UARK Managing People and Organizations Exam #3
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
Decision Support Systems
•Computer-based interactive systems that help decision makers use data and models to solve unstructured problems
Information, Technology, & Management
•Managers must have
•Technological competency
•Ability to understand new technologies and to use them to their best advantage
•Information competency
•Ability to locate, gather, organize, and display information for decision making and problem solving
•Analytical competency
•Ability to evaluate and analyze information to make actual decisions and solve real problems
What is Decision Making?
•Identifying and choosing alternative solutions that lead to a desired state of affairs.
Two Models
Rational and Nonrational
Nonrational Decision Making
Relies on intuition, involves mental short cuts, so it's quicker
•Automatic, instinctive and emotional mode of decision making
•Can be quick, requires little cognitive effort
Rational Decision Making
Utilize analytical and conscious thought
•Slow, logical, deliberate and requires more cognitive effort
Identifies when emotion is clouding judgment, intuition is wrong
How mangers should make decisions
Rational Decision Making
•Assumes managers are completely objective and possess complete information
•Demonstrates excellent logic and promote the organization's best interests
•Occurs in four stages
Rational Model of Decision Making
Stage 1: Identify the problem or opportunity
Stage 2: Think up alternative solutions
Stage 3: Evaluate alternatives and select a solution
Stage 4: Implement and evaluate the solution chosen
Rational Decision Making: Pros
There are three benefits to at least trying this approach.
-The quality of the decision is likely to be enhanced.
-Greater transparency surrounds the process.
-Greater responsibility accompanies this approach.
Rational Decision Making: Cons
There are downsides to this approach.
-Not having complete information
-Leaving emotions out
-Honestly and accurately evaluating alternatives
-Limit of time and resources
-People may be unwilling to implement and support decisions
Non-Rational Decision Making Model
Actual decisions are often generally nonrational
The normative model
•Guided by bounded rationality
•Our ability to make decisions restricted or bounded by a series of constraints: e.g., resources and personal attributes
•Manageable amounts of information sought, rather than complete or optimal amounts
•Results in satisficing when arriving at a solution
Nonrational Models of Decision Making Pros:
•Useful When Resources are Limited
•Speeds up Decision Making
Nonrational Models of Decision Making Pros:
•Good Ideas May be Ignored
•May have Difficulty Convincing Others
•Subject to Bias
Herbert Simon
created the theory of bounded rationality, earned him a Nobel Prize in 1978 and is also known as the administrative man theory
bounded rationality model
There are four assumptions to his model:
1. Managers select the first alternative that is satisfactory.
2. Managers recognize that their conception of the world is simple.
3. Managers are comfortable making decisions without determining all the alternatives.
4. Managers make decisions by rules of thumb or heuristics.
Satisfice
accepting solutions that are "good enough"
Heuristics
Mental shortcuts or "rules of thumb" that often lead to a solution (but not always).
Judgmental Heuristics
-cognitive shortcuts or biases that are used to simplify the process of making decisions
-can help managers make decisions but can lead to bad decisions
Anchoring Bias
making decisions based off of the first information received even if it is irrelevant. E.g. Walking the car lot and deciding to buy a car based off a color you like.
Hindsight Bias
when knowledge of an outcome influences belief about the probability of the outcome occurring. Individuals are affected by a hindsight bias when they look back on a decision and try to reconstruct why they decided to do something. E.g. Why did I go to that party when I just knew there would be a quiz.
Framing Bias
relates to the way something is framed.. It is a tendency to consider risks in gains and losses differently. “60 % chance of gains vs. 40% chance of loss”.
Escalation bias
The escalation of commitment bias refers to the tendency to stick to an ineffective course of action when it is unlikely that the bad situation can be reversed. E.g. bringing in a new software to the company, learning it isn’t going to work…but sticking to it anyway.
