Chapter E6: Understanding ELISA Techniques in Chemistry
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
involves an antibody or antigen (immunologic molecules) that may form an antigen-antibody reaction to provide a positive result or, if they do not react, a negative result.
Describe the basic process of an ELISA.
+ Antigen → primary antibody → secondary antibody → conjugated enzyme --> substrate
What binds to what in ELISA
Positive = blue and shows antigen is in well (conjugated enzyme binds to secondary antibody)
Negative control shows nothing, indicates no antigen in well
When you get a positive or negative result from an ELISA, what are you actually seeing?
Positive control = establish that reagents bind together
Negative control = to check for no contamination, antigen or antibody is missing
What are negative and positive controls and their functions?
Positive test would show color change and antigen existed, which indicates disease
Given wells containing tested samples, be able to classify them as positive or negative results.
The second well is incorrect because it is supposed to be blue to indicate antigen is present
perhaps not enough antibodies from adding the primary or secondary.
Suppose assay was blue in first well, but clear in second well of Positive control samples. Possible errors?
The first well, because it is supposed to be clear.
perhaps not washing the wells throughly, causing cross contamination
suppose a group's assay was blue in the blue in the first well but clear in the second well of the NEGATIVE control. which well is incorrect and what may have happened
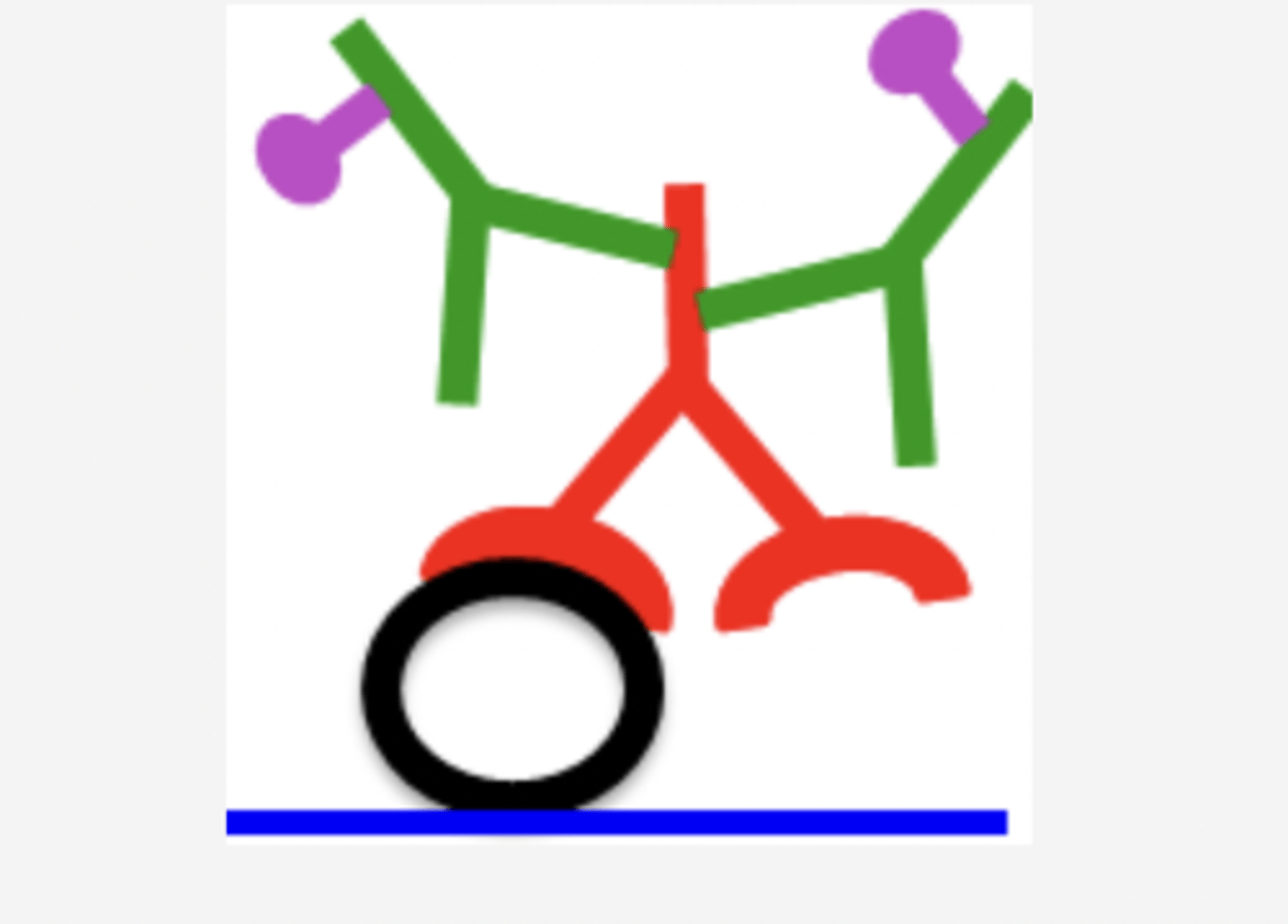
Black circle: antigen
Red restructure: primary antibody
Green "Y": Secondary antibody
purple "knob": conjugated enzyme
Label the parts
Failure to perform the wash step after incubation with secondary antibody.
Which of the following errors would result in positive results for all samples in an ELISA assay (including negative controls)
1. failure to add antigen
2. Failure to add functional primary antibody.
3. Failure to add functional secondary antibody.
4. Failure to add functional substrate
Which of the following errors would result in a negative result for all samples in an ELISA (including positive controls)?
is more likely to cause false positives than false negatives.
Reusing a pipet tip when transferring controls and samples from tubes to wells