UWorld MCAT QBank
1/320
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
321 Terms
racialization
one group designates another group with a racial identity, often based on shared group qualities, such as physical attributes (eg, skin pigmentation) or behaviors (eg, religious practices)
designating group has more social power (dominant group) and exerts social control over the designated group, which has less social power (subordinate group).
stereotype threat
a self-confirming concern that one will be evaluated based on a negative stereotype
example: awareness of the stereotype "women are bad at math" before a math task hinders women's performance
cultural transmission
the process by which one generation passes culture to the next
normative organization
an organization where membership is based on morally relevant goals (volunteers)
false consciousness
situation in which people in the lower classes come to accept a belief system that harms them; the primary means by which powerful classes in society prevent protest and revolution
hidden curriculum
informal and unofficial aspects of culture that children are taught in school
humanistic psychotherapy
a type of therapy that focuses upon the more POSITIVE aspects of human beings in general and rejects the medical model
emphasis upon maladaptive personality traits, and the labeling of individuals as pathological
According to the early theory of emotion described in the second paragraph, which of the following brain structures is most critical to the experience of emotion?
hypothalamus
responsible primarily for the physiological component of emotion, such as changes in heart or respiration rate
cingulate gyrus
emotional processing/memory
escape learning vs avoidance learning
escape learning seeks to reduce the unpleasantness of something that already exists
avoidance learning is meant to prevent the unpleasantness of something that hasn't happened yet
Habituation vs. Sensitization
habituation: decreased response to a stimulus over time
sensitization: increased response to a stimulus over time
secondary reinforcer
neutral object that becomes associated with a primary reinforcer
top-down processing
guided by information, beliefs, or ideas already stored in our brain
bottom-up processing
often sensory information
95% confidence intervals for the two experimental groups are shown to overlap,
implying that the difference may or may not be statistically significant
left hemisphere of brain
controls touch and movement on the right side of the body
urea
induces UNFOLDING of proteins
average weight of single amino acid
110 Da
statistically significant
if p < .05
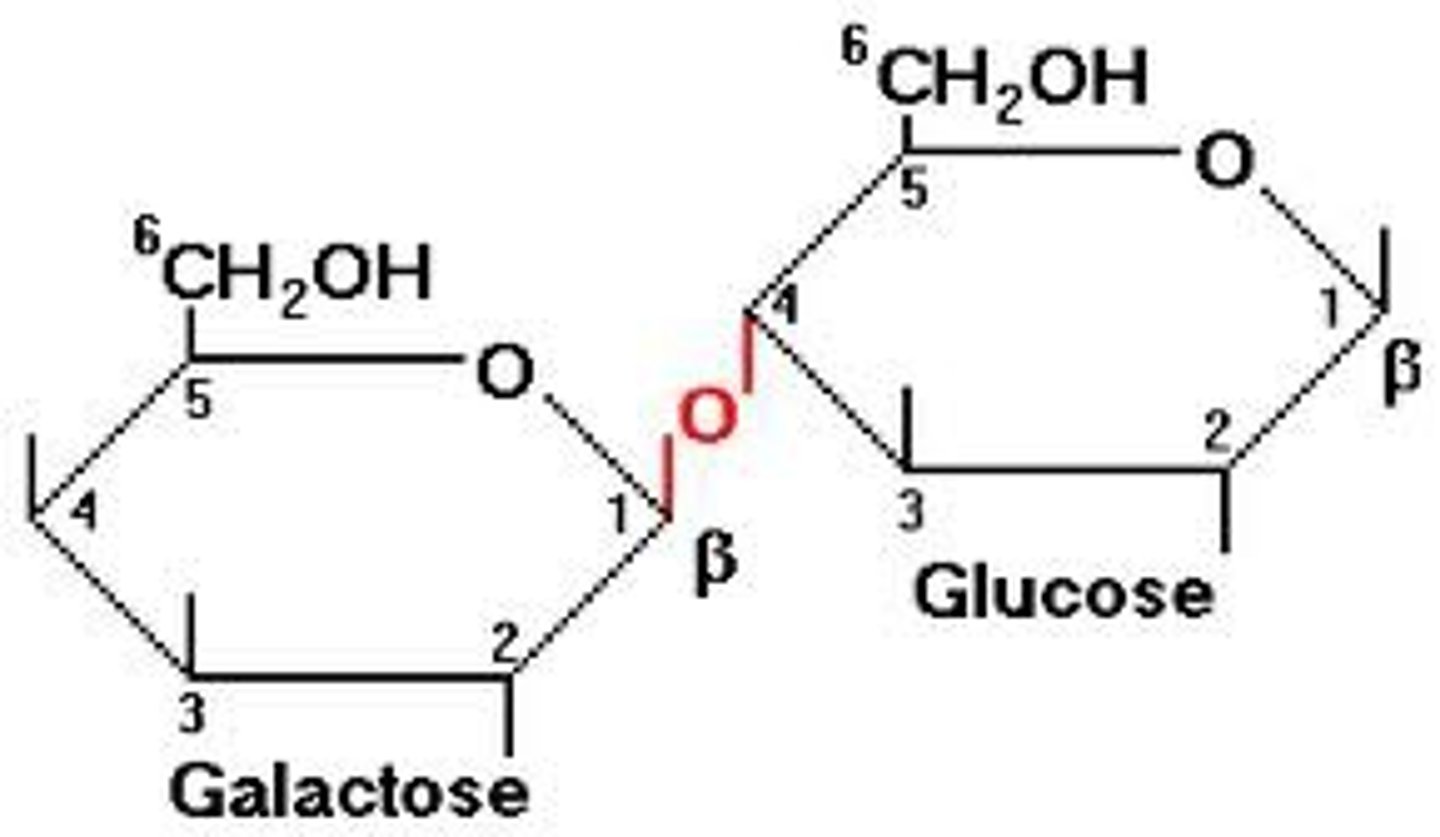
glycosidic bond
carbohydrate binds to another group, which could also be a carbohydrate. A glycosidic bond is found between the two glucose molecules in maltose.