Evidence Based Decision Making
process of conscientiously using the best available data and evidence when making managerial decisions
Big Data
•Reflects the vast quantity of data available for decision making used to create a competitive advantage by:
•Making information transparent and usable
•Allowing organizations to measure and collect all types of performance information to enhance productivity
•Allowing for more narrow segmentation of customers
•Being used to develop new products
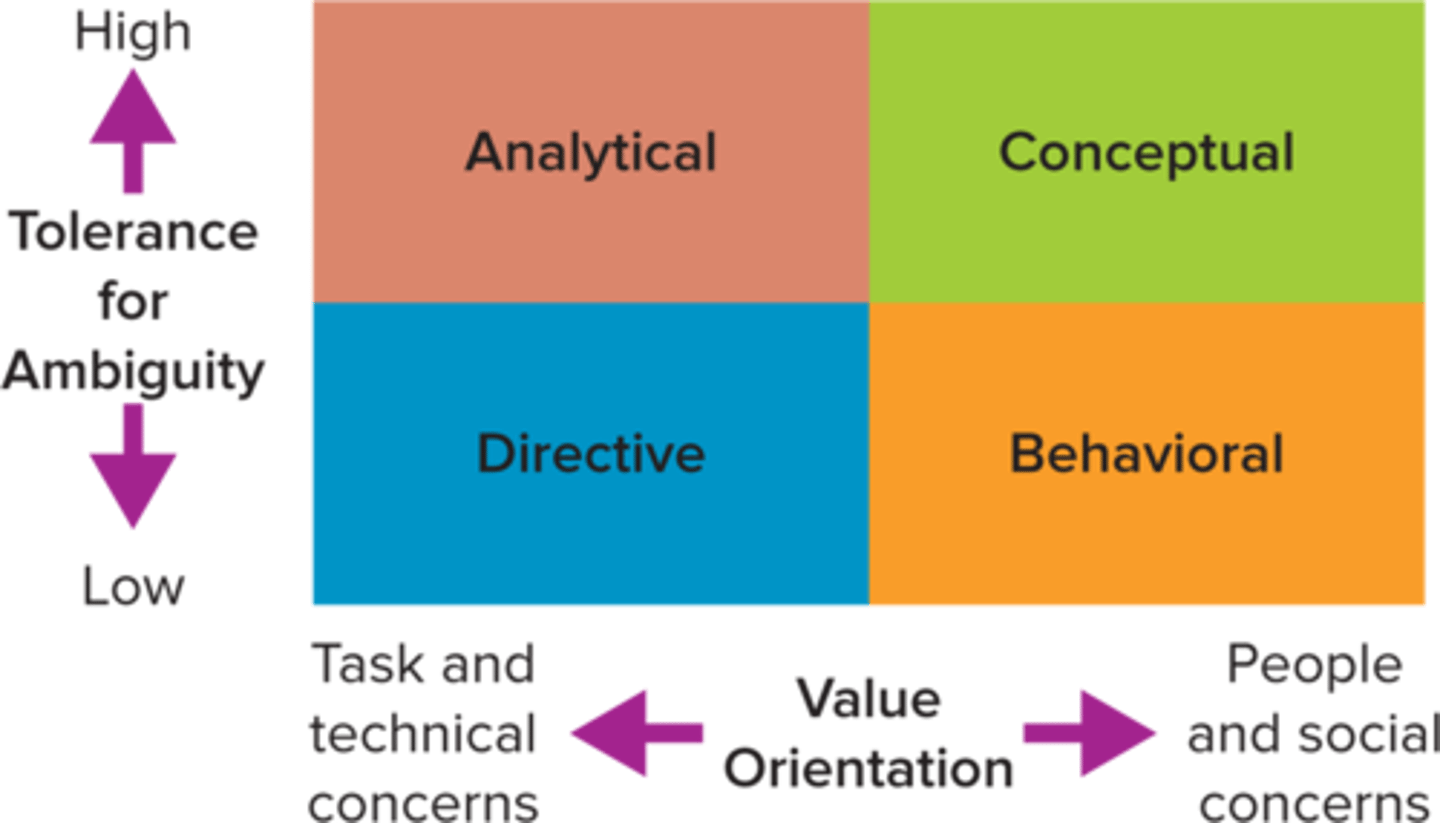
Four Decision Making Styles
directive, analytical, conceptual, behavioral
Advantages of Group Decision Making
Greater Pool of Knowledge
Different Approaches to a Problem
Greater Commitment to a Decision
Better Understanding of Decision Rationale
More Visible Role Modeling
Disadvantages of Group Decision Making
•Diffusion of Responsibility
•Lower Efficiency
•Groupthink
Groupthink
A mode of thinking that people engage in when:
-They are deeply involved in a cohesive in-group
-Members' strivings for unanimity override their motivation to realistically appraise alternative courses of action
Symptoms of Groupthink
•Invulnerability - Illusion providing reassurance
•Inherent Morality - Unquestionable belief, ignore consequences
•Rationalization - Ignore warnings
•Stereotyped Views of Opposition- typically of the leaders
•Self-Censorship - avoid deviating from consensus
•Illusion of Unanimity - results from censorship, avoids conflict
•Peer Pressure - applied to any individual who attempts to question decisions.
