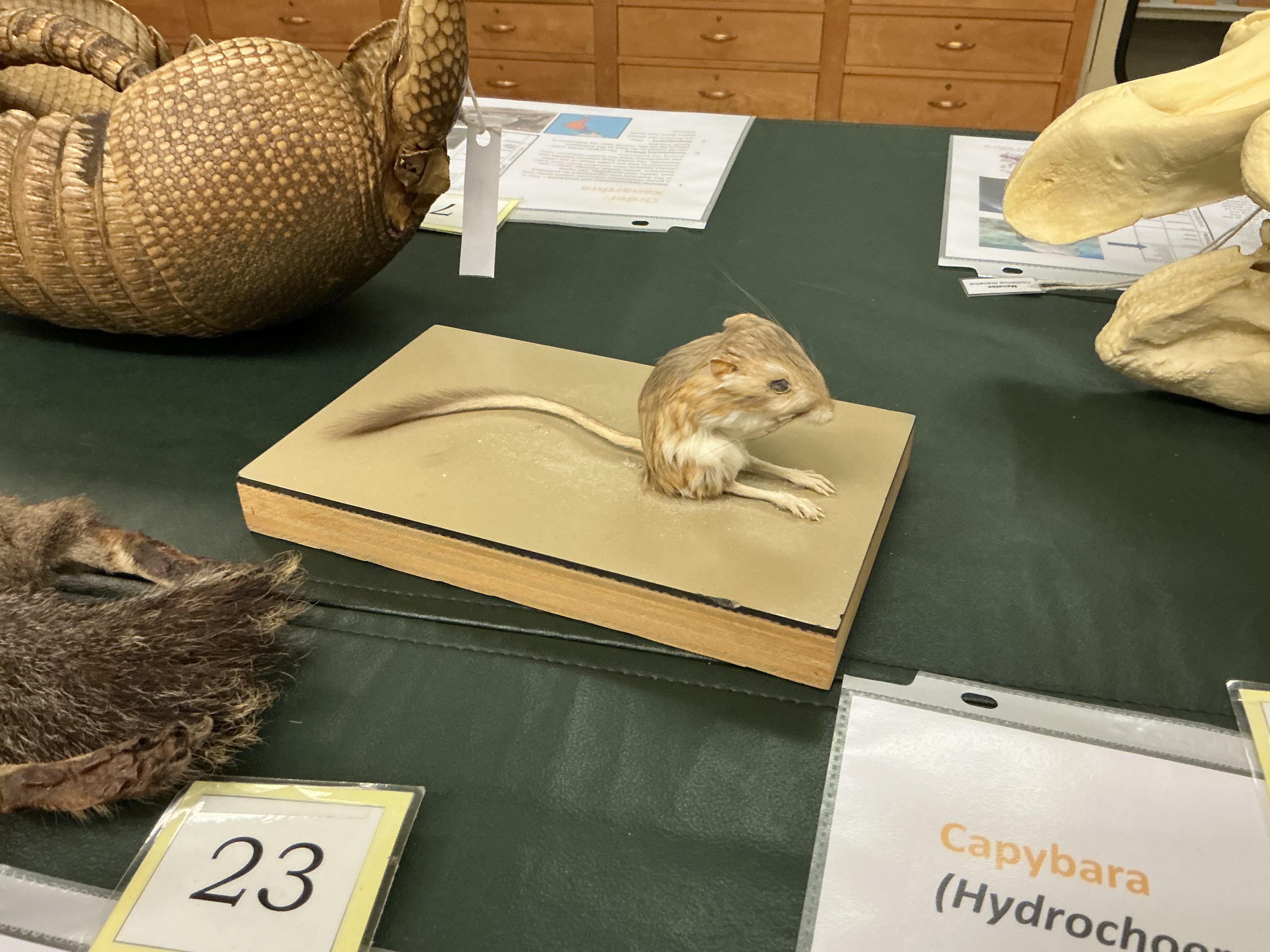

What adaptation are seen in kangaroo rats for their existence in the desert?
breaking down seeds and not needing to drink water; also lower metabolic rate

What are capybaras known for? What is the term for how they eat? What does it mean? Where are they found?
Largest rodent in the world; graminivores (primarily eat grass and plants); South America

Char of Pocket Gopher? Where are they found?
Large cheek pouches; fossorial (underground)
What does Peromyscus mean? What id the CA deer mouse notorious for?
“booted mouse”; carrier of hantavirus

