1-Neoplasms I
Tumor
Swelling
Neoplasia
New uncontrolled growth
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Tumor
Swelling
Neoplasia
New uncontrolled growth
Neoplasia - Clonal
Comes from one altered cell
Benign tumor
Does not lead to death
Malignant tumor
Leads to death or destruction
Malignancy - Key ability
Local invasion due to mutations
Cancer
Another word for malignant neoplasm
Carcinoma
Epithelial malignant neoplasm
Sarcoma
Mesenchymal malignant neoplasm
Leukemia
Malignancy of hematopoietic (blood) cells
Carcinosarcoma
Malignancy of both mesenchymal and epithelial origin
Blastoma
Tumor of undifferentiated cells
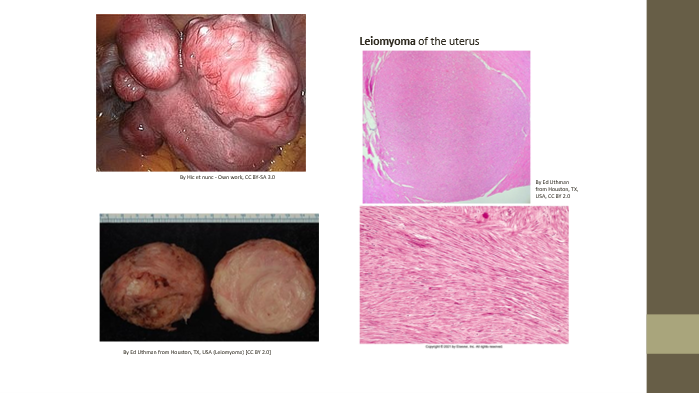
Leiomyoma
