Week 7 - Digestive System (Digestive tract Wall, Mouth, Pharynx, Oesophagus and Peritoneum)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
gastrointestinal (GI) tract
continuous muscular digestive tube that extends from the mouth to the anus
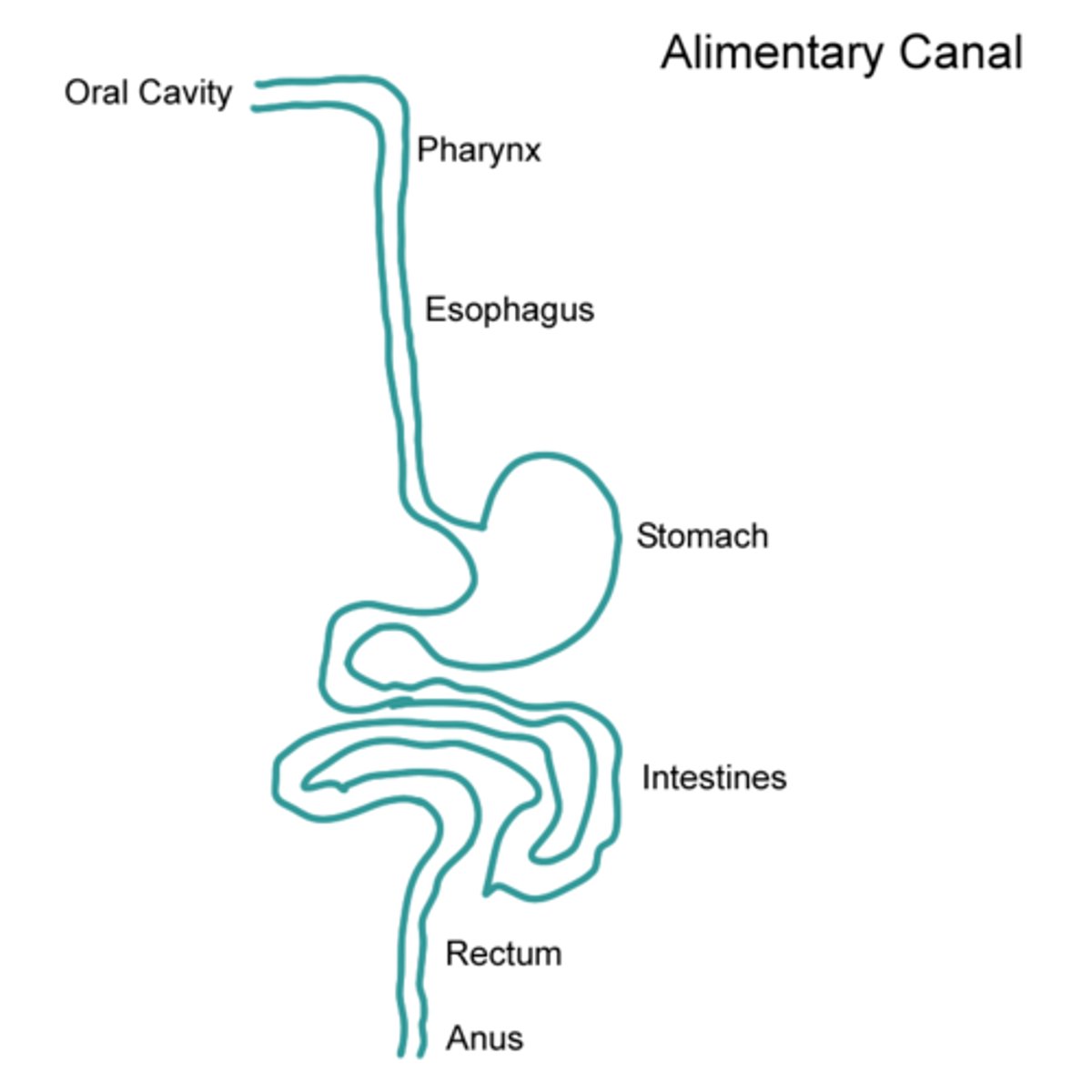
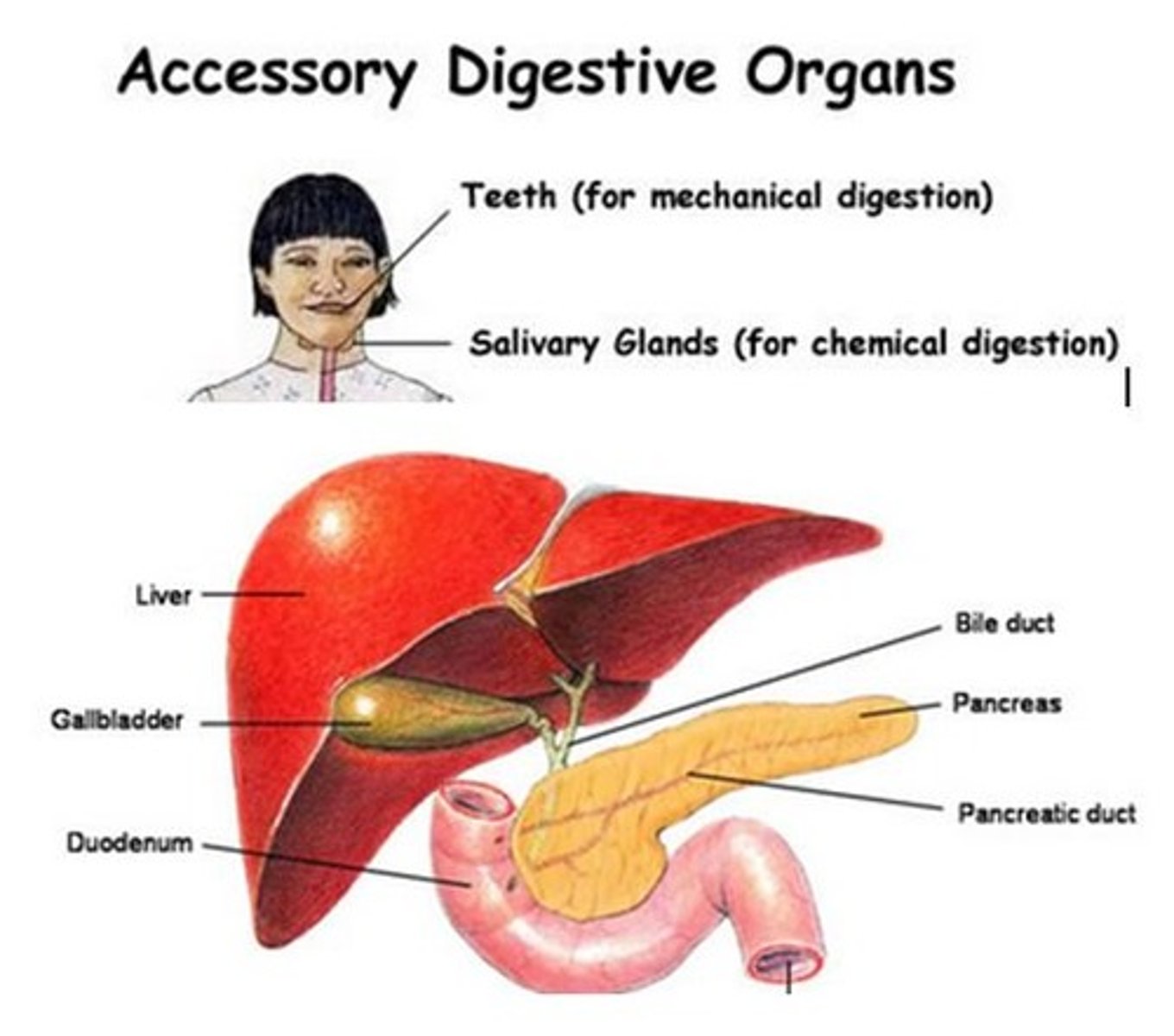
