Memory
1/85
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
long term memory (LTM)
found the average span was 9.3 for digits and 7.3 for numbers
said that 5 words can be recalled as easily as 5 letters due to chunking - grouping sets of digits or letters into units or chunks to aid recall
size of the chunk - simon (1974) said there may be a shorter memory span for larger chunks, e.g. phrases
individual differences - jacobs (1887) said digit span increases with age, could be due to an increase in brain capacity or development of strategies such as chunking
coding for STM is acoustic
coding for LTM is semantic
1) acoustically similar words
2) acoustically dissimilar words
3) semantically similar words
4) semantically dissimilar words
participants were shown the original words and asked to recall them in the same order
when asked to recall immediately, they did worse with acoustically similar words
when asked to recall 20 minutes later, they did worse with semantically similar words
what is the evaluation of coding?
baddeley - may not be testing LTM, as it was performed in a laboratory setting with artificial stimuli
STM may not be exclusively acoustic - brandimok et al (1992) showed that visual coding is used for visual tasks when there was not verbal rehearsal in the retention period
LTM may not be exclusively semantic - frost (1972) showed long-term recall is related to visual categories as well as semantic, nelson and rothbart (1972) found evidence of acoustic coding in LTM
duration for STM is around 18-30 seconds
duration for LTM is unlimited
what did bahrick (1975) find about LTM duration?
tested the duration of LTM
used graduates of a high school aged 17-74 - tested recall using a yearbook
tested 2 types of recall
free recall - participants recalled names of individuals in their class, if they had left 15 years ago this had 60% accuracy, if they had left 48 years ago this had 30% accuracy
photo recognition - participants recalled the names of individuals whilst looking in their pictures, if they had left 15 years ago this had 90% accuracy, if they had left 48 years ago this had 70% accuracy
showed the length of time since attendance impacted the success of recall
low levels of control - many variables that could have affected recall, e.g. rehearsal (looking at yearbook) and popularity
participants were given a trigram (3 letters) and then told to count back from a 3 digit number until told to stop - could be for 3, 6, 9, 12, 15 or 18 seconds (retention interval)
they were then told to recall the trigram - recall was best after a retention interval of 3 seconds and worst for 18 seconds
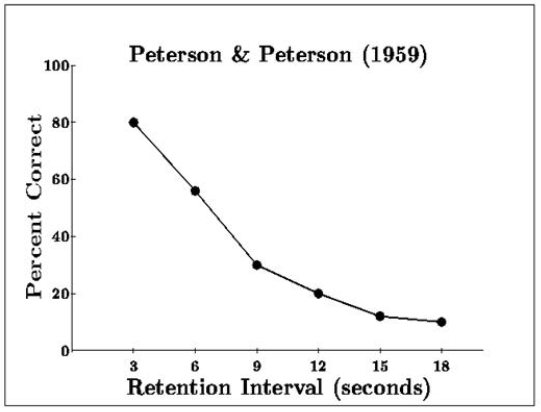
displacement - may be that the letters are displaced by the counting, rather than forgetting the information
describes how information moves through the memory stores
suggests memory is made up of three stores linked by processing
STM
LTM
has 2 main sensory stores:
1) ionic (visual)
2) echoic (auditory)
capacity is very large - the sensory register receives lots of different information, but not all of it receives attention so it doesn’t move to STM
duration is very short (milliseconds)
maintenance is performed to maintain information in STM - information is repeated over and over to remember it
capacity is 7 +/- 2 - miller’s magic number
duration is 18-30 seconds
in order to recall something from LTM, information is transferred back to STM - retrieval
capacity is unlimited
duration is unlimited
following the surgery he lost the last 10 years of his memories, and could no longer make long-term memories - his memory only lasted for the duration of STM
participants were given a list of 20 words and asked to recall them from memory
they remembered the words at the beginning of the list - due to primacy effect (they are able to rehearse these words and transfer them to LTM)
they remembered the words at the end of the list - due to recency effect (words had not yet been lost from STM)
serial position effect - primacy and recency effect supports how information moves from sensory register to STM and LTM
model is too simple - defines STM and LTM as single stores, alternative models suggest STM and LTM are divided, model has a limited explanation
maintenance vs elaborative rehearsal - may be more than one type of rehearsal, maintenance keeps information in STM and elaborative is needed to transfer information to LTM (adds information/links it to other information in LTM)
semantic
procedural
memories are ‘time-stamped’ - remember when they happened
memories have multiple elements - e.g. surroundings, objects, people present
context may also be remembered as well as emotions felt
memories are not ‘time-stamped’
less personal and easily shared with other people
may start as episodic memories as they are learnt based on personal experiences - as associations with events are lost, they become semantic
can be recalled with little effort - many become automatic, e.g. tying a tie or shoelaces
might find these skills difficult to explain to others
neuroimaging evidence - different types of memories are stored in different areas of the brain, tulving (1994) PET scans
real life applications - can help people’s lives in a positive way and develop treatments, e.g. belleville (2006) showed episodic memories can be improved in older people with mild cognitive impairments