What are the only Norway rat-free zones? Why are they not there?
Arctic and Antarctic because of the cold
Where did Norway rats originate? What is the only other mammal that is more successful?
n. China; humans
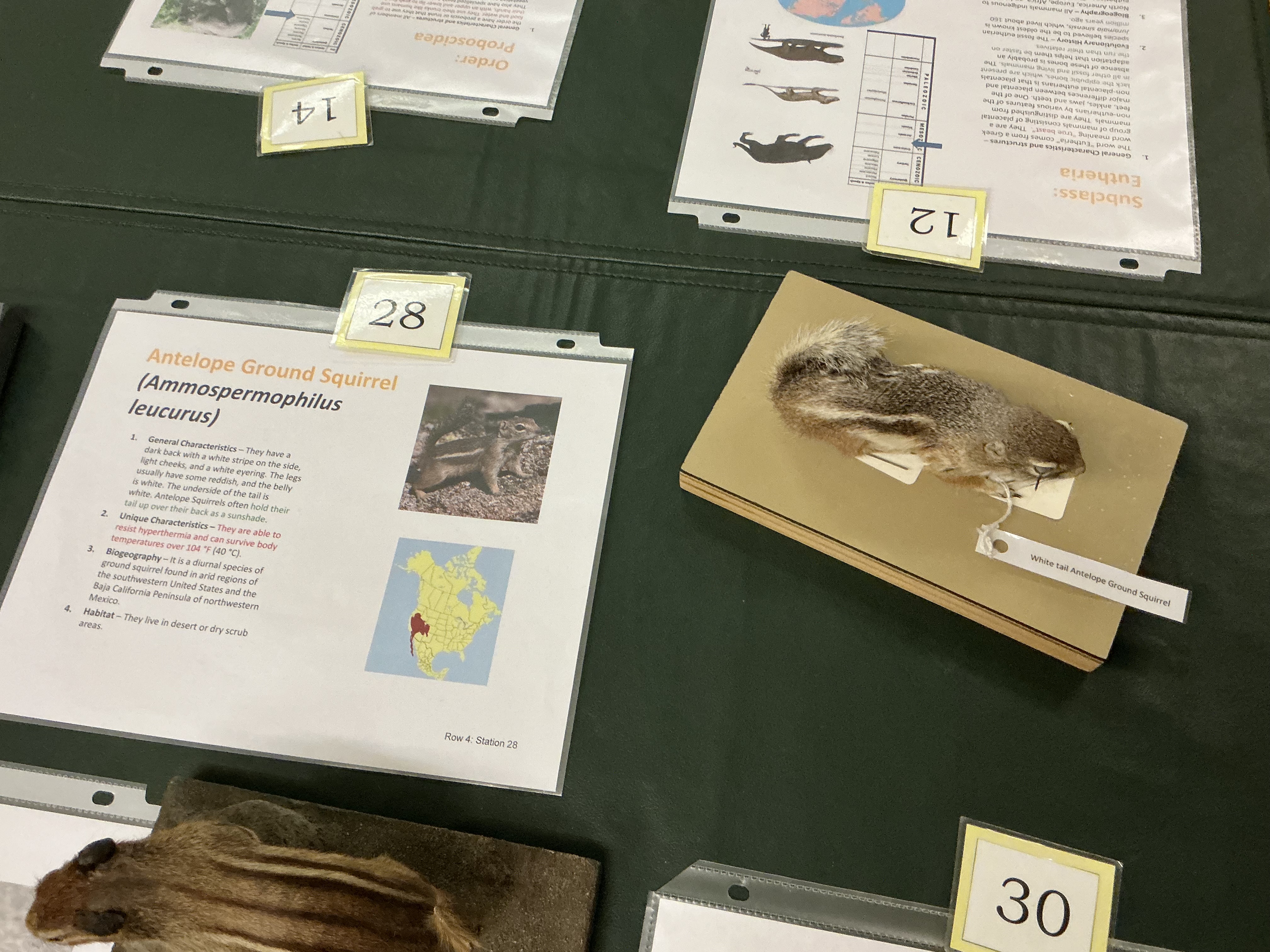
How do Antelope Ground Squirrel hold their tail? Why? Uniqueness?
hold tail up as a sunshade; able to resist hyperthermia (104F+ degrees)

Four main calls in chipmunks?
chuck, chip, trill, chipper

What is the other name for Groundhogs? Why do they build a winter burrow?
Woodchuck; see their shadow for us to predict when spring arrives
What order are rabbits, hares, and pika? How are they different from rodents?
Lagomorpha; four incisors in upper jaw and strictly herbivores
Why do lagomorphs eat their own feces? When did they appear in fossil record?
(coprophagy) to obtain more nutrients from diet; Late Paleogene/early Eocene
What are black-tailed rabbits known for?
breeding prowess; high reproduction
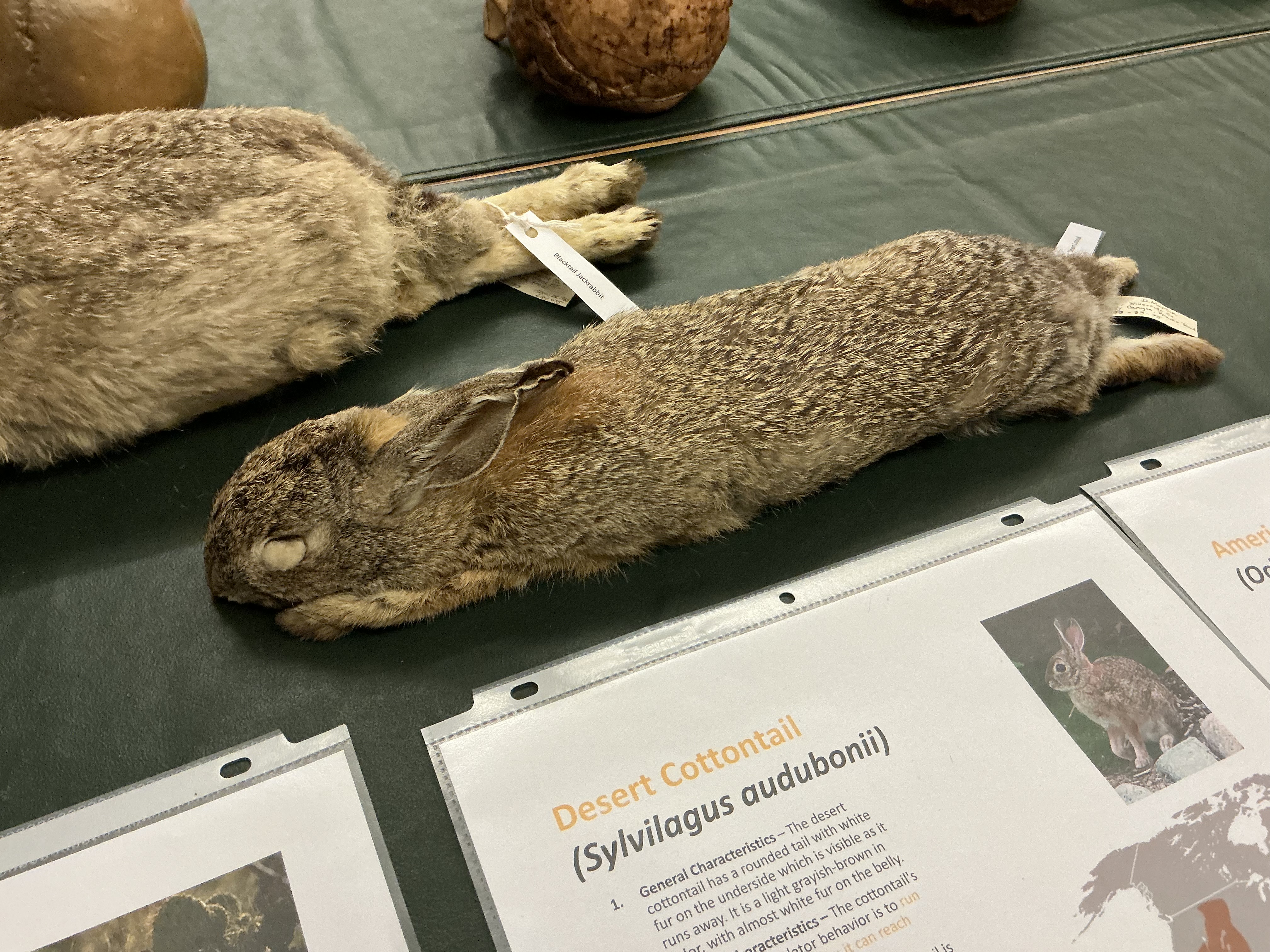