Benign mesenchymal muscle neoplasm
Leiomyosarcoma
Malignant mesenchymal muscle neoplasm
Squamous cell papilloma
Benign stratified squamous epithelial neoplasm
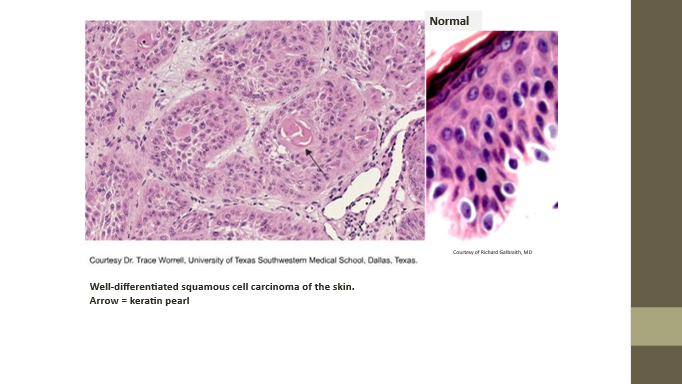
Squamous cell carcinoma
Malignant stratified squamous epithelial neoplasm
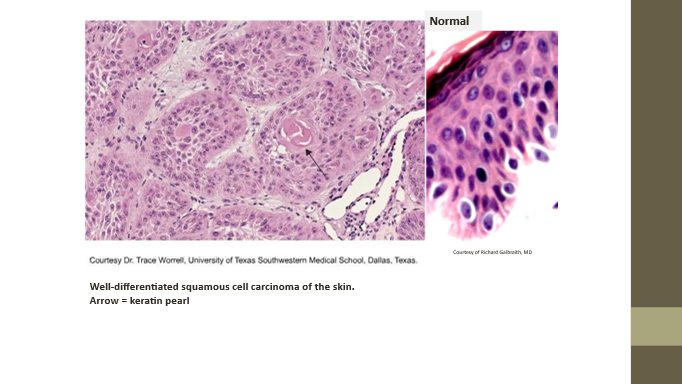
Keratin pearls
Histologic sign of squamous cell carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma
Malignant neoplasm from basal cells of skin/adnexa
Adenoma
Benign neoplasm of glandular epithelium
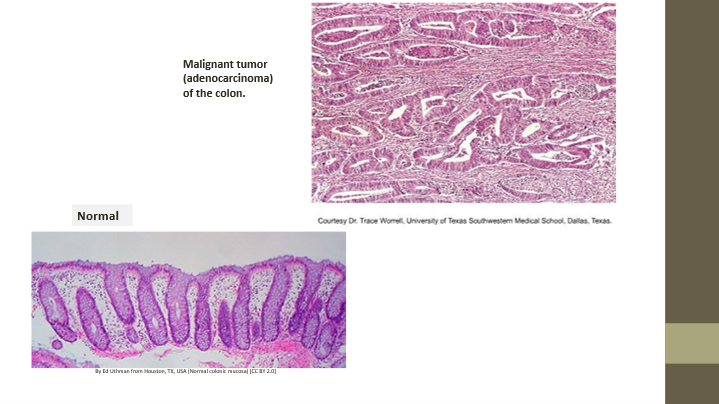
Adenocarcinoma
Malignant neoplasm of glandular epithelium
Hepatic adenoma
Benign liver cell neoplasm
Hepatocellular carcinoma (Hepatoma)
