Venomous Snakes
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
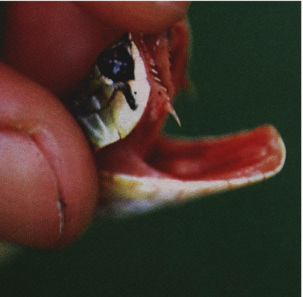
Small rear fangs indicate what
MINIMALLY venomous snake

No fangs indicate what
NON venomous snake

Long foldable fangs with sheath
VIPER
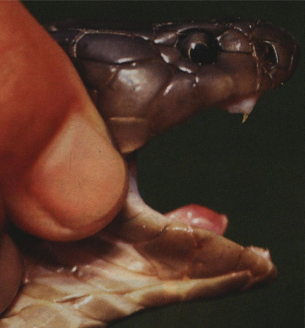
Short, permanent erect
Elapid
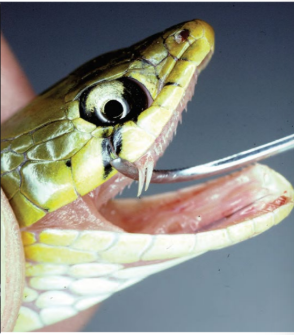
Rear fangs
Colubrid
What are in snake venoms
Digestive enzymes (SVMP), Phospholipase A2, Procoag enz, Polypeptide postsynaptic (a) neuron, presynaptic (b) neurotoxin
SVMP function
Damage basement membrane → EC damage and systemic bleeding
Phospholipase A2 function
Damage MT, blood cells and affects almost every organ
Procoagulant enzyme function
Cause DIC, coagulopathy
Polypeptide postsynaptic (a) neurotoxin function
Bind to AChR at motor endplate
Postsynaptic (b) neurotoxin funtion
Phospholipase that PERMANENTLY damage nerve endings
What are Elapidae
NEUROTOXIC snakes; include cobras, kraits and sea snakes

Banded krait (งูส้ามเหี่ลยม)

Flat tail
Sea snake (งูทะเล)

Malayan krait (งูทับสมิงคลา)

Viperidae
HEMATOTOXIC snakes; can be split into regular vipers and pit vipers
What are crotalidae (pit vipers)
Vipers with pit between the eye and nostril to sense infrared light

Russell’s viper (งูแมวเซา)

Malayan pit viper (งูกะปะ)

Green pit viper (งูเขียวหางไหม้)
Snakes found in urban areas
Green pit, malayan krait
Snakes found in rice field
Cobra, Russell’s viper
Snakes found in the garden
Malayan pit, GPV, Cobra, krait
Snakes found in the sea or mangrove
MPV, sea snake
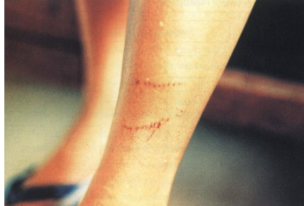
Teeth marks; snake was NOT venomous
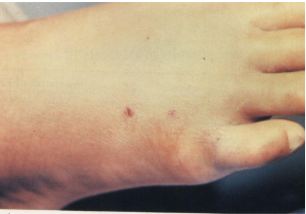
Fang marks; snake IS venomous
Syndrome 1 = Local swelling with bleeding/clotting disturbance
All species of Viperidae
Syndrome 2 = Local swelling + bleeding/clotting problem + shock/acute kidney injury
Russell’s viper
Syndrome 3 = local swelling + paralysis
Cobra or King Cobra
Syndrome 4 = Paralysis with minimal swelling with or without abdominal pain
Krait
Syndrome 5 = Paralysis + dark brown urine + acute kidney injury
SEA = krait or sea snake; India and Sri lanka = Russell’s viper
Neurological symptoms of snake bites
Bilateral ptosis and ophthalmoplegia
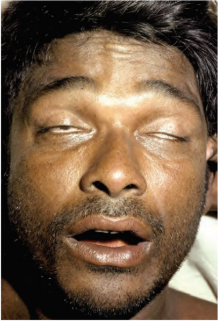
Bilateral ptosis
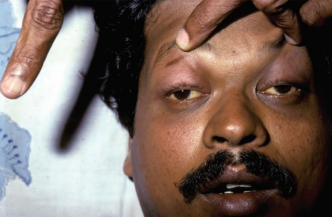
Ophthalmoplegia
First aid for snake bite
Immobilize limb, wrap wound loosely, DO NOT USE TOURNIQUET AND DO NOT SUCK OUT THE POISON