A level Bio 1.1 Monomers and Polymers
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pls rate it 5 stars if you find it helpful :)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS) are polymers of galactose.
Explain why GOS are described as polysaccharides. (2)
Any two from:
1. Galactose is a monosaccharide/monomer
2. (Polysaccharide is a) carbohydrate polymer
3. (Several) monosaccharides/monomers/galactose joined by condensation reactions
Explain why amylase produced in the human digestive system does not digest GOS.(2)
Active site (only) complementary to starch (1)
Due to tertiary structure (1)
Prebiotics are foods used to promote good health in humans.
Prebiotics stimulate the growth of ‘healthy’ bacterial populations in the human digestive system.
The bacteria in these ‘healthy’ populations produce enzymes that hydrolyse GOS. Suggest how GOS can work as a prebiotic. (3)
Provides galactose/sugar/monosaccharide (1)
(Bacteria use the galactose/sugar) for respiration (1)
(Bacteria use the galactose/sugar) for binary fission (1)
Describe the chemical reactions involved in the conversion of polymers to monomers and monomers to polymers.
Give two named examples of polymers and their associated monomers to illustrate your answer. (5)
A condensation reaction joins monomers together and forms a (chemical) bond and releases water(1)
A Hydrolysis reaction breaks a (chemical) bond between monomers and uses water (1)
Suitable examples(2 points) : nucleotides and polynucleotide(phosphodiester bond) , Amino acid and polypeptide (peptide bond) , Beta glucose and cellulose (beta glycosidic bond)
Rf to a correct bond within a named polymer
What is a monomer? (1)
(a monomer is a smaller / repeating) unit / molecule from which larger molecules / polymers are made
When the larva is fully grown, it changes into a pupa. The pupa does not feed. In the pupa, the tissues that made up the body of the larva are broken down. New adult tissues are formed from substances obtained from these broken-down tissues and from substances that were stored in the body of the larva.
Hydrolysis and condensation are important in the formation of new adult proteins.
Explain how. (2)
Hydrolysis breaks proteins / hydrolyses proteins / produces amino acids (from proteins) (1)
Protein synthesis involves condensation (1)
Most of the protein stored in the body of a fly larva is a protein called calliphorin.
Explain why different adult proteins can be made using calliphorin. (1)
Amino acids (from calliphorin) can be joined in different sequences /
rearranged. (1)
Suggest an explanation for the change in RNA concentration in the first 40% of the time spent as a pupa. (2)
Age of pupa as percentage of total time spent as a pupa | Mean concentration of RNA / μg per pupa |
0 | 20 |
20 | 15 |
40 | 12 |
60 | 17 |
80 | 33 |
100 | 20 |
Tissues / cells are being broken down (1)
RNA is digested / hydrolysed / broken down (1)
Age of pupa as percentage of total time spent as a pupa | Mean concentration of RNA / μg per pupa |
0 | 20 |
20 | 15 |
40 | 12 |
60 | 17 |
80 | 33 |
100 | 20 |
Suggest an explanation for the change in RNA concentration between 60 and 80% of the time spent as a pupa. (2)
(RNA) associated with making protein (1)
New/adult tissues are forming (1)
A student investigated the effect of chewing on the digestion of starch in cooked wheat.
He devised a laboratory model of starch digestion in the human gut. This is the method he used.
1. Volunteers chewed cooked wheat for a set time. The wheat had been cooked in boiling water.
2. This chewed wheat was mixed with water, hydrochloric acid and a protein-digesting enzyme and left at 37 °C for 30 minutes.
3. A buffer was then added to bring the pH to 6.0 and pancreatic amylase was added. This mixture was then left at 37 °C for 120 minutes.
4. Samples of the mixture were removed at 0, 10, 20, 40, 60 and 120 minutes, and the concentration of reducing sugar in each sample was measured.
5. Control experiments were carried out using cooked wheat that had been chopped up in a blender, not chewed.
What was the purpose of step 2, in which samples were mixed with water, hydrochloric acid and pepsin? (2)
(Mimics / reproduces) effect of stomach (1)
A student investigated the effect of chewing on the digestion of starch in cooked wheat.
He devised a laboratory model of starch digestion in the human gut. This is the method he used.
1. Volunteers chewed cooked wheat for a set time. The wheat had been cooked in boiling water.
2. This chewed wheat was mixed with water, hydrochloric acid and a protein-digesting enzyme and left at 37 °C for 30 minutes.
3. A buffer was then added to bring the pH to 6.0 and pancreatic amylase was added. This mixture was then left at 37 °C for 120 minutes.
4. Samples of the mixture were removed at 0, 10, 20, 40, 60 and 120 minutes, and the concentration of reducing sugar in each sample was measured.
5. Control experiments were carried out using cooked wheat that had been chopped up in a blender, not chewed.
In the control experiments, cooked wheat was chopped up to copy the effect of chewing.
Suggest a more appropriate control experiment. Explain your suggestion. (2)
Add boiled saliva (1)
Everything same as experiment but salivary amylase denatured (1)
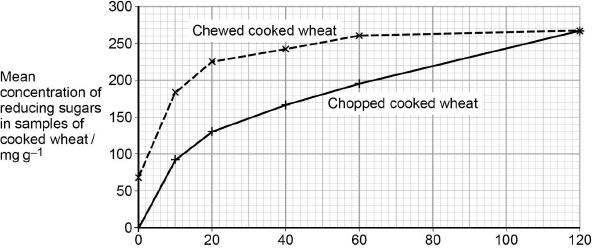
Explain what these results suggest about the effect of chewing on the digestion of starch in wheat. (3)
Some starch already digested when chewing / in mouth (1)
Faster digestion of chewed starch (1)
Same amount of digestion without chewing at end (1)
Compare and contrast the structure of starch and the structure of cellulose.(6)
Both are polysaccharides (1)
Both contain glycosidic bonds (between monomers) (1)
Starch made of α-glucose and cellulose made of β-glucose (1)
Starch (molecule) is helical/coiled and cellulose (molecule) is straight (1)
Starch (molecule) is branched and cellulose is not/unbranched (1)
Cellulose has (micro/macro) fibrils and starch does not (1)