What is the Desert Cottontail’s anti predator behavior?
run in zigzag; speeds up to 19 mph
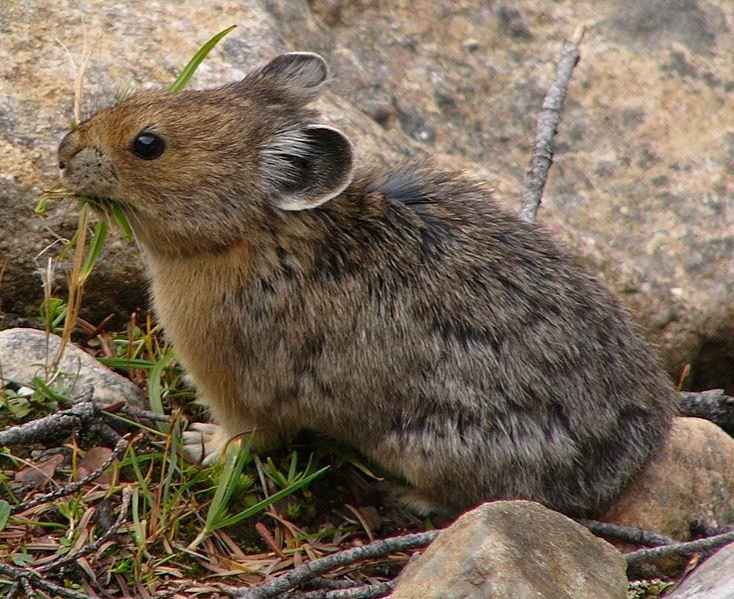

What are Pika’s food piles called? What are they an indicator in n Amer.?
“Haystacks”; global warming

What are the gliding membranes in Dermoptera (flying lemurs) called?
patagium
What are flying lemurs similar to in their breeding habits? What do they use as a pouch?
Marsupial-like breeding habits; flap of tain
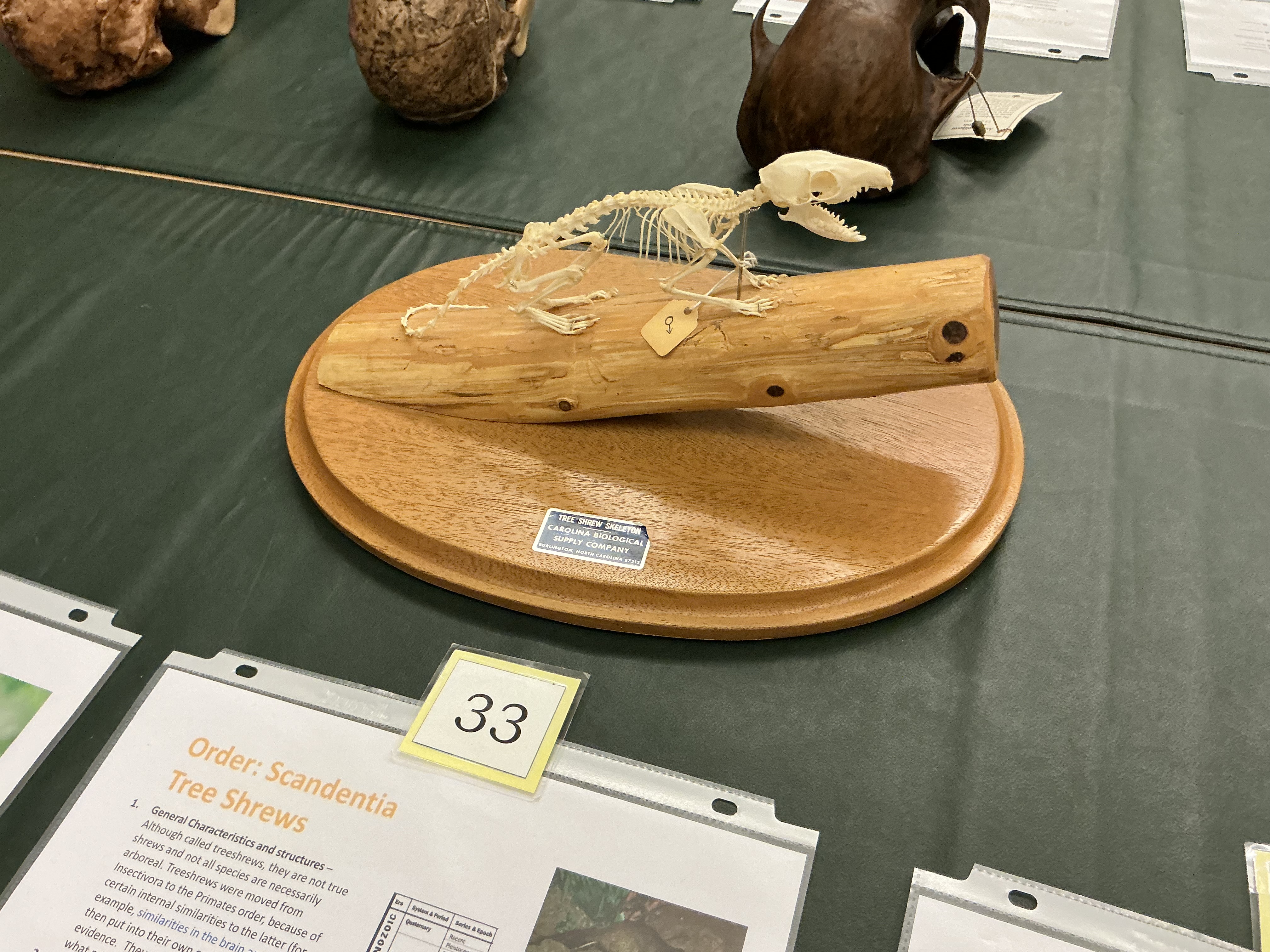

