Drug Discovery and Development Process
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A collection of vocabulary flashcards based on the Drug Discovery and Development Process lecture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Drug Discovery
screen for the effect
Preclinical Studies
3-6 years
proof of mechanism
how it works
does what you claim
minimal study
dosing limits
Phase I Trials
safety
does it work in humans
establish dosing range
Phase II Trials
safety
efficacy
dose selection
Follow-up studies to evaluate effectiveness, further assess safety, and determine the optimal dose for further testing.
Phase III Trials
safety
efficacy
Large-scale trials to confirm the effectiveness of the drug, monitor side effects, and compare it to commonly used treatments.
comparrison between different demographics (race, age location)
Phase IV Trials
Studies done after the drug has been approved to gather more information on the drug's safety and long-term effectiveness.
NDA (New Drug Application)
Formal proposal to the FDA for approval to market a new drug after it has completed clinical trials. first application with human data
who approves a new drug
health product and food administration (HPFB) in Canada
post marketing activities
1 new drug is approved
health canada
canadian food inspection agency
CADTH (Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health)
Organization that provides evidence-based information on the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of drugs to inform healthcare decision-making.
Pharmacovigilance
The science related to the detection, assessment, understanding, and prevention of adverse effects or any other drug-related problems.
Post-marketing Surveillance
Monitoring of drugs after they have been released into the market to identify any long-term effects.
Priority Review (PR)
Applies to drugs that shows substantial evidence of clinical effectiveness at the end of the clinical trial phases.
Notice of Compliance with Conditions (NOC/c)