accessory digestive organs
includes teeth, tongue, salivary glands, gallbladder, liver, and pancreas
chemical digestion
enzymatic breakdown of food
mechanical digestion
chewing, mixing, and segmentation that prepares food for chemical digestion
Mucosa
innermost lining of the gastrointestinal tract
lamina propria
a layer of loose connective tissue
muscularis mucosa
thin layer of smooth muscle; adjacent to the submucosa
submucosa
layer of dense connective tissue in the alimentary canal wall that binds the overlying mucosa to the underlying muscularis
muscularis externa
muscle (skeletal or smooth) layer of the gastrointestinal wall
serosa
outermost layer of the alimentary canal wall present in regions within the abdominal cavity (stomach, small and large intestines)
adventitia
A thin layer of loose connective tissue that binds an organ to surrounding tissues or organs present in mouth, pharynx, and oesophagus
oral cavity
Consists of cheeks, tongue, and palate; lies posterior to the opening of the mouth; bounded posteriorly by the soft palate
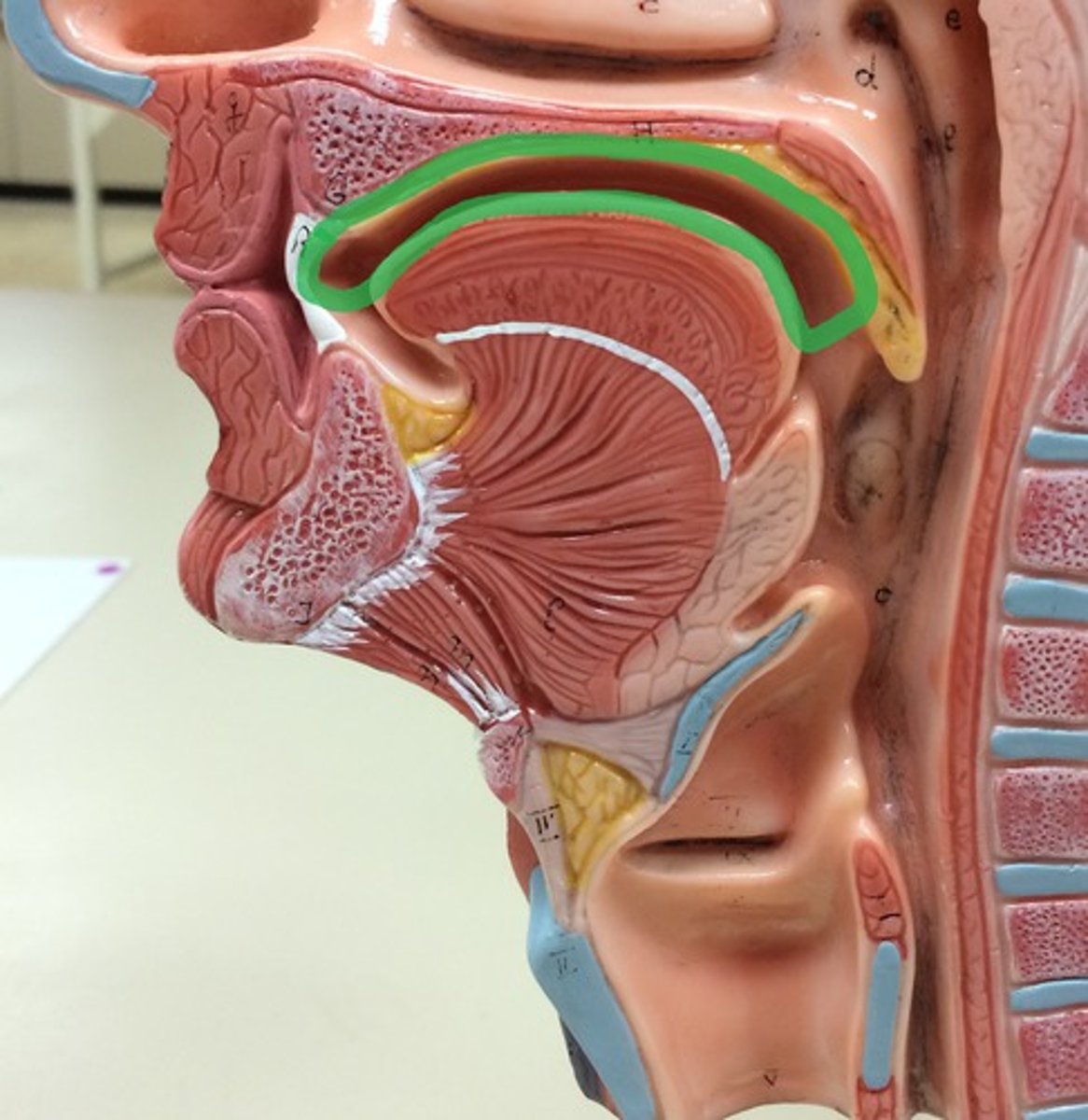
hard palate
anterior portion, supported by bone tissue and an external mucous membrane covering
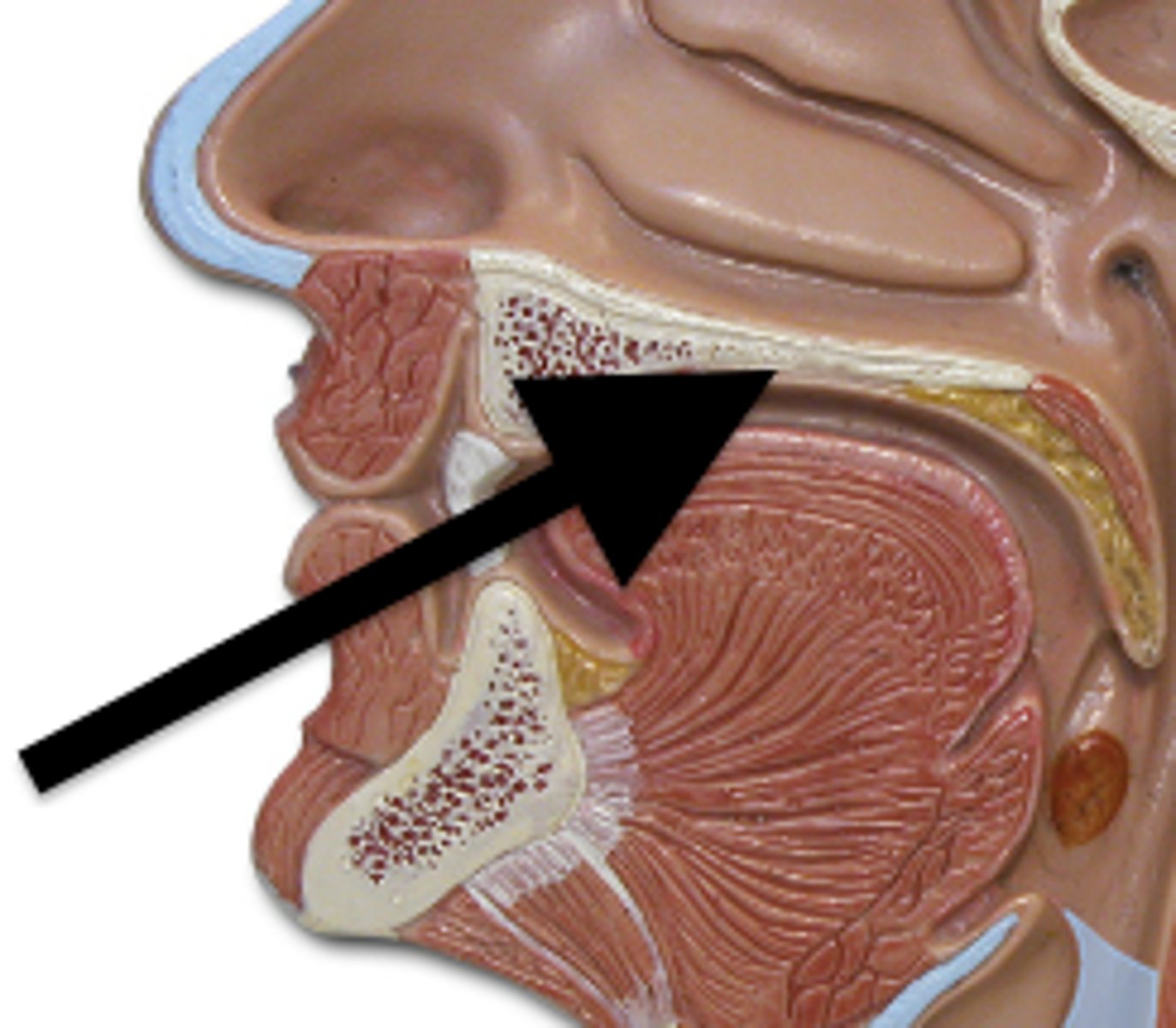
soft palate
posterior region of the bottom portion of the nasal cavity that consists of skeletal muscle
