Plant Phylogeny Review Flashcards
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of flashcards to help understand key terminology and concepts related to plant phylogeny and development.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
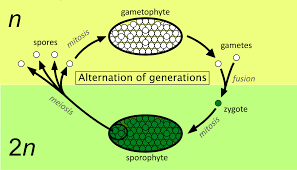
Haplodiplontic
A type of plant life cycle that includes both a haploid and diploid multicellular stage.
Gametophyte
The haploid stage in the plant life cycle that produces gametes.
Sporophyte
The diploid stage in the plant life cycle that produces spores.
Heterospory
The production of two distinct types of spores by a plant; megaspores and microspores.
Homospory
The production of one type of spore that is usually identical in shape and size.
Phylogeny
The evolutionary history and relationships among a group of organisms.
Cladogram
A diagram that shows the evolutionary relationships among species based on shared derived characteristics.
Viridiplantae
The monophyletic group that includes both green algae and land plants.
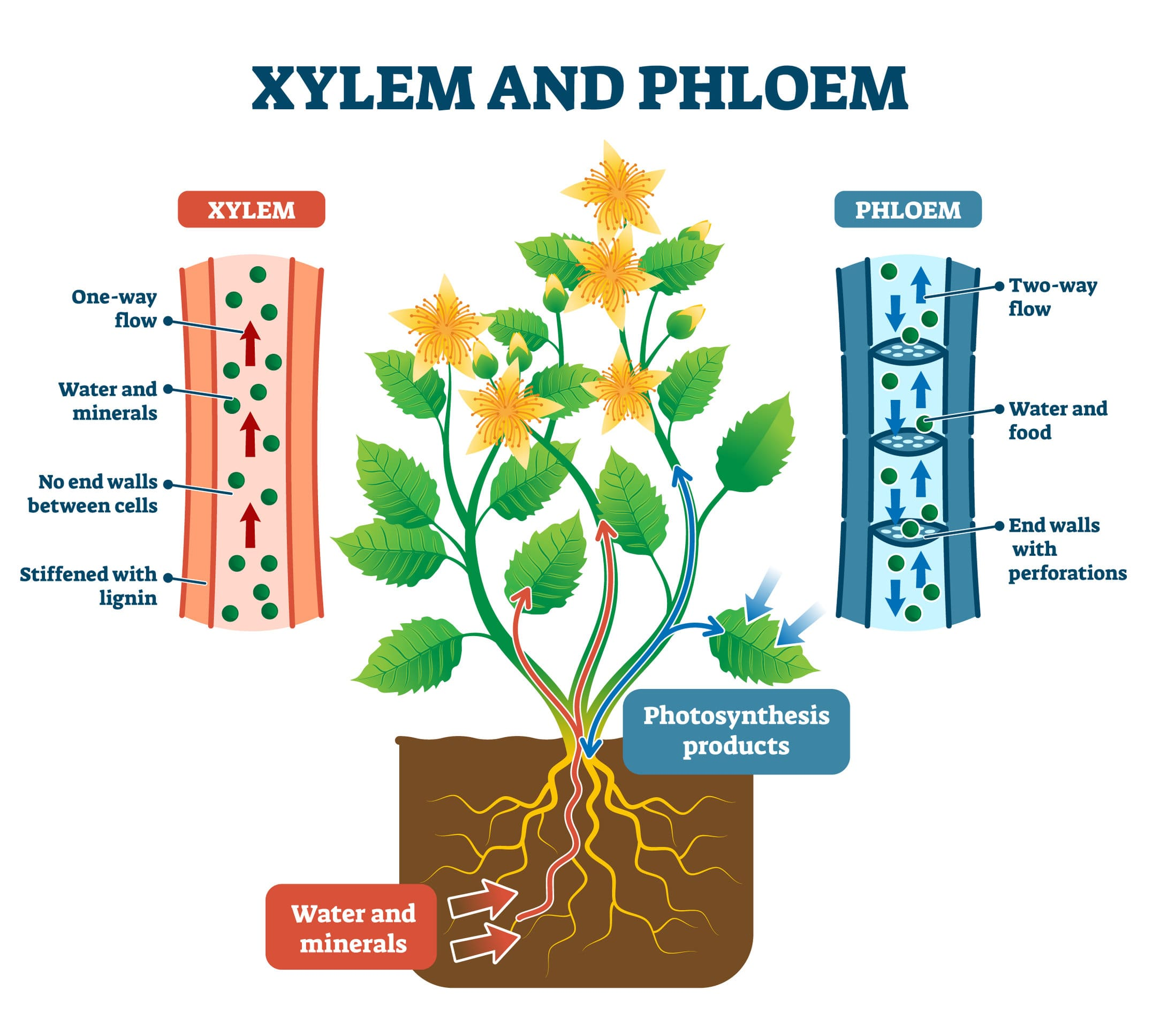
Vascular Tissue
Specialized tissue in plants (xylem and phloem) responsible for the transport of water, nutrients, and sugars.