sphingolipid
one fatty acid
structural
Acetylation of lysine residues in histones increases gene expression because:
the salt bridges between charged amino acids and phosphate groups are disrupted
DNA unwinds and becomes more accessible to transcription machinery
muscle tissue
not connective
Which of the following sequences accurately describes the pathway of communication between neurons?
Axon, synapse, dendrite, soma
prostaglandin
produce a localized inflammatory response
coordination number
number of ions of opposite charge that surround each ion in a crystal
atria
pump blood intro ventricles
left ventricle
pumps oxygenated blood into the aorta
heart circulation
vena cava -> RA -> RV -> pulmonary valve -->pulmonary artery to lungs (become oxygenated)
pulmonary veins -> LA -> LV -> aorta -> body
Which series depicts the order in which the precursors of steroid hormones are synthesized?
Isoprene → monoterpene → squalene → cholesterol
Michaelis-Menten equation
v = (vmax [S])/ (Km+[S])
higher Km
lower affinity for substrate
Amino acid catabolism releases nitrogen in the form of ammonia. In the liver, the urea cycle prepares ammonia for excretion. Which amino acid could undergo deamidation to produce ammonia for the urea cycle?
Glutamine
confounding variable
a factor other than the independent variable that might produce an effect in an experiment
gene duplication
genes with similar sequences, or high sequence similarity
evolutionarily related
mosaic phenotype
heterozygous
cells express only one allele
bacteriophage
exclusively infect bacteria but do not enter host cells to replicate their genetic material
reverse transcriptase
enzyme encoded by some certain viruses (retroviruses) that uses RNA as a template for DNA synthesis
increased osmotic pressure of filtrate
increases urine output
pathway of sperm
spermatogonium, spermatocyte, spermatid, spermatozoon
kinesin
to periphery of cell
dynein
to nucleus
desmosome
anchor the cytoskeletons, specifically the intermediate filaments, of two cells together
in areas of high stress
B lymphocyte
antibody production
cytokine
Any of a group of proteins secreted by a number of cell types, including macrophages and helper T cells, that regulate the function of lymphocytes and other cells of the immune system
stereotype boost
enhancement in an individual's performance that may occur when one is made aware of a positive stereotype regarding the group that he or she belongs to
master status
dominates in social situations
dramaturgical approach
a view of social interaction in which people are seen as theatrical performers
elaboration likelihood model
theory identifying two ways to persuade: a central route and a peripheral route
most persuasive strategy for people who have low motivation and/or ability to process the message is to use the peripheral route of processing
Heuristic
a problem solving approach (algorithm) to find a satisfactory solution where finding an optimal or exact solution is impractical or impossible
Algorithm
a step-by-step procedure for solving a problem
incentive theory
organisms are motivated to act in order to obtain external rewards
exchange-rational choice theory
rational individuals choose the course of action that is likely to give them the greatest satisfaction
semantic memory
memory for knowledge about the world
stable with age
recalling vocabulary words
flashbulb memory
Individuals feel extremely confident about the memory, even after a long time has elapsed (may not be completely accurate)
Individuals are able to vividly recall specific details surrounding the event, including ones of seeming insignificance, such as what one was wearing or doing at the time of the event
instinctive drift
an animal's innate behaviors overshadowing a learned behavior
Animals trained to perform a specific behavior will often lose that behavior in favor of innate behaviors, even when reinforcement is present.
fixed-interval schedule
not an optimal way to train an animal to perform a new behavior because it is more difficult for the animal to associate the desired behavior with the reward
Sociological Paradigm
a set of assumptions about how society works and influences people
social constructionism
deals with social interactions
"reality" is created through interactions, resulting in an agreed-on shared meaning.
