Class 11 lecture: Health Implications of Tobacco and Alcohol
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
in the US, a standard drink contains ___oz (___g) of pure alcohol
0.6; 14.0
blood alcohol concentration (BAC)
% of alcohol in a person’s bloodstream
a person is legally intoxicated with a BAC of ____%
0.08
alcohol (ethanol) is metabolized in what organ
liver
alcohol (ethanol) is metabolized by what 2 key enzymes
alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase
factors that affect how alcohol is absorbed and metabolized
1) quantity of alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase
2) body weight
3) body composition (inc muscle —> lower BAC)
4) sex
5) race/ethnicity
6) medications
7) hormones
alcohol is metabolized at different rates in men and women of the same weight due to differences in what 2 factors?
1) body composition (women have higher proportion of body fat)
2) production of alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase (women’s liver prooduces lower conce
essential body fat % in men
3
essential body fat % in women
12 (b/c of capacity for reproduction)
total body fat % for women
20-25
total body fat % for men
15-20
people of this race/ethnicity tend to have very low alcohol tolerance?
East Asians (think Asian flush) → produce less enzymes to metabolize alcohol
people of this race/ethnicity tend to have higher alcohol tolerance?
blacks/African Americans
premenstrual hormonal changes cause intoxication to set in _________(faster/slower) during the days before a woman gets her period
faster
heightened levels of what hormones during luteal phase?
estrogen and progesterone
estrogen _______(slows/speeds up) alcohol metabolism
slows
birth control methods containing estrogen ______(speed up/slow) the rate at which alcohol is metabolized and eliminated from the body
slow
majority of alcohol metabolized in the liver by what enzyme?
alcohol dehydrogenase
converts ethanol → acetaldehyde
acetaldehyde is _____ ______ to the body
highly toxic (even in low concentrations)
what enzyme rapidly oxidizes acetaldehyde to acetate
aldehyde dehydrogenase
____ is the limiting factor for the rate at which we can metabolize alcohol
liver
liver can only produce enough alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase to metabolize ~______ drinks/hr
1-2
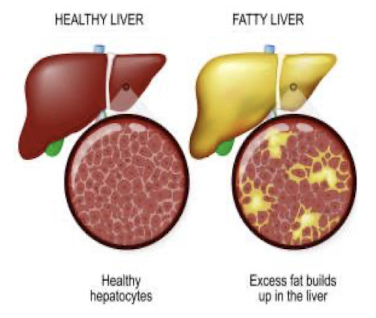
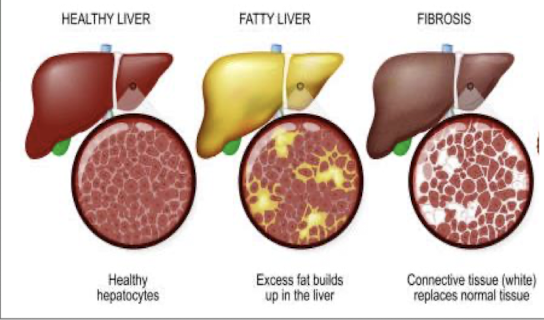
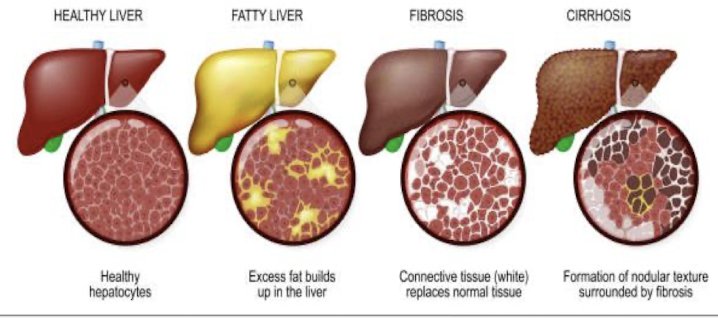
fatty liver
accumulation of fat on liver
alcohol disrupts the liver’s ability to metabolize fats, leading to fat deposits
REVERSIBLE with abstinence
alcoholic hepatitis
widespread inflamm and destruction of liver tissue
fibrosis → scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue
may be REVERSIBLE with abstinence
alcoholic cirrhosis
extensive fibrosis → stiffens blood vessels and distorts internal structure
severe function impairment → malfunction of OTHER ORGANS
often fatal, but can stabilize with abstinence
why does alcohol provide a “feel good effect”
alcohol consumption inc secretion of endorphins (“pleasure” hormones) → bind to opiate receptors on the brain → enhances mood
neurotoxicity
condition in which neurons overreact to neurotransmitters for too long
too much exposure to neurotransmitter can cause neurons to eventually “burn out” → delayed response and activation of these pathways → impaired cognitive and motor functioning (short-term and long-term)
alcohol acts as a _____ (inc urine output)
diuretic
inhibits vasopressin (aka ADH; regulates fluid balance)
alcohol can inc urine output as quickly as _____ min after intake
20
excessive urination can lead to
excessive thirst
dehydration (electrolyte imbalances → potentially fatal)
in the short-term, alcohol has what effect on blood vessels?