Xylem
Vascular tissue that transports water and minerals from the roots.
Phloem
Vascular tissue that transports sugars and nutrients throughout the plant.
Sporangium
A specialized structure where spores are produced.
Endosperm
Nutritive tissue in seeds that provides energy for the developing embryo.
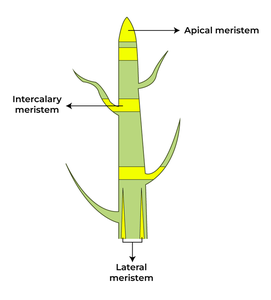
Apical Meristem
Regions of active growth in plants located at the tips of roots and shoots.
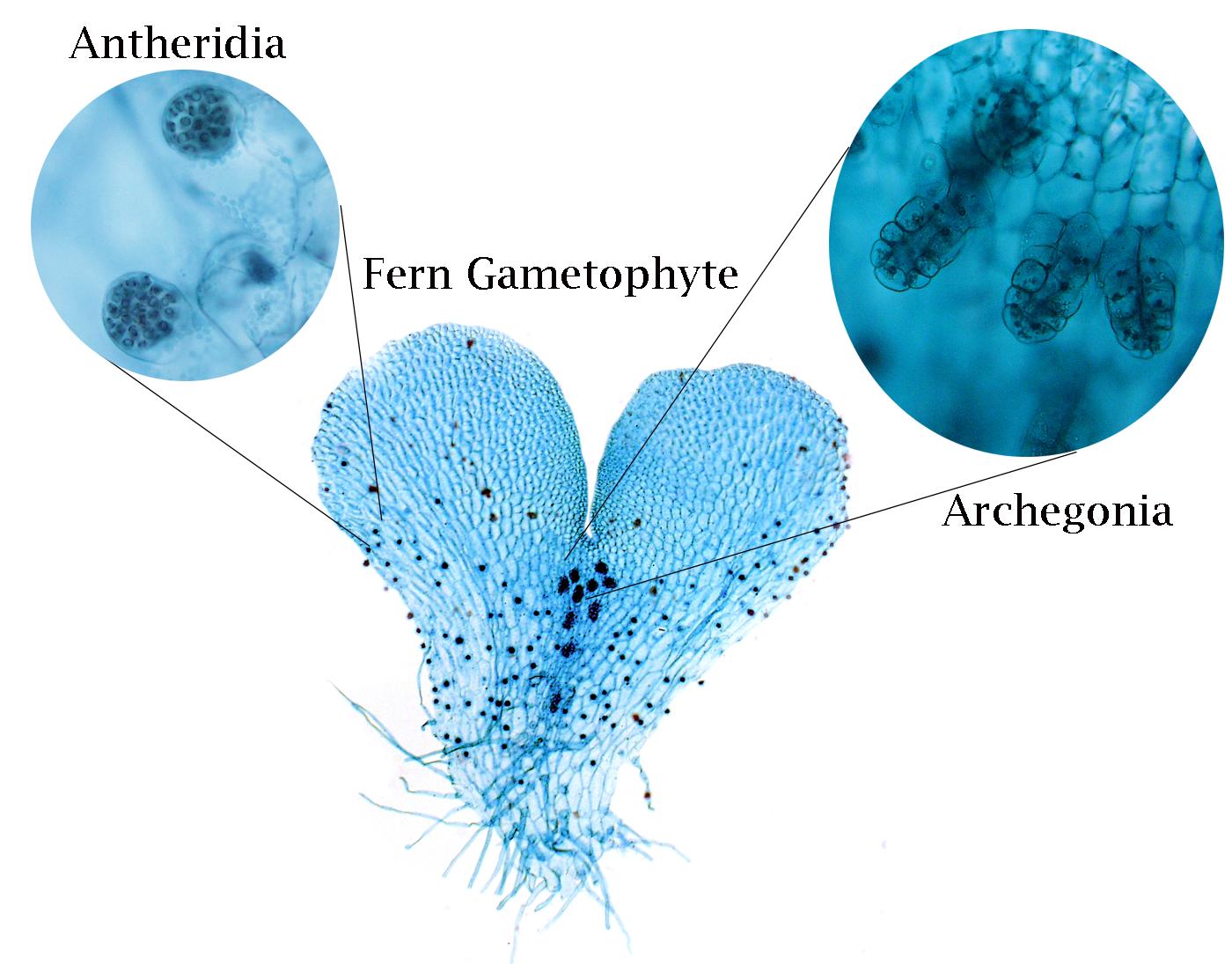
Archegonia
Female gametangium that produces eggs in plants.
Antheridia
Male gametangium that produces sperm in plants.
Seed Coat
The protective outer layer of a seed.
Pollination
The transfer of pollen from the male anther to the female stigma.