Symbolic Interactionism
meaning and value attached to symbols
individual interactions based on these symbols
buffers
weak acid and the salt of its conjugate base
CH3COOH(aq) and CH3COONa(aq)
conjugate acid
one more proton
When aqueous solutions of the various anions and cations were mixed, precipitates formed because:
the solubility product of a compound was exceeded.
pH at the equivalence point in any titration
pH of the salt solution formed
alpha decay
top number down four
bottom number down two
B- decay
up one on periodic table
B+ decay (positron emission)
one down on periodic table
Gamma decay
no change in protons or neutrons
Which gas would occupy more volume at a constant temperature and pressure, 1.5 g of N2 gas or 1.5 g of O2 gas?
Both gases occupy equal volumes.
power vs authority
power: the ability to exercise one's will over others
authority: the socially approved use of power
ethnography
study people in their natural environments (within their own communities) and provide descriptive information about the cultures, behaviors, norms, and values in a given geographic location.
dependency ratio
number of people under age 15 and over age 64 compared to the number of people active in the labor force
total fertility rate
average number of children born to a woman during her childbearing years
mechanoreceptor
sensitive to mechanical stimulation caused by pressure, vibration, or movement
includes sound
central executive system
controls deployment of attention
visuospatial sketchpad
component of working memory where we create mental images to remember visual information
phonological loop
that holds and processes verbal and auditory information
employed when manipulating spoken and written information (eg, reading a book
cocktail party effect
ability to attend to only one voice among many
speech shadowing
experimental technique in which subjects repeat speech immediately after hearing it (usually through earphones)
survey
observational
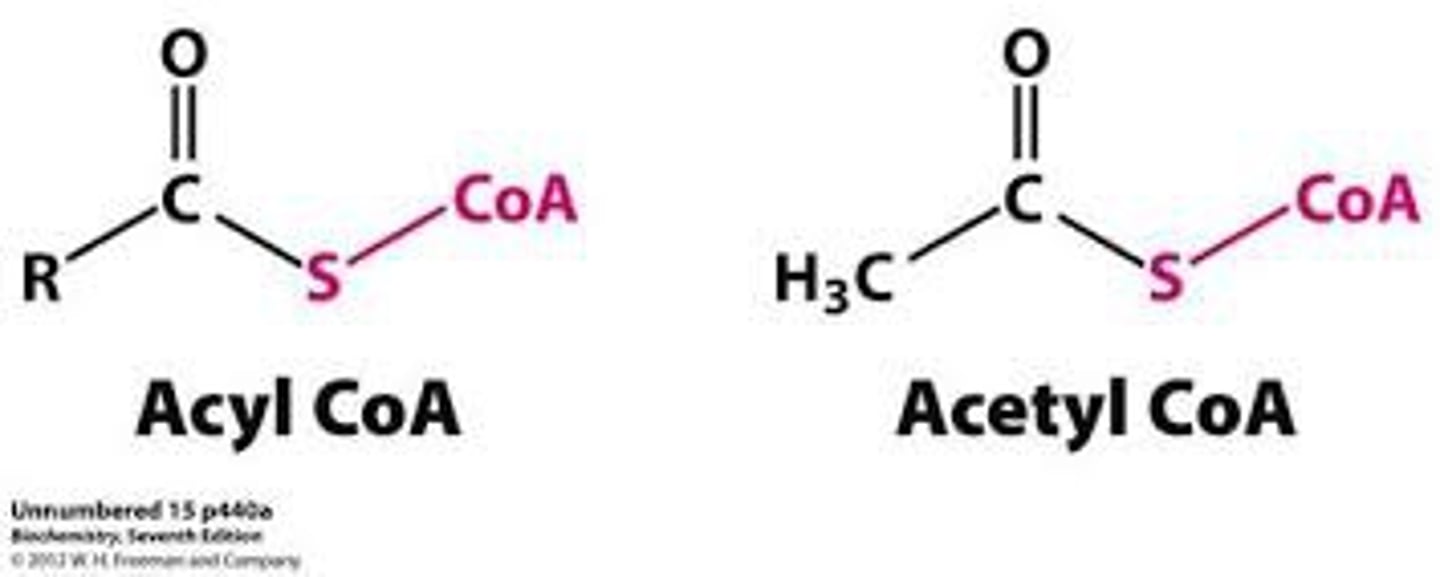
Acetyl CoA
higher ETC activity
higher ATP production
less oxygen (it is reduced to water in the last step)
PDH
pyruvate dehydrogenase
part of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
irreversible (cannot get pyruvate or glucose from acetyl CoA)
inhibited by its product - acetyl CoA
Beta oxidation
lipoic acid
cofactor for mitochondrial enzymes needed for oxidative phosphorylation especially pyruvate dehydrogenase
tertiary structure
stabilized by interactions between R groups
including hydrogen bonding, ionic, and hydrophobic interactions and disulfide bonds
epitope
the part of an antigen molecule to which an antibody non-covalently attaches itself
negatively charged amino acids
Asp, Glu
positively charged amino acids
arginine, histidine, lysine
Scientists could confirm that an allosteric effector increases the catalytic efficiency of an enzyme if it has what effect on kcat and Km?