Malignant liver cell neoplasm
Melanocytic nevus
Benign melanocyte tumor
Malignant melanoma
Malignant melanocyte tumor
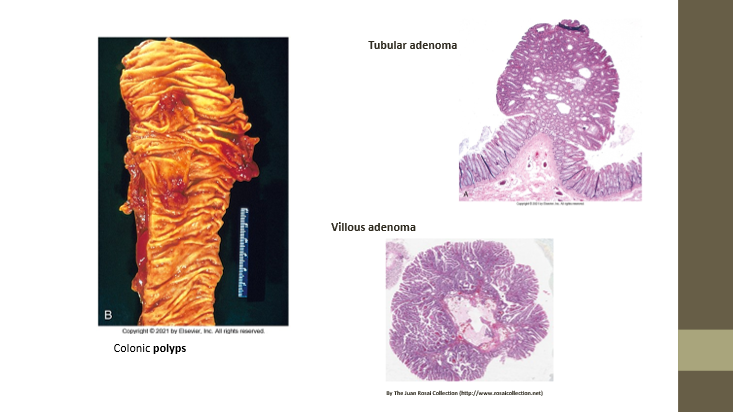
Tubular adenoma
More columnar appearance; future malignant potential
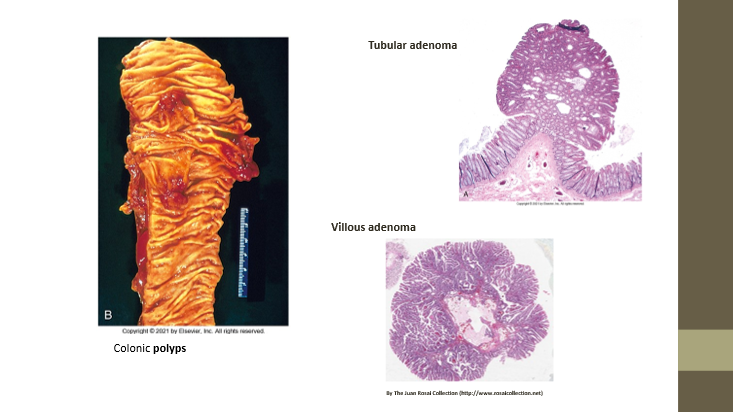
Villous adenoma
Finger-like projections; future malignant potential
Mixed tumors
Neoplasms with more than one neoplastic tissue type from one germ cell layer
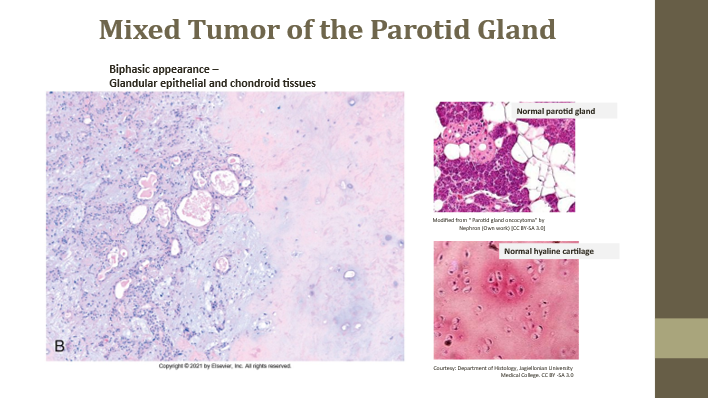
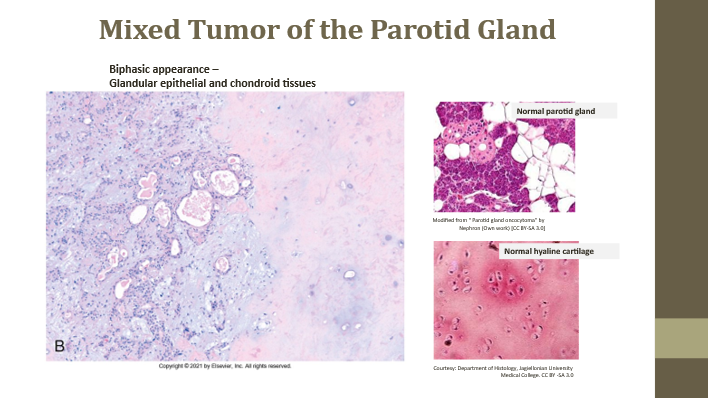
Pleomorphic adenoma
Benign mixed tumor of salivary glands
Malignant mixed tumor
Malignant mixed tumor of salivary glands
Wilms tumor (Nephroblastoma)
Malignant renal anlage tumor