What is the term for a tree depicting evolutionary relationships?
Phylogeny or cladogram.
What is the monophyletic group that includes green algae and land plants?
Viridiplantae.

What are the six major phyla covered in Lab 5?
Hepatophyta, Bryophyta, Lycophyta, Monilophyta, Coniferophyta, Anthophyta.
Which phylum includes flowering plants?
Anthophyta.

What is the life cycle of most plants called?
Haplodiplontic life cycle (alternation of generations).
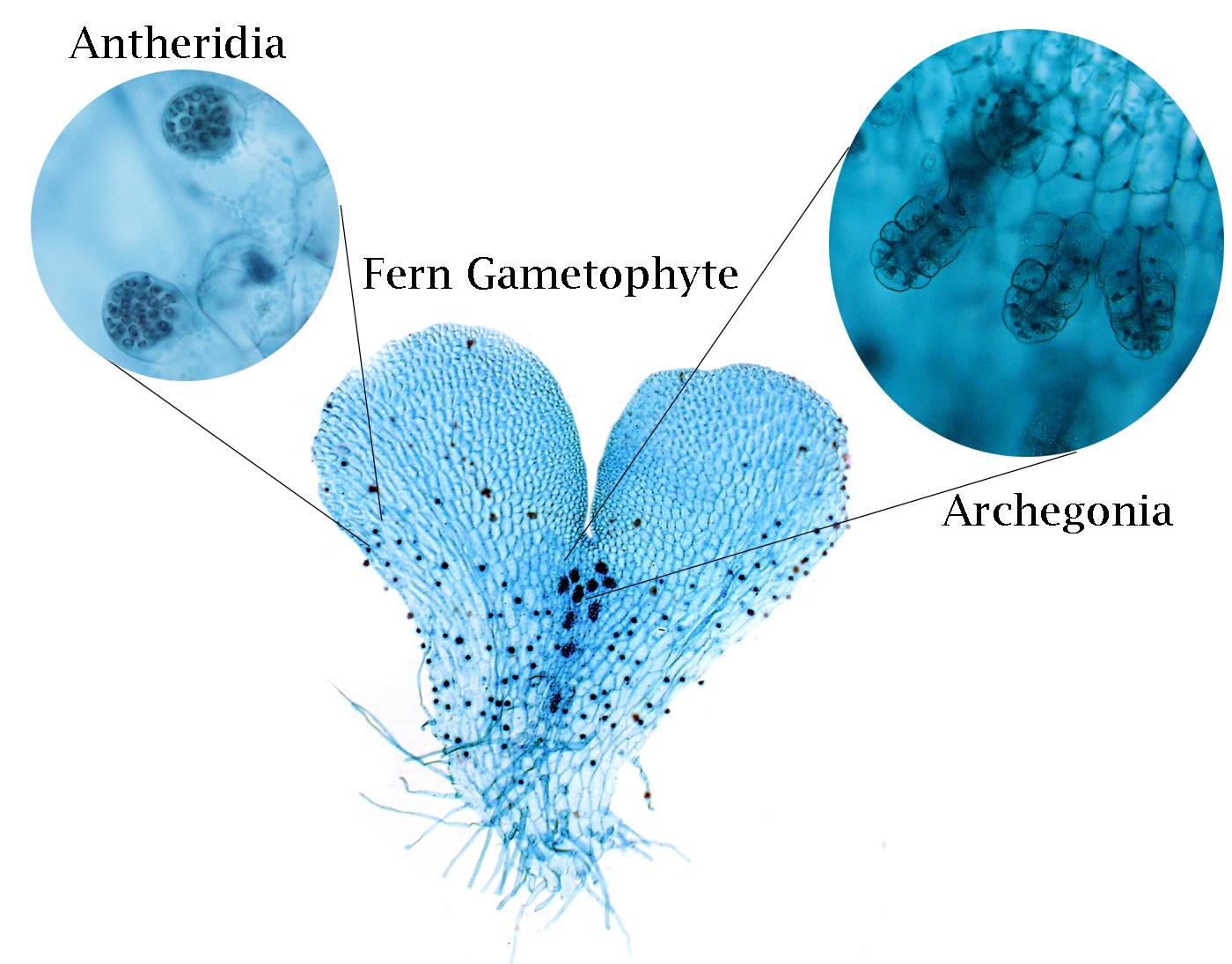
Where are eggs produced in plants?
Archegonia.
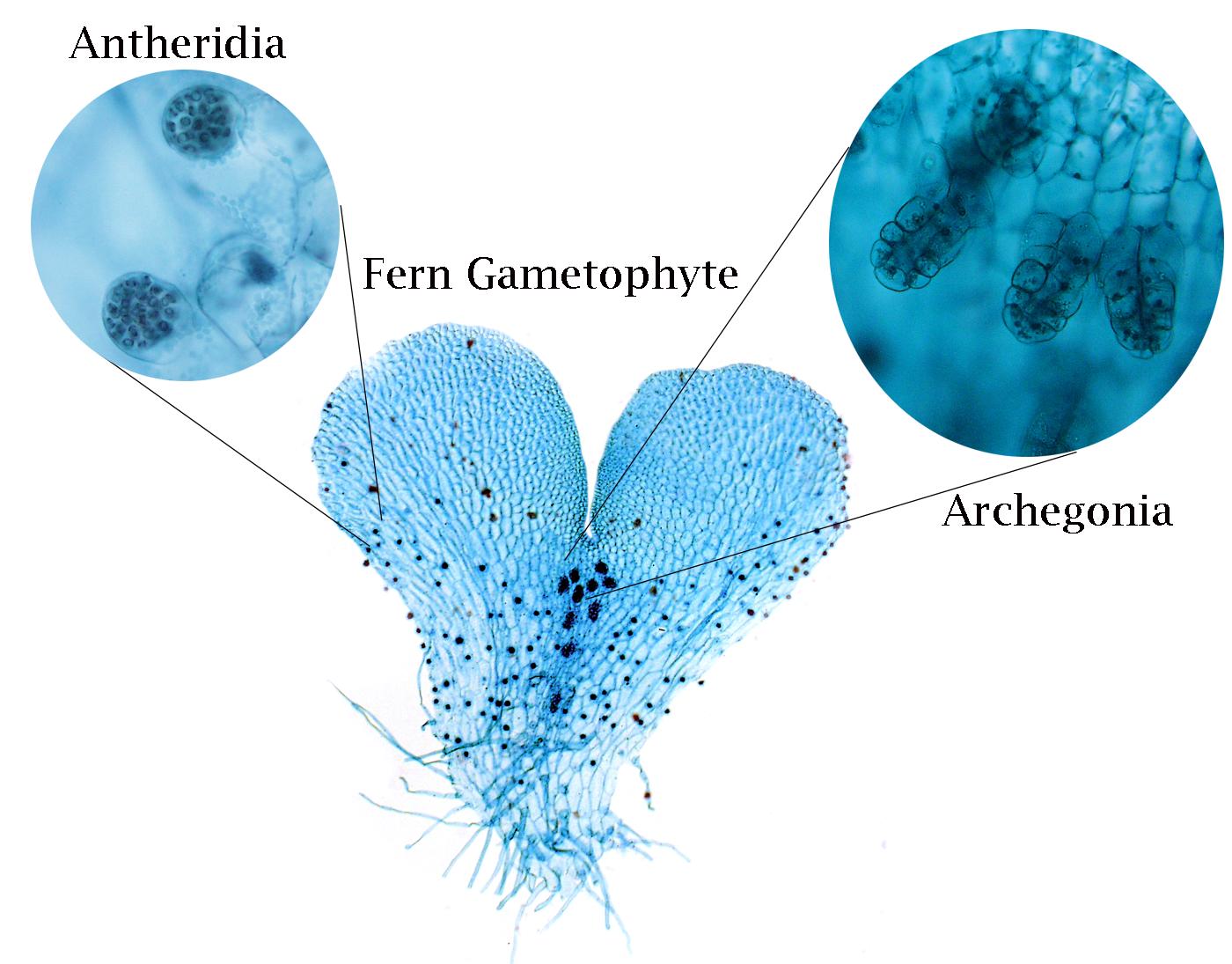
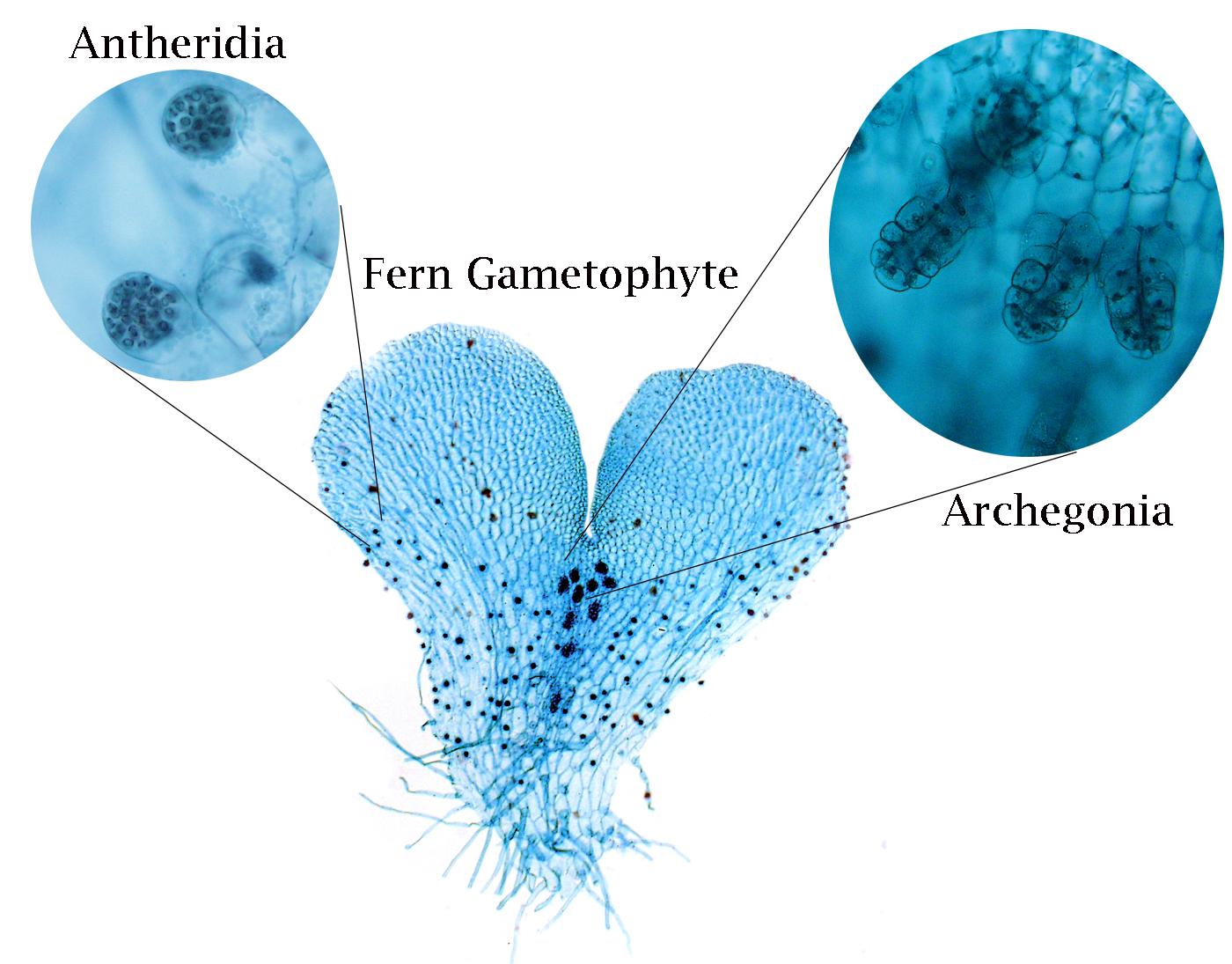
What structure produces sperm in plants?