What order are tree shrews? What do they have in common with primates? Used for what kind of studies?
Scandentia; similar brain anatomy; primate behavior
What char are shared by all primates? What do most have? When did they arise?
large brains and increased reliance on stereoscopic vision; opposable thumbs and prehensile tails; late Paleocene
What mammals are included in Prosimians? What do they lack and why? In common?
Lemurs, lorises, bushbabies, tarsiers; color vision for being nocturnal; flattened toilet claws for grooming
What mammals are in old world monkeys? In common?
baboons, mangabeys, mandrills, guenons, patas monkeys, macaques; external nares that are close together

What is the name of the bare patch in olive baboon?
rump or calloused ischial tuberosities
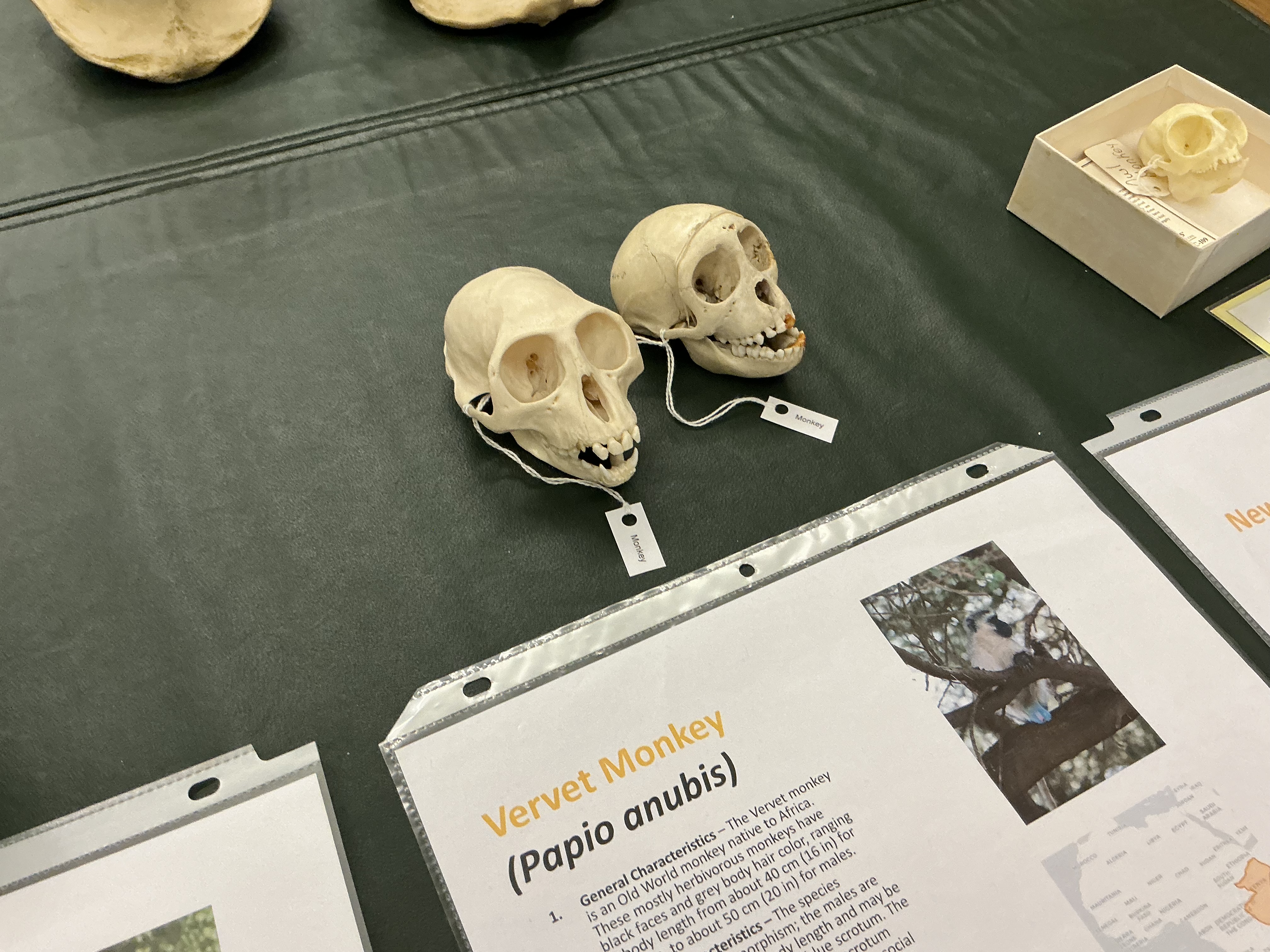

