BSCI 160 Shapiro Spring 2022
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
Deserts are common at -30 deg latitude north and south
Hadley cells moves air typically bring hot dry air to this region
earth's latitudinal temp gradient is due to
tilt of the earth relative to is axis of rotation,
add a billion people to the planet most recently took x years
10 years
pop with logistic growth model, N>K
R is going to be negative
n=K
r=0
n
r=positive
if doubling time is getting shorter than
r is increasing, because per capita growth rate is increasing
west side of mountains is dry due to rain shadow, where are prevailing winds blowing?
from east to west, air cools and drop moisture before crossing peaks
if age structure is a triangle
pop will increase
if fertility rate drops to 2 per female but large number of females in population will start reproducing when they reach sexual maturity
population momentum will sustain growth
max # of individuals sustained in a habitat
carrying capacity
earth is home to how many people
7.9 billion people
if r decreases but population increases
density dependent
Coriolis effect
westward deflection of air currents as they move towards the equator
Coriolis effect is due to earth's
shape and rotation speed
spring and fall equinox day length is
12 hours at all latitudes, angle is like parallel to sun
pop size 200, 50 born, 40 die, per capita death rate (d) =?
40/200 = 0.2
pop size 200, 50 born, 40 die per capita pop growth rate (r) =?
r=b-d or 50/200=b, 0.5 =r
if r = 0 "stable over time" "constant"
b = d
demographic transition
decrease in b and d due to industrialization, decrease in d first
antibiotic resistance
mutation is random, chance, only survivors are resistant and they reproduce
Darwin + Wallace
species related by shared ancestry, split and diverge, decent w/ modification
d x n=
D = total death in pop
r x n
number of people added to original n
temp and percipitation
summer months are in the middle of x axis, growing season (temp > 0, precipitation > temperature)
ideal population growth
exponential
Susceptible-Infected-Resistant (S-I-R) model
disease spreads in pop: sus # declines, infected # increases, resistant # increases
R0 (basic reproductive rate) of disease drops to 1
# infested indivi in pop not growing
in ant-plant mutualism
plant feeds ant, ants protects plants from herb insects, ants protect plants from plant
# species of in an area (Y) vs area (x)
logarithmic
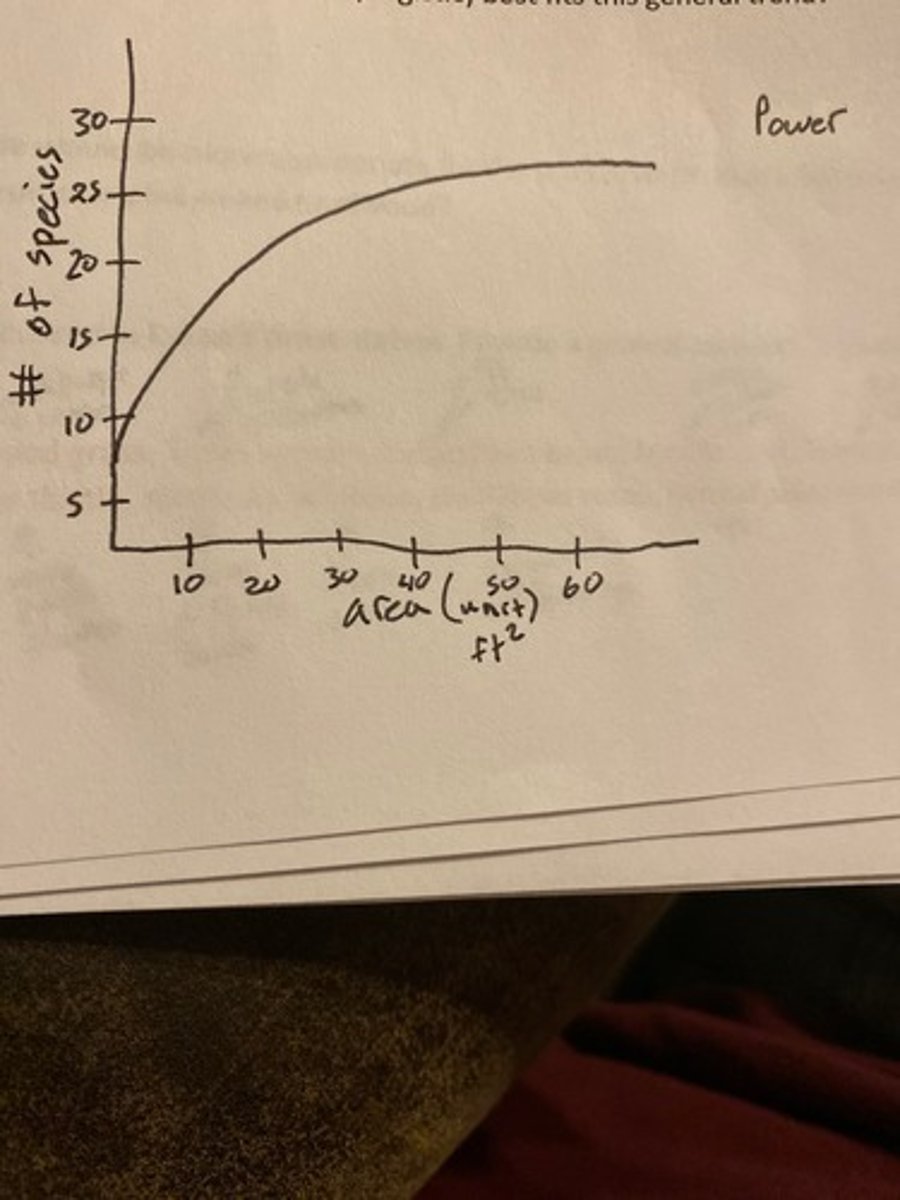
if # species of in an area (Y) vs area (x) log transformed
linear positive graph
half of the earth's primary production from
tropical forests and ocean
species diversity
evenness (distribution) and species richness (diversity)
keystone
bigger impact than biomass and abundance suggests
trophic cascade
Eco phenomenon triggered by add or sub of top predators
eggs in host and eat host alive with only one host
parasitoid
interaction that benefits both
mutualism
defensive response
thicker shells living with predators
if species evolve to have less similar niches (increase niche differentiation) on competition
less intense interspecific, intraspecific (same species) more intense
if species evolve to have less similar niches (increase niche differentiation) on coexistence
increase likelihood of long-term coexistence (intra comp > inter comp)
mechanisms for competition:
Exploitation: depletion of resources
Interference: decreasing someone else's ability to use a resource
fundamental niche
all the possibilities of where an organism can occupy
realized niche
where do they actually land in their niche (competition)
parasitism
one organism hurts another to benefit itself (living off of it)
predation
One eats the other
deleterious allele more likely to become fixed if
population is very small (genetic drift) or tightly linked to a highly beneficial allele
mieosis vs mitosis
homologous chromosomes pair up in tetrads during meiosis but not mitosis
complete dominance
Aa same phenotype as AA
imcomplete dominance
can result in offspring with phenotypes that are intermediate relative to their parents
antagonistic pleiotropy hypotheses of aging
old ladies might get cancer BUT they have higher fertility when young
late in life has ___ selection