distinguishing between episodic and semantic - possibility of forming semantic memories without them being episodic first, e.g. hodges and patterson (2007), irish et al (2011)
declarative memory - cohen and squire said episodic and semantic memories are in one store called declarative memory, and procedural memories are non-declarative
explanation of how STM is organised
concerned with the part of the mind that temporarily stores and manipulates information
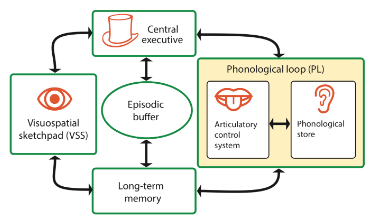
monitors incoming data, makes decisions, allocates slave systems (3 middle components) to tasks
coding is not limited - different information is coded in different ways
capacity is limited - CE can’t attend to too many things, no capacity for storing data
deals with auditory information and preserves the order in which information arrives
divided into 2 parts:
1) phonological store - inner ear, stores words you hear
2) articulatory process - inner voice, words that are heard or seen, silently repeated as a form of maintenance rehearsal to keep them in working memory
capacity is 2 seconds
stores visual and/or spatial information
logie (1999) - can be split into 2 parts:
1) visual cache - stores visual data
2) inner scribe - records arrangement of data in the visual field
capacity is limited - around 3-4 objects
temporary store for information - integrates visual, spatial and verbal information
maintains a sense of time sequencing - recording events that are happening
storage component of the CE and links working memory to LTM and wider cognitive processes
capacity is limited - around 4 chunks
brain scans - braver el al (1997), greater activity in the left prefrontal cortex when the CE was engaged
KF case study - poor STM for verbal information, but not for visual information, phonological loop was damaged
unclear about role of CE - may have separate components, EVR case study
unclear link between WMM and LTM - does not specify how information moves to LTM, LTM present but not explained
musical memory - can listen instrumental music and complete acoustic tasks, should not be possible
lab experiments and case studies - artificial stimuli, lack external validity, can’t generalise case studies
WMM - has many short term stores that process information differently as directed by the CE
WMM - suggests previous experiences stored in LTM have an influence on STM
what is the comparison of research support in the MSM and WMM?
MSM - murdock’s serial position effect (primary and recency effects), HM (could not transfer information from STM to LTM)
WMM - baddeley and hitch (1976) said that one store can’t do two tasks, KF had poor STM for verbal but good for visual (only phonological loop was damaged)
retrieval failure
retroactive interference - when a newer memory interferes with an older one
mcgeoch and mcdonald (1931)
baddeley and hitch (1977)
participants had to remember a list of paired words from list A and list B
the experimental group were then another list of paired words from list A and list C
the control group were not given this second list
all participants had to recall the words on list A and list B - the recall of the control group was more accurate than the experimental group
showed the words from the second list interfered with the ability to recall the first list
participants learnt a list of 10 words until they were 100% accurate
they then learnt a new list of words - antonyms, synonyms, unrelated words, nonsense syllables, 3 digit numbers or no new list
recall of the first list depended on the second list - the more similar the list, the more interference occurred and worse performance was
rugby players were asked which teams they had played so far in the season - some players had missed games
accurate recall depended whether the players had played games since
showed retroactive recall
artificial materials - greater chance interference will be displayed in a lab, studies have low ecological validity, interference in everyday life may not be as strong as in a lab
interference only explains some situations of forgetting - the two memories need to be similar, anderson (2000) showed the extent of interference in forgetting is unclear
accessibility vs availability - interference could be temporary,
can be meaningful or indirectly linked by being encoded at the time of learning - stored in memory at the same time as information
there are two types of cues:
1) external cues - context dependent learning
2) internal cues - state dependent learning
if the cues available at encoding and retrieval are different, there will be some forgetting
godden and baddeley (1975)
tulving and posta (1971)
1) in the same room they had learnt the information in with the same instructor
2) in the same room they had learnt the information in with a different instructor
3) in a different room with the same instructor
4) in a different room with a different instructor
found that those tested in the same room with the same instructor performed best
1) learn on land, recall on land
2) learn on land, recall underwater
3) learn underwater, recall on land
4) learn underwater, recall underwater
accurate recall was 40% lower in the non-matching conditions
what did tulving and posta (1971) find about cues?