Why are vervet monkeys scrotum blue? advantage?
tyndall scattering over melanin layer; show suitability
What mammals are in new world monkeys? In common?
marmosets, tamarins, squirrel, capuchin, monkeys, howler and spider monkey, uakaris, sakis; broad flat nasal spetum
When did new world monkeys appear in the new world?
40 MYA to s. Amer
What mammals are in apes? In common?
gibbons, gorilla, orangutan, chimpanzee, bonobos; sexual dimorphism
How do apes different from monkeys?
apes do not have tails
How are gorillas different from chimps? Where are they found? diet?
largest of primates by size; 7 MYA central Africa; folivore (leaf and stem)
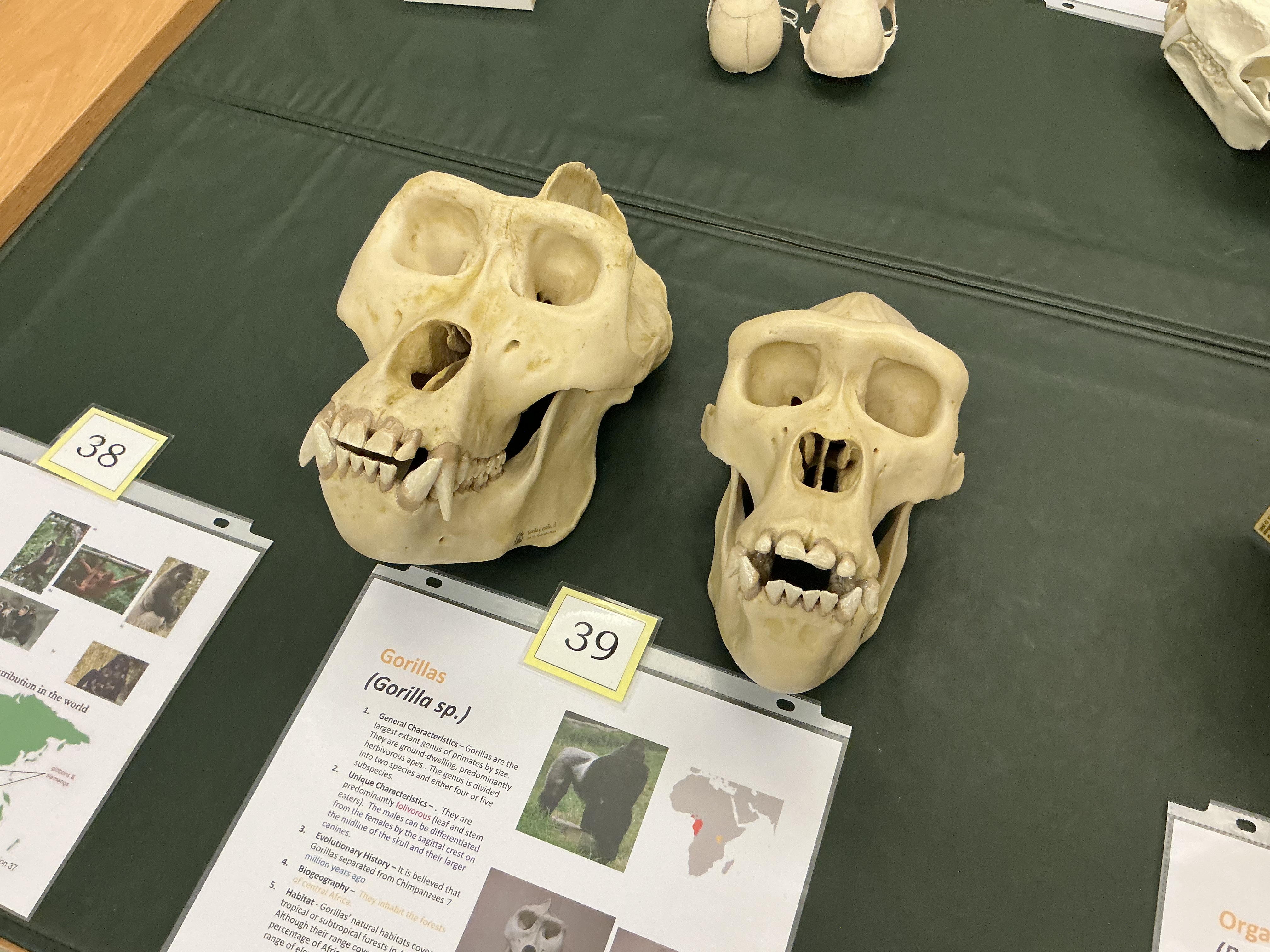

How can you tell male gorilla from female?
Males have sagittal crest above head
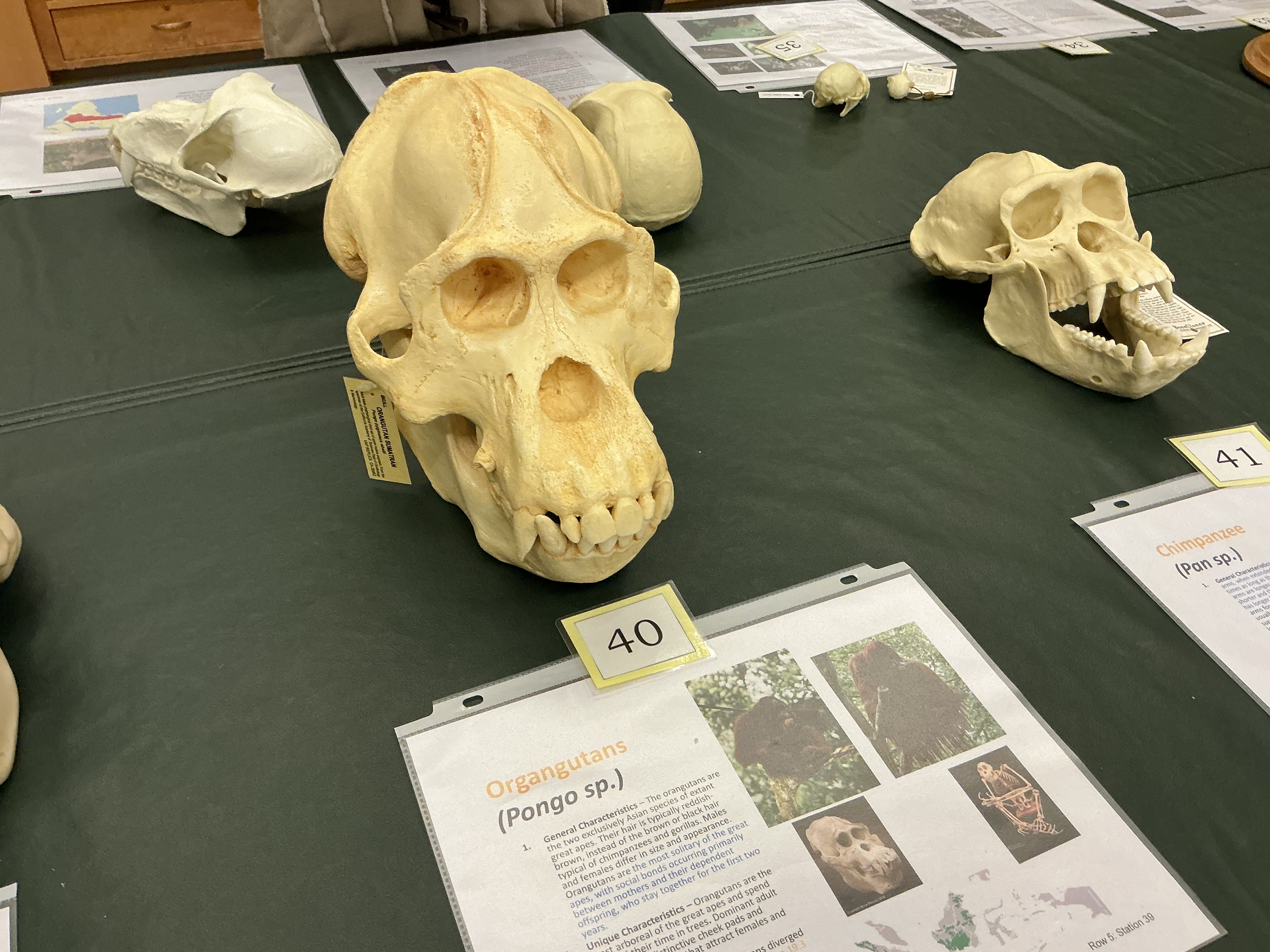