•Mindguards - filters the information to protect conformity
Techniques for Preventing Groupthink
-Each member of the group should be assigned the role of critical evaluator. This role involves actively voicing objections and doubts
-Top-level executives should not use policy committees to rubber-stamp decisions that have already been made
-Different groups with different leaders should explore the same policy questions
-Managers should encourage subgroup debates and bring in outside experts to introduce fresh perspectives
-Someone should be given the role of devil's advocate when discussing major alternatives. This person tries to uncover every conceivable negative factor
-Once a consensus has been reached, everyone should be encouraged to rethink their position to check for flaws
What is Consensus in Group Decision Making?
Reached When:
-All members can say they either agree with the decision or have had their say and were unable to convince others of their viewpoint
-Everyone agrees to support the outcome
Problem Solving Techniques- Brainstorming
•Used to help groups generate multiple ideas and alternatives for solving problems
•Rules for brainstorming:
•Defer judgment
•Build on the ideas of others
•Encourage wild ideas
•Go for quantity or quality
•Be visual
•Stay focused on the topic
•One conversation at a time
What can a manager do to maximize group decision making?
•Establish a team goal
•Facilitate a working environment
•Set clear expectations and responsibilities
•Provide resources
•Get out of the way
•Open communication process
Delphi Technique
•Group process that anonymously generates ideas or judgments from physically dispersed experts
•The Delphi method was originally developed in the early 1950s at the RAND Corporation by Olaf Helmer and Norman Dalkey
•Systematically solicit the view of experts - the Delphi method may thought of as an expert brainstorm.
•In Delphi decision groups, a series of questionnaires, surveys, etc. are sent to selected respondents (the Delphi group) through a facilitator who oversees responses of their panel of experts. The group does not meet face-to-face.
•All communication is normally in writing (letters or email).
•Members of the groups are selected because they are experts or they have relevant information.
Delphi Technique Cons;
•Disagreements and conflict may occur
•Group domination is an issue
•Groupthink is likely
Delphi Technique Pros:
•Elimination of interpersonal problems.
•Efficient use of expert's time.
•Diversity of ideals.
Accuracy of solutions and predictions
Creativity
•Rational Decision Making; Intuitive Decision Making and Creative Decision Making
•Way of generating new and innovative ideas
•Similar to other two models - Identify the problem or opportunity
•Immersion - gather data/information, think about possible solutions
•Incubation - taking time to step back and let it sit
•Illumination - the solution is determined, the “aha”
•Verification and Application - verifies feasibility, execution of the solution
At all steps during decision making, think about the ethics:

Team Structure and Composition
•Diversity on the team
•Creating an environment that encourages risk taking
•Rotate individuals in and out of the group
•Don't assign a leader to the group.
Team Processes
•Developing a peer environment: the group is more important than the individual
•Engage in brainstorming
•Being willing to get and give feedback
•Hiring great people possessing required person factors
•Staying connected with innovations taking place in academia
Leadership
•Keep team members challenged
•Ensure they have a voice in the goals
•Enable creativity
•Role model creativity in your decision making
What is Power?
•The discretion and the means to enforce your will over others”.
•The ability to marshal human, informational, and other resources to get something done.
•Most importantly, power is about influencing others.
•
The more influence you have, the more powerful you are.
Five Bases of Power
legitimate, reward, coercive, expert, referent
Legitimate Power
•Obtain compliance because of formal authority (can be positive or negative)
Reward Power
•Obtain compliance by promising or granting rewards(pay for performance)
Coercive Power
•Make threats of punishment and deliver actual punishment (NASA)
Expert Power
•Have valued knowledge or information over those who need the knowledge or information (role, past experiences)
Referent Power
•Using one's personal characteristics and social relationships to obtain compliance (charisma, age, social status, relationships, reputation)
Resistance
•Different forms: indifference, passive aggressive, resistance, undermining/sabotaging the efforts of the one in power.
Compliance
•Do what is expected, but no more than that. No extra effort or input.
Commitment
•Believe in the cause, go the extra effort / above and beyond. Fully supportive.
The Affect of Org Behavior
Bases of Power and Outcomes
•Different bases of power affect important outcomes such as job performance, job satisfaction, and turnover:
•Expert and referent power have a generally positive effect
•Reward and legitimate power have a slightly positive effect
•Coercive power has a slightly negative effect
Empowerment
Definition:
•authority or power given to someone to do something.
•the process of becoming stronger and more confident, especially in controlling one's life and claiming one's rights.