participants were given 6 word lists of 24 words in 6 categories
after each list was presented, participants were asked to write down what they remembered, and after all of the lists were presented, there was a final recall of all of them - free recall
they were then given the categories of the lists and asked to recall what they could - cued recall
some participants had more lists than others, and those with more lists had worse performance - retroactive interference
when participants were given cues, effects of interference disappeared - remembered 70% of words regardless of the number of lists
suggested cues are more important than interference in explaining forgetting
research studies:
carter and cassaday (1998) - tested learning and recall using antihistamines, performance was worse when conditions didn’t match
goodwin (1969) - people who drank a lot they forgot where things were when they were sober, but when they drank again they could recall the locations
miles and hardman (1998) - people who learned words on an exercise bike recalled them better when exercising
real life applications - smith (1979) said remembering the room the information was learnt in can assist recall
research support for importance of cues in recall - cues could be the biggest factor in forgetting from LTM
recall vs recognition - retrieval failure doesn’t apply to recognition, can’t explain why people forget this type of memory
cues don’t always work - effectiveness depends on the complexity of the memory
environments have to be very different for retrieval failure to have a significant effect
anxiety
can affect the accuracy of EWT as information used after an event can have a retroactive interfering effect on recall
participants watched the video and then answered questions about the speed of the car, with different verbs describing the crash - 'how fast were the cars going when they hit/smashed/collided/bumped/contacted each other?'
estimates varied based on the verb used - estimates were highest for ‘smashed’ and lowest for ‘contacted’
participants watched a video of a car crash and were placed in three groups:
1) were interviewed after and asked a question with the verb 'hit'
2) were interviewed after and asked a question with the verb 'smashed'
3) were not interviewed after
a week later they were asked a question about seeing any broken glass in the video when there had been none - positive answers for broken glass was highest for the 'hit' group and lowest for the control group
this is because they combine information and misinformation from other witnesses with their own memories
eyewitness can recall information about the event (both accurate and inaccurate) but can’t recall where it came from - source confusion
eyewitness recall only appears to change because they go along with the accounts of co-witnesses - social desirability bias or because they genuinely believe that other witnesses are right and they are wrong
what did gabbert (2003) find about post event discussion?
looked at post event discussion
participants watched videos of the same crime from different points of view - each participant could see elements that others could not
the participants engaged in post-event discussion
found 71% of participants recalled aspects of the video that they didn't see but had picked up in the discussion - a control group with no discussion had 0% in comparison
artificial tasks - studies are in lab settings and they only watch a video, lacks ecological validity
response bias - individuals are biased to certain expectations, misleading information can impact bias and affect recall
individual differences - memory is biased towards certain information, misleading information can be quite powerful
there is research support for anxiety making eyewitness recall both better and worse
what did johnson and scott find about weapon anxiety?
investigated the effect of weapon anxiety on recall
participants heard an argument in another room whilst in the waiting room in one of two conditions:
low anxiety condition - participants heard the argument then saw a man holding a pen with grease on his hands
high anxiety condition - participants heard the argument, then heard breaking glass and saw a man holding knife covered in blood
participants later picked the man out of a set of 50 photos - 49% of the low anxiety participants correctly identified him compared to 33% of the high anxiety participants
fight or flight is triggered - increases alertness and improves memory for the event, creating awareness of cues in the situation
they were interviewed 4-5 months after the incident, and these interviews were compared with the original police interviews
witnesses also rated how stressed they had felt on a 7 point scale
there was little change in levels of accuracy - participants who reported higher stress levels were 88% accurate, compared to 75% for the less stressed group
the relationship between emotional arousal and performance looks like an upside down U
deffenbacher (1983) - applied the yerkes-dodson law to EWT, found as anxiety increases memory becomes more accurate, but there is a point where the optimum level of anxiety is reached, and if an eyewitness experiences more stress than this, recall declines
weapons focus effect - not necessarily anxiety, could be surprise, pickel study, hair salon with raw chicken
alternative model - after the optimum level, anxiety doesn’t decline gradually, but rapidly due to mental effects (catastrophe theory)
lab studies - more vulnerable to demand characteristics, participant changes behaviour after figuring out experiment
neutral/field experiments lack control
said EWT could be improved by better interviewing techniques
based on psychological insights into memory
order
perspective
everything
(ROPE acronym)
they try to recall the environment and their mood
prevents people reporting expectations of how the events must have happened
disrupts the effect of expectations and schema on recall
seemingly trivial details may be important or trigger other memories
leading questions - cognitive interview does not use leading questions so recall is improved
includes reducing eye witness anxiety, minimising distractions, getting the witness to speak slowly, asking open-ended questions
inaccurate information - increases the amount of inaccurate information (61%) as well as accurate information (81%)
some elements more valuable - reinstate context and report everything are the best combination of techniques
time consuming - requires training and longer interviews