Teratogenous tumors
Derived from more than one germ cell layer
Totipotential cells
Located in gonads or embryonic rests; origin of teratomas
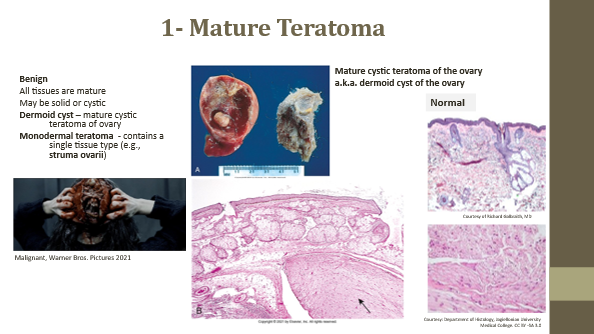
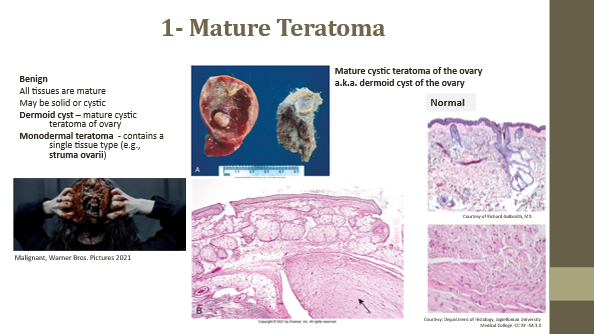
Mature teratoma
Benign tumor with all mature tissue types
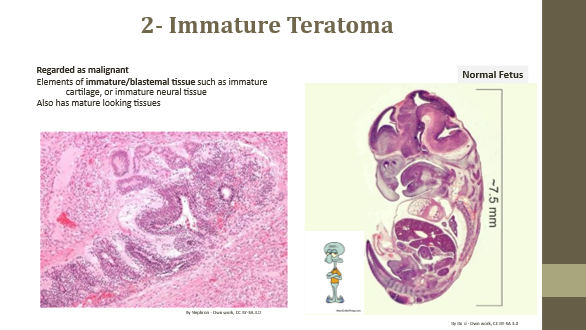
Immature teratoma
Malignant tumor with immature/blastemal tissue (e.g., cartilage, neural tissue)
Dermoid cyst
Mature cystic teratoma of ovary (benign)
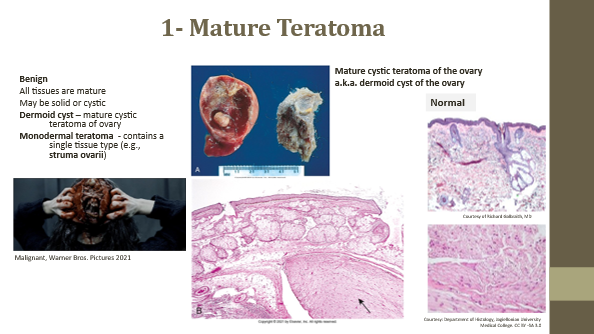
Monodermal teratoma
Contains a single tissue type (e.g., struma ovarii with thyroid follicles)
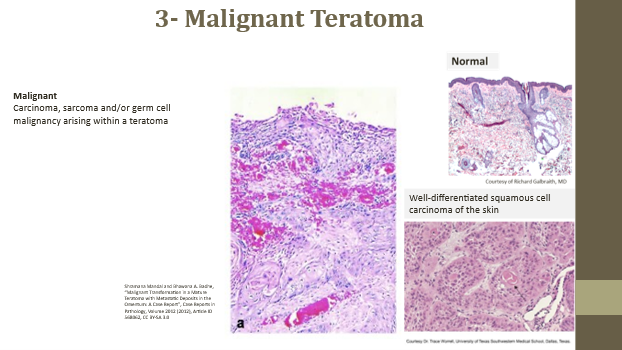
Teratocarcinoma