kcat increases, Km decreases
lyase
removal of atoms without hydrolysis
pyruvate structure
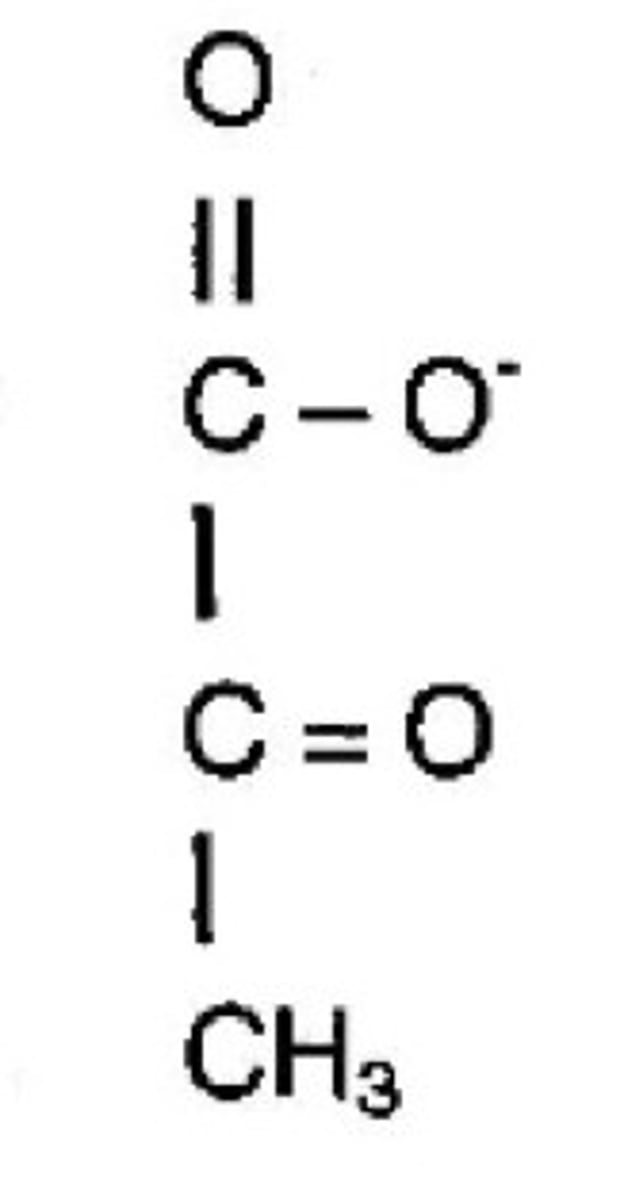
decoupling
protons that enter the mitochondrial matrix will not interact with ATP synthase
positive cooperativity
the first substrate changes the shape of the enzyme allowing other substrates to bind more easily
more than one active site
sigmoidal curve
Which experimental procedure(s) must scientists use to determine Vmax and Km of an enzymatic reaction using the Michaelis-Menten model? They must ensure that:
they only measure the initial reaction rate for each substrate concentration.
each initial substrate concentration tested is much greater than enzyme concentration.
randomized controlled trial
researchers randomly assign individuals to either an experimental or a control group and expose the experimental group to the manipulated variable of interest
sick role theory
a term associated with the functionalist Talcott Parsons to describe the patterns of behavior that a sick person adopts in order to minimize the disruptive impact of his illness on others
Rights:
1. Exemption from normal social roles & responsibilities
2. Lack of accountability for illness
Obligations:
1. Must attempt to get well
2. Must seek & comply with treatment
biomedical approach to health and illness
physiological causes (abnormal brain chemistry) result in psychological symptoms, and therefore medical treatment is advised to fix the underlying problem
emphasizes diagnosis and treatment
availability heuristic
estimating the likelihood of events based on their availability in memory; if instances come readily to mind (perhaps because of their vividness), we presume such events are common
consanguineal kin
relatives by blood
fictive kin
someone who becomes accepted as part of a family to which he or she has no blood relation (adoption)