Antheridia.
What transports water and minerals in vascular plants?
Xylem
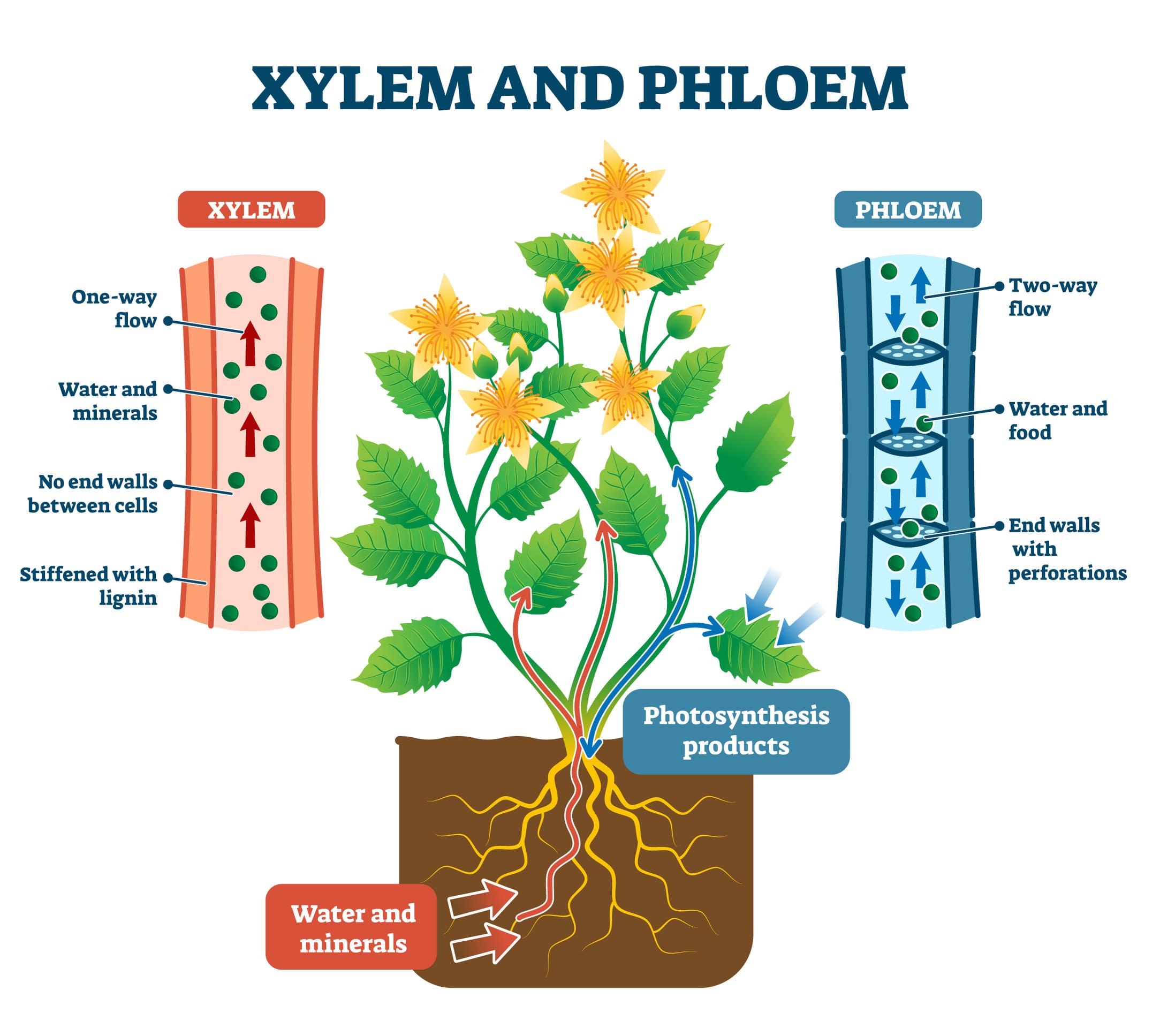
What transports sugars throughout the plant?
Phloem.
What is the evolutionary advantage of seeds?
Protection and nourishment of the embryo.
What substance provides nutrients inside a seed?
Endosperm.
What are the two main types of seed plants?
Gymnosperms and angiosperms.
How are gymnosperm seeds different from angiosperm seeds?
Gymnosperm seeds develop exposed on cones, while angiosperm seeds develop within fruit.
Which phylum includes cone-bearing trees?
Coniferophyta
What are the two types of cones in gymnosperms?
Ovulate cones (female) and pollen cones (male).
