Earth and Space Unit 5 (Earth's Structure) Review
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
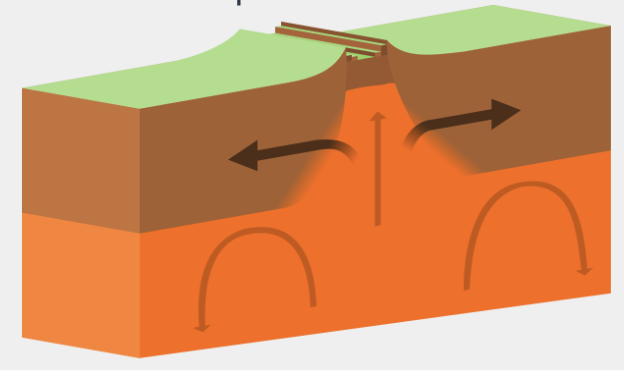
Divergent Boundary
A tectonic plate boundary where two plates move away from each other, often resulting in the formation of new crust in the form of rift valleys on land and ridges underwater.
Oceanic-Oceanic Convergent Boundary
A tectonic plate boundary where two oceanic plates collide, leading to the subduction of one plate beneath the other, often forming deep ocean trenches and underwater volcanoes.
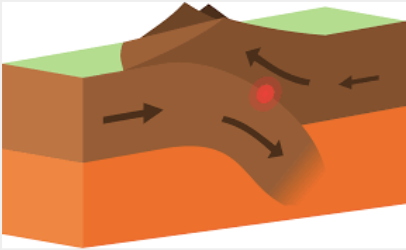
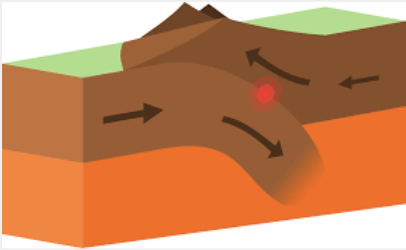
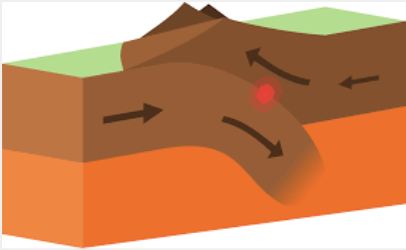
Oceanic-Continental Convergent Boundary
A tectonic plate boundary where an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate, resulting in the subduction of the denser oceanic plate under the less dense continental plate, which can create mountain ranges, volcanic activity, and deep ocean trenches.
Continental-Continental Convergent Boundary
A tectonic plate boundary where two continental plates collide, leading to the formation of mountain ranges and significant geological uplift, as neither plate is subducted.
Transform Boundary
A tectonic plate boundary where two plates slide past each other horizontally, causing earthquakes and fault lines, but no significant geological features are created.
Rift fault
Divergent faults in which the material between sinks, creating a rift
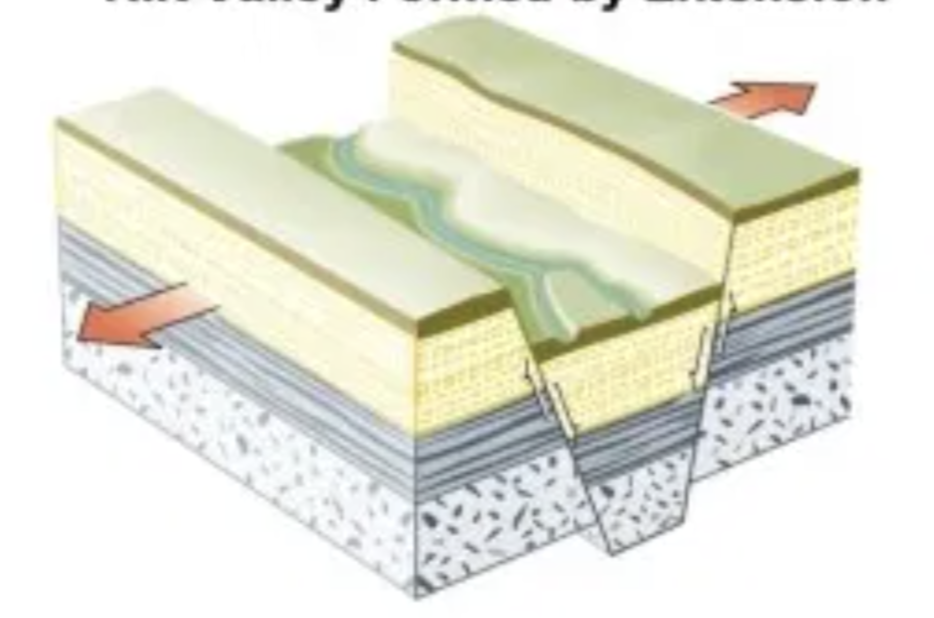
Ridge
Divergent faults in which new material is created from rising magma that cools when it touches water
Reverse/thrust fault
A convergent boundary in which the middle crumples upward, creating folded mountains
Subduction zone
A convergent boundary where the denser tectonic plate moves under the other, creating coastal mountain ranges
Strike-slip fault
A transform boundary that causes linear shifts and earthquakes.
Hotspots
Active volcanoes that are not on plate boundaries
Volcano
Magma rises where Earth’s crust is weak at convergent or divergent boundaries.
Earthquake
Caused by built-up stress at a plate boundary and the sudden release of pressure, sending seismic waves through Earth.
Tsunami
MASSIVE waves usually caused by underwater earthquakes.
Mountains
They rise up as two tectonic plates collide at convergent boundaries.
Inner core
The innermost layer of Earth, made of solid iron, nickel, and other heavy metals.
Outer core
The churning of liquid iron, nickel, and other heavy metals in this layer of Earth creates the planet’s magnetic field.
Mantle
The layer of Earth that is made of viscously solid molten rock and lots of silicates
Crust
The outermost layer of Earth, made of solid rock, that comes in two types, oceanic (denser because of the pressure of ocean water) and continental.
Mantle convection
The movement of materials in the mantle. Lower mantle gets heated, rises, then cools off and sinks, similar to how a lava lamp works.
Slab pull
The pulling force exerted by a falling cold and dense oceanic plate.
Ridge push theory
When new crust forms on a ridge, old crust is pushed away
Wind erosion
Particles get moved from the force and kinetic energy of the wind
Water erosion
Moves particles with kinetic energy of rain, rushing river, mechanical energy of surface runoff, etc.
Gravity erosion
Mass moves down steep slopes due to gravity, e.g. in a landslide
Freeze-thaw weathering
When water seeps into cracks, freezes, and expands, breaking things. This process is what causes potholes to form.
Onion skin weathering/exfoliation
The process of layers of rock flaking off
Chemical weathering
When a reaction causes a chemical change, e.g. acid rain
Biological weathering
When a living thing breaks up rocks, e.g. tree roots, animals
Glaciation
When the weight of a glacier drags it downward, creating glacial sheets and U-shaped valleys. Then our climate warms, glaciers melt, causing erosion, weathering, and for the sea levels to rise.
Alfred Wegener’s evidence for his Theory of Continental Drift
Fossilized tropical plants in cold climates, mountain and fossil patterns line up on different continental coastlines, and continents fit together like puzzle pieces (especially South America & Africa)
Pangea
A supercontinent from 250 million years ago that was made up of all the different continents