When did orangutans diverge? Found where? Social Structure?
15.7 to 19.3 MYA; Borneo and Sumatra; most solitary
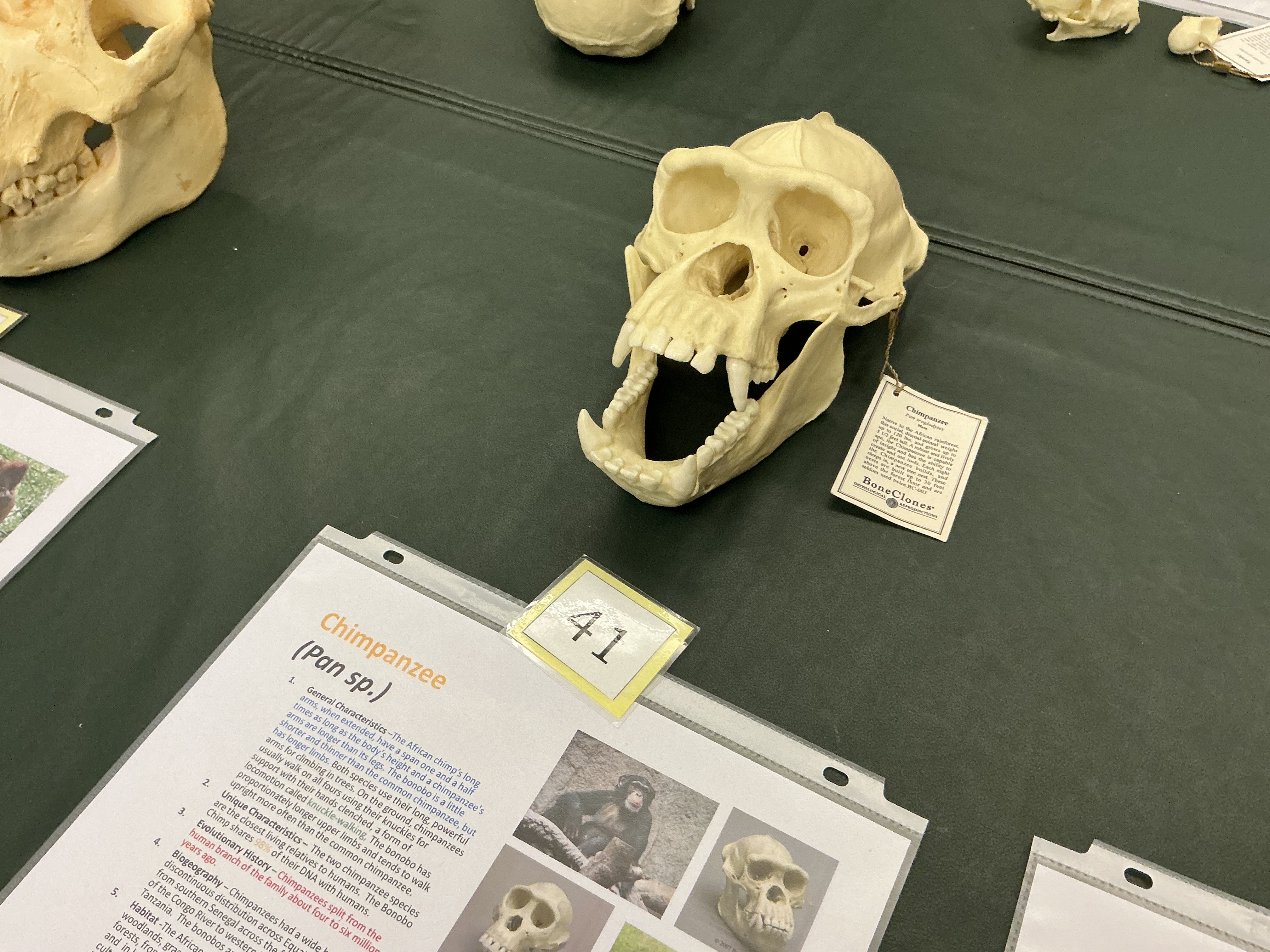

What did chimps split from human branch? How are they different from bonobos?
4-6 MYA; shorter limbs
What are chimp locomotion type called? How much DNA do humans share with bonobos?
Knuckle-walking; about 98%
African chimp diet type? bonobo?
omnivorous; frugivorous
What is the one char that separates hominids from other primates? Others?
Bipedalism; larger brain size
What does Australopithecus mean? First appeared when?
“southern ape”; 3.9 to 3.2 MYA early Pliestocene

