Comprehensive Study of Chapter 57: Stomach Disorders in Medicine
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
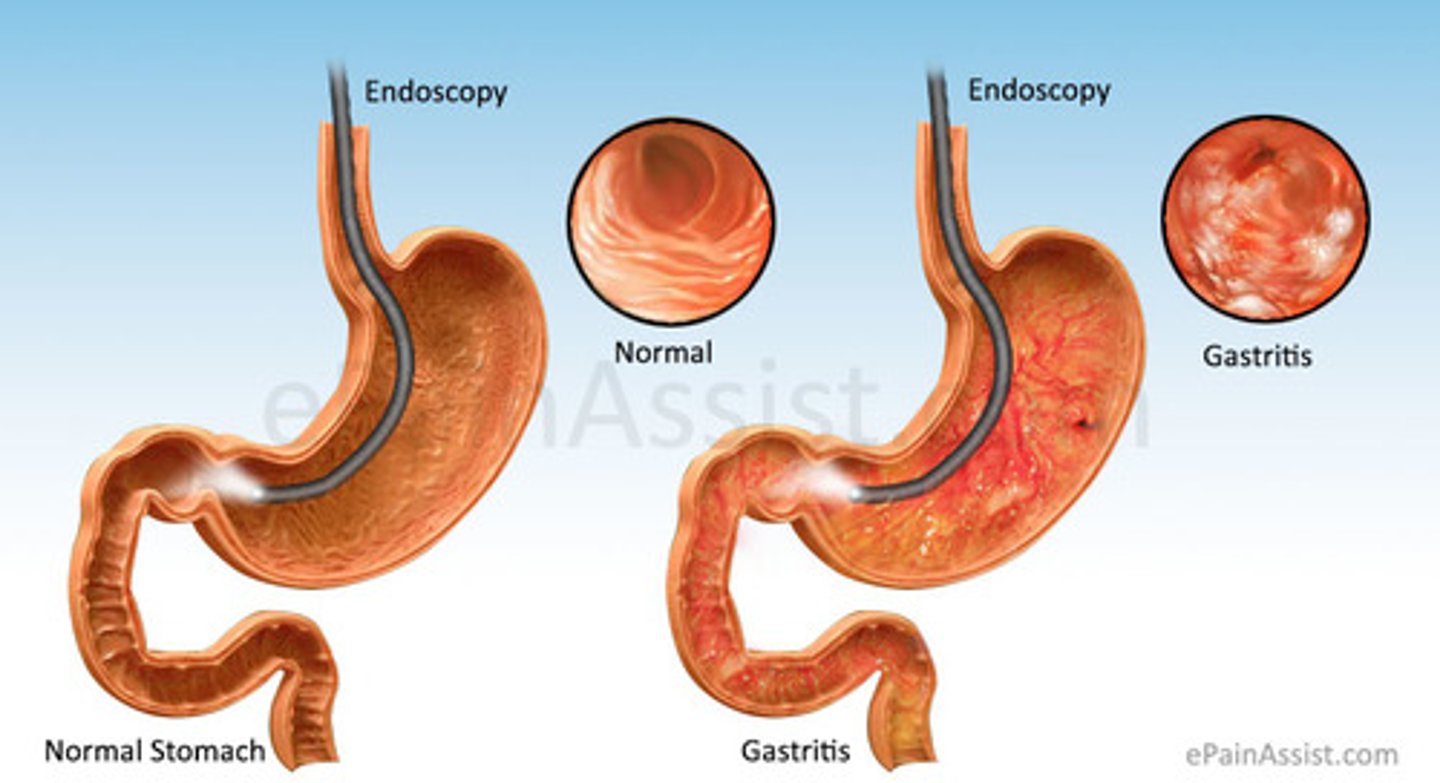
Gastritis
epi
patho
c/m
dx
surgery tx
med tx
assessment and analysis
assessment
teaching
EPI
- Inflammation of gastric mucosa caused by chronic stress to stomach lining
- Chronic ingestion of irritating foods
- Pathogens like H.Pylori, E.coli, and salmonella
- Overuse of aspirin or NSAIDs
- Stress
PATHO
- Prolonged irritation of the stomach (NSAIDS, alcohol, H-pylori, pernicious anemia)
- Helicobacter pylori-gram negative bacterial may also come from contaminated food that has not been washed well or cooked properly and contaminated water
- Acute (quick onset) and chronic (prolonged)
C/M
- Can be asymptomatic
- Epigastric pain
- N/V
- Decreased appetite
- Change in color of stool
- Pain can be exacerbated with the ingestion of spicy foods
- Acute or exacerbations of chronic gastritis, there may be evidence of dehydration or upper GI bleeding. With significant fluid or blood loss, the patient may develop signs of hypovolemic shock
DX
- Biopsy
- Upper GI x-ray series or endoscopy and histological exams of tissue specimen from biopsy
- Stool testing for presence of occult (blood) in stool
- Urea breath testing to detect active infection with H.Pylori
SURGERY
- very rare
- vagotomy
- partial or total gastrectomy
- pyloroplasty
MEDS
- supportive care for relieving clinical manifestations
- IV fluids and clear liquids
- Reducing cause of discomfort
- Medications for H.Pylori (antacids, PPIs, Antibiotics, aka triple therapy)
- Sucralfate (Carafate)
- GI rest
ASSESSMENT/ANALYSIS
- epigastric pain
- N/V
- decreased appetite
- weight loss
- change in color of stool
ASSESSMENT
- vitals
- hx of presenting s/s
- lab assessments for H.Pylori
- serum electrolytes
- I/Os
TEACHING
- immediately report hematemesis
- take medications are prescribed
- avoid irritants associated with gastric episodes
- NPO (6 to 12 hrs) then introduce clear liquids slowly then progress diet
- Antiemetics
Gastroenteritis
epi
patho
c/m
dx
assessment
action
teaching
EPI
- Inflammation of stomach and intestines caused by ingestion of virus, bacteria, or parasite (Norovirus, C.Diff, salmonella, E.coli)
PATHO
- Increased luminal fluid that can not be absorbed
- Depletion of intracellular fluid
- Dehydration and electrolyte loss
- Chronic diarrhea
C/M
- Diarrhea
- N/V
- Anorexia
- Abdominal distention
- Poor skin turgor
- Severe dehydration
- Hyperactive bowel sounds
- Decreased blood pressure
- Dry mucous membrane
DX
- Stool culture
- Biopsy
- Upper GI x-ray series
- Rehydration with IVF
ASSESSMENT
- vital signs
- abdominal distention
- Bowel sounds and bowel elimination
- Serum electrolytes
- I/O
- Perineal skin status
- Skin and mucous membranes for signs of dehydration
- Pain level
ACTION
- Perform hand hygiene
- IV fluids
- Medications like antidiarrheals (loperamide)
- Give clear liquids or oral rehydration solutions
- Allow uninterrupted rest periods
- Venous thromboembolism (VTE) prophylaxis
- Meticulous perineal care
- Frequent oral care and lip emollients
TEACHING
- Include patient family or caregiver
- Dietary modifications