Malignant teratoma (carcinoma, sarcoma, or germ cell malignancy)
Teratoma origin
Totipotent germ cells → tissues from ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
Common teratoma sites
Ovary, testis, midline of body
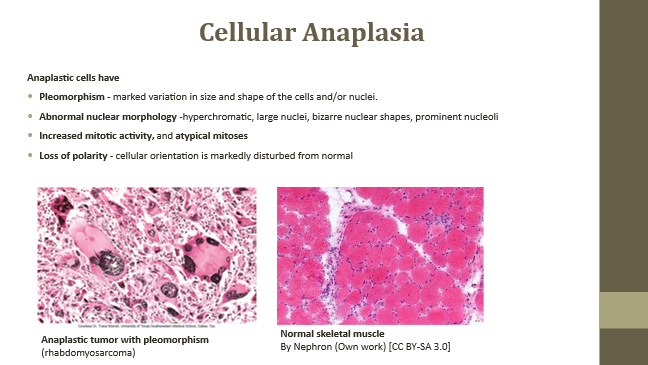
Anaplasia
Decreased differentiation (de-differentiation)
Tumor differentiation types
Well, moderate, poor, or undifferentiated
Benign tumors
Usually well-differentiated
Malignant tumors
Can be any differentiation level
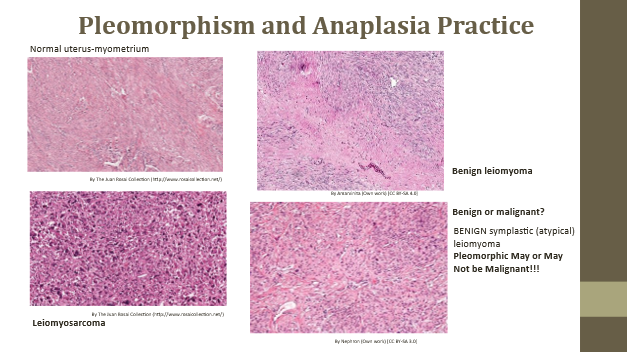
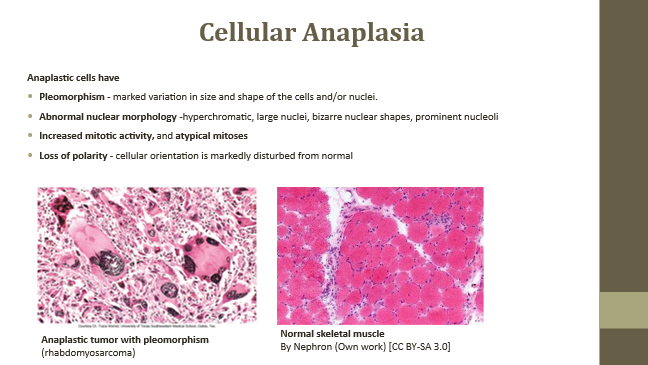
Pleomorphism
Variation in tumor cell appearance
Loss of polarity
Tumor cells lose alignment with each other or basement membrane