weaker (natural selection thinks about survival and reduction)
paraphyletic groups
almost all (double snip)
clade (monophyletic group)
snip test
pop has 50 AA, 20 Aa, 30 aa f(A) f(a)
(2(AA)+1(Aa)/tot) = .6 and (2(aa)+1(Aa) / tot)= .4 (check p + q = 1.0
pop has 50 AA, 20 Aa, 30 aa geno freq HWE
P^2+2pq+q^2 = 1) if observed match expected then yes
pop has 50 AA, 20 Aa, 30 aa f(AA) f(Aa) f(aa)
50/100=0.5f(AA)
20/100 = 0/2 f(Aa)
30/100 = 0.3f(aa)
(check: P^2+2pq+q^2 = 1)
pop has 50 AA, 20 Aa, 30 aa why/why not HEW
observed doesn't match expected frequency
recessive allele causes disease with frequency 1/25, at HWE, expected frequency of carriers
.32 or 32%
D= no disease f(D) = p, d = disease f(d) = q, f(dd) = (1/24) ^1/2, 1-q=p
phylogeny diagram that represents relationships no info on time or amount of change
cladeogram
alternate forms of a gene (normal vs disease causing)
alleles
phenomenon of one gene having an effect on multiple traits
pleiotropy
if the phenotypic effect of the genotype at one locus depends on the genotype at another locus
epistasis
polygenic
multiple genes affecting one trait
four mechanisms of evolutionary change
natural selection, gene flow/migration, mutating, genetic drift
natural selection
alleles that improve sexual reproduction and survival increase in frequency
gene flow/migration
alleles transfer from one pop to another
mutating
random changes in gene create new alleles
genetic drift
random changes in allele frequency
Heterozygous
Aa or A1A2
homozygous
AA aa A1A1 A2A2
parsimony
least changes
mitosis and meiosis
1) diploid cell
2) Mit (one long line) Mei (all next to each other tetrad)
3) Mit: one copy of each and they are identical Mei: 2 identical cells split and become haploid with 1/2 info
loci on same chromosome
how the parents alleles are aligned tells about gametes
sex traits in bird on Z allele
male: ZtZT
Femal: ZTW
all males T, femals 50/50
biological species concept
potential to interbreed under natural conditions and produce viable, fertile offspring
Sexual reproduction predominates because
deleterious mutations are more easily purged (removed) from sexually reproducing populations
Mutational meltdown
s the accumulation of harmful mutations in a small population, which leads to loss of fitness and decline of the population size, which may lead to further accumulation of deleterious mutations due to fixation by genetic drift.
associative learning
acquired ability to associate an environmental feature with another (i don't eat pasta)
Imprinting
rapid irreversible learning during a critical period
alopatric speciation
speciation because a population diverges due to a physical barrier
shifting baseline
normal for each generation keeps moving up or down
sexual selection
natural selection for access to mates
inclusive fitness
combo of direct and indirect fitness that increases genetic representation in future gens
externalities
costs that affect a party who did not choose to incur those costs
what is a pre-zygotic reproductive barrier
prevents formation of a zygote, sperm wont fertilize egg (also post-mating)
pre mating reproductive barrier
prevents mating from happening
Mechanical Reproductive barriers
sex organs don't match up in a population
temporal Reproductive barriers
different times when they mate
behavioral Reproductive barriers
different mating calls and dances
why do males typically have sexually selected characters
sperm are cheap eggs are expensive, females are more picky, males fight for mates, males show they have good genes or attractive
when would sexual selection in females be stronger than males
mating is more costly to males, males invest more in offspring (seahorses)
tradgedy of the commons
individual behave in self interest and degrade the population and community and environment
addressing tragedy of the commons
create public policies that incentivize acting for the collective
disruptive selection
favoring both extremes and avoiding the middle, gametes produce at different loci create alleles that are new phenotypes, and mutations
directional selection
favors one extreme trait (IE super long beak)
when meiosis produces gametes
it creates and new combos of alleles
Michael Carmichael
University of Maryland's first Stormwater Management and Maintenance Inspector