What basic char are found in “Lucy”? Where are the fossils from?
bipedalism with primitive face; e. Africa
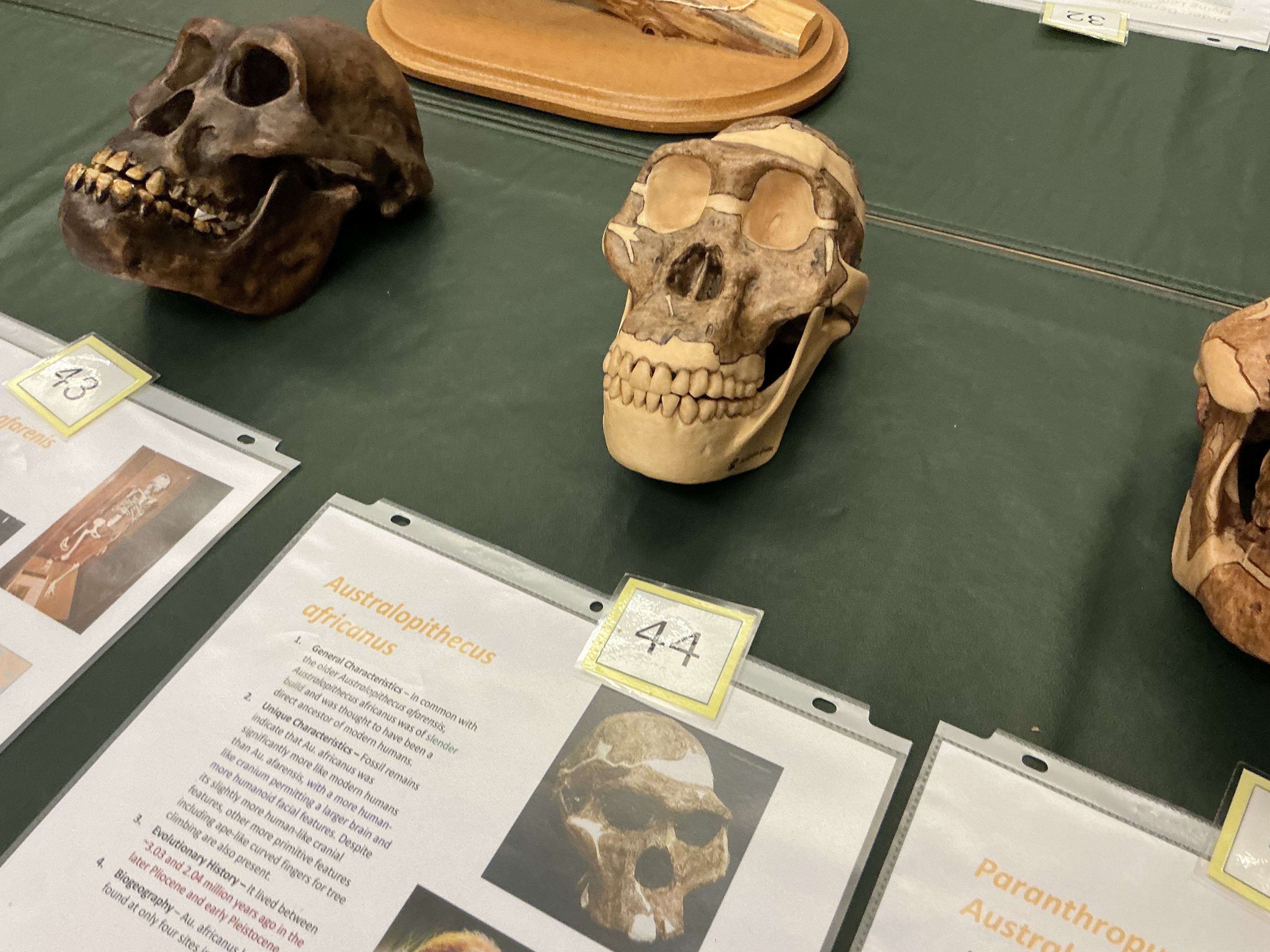

When did Australopithecus africanus appear? How are they similar to a. afarenis? Fossils from where?
3.03 to 2.94 MYA; slender build; s. Africa
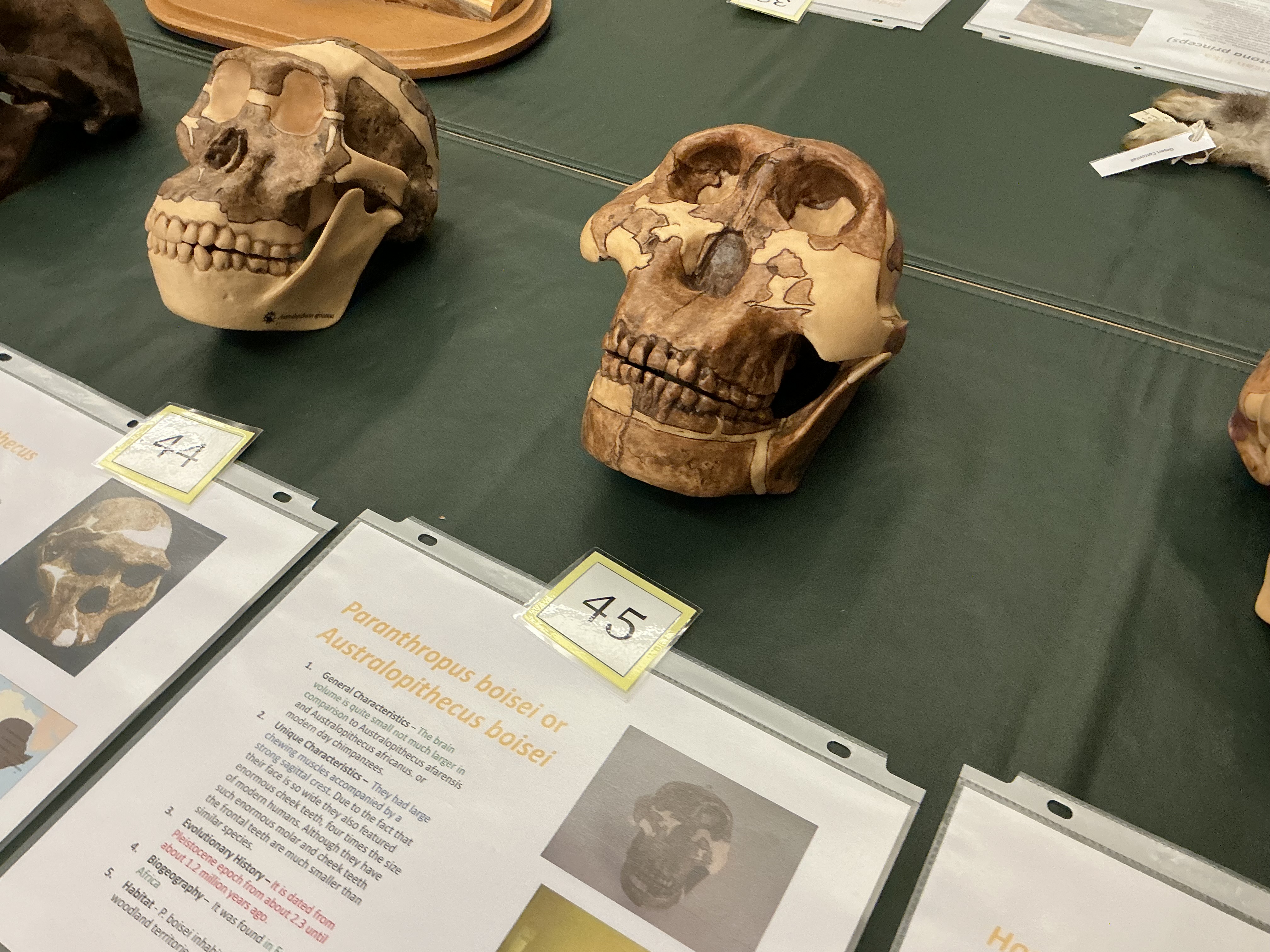