Efforts to enhance employee performance, well-being, and positive attitudes by:
•Giving employees greater influence
•Use of centralized management practices
Psychological empowerment
Through enhancing self-efficacy and intrinsic motivation
•We feel a sense of meaning (our work values and goals align with our manager, team or organization)
•We feel a sense of competence (our personal evaluation of our own abilities to do the job)
•We feel a sense of self determination (we have control over work and its outcomes)
•We feel a sense of impact (what we are doing, our efforts make a difference and affect the organization positively)
Structural Empowerment
Job redesign to transfer of power to employees
Domination Authoritarian Power
decisions are imposed
Consultation
-Influence/sharing - consulting with followers on decisions
Participation
-Power sharing - decisions are made jointly by managers/followers.
Delegation
Followers granted authority to make decisions.
Soft Tactics
•Rational persuasion
•Inspirational appeals
•Consultation
•Ingratiation
•Personal appeals
Hard Tactics
•Exchange
•Coalition tactics
•Pressure
•Legitimizing tactics
Influence Tactics
are conscious efforts to affect and change behaviors in others.
Rational Persuasion
Trying to convince someone with reason, logic, or facts
Inspirational appeals
trying to build enthusiasm by appealing to others' emotions, ideals, or values
Ingratiation
getting someone in a good mood prior to making a request. Being friendly and helpful and using praise, flattery, or humor. A particular form of ingratiation is "brownnosing"
Personal Appeals
referring to friendship and loyalty when making a request
Exchange
making explicit or implied promises and trading favors
Coalition tactics
Getting others to support your efforts to persuade someone
Pressure
demanding compliance or using intimidation or threats
Legitimating tactics
basing a request on one's authority or right, organizational rules or policies, or express or implied support from superiors
Effectively Influencing Others
Six principles of persuasion
1.Liking-Learn about another person’s likes / dislikes.
2.Reciprocity – Belief that deeds (good / bad) need to be repaid in kind. (You help me…I help you)
3.Social proof – People tend to follow the lead of those most like themselves. Build support with others who can also help you influence.
4.Consistency – People tend to follow through on a commitment, if you can get them there.
5.Authority – People tend to defer to and respect credible experts.
6.Scarcity – People tend to like items, information, benefits that have limited availability. Can help influence them.
Impression Management
•Any attempt to control or manipulate the images related to a person, organization, or idea using
•Speech
•Behavior
•Appearance
How does one make a good impression?
•Set an intention
•Consider your ornaments
•Remember your body speaks
•Bust bad moods and bad days
•Be interested to be interesting
Favorable upward impression management tactics
A moderate amount of upward impression management is a necessity for the average employee today.
•Job-focused
•Supervisor-focused
•Self-focused
How do bad impressions happen?
•Doing only the minimum
•Having a negative mindset
•Overcommitting
•Taking no initiative
•Waiting until the last minute to deliver bad news
Apologies:
a form of trust and influence repair when harm—real or perceived—has been done
•Characteristics of apologies?
•Acknowledgement of wrongdoing
•Acceptance of responsibility
•Expression of regret
•Promise that the offense will not be repeated
Organizational Politics
Intentional acts of influence to enhance or protect the self-interest of individuals or groups that are not endorsed by or aligned with those of the organization
