BioChemistry
1/64
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Four macromolecules
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids
Dehydration Synthesis
builds polymers, removes water, forms covalent bonds
Hydrolysis
breaks polymers into monomers, adds water
Enzymes
speed up reactions
Ratio of C,H,O
1,2,1
Formula for glucose
C₆H₁₂O₆
Carb Function
Main energy source
Carb Monomer
Monosaccharide (glucose, fructose, galactose)
Disaccharide
2 monosaccharides (sucrose, maltose, lactose)
Carb Polymer
Polysaccharide (starch, glycogen, cellulose, chitin)
Carb Storage
Plants store glucose as starch. Humans store glucose as glycogen
Carb: Structural
Cellulose = plant cell walls
Chitin = insect exoskeletons
Nonpolar:
hydrophobic (doesn’t mix with water)
Lipid Monomers
Glycerol + Fatty acids
Lipid Polymers
Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Steroids, Waxes
Lipids Functions
Long-term energy storage, insulation, cushioning, hormones, cell membranes
Saturated fats =
single C–C bonds, solid
Unsaturated fats =
double C=C bonds, bent, liquid
Waxes
= prevent water loss (plants)
Phospholipids
= make up cell membranes (bilayer with hydrophilic heads, hydrophobic tails)
Steroids =
ring structure (cholesterol, estrogen, testosterone)
Protein Monomer
Amino acids (20 types)
Protein Bond
Peptide bond
Protein Functions
Transport (hemoglobin)
Immunity (antibodies)
Movement (actin/myosin)
Enzymes (catalysts like lactase)
Structure (collagen, keratin)
Protein Structure Levels
Primary = amino acid sequence (DNA codes this)
Secondary = coils (α-helix) or sheets (β-pleated) via H-bonds
Tertiary = 3D folding (R-group interactions, disulfide bridges)
Quaternary = multiple polypeptides together (hemoglobin, collagen)
R group
variable side chain that gives amino acids unique properties (polar, nonpolar, acidic, basic)
Nucleic Acid Monomer
Nucleotide
Nucleotide parts
Sugar, Phosphate, Nitrogen base
Nucleic acid Polymers
DNA, RNA, ATP
DNA
stores genetic info (double helix)
RNA
helps make proteins (single strand)
ATP
energy molecule (phosphate bonds release energy when broken)
Sugar in RNA
Ribose
Sugar in DNA
Deoxyribose
Hydroxyl (–OH)
polar, H-bonds → carbs, proteins
Carbonyl (C=O)
polar, reactive → carbs, nucleic acids
Carboxyl (–COOH)
acidic (–COO⁻ at pH 7) → proteins, lipids
Amino (–NH₂)
basic (–NH₃⁺ at pH 7) → proteins, nucleic acids
Sulfhydryl (–SH)
forms disulfide bridges → proteins (cysteine)
Methyl (–CH₃)
nonpolar, hydrophobic → lipids, proteins (gene regulation)
Phosphate (–PO₄²⁻)
acidic, negative charge → nucleic acids, ATP, phospholipids
Quick energy
monosaccharide
Stored energy
polysaccharide (short-term), lipids (long-term)
Strong nails/hair
protein (keratin)
Bigger muscles
protein
Immunity boost
protein (antibodies)
Cell membranes
lipids (phospholipids, cholesterol)
What are the four main types of Polysaccharides and what are their uses?
Starch: stored energy in plant cells. Plants stockpile extra glucose
Glycogen: Stored energy in animals cells. Do not last as long.
Cellulose: Structural support in cell walls (plants). Humans cannot digest
Chitin: Structural support for insects, crustaceans’ exoskeletons.
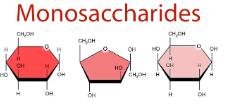
What are these carb monosaccharides?
Glucose, Fructose, Galactose
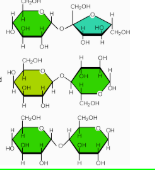
What are the three important Disaccharides
Sucrose, Lactose, Maltose
Major Categories of Lipids
Storage Lipids
Fats: Fatty acid(s) & glycerol
Structural Lipids
Phospholipids
Waxes
Steroids
-Cholesterol
-Hormones
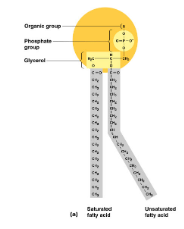
What is this?
Phospholipids
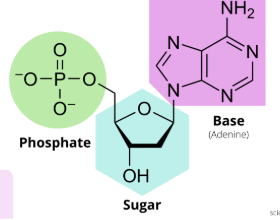
What is this the structure of?
Structure of nucleotide
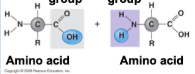
What groups are the two highlighted?
Carbpxyl group, Amino group
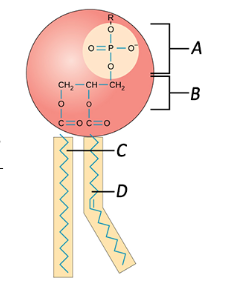
Label the phospholipids
A = Phsophate
B = Glycerol
C = Saturated Fat
D = Unsaturated Fat
3 components of a nucleotide?
A phosphate group, sugar group, and a base
What sugar is found in RNA?
Ribose
What is a peptide bond
A peptide bond is a covalent bond linking the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of another, formed by dehydration synthesis, which releases a water molecule
Hydroxyl (–OH):
polar, H-bonds → carbs, proteins
Carbonyl (C=O):
polar, reactive → carbs, nucleic acids
Carboxyl (–COOH):
acidic (–COO⁻ at pH 7) → proteins, lipids
Amino (–NH₂):
basic (–NH₃⁺ at pH 7) → proteins, nucleic acids
Sulfhydryl (–SH):
forms disulfide bridges → proteins (cysteine)
Methyl (–CH₃):
nonpolar, hydrophobic → lipids, proteins (gene regulation)
Phosphate (–PO₄²⁻):
acidic, negative charge → nucleic acids, ATP, phospholipids