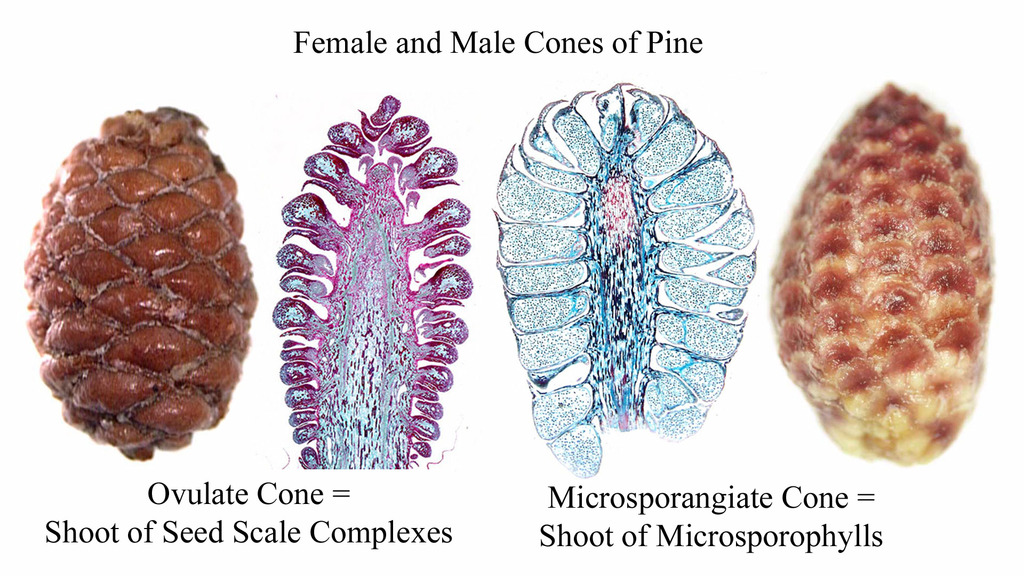
What structure carries pollen in conifers?
Pollen grains with air sacs for wind dispersal.
What is unique about angiosperm fertilization?
Double fertilization—produces zygote and triploid endosperm.
What is the function of fruit in angiosperms?
Seed dispersal.
How do monocots differ from eudicots?
Monocots have one cotyledon, flower parts in multiples of 3; eudicots have two cotyledons, flower parts in multiples of 4 or 5.
What is the name for flowering plants?
Angiosperms.
What initiates germination?
Uptake of water and the activity of gibberellins.
What is the function of gibberellins?
Promote germination and stem/root elongation.
What are the two types of meristems?
Root Apical Meristem (RAM) and Shoot Apical Meristem (SAM).
What type of growth increases length?
Primary growth.
What type of growth increases girth?
Secondary growth
What are the three major tissue types in plants?
Dermal, vascular, and ground tissues.
What is the outer protective layer of plants?
Dermal tissue (epidermis or periderm)
Which tissue conducts water and minerals?
Xylem
Which tissue conducts sugars and organic materials?
Phloem
What are the three types of ground tissue?
Parenchyma, Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma.
What is the primary function of leaves?
Photosynthesis.
What structure allows gas exchange in leaves?
Stomata
How do trichomes protect plants?
They reduce water loss and deter herbivores.
What are the three main plant organs?
Roots, stems, and leaves.
What type of leaves are adapted to reduce water loss?
Leaves with thick cuticles, fewer stomata, or trichomes
What type of plants complete their life cycle in one year?
Annuals
What type of plants take two years to complete their life cycle?
Biennials
What type of plants can live and reproduce for multiple years?
Perennials
Which of the following plant phyla includes mosses?
Bryophyta
Hepatophyta includes
liverworts, which are also non-vascular but not mosses
What structure produces sperm in non-vascular plants?
Antheridia
Microsporangium is related to
seed plants and produces microspores that develop into male gametophytes (pollen grains).
In gymnosperms, which structure contains the female gametophyte?
Ovule
What feature distinguishes monocots from eudicots?
Number of cotyledons
Which of the following groups does not produce seeds?
Lycophyta
What is the result of double fertilization in angiosperms?
Embryo and triploid endosperm
What type of growth increases the girth of woody plants?
Secondary growth
Which of the following is a characteristic of gymnosperms?
Naked seeds
What is the function of the cuticle on leaves?
Prevent water loss
What is the function of trichomes on leaves?
Protect against herbivores and water loss
Which type of ground tissue provides flexible support in growing plant parts?
Collenchyma
In which structure does fertilization occur in angiosperms?
Ovary
Which type of plant has a life cycle that spans more than two years?
Perennial
What is the primary function of the root cap?
Protects the root apical meristem