vasodilation → temporary feelings of warm, dec HR/BP
heavy drinking has been associated with what negative cardiovascular health effects
HTN → inc production of renin (hormone causing vasoconstriction)
cardiac arrhythmias and cardiomyopathy (dec heard muscle activity)
HF
in the pituitary gland, alcohol can decrease production of what 2 hormones
LH and FSH
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
stimulates Leydig cells of the testes to produce testosterone
spermatogenesis and sperm maturation
secondary sex characteristics (inc muscle mass, body hair, deeper voice)
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
spermatogenesis
outcomes of alcohol on reproductive system (testes) in males
impotence, infertility, erectile dysfunction, low libido
LH and FSH in women
both responsible for maturing / developing a follicle each cycle
secrete estrogen and progesterone to thicken endometrium
LH causes ovulation
which hormone causes ovulation
luteinizing hormone (LH)
effect of alcohol on secretion of LH and FSH
alcohol impairs secretion
excessive drinking includes
any drinking by pregnant women and people <21 y/o
binge drinking quantity in men and women
women: at least 4 drinks in a single occasion
men: at least 5 drinks in a single occasion
heavy drinking quantity in men and women
women: at least 8 drinks per week
men: at least 15 drinks per week
binge drinking most common in who
young adults (18-34 y/o) and males
binge drinkers with lower incomes and educational levels consume _______ drinks/binge
more
high aldehyde levels side effects
inc skin temp, facial flushing, inc HR, dec BP, dry mouth, N, and headache
headaches of a hangover caused by
shrinking of our brain dura (membrane encasing the brain) due to dehydration
b/c alcohol is a diuretic
gastrointestinal complications from hangover
inc in production of stomach acid and delay of stomach emptying → heart burn, abdominal pain, N&V
hangover causes _____glycemia which causes
hypo(glycemia) → fatigue, weakness, shakiness, and mood disturbances
hangovers cause poor quality sleep which causes
prevents deep sleep (dec time in stage 3) → results in grogginess
congeners
natural by-products of alcohol fermentation (e.g. ketones, esters, acids) → provide taste and aroma
higher content in darker colored alcoholic beverages
body must metabolize alcohol + congeners → more severe hangover sx
hangovers cause a reduction in vitamin ___?
B
processing alcohol places strain on body → inc requirements for energy and vitamins crucial in metabolism
SE is reduction in B vitamins → fatigued, tired
caffeine can ___ the depressant effects of alcohol
mask → makes drinkers feel more alert than they would otherwise → ppl may drink more alcohol and become more impaired than they realize
should you mix alcohol and caffeine?
NO
alcohol use disorder (AUD)
chronic disease characterized by uncontrolled alcohol intake and preoccupation with alcohol
encompasses: alcoholism, alcohol abuse, alcohol dependence, alcohol addiction
both physical AND emotional dependence
mild, moderate, severe
tobacco’s effect on brain
Regular nicotine use alters the physiological structure of the brain, causing it to develop extra nicotine receptors. When nicotine stops, the user experiences withdrawal.
tobacco’s effect on ears
Smoking reduces oxygen supply to the cochlea (inner ear), which can result in permanent damage and mild to moderate hearing loss.
tobacco’s effect on eyes
It also threatens vision by restricting the production of a chemical necessary for night vision, significantly increasing the risk for cataracts and macular degeneration, both of which can lead to blindness.
tobacco’s effect on heart
Smoking raises blood pressure due to vasoconstriction, putting added stress on the heart. Carbon monoxide decreases oxygen intake, forcing the heart to work harder and increasing the risk of heart disease and myocardial infarction.
tobacco’s effect on blood
Smoking also thickens the blood, increases risk for blood clots, damages blood vessel linings, and increases circulating cholesterol and unhealthy fats, which narrows arteries.
tobacco’s effect on lungs
Smoking results in inflammation in the bronchioles and tissues, leading to scar tissue. It causes Emphysema by destroying the tiny air sacs (alveoli) responsible for oxygen exchange, which do not regrow, leading to permanently compromised lung function, persistent shortness of breath, and increased mortality risk.
tobacco’s effect on DNA and cancer
Tobacco directly alters and damages an individual's DNA. While the body attempts to repair this damage, tobacco overly strains the repair system, often resulting in the development of cancer.
tobacco’s effect on mouth
significantly impair and denature taste buds and reduces blood flow to the mouth → inc r/f mouth/throat cancer, mouth sores, gum disease, cavities
significantly reduces saliva flow → dry mouth, very bad breath
DGAs definition of moderate drinking
women: 1drink/day
men: 2 drinks/day