Uncertainty: may trigger political behaviors
Sources of uncertainty
•Unclear objectives
•Vague performance measures
•Ill-defined decision processes
•Strong individual or group competition
•Any type of change
Levels of Political Action
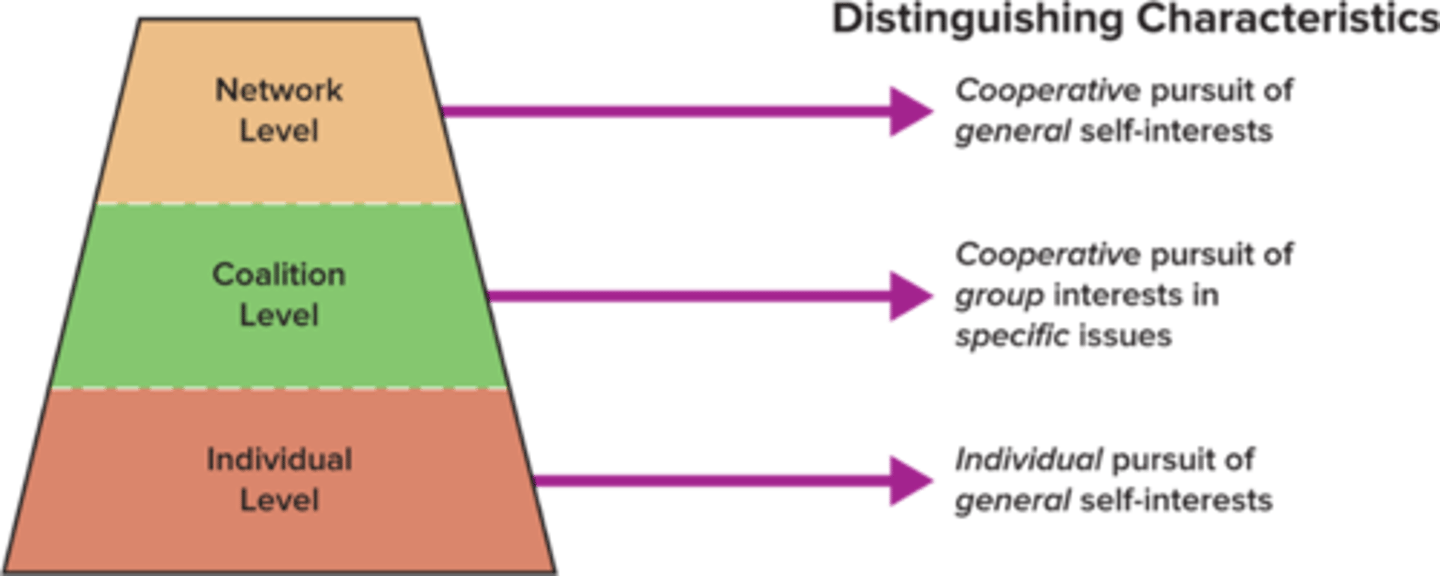
Individuals who are highly political
•Run the risk of being called self-serving
•May lose credibility
•May be considered poor team players
Individuals who are strictly non-political
•May experience slower promotions
•May feel left out
•May be considered poor team players
Leadership
•A process whereby an individual influences a group of individuals to achieve a common goal
Effective Leadership
•To be effective requires a mix of traits, competencies, and interpersonal attributes
•From contingency theory we know effective leaders match their choice of behavior to the situational context
Manager
•Short term focus
•Task Driven
•Directs
•Follows process and rules
•More reactive
•Oversees employees
•Authoritative
•Administrative
•Detail oriented
Leader
•Has a longterm vision
•Strategic and planning
•Strong Emotional Intelligence
•Influences
•Inspires Trust
•Challenges the status quo
•Proactive
•Coaches followers
•Collaborative
•Innovative
Trait Approach
•Attempts to identify personality characteristics or interpersonal attributes that can be used to differentiate leaders from followers
•Trait theories of leadership seek personality, social, physical or intellectual traits which differentiate leaders from non-leaders.
Recent research using meta-analysis techniques discovered the following attributes
Narcissism
•Self-centered, strong drive for personal power
•More charismatic and passionate yet more likely to promote counterproductive behaviors from others
Machiavellianism
•Entails the use of manipulation, puts results ahead of principles
•Linked to counterproductive behaviors
Pyschopathy
•Lack of concern for others
•Lack of remorse or guilt
What Are the Takeaways from Trait Theory?
•We can no longer ignore the implications of leadership traits
•Positive traits should be cultivated and "dark side" traits avoided
•Organizations should include personality testing and trait assessments in hiring and promotion
•It is important to develop a "global mind-set"
Implicit Leadership Theory
Is based on the idea that people have beliefs about how leaders should behave and what they should do for their followers.
Emotional Intelligence & Leadership Effectiveness
•The ability to manage oneself and one's relationships in mature and constructive ways
-Likely to be associated with leadership effectiveness
-An input to transformational leadership
What is the Behavioral Styles Approach?
•Attempts to identify the unique behaviors displayed by effective leaders versus non leaders.
•Patterns of actions used by different individuals determines leadership potential.
Four categories:
-Task-oriented
-Relationship-oriented
-Passive
Transformational
Task Oriented Leader Behavior
•Primary purpose - ensure that people, equipment, and other resources are used in an efficient way
•Types:
-Initiating structure
-Transactional leadership
Primary purpose
ensure that people, equipment, and other resources are used in an efficient way
Initiating Structure
•Organizes group behavior to maximize productivity
•Moderately strong positive relationship with leader effectiveness
Transactional Leadership
•Focuses on clarifying roles and requirements
•Uses contingent rewards and punishments
Consideration
•Creating mutual respect or trust and focusing on a concern for group members' needs and desires
•Promotes social interaction
Empowerment
•Creates perceptions of psychological empowerment in others
•Reflects employees' beliefs that they have control over their work