class 17 - cell signaling basics and receptors
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
signaling cell
source of a signaling molecule
signaling molecule
also called ligand
substance secreted by signaling cell
examples: peptides, lipids, gases, hormones, neurotransmitters, etc
secretion
process where signaling cell releases signaling molecules
receptor protein
on responding cell, binds to signaling molecule
is an integral/transmembrane protein because it takes extracellular signals and causes intracellular change
responding cell
the cell that receives information from the signaling molecule
what happens if the signaling molecule and receptor can’t bind to each other?
the cell doesn’t detect/respond to the signal, even if the signal is present
what happens if the receptor’s shape changes?
receptor and signaling molecule won’t bind properly → prevents/changes signal activation
what happen if the internal signal proteins are altered?
signal transduction pathway changes/fails → incomplete/incorrect cellular response
receptor activation
when the ligand/signaling molecule binds to the receptor on responding cell, turning the receptor on
what are the responses to receptor activation?
they vary:
enzymes: activation → shape/activity of enzyme changes
channel proteins: activation → opens/closes in response
some receptors activate other proteins in the cell
signal transduction
the chain reaction (one molecule sets of another, etc)
activation → transmits through cytoplasm and connects to intracellular proteins → signal transduction cascade
the signal is amplified at every step of the pathway
low signal concentration → amplification → large impact on responding cell
cellular response
change in cellular behavior due to the signal
ex: cell division, DNA replication, DNA expression (gene expression), protein synthesis, change in enzyme activation, etc
termination
stopping the signal transduction
methods to terminate
ligand detaches - receptor changes shape to inactive form → receptor becomes inactive
dephosphorylation - G proteins convert GTP → GDP, turning off and stopping further activation
any downstream protein could be activated
most signaling pathways are counteracted at one or more points to terminate a cell’s response
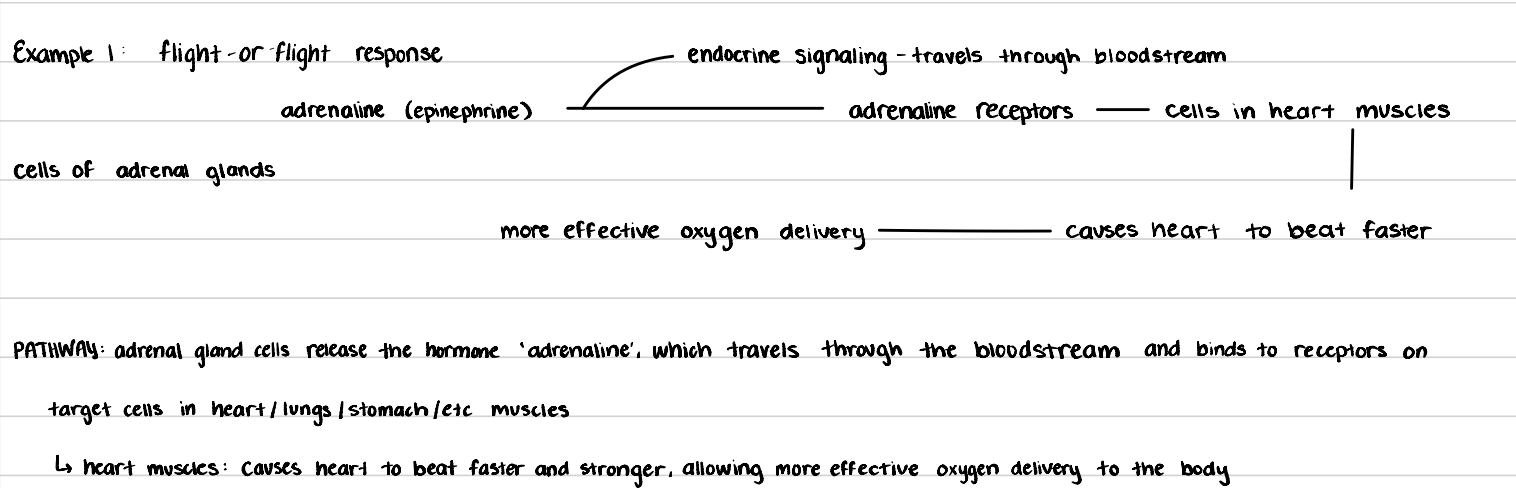
explain cell signaling in a flight or flight response
signaling cell: cells of adrenal glands
signaling molecule: adrenaline (travels by endocrine signaling)
receptor protein: adrenaline receptors
responding cell: heart muscles
cell response: causes heart to beat faster, leading to more effective oxygen delivery
explain cell signaling in bacteria
signaling cell: pneumococcal cells
signaling molecule: 17 amino acid peptide
receptor protein: peptide receptor on surface of pneumococcal cells
responding cell: pneumococcal cells
cell response: when enough receptors are bound (known by quorum sensing), an expression of genes for DNA uptake is triggered
quorum sensing
detects population density and responds by turning on specific genes across entire community
used to control + coordinate different types of bacterial behaviors
low cell density = low probability of receptor binding, and high cell density = high probability of receptor binding. more receptor binding = more DNA uptake
DNA uptake
when bacteria take in foreign DNA
endocrine signaling
between cells far apart from each other
carried by circulatory system (bloodstream)
ex: adrenaline
paracrine signaling
molecule travels to neighboring cell by diffusion
ex: neurons release neurotransmitters that diffuse across a synapse
if responding cell = neuron: response releases more neurotransmitters + a nerve impulse
if responding cell = a muscle cell: muscle may contract
synapse
junction where nerve cell transmits a signal to another cell during paracrine signaling
growth factor
small soluble signaling molecule that tells cells to grow, divide, or survive (prevent cell death)
autocrine signaling
signaling between different parts of one cell
signaling cell = responding cell (they’re the same)
contact-dependent signaling
direct contact between two cells
typically a ligand + receptor on another cell
how cells respond to threat
ex: gap junctions in animal cells