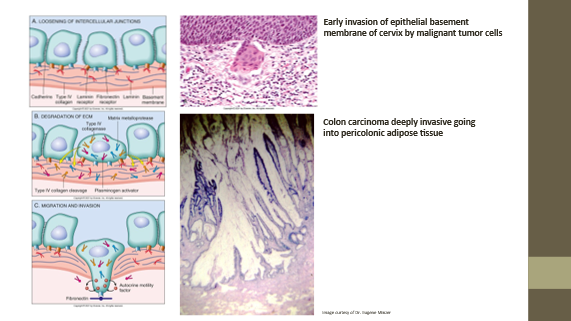
Metastasis
Spread of neoplastic growth to distant site
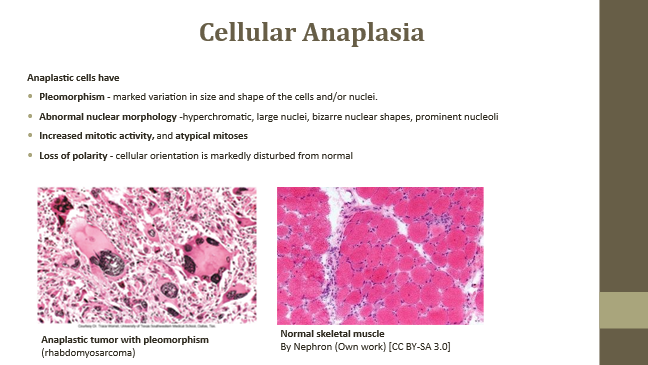
Pleomorphism (Anaplastic cell feature)
Variation in shape, size, and nuclei
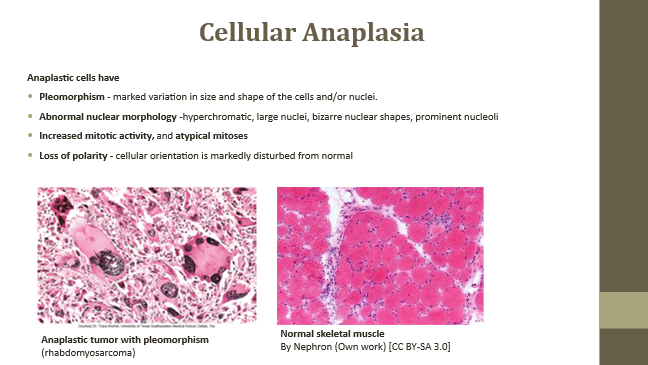
Abnormal nuclear morphology
Dark, irregular, lumpy nuclei
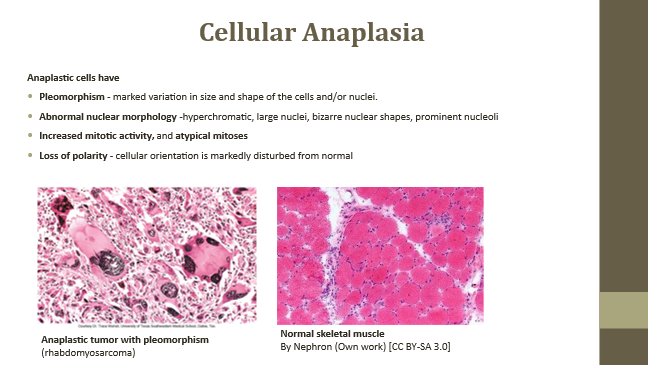
Increased mitotic activity
Atypical mitoses observed
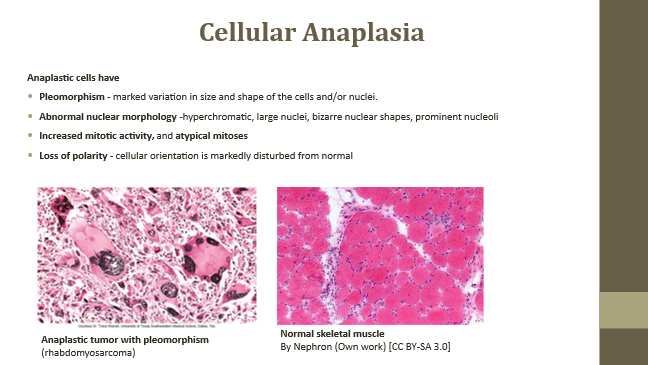
Loss of polarity (Anaplastic feature)
Disruption of normal cellular orientation
Hyperplasia
Increase in cell number
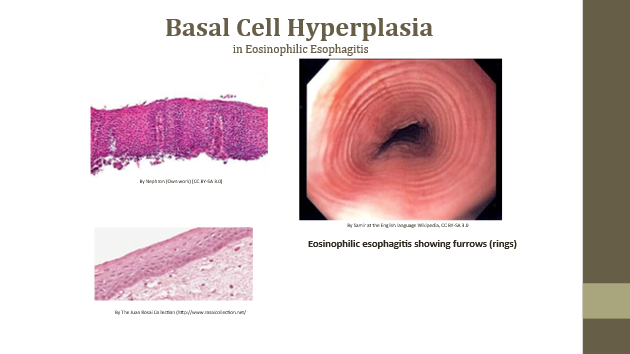
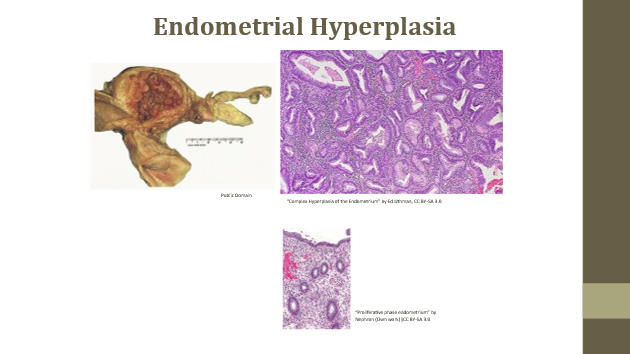
Hyperplasia examples