Applies to drugs with promising evidence of clinical effectiveness throughout the clinical trial phases. Approval would be granted to a manufacturer to market and sell that drug in Canada with the condition that the manufacturer execute additional studies to confirm the drug’s benefit and safety, quality and marketing
what are the regulatory bodies reviewing?
safety, effectiveness and quality of the product.
Major regulatory bodies
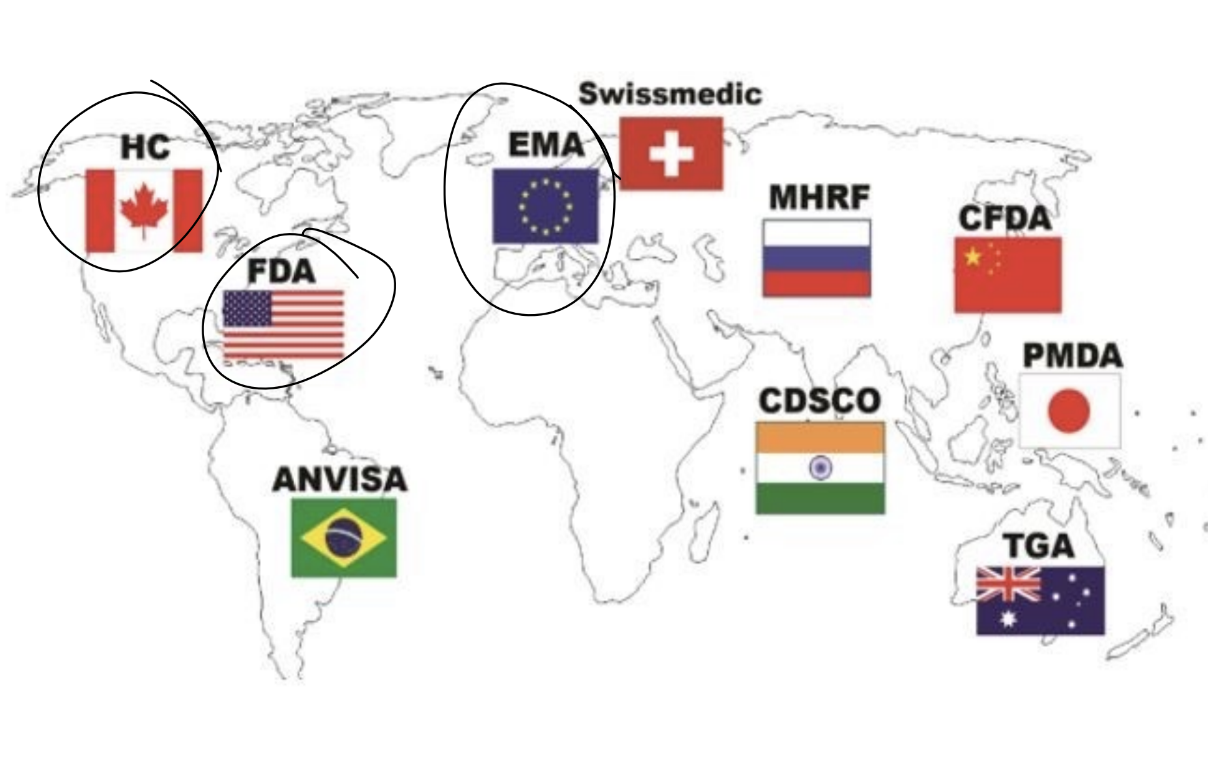
what factors influence the accelerated review process from health canada
For health conditions that are serious, life-threatening or for a severely debilitating disease (such as Alzheimer’s disease, cancer, AIDS, or Parkinson’s Disease), the HPFB can provide faster authorization of a drug
stage 1 “pre-discovery“

stages 2 and 3 - drug discovery & preclinical studies
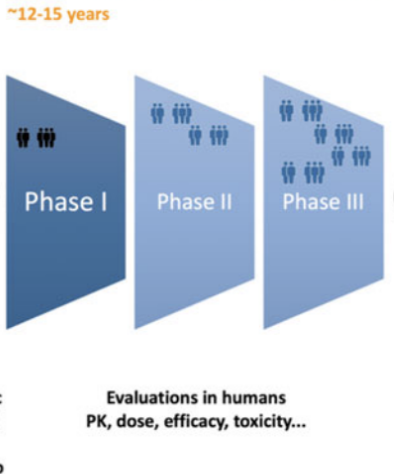
stage 4 - clinical trials
stage 5 - review & approval + stage IV
project ORBIS
an initiative that aims to improve the efficiency of clinical trials by streamlining the regulatory process and utilizing real-world evidence across multiple countries.
Madical device regulations
are regulated by Health Canada
part 1 - Medical devices other than in vitro diagnostic devices
part 2 - in vitro diagnostic devices
clinical trial phases
preclinical - phase 1 - phase 2 - phase 3 - phase 4
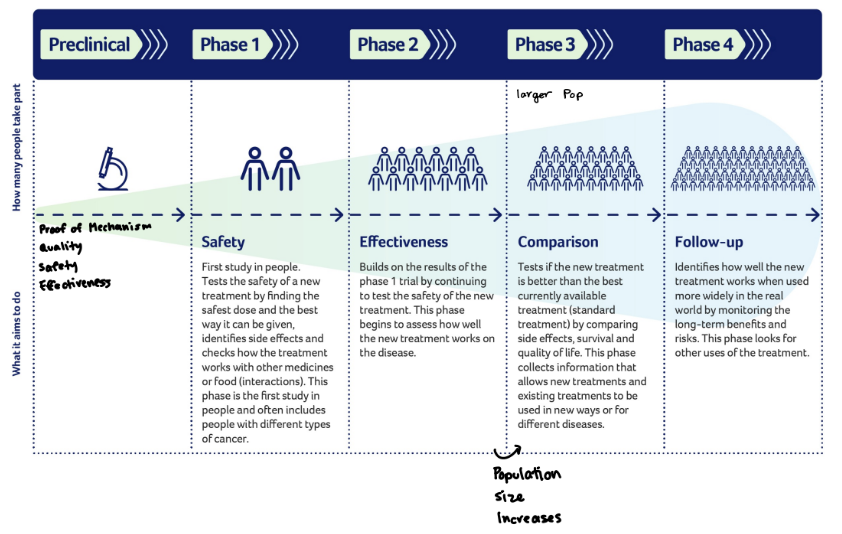
phase 1
the safety phase - placebos are administered
phase 2
the effectiveness phase - drug is given to a larger group of individuals
phase 3
the confirmation phase - if results from phase 2 look promising, then the drug is given to an even larger group of individuals
phase 4
the monitoring phase - after the drug is already approved and being sold. more information is gathered on the best ways to utilize the drugand monitor long-term effects.
what If the drug is to be used outside the terms of the market approval?
to make a new claim, the produce will have to go through the whole process again. a CTA will need to be submitted to health Canada in order to obtain a NO Objection Letter.
what phase of brug development cost the most
Drug discovery & preclinical