Public Policy and Advocacy
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
political science
the systematic study of government and politics
Role of Political Parties
Is for groups of like-minded individuals who share common beliefs and ideas to work together in hopes of electing their members to political offices.
Politics and Government
laws and how society is run under it's leaders.
Democracy
A political system in which the supreme power lies in a body of citizens who can elect people to represent them
Capitalism
an economic and political system in which a country's trade and industry are controlled by private owners for profit, rather than by the state.
Constitutionism
Basic principle that government and those who govern must obey the law; the rule of law
Dictatorship
A form of government in which the ruler is an absolute dictator (not restricted by a constitution or laws or opposition etc.)
Authoritarianism
A political system in which a small group of individuals exercises power over the state without being constitutionally responsible to the public.
Aristocracy
A government in which power is in the hands of a hereditary ruling class or nobility
Direct Democracy
A form of government in which citizens rule directly and not through representatives
Representative Democracy
A system of government in which citizens elect representatives, or leaders, to make decisions about the laws for all the people.
referent power
power that comes from subordinates' and coworkers' respect, admiration, and loyalty
coercion
the practice of persuading someone to do something by using force or threats
political culture
commonly shared attitudes, beliefs, and core values about how government should operate
Political Opinion
citizens' attitudes about political issues, leaders, institutions, and events
bipartisan
Involving two political parties
party system
the categorization of the number and competitiveness of political parties in a polity
Minor political parties
political parties that do not have elected representatives to win government but are able to place pressure on the government to address specific issues and introduce law reform
interest group
An organization of people sharing a common interest or goal that seeks to influence the making of public policy
Libertarian Party
A minor party that believes in extremely limited government. Libertarians call for a free market system, expanded individual liberties such as drug legalization, and a foreign policy of nonintervention, free trade, and open immigration.
Green Party
A minor party dedicated to the environment, social justice, nonviolence, and the foreign policy of nonintervention. Ralph Nader ran as the Green party's nominee in 2000.
14th Amendment
Declares that all persons born in the U.S. are citizens and are guaranteed equal protection of the laws
16th Amendment
Amendment to the United States Constitution (1913) gave Congress the power to tax income.
19th Amendment (1920)
Ratified on August 18, 1920 (drafted by Susan B. Anthony and Elizabeth Cady Stanton), prohibits any United States citizen from being denied the right to vote on the basis of sex. The Constitution allows the states to determine the qualifications for voting, and until the 1910's most states disenfranchised women. The amendment was the culmination of the women's suffrage movement in the U.S.
Feminism
the belief that women should possess the same political and economic rights as men
Women's Rights
voting rights, own property, buy and sell goods, and other rights getting better for British women
Americans with Disabilities Act
Passed by Congress in 1991, this act banned discrimination against the disabled in employment and mandated easy access to all public and commerical buildings.
Transitional Government
an emergency or temporary government set up after the collapse or defeat of the former government; these governments are unelected and are often unstable, featuring alliances between some groups and/or competition with other groups for power
Congress vs. Parliament
In a congressional system, the legislature and the executive are separate;
in a parliamentary system, they're combined in the Prime Minister, so this one person has a great deal of control and his power cannot easily be checked
In a parliamentary system, the party that wins a majority can basically push through its entire agenda without any formidable opposition.
In the US congressional system, there are many barriers to a passage of a law - committees, votes in both houses, and a presidential sign-off.
In a congressional system, individual members can disagree with their parties and party leadership.
In a parliamentary system individuals are expected to vote with the party
election runoff
two-round system
voting method used to elect a single candidate, where voters cast a single vote for their preferred candidate. It generally ensures a majoritarian result, not a simple-plurality result as under first past the post
Election recall
A recall election (also called a recall referendum or representative recall) is a procedure by which voters can remove an elected official from office through a direct vote before their term has ended.
Electoral College
A group of people named by each state legislature to select the president and vice president
Electoral College System
delegates assign to each state a number of electors equal to the total of that state's representatives and senators; instituted because the delegates at Philadelphia feared that too much democracy might lead to mob rule
Bureaucracy
a system of government in which most of the important decisions are made by state officials rather than by elected representatives.
federal bureaucracy
the thousands of federal government agencies and institutions that implement and administer federal laws and programs
Federal Judiciary
the branch of the federal government that interprets and applies the laws of the nation
judicial system
the system of law courts that administer justice and constitute the judicial branch of government
Yellow Media
Media that presents little or no legitimate well-researched news while instead using eye-catching headlines for increased sales
censorship laws
Acts that ban or limit access to materials (e.g. magazines, movies) that are deemed to be obscene; enacted to protect public morality.
public opinion
the distribution of the population's beliefs about politics and policy issues
public culture
A dominant set of values, ideas, and practices that circulate in public discourse. Social groups may speak in the language of these values, ideas, and practices to gain a voice in a society.
code law
a written set of laws that apply to everyone under a government
American law
-Congress makes laws
-the courts interpret them
-the police enforce them
Statutory Law
The body of law enacted by legislative bodies (as opposed to constitutional law, administrative law, or case law).
Government Fiscal Policy
- Government policy: reduces swings in business cycle and it creates stable prices.
- Fiscal policy: government intervention through spending and taxation to stabilize pace of economic activity.
Federal Reserve System
The country's central banking system, which is responsible for the nation's monetary policy by regulating the supply of money and interest rates
National Security Council
An office created in 1947 to coordinate the president's foreign and military policy advisers. Its formal members are the president, vice president, secretary of state, and secretary of defense, and it is managed by the president's national security assistant.
international relations
A field in political science which concentrates on relations between countries, such as foreign policy, war, trade, and foreign aid.
human rights
the basic rights to which all people are entitled as human beings
defence policy
A subset of national security policies pertaining to the U.S. armed forces.
Criminal Law
A law that defines crimes against the public order.
Civil Law
A law that governs relationships between individuals and defines their legal rights.
Criminal Law vs. Civil Law
Criminal Law: Cases involving a violation of local, state, or federal laws (Public Law)
Civil Law: Cases involving one party attempting to seek payment or resolution of damages caused by another party.
Religious Law
based on the officially established rules governing the faith and practice of a particular religion
measure public opinion
polls
Congress Elections
every 2 years
Hosue of Representatives
2 years, represent districts, 435, more power to majority, limit debates
U.S. Senate
a part of Congress; based on a equal number. 2 per state
party nomination
the official nomination of a candidate to run for office. This means that the party will fully support this candidate's campaign.