When do A. boisei appear? Brain size comparison? Uniqueness? From where?
2.3 to 1.2 MYA; smaller; large chewing muscles and strong sagittal crest; e. Africa
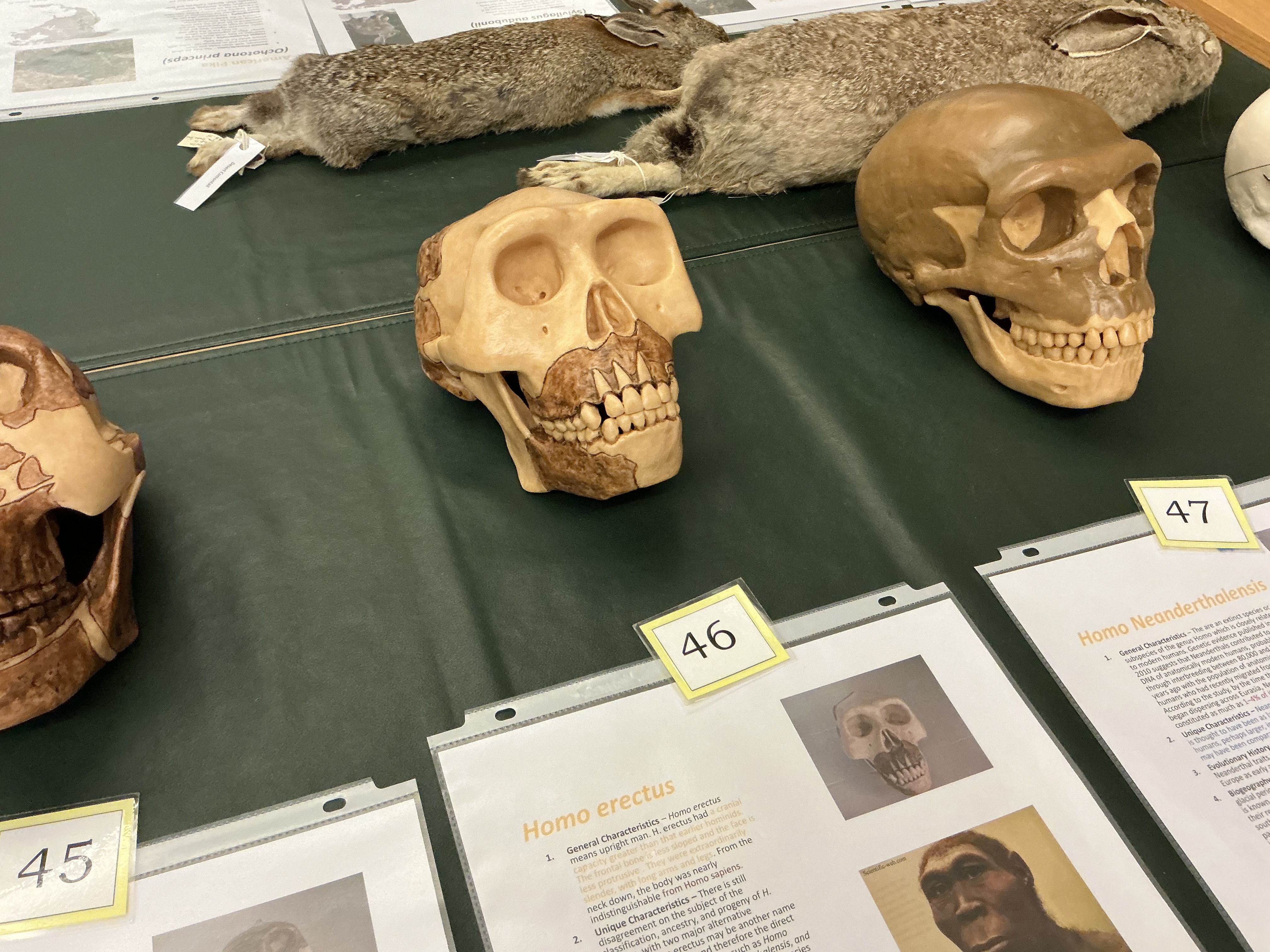

When did homo erectus appear? Name meaning? Look like what? Neck down resemblance? Found where?
1.8 MYA to 300,000 YA; upright man; similar to modern humans; more apelike; widely distributed

When do Neanderthals appear? How much of their genes constitute Eurasian population? Cranial capacity comparison?
600,000-350,000 MYA; 1-4% genes; larger than modern humans

When did homo sapiens appear? Char?
200,000-50,000 YA; large brain relative to body size
Shared char of all carnivores? Name meaning? When and where evolved?
carnassial/sectorial teeth; devour meat; 42 MYA in n Amer