Eosinophilic esophagitis (rings/furrows), endometrial hyperplasia
Metaplasia
Reversible replacement of one differentiated cell type by another
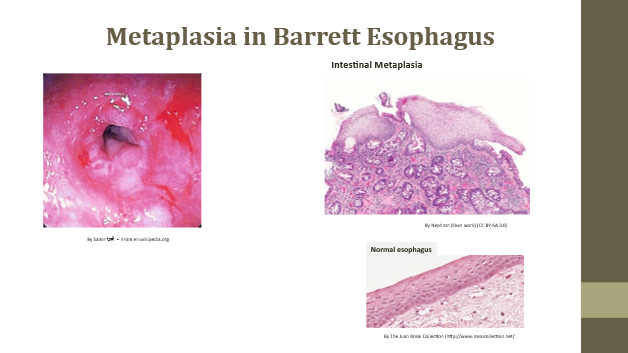
Metaplasia mechanism
Adaptation to stress (e.g., Barrett esophagus)
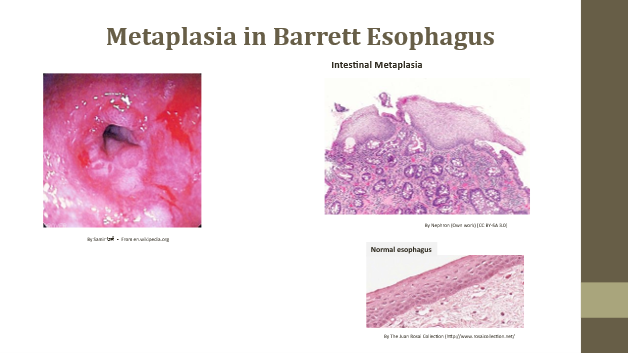
Metaplasia risk
May progress to dysplasia if irritant persists
Dysplasia
Disordered pre-cancerous growth, not adaptive
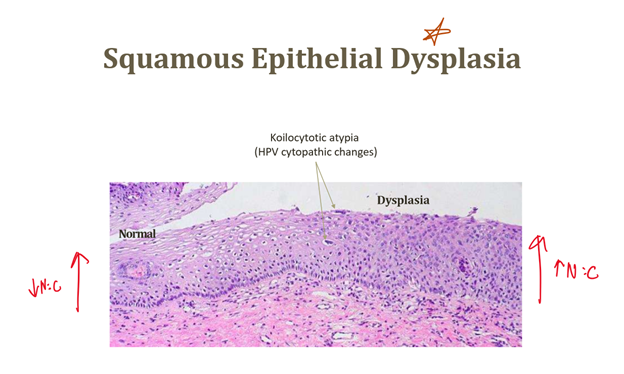
Dysplasia features
Increased N:C ratios, clumped chromatin
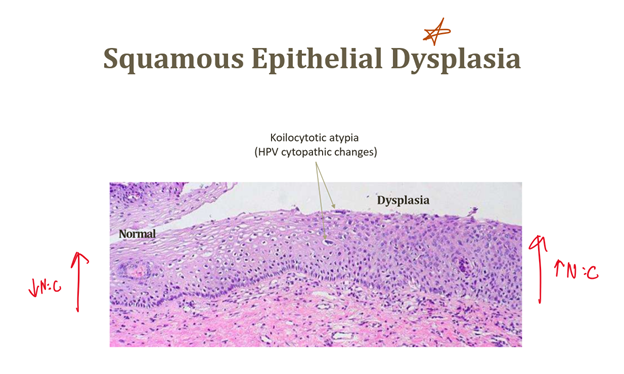
Dysplasia reversibility
Possibly reversible if irritant removed
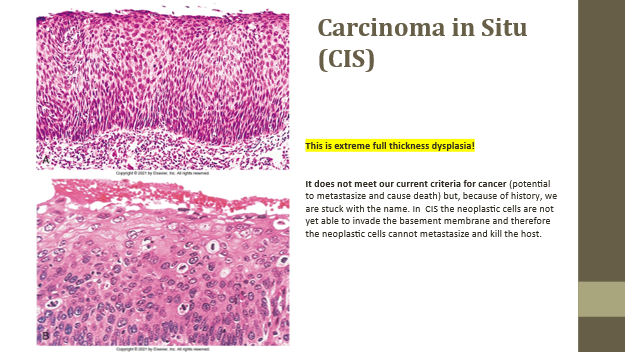
Carcinoma in situ (CIS)
Severe dysplasia with full thickness involvement, no invasion