- Preventative measures, especially when traveling
- Proper food preparation
- Preventive measures
Peptic Ulcer Disease
patho
c/m
dx
meds
surgery
complications
assessment
actions
teaching
outcome
PATHO
- Damage to gastric mucosa (can be gastric or duodenal)
- Erosions due to corrosive action of gastric juice (H.Pylori, smoking, NSAIDs)
C/M
- Depends on ulcer location and pt age
- Gastric ulcers, pain is triggered or worsened by eating, shortly after meals with little or no relief from antiacids
- Duodenal ulcers pain is better with food and gets relief from antacids
- Pain usually located over a small area near the midline in the epigastrium
DX
- Upper GI endoscopy
- Liver function test
- Amylase/lipase
- CBC
- small bowel x-ray series
- Stool tests
MEDS
- Antacids
- PPI's
- Carafate
SURGERY
- Indicated with non healing and bleeding ulcers
- Endoscopic procedures
- BillRoth 1
- BillRoth 2
COMPLICATIONS
- GI hemorrhage
- Abdominal or intestinal infarction
- Perforation and penetration into attached structures
- Obstruction
- Peritonitis
ASSESSMENT
- vital signs
- CBC
- blood culture
- Gastric pH, check emesis and feces for occult blood
- Use of alcohol or other meds
- Smoking
- Serum electrolytes and BUN
- Pain
- Diet
- Weight
- Stress
- NSAID usage
ACTIONS
- Maintain IV infusions
- Prescribed medications
- Assist with gastric lavage
- Prepare pt for endoscopy
- Limit food intake after evening meal
- Document and report c/m
- Pain documentation
TEACHING
- Take meds as prescribed
- Avoid eating within 2 hours of bedtime
- Advise pt to avoid risk factors
OUTCOME
- Increased comfort
- pain control
- tolerating diet
Duodenal vs Gastric Ulcers
Duodenal Ulcer
- 30-60 years old
- Stomach acid high
- Food relieves pain
- Night pain
- Vomiting and bleeding less likely
- Perforation more likely
Gastric Ulcer
- Greater than 50 years old
- Stomach acid low to normal
- Food does not help with pain
- Vomiting and bleeding likely
- Perforation less likely
Gastric Cancer
epi
patho
c/m
dx
meds
surgery
complications
assessments
actions
teaching
EPI
- Second leading cause of cancer mortality worldwide
PATHO
- Begins as chronic gastritis
- Progress to atrophy, intestinal metaplasia, dysplasia, and then adenocarcinoma
C/M
- Usually asymptomatic until late disease process
- Indigestion
- Anorexia
- Weight loss
- vague epigastric pain
- Vomiting
- Abdominal mass
- Secondary anemia
DX
- Barium X-ray with fluoroscopy
- Endoscopy
- Cytology
- Biopsy
MEDS
- Antiemetics
- Opioid analgesics
SURGERY
- Gastric resection
COMPLICATIONS
- Dumping syndrome
- Wound infections
- Leaking of anastomotic sites
- Strictures
- Internal bleeding
ASSESSMENTS
- Physical examination, assessing for signs of metastasis
- Hematocrit and hemoglobin
- Serum electrolytes
- Bilirubin and alkaline phosphate
- Modified oral glucose test with hematocrit measure
- Comprehensive pain assessment
- Early signs of dumping syndrome
- Anxiety
- End of life care
ACTIONS
- Small, frequent meals
- Verbalize feelings and concerns
- Prepare for surgery
TEACHING
- Medication teaching
- Pain and precipitating factors
- High calorie, high protein meals
- Nutritional supplements
- Main signs of dumping syndrome
- Relaxation techniques