party nominating convention
where party politicians and voters would gather in a large meeting hall to nominate the party's candidates (Anti-Masonic Party was the first to do such a thing), replaced the king caucus
Supreme Court
Consists of nine justices, each appointed by the President and confirmed by Congress. Appointment is for life. Supreme Court exercises the power to determine constitutionality of statutes

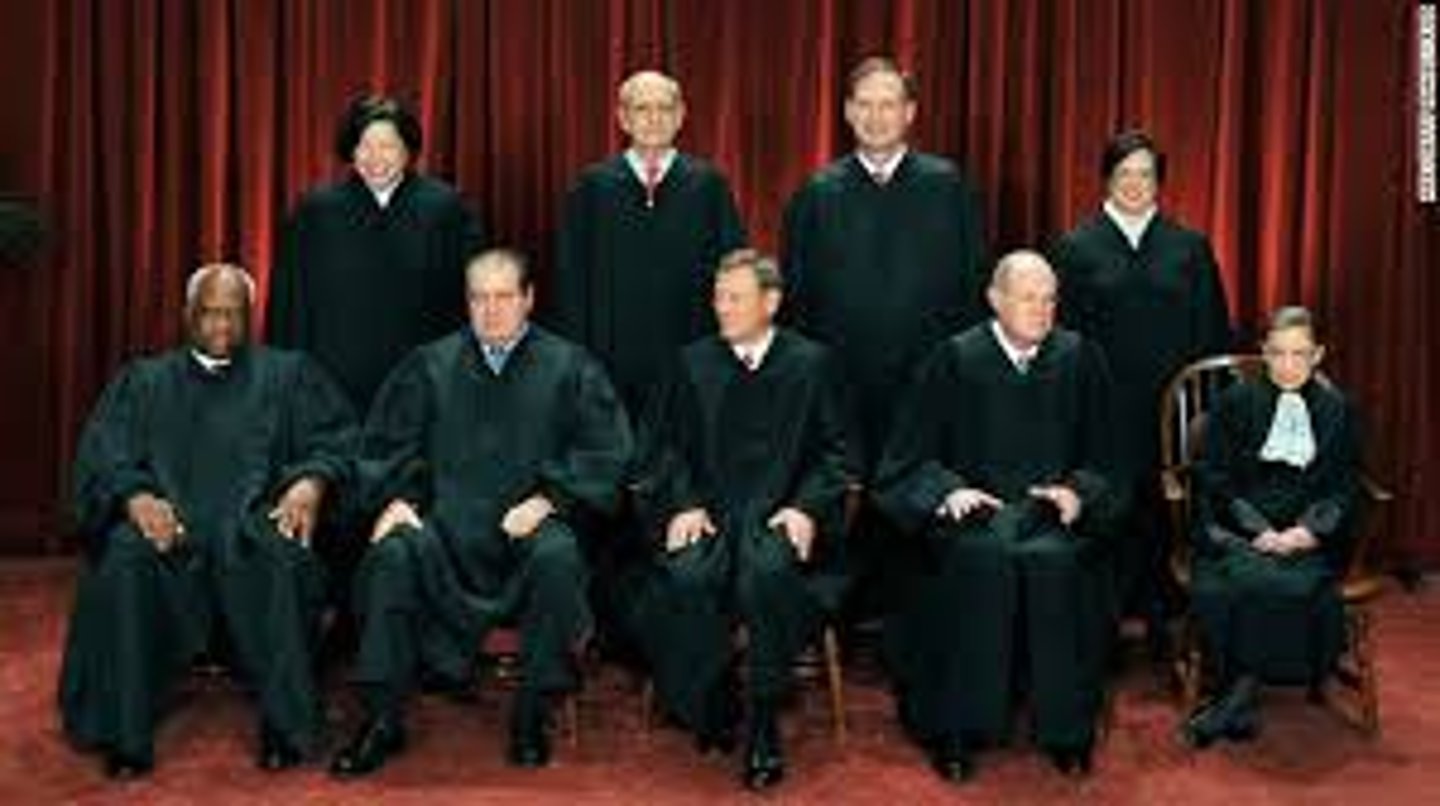
Supreme Court Justices
9 justices, lifetime appointment, nominated by the president,approved by the Senate

primary election
Nominating election held to choose party candidates who will run in the general election