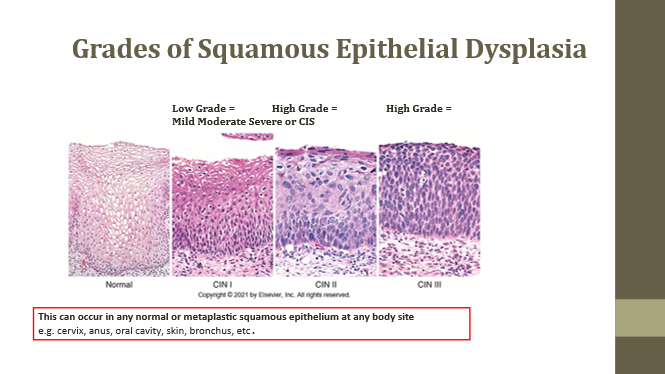
Normal squamous epithelium
Baseline
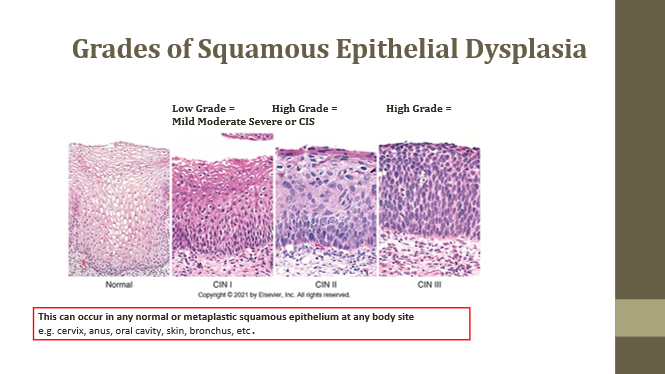
Low grade/Mild dysplasia
Slightly increased N:C ratio
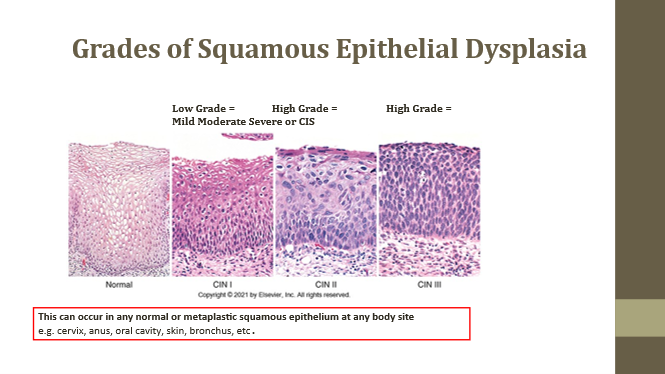
High grade/Moderate dysplasia
Increased N:C and disorganization
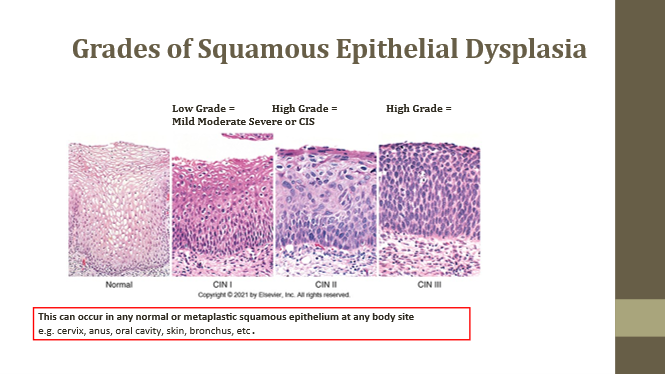
High grade/Severe dysplasia or CIS
No polarity, very high N:C ratio
CIS key trait
Abnormal cells fill epithelium but don’t breach basement membrane
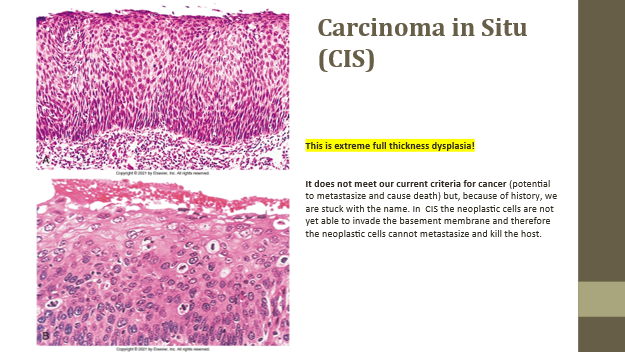
CIS significance
Not invasive cancer, but may metastasize if it progresses
Malignant tumors
Invade tissue, metastasize, not fully/partially encapsulated