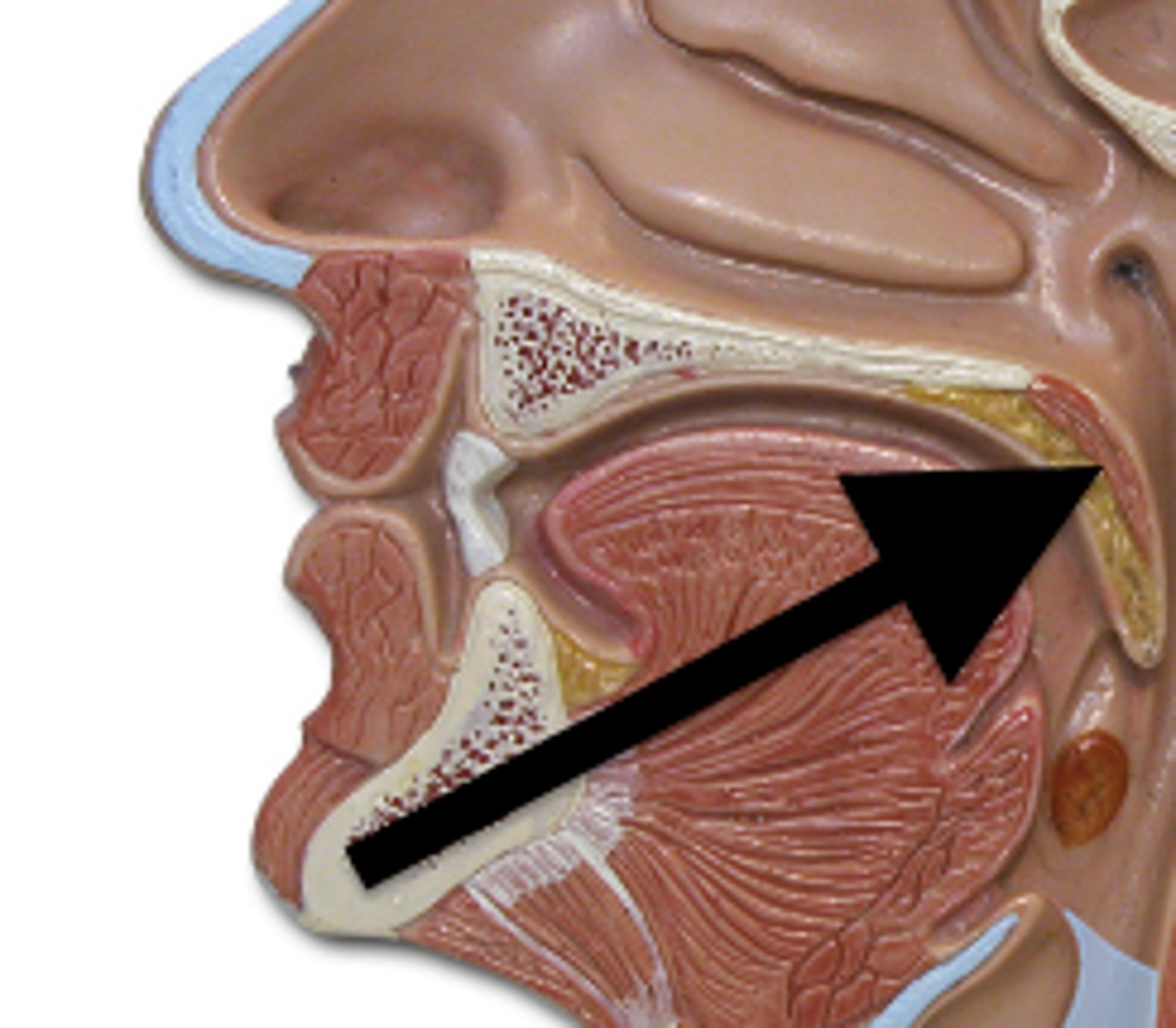
uvula
soft tissue hanging from the middle of the soft palate
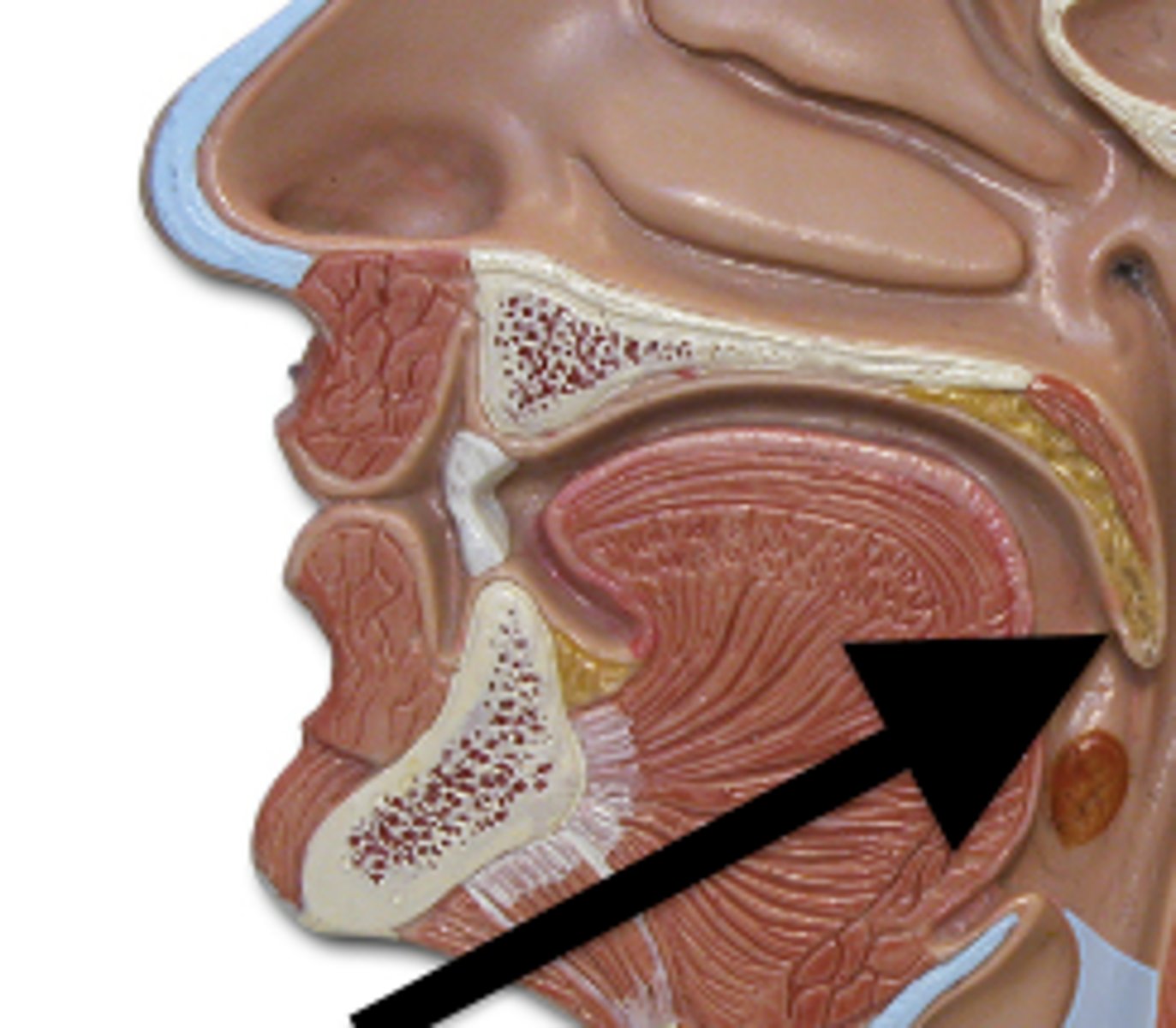
tonuge
located over the floor of the oral cavity. Facilitates ingestion, mechanical digestion, chemical digestion, sensation (taste, texture and temperature of food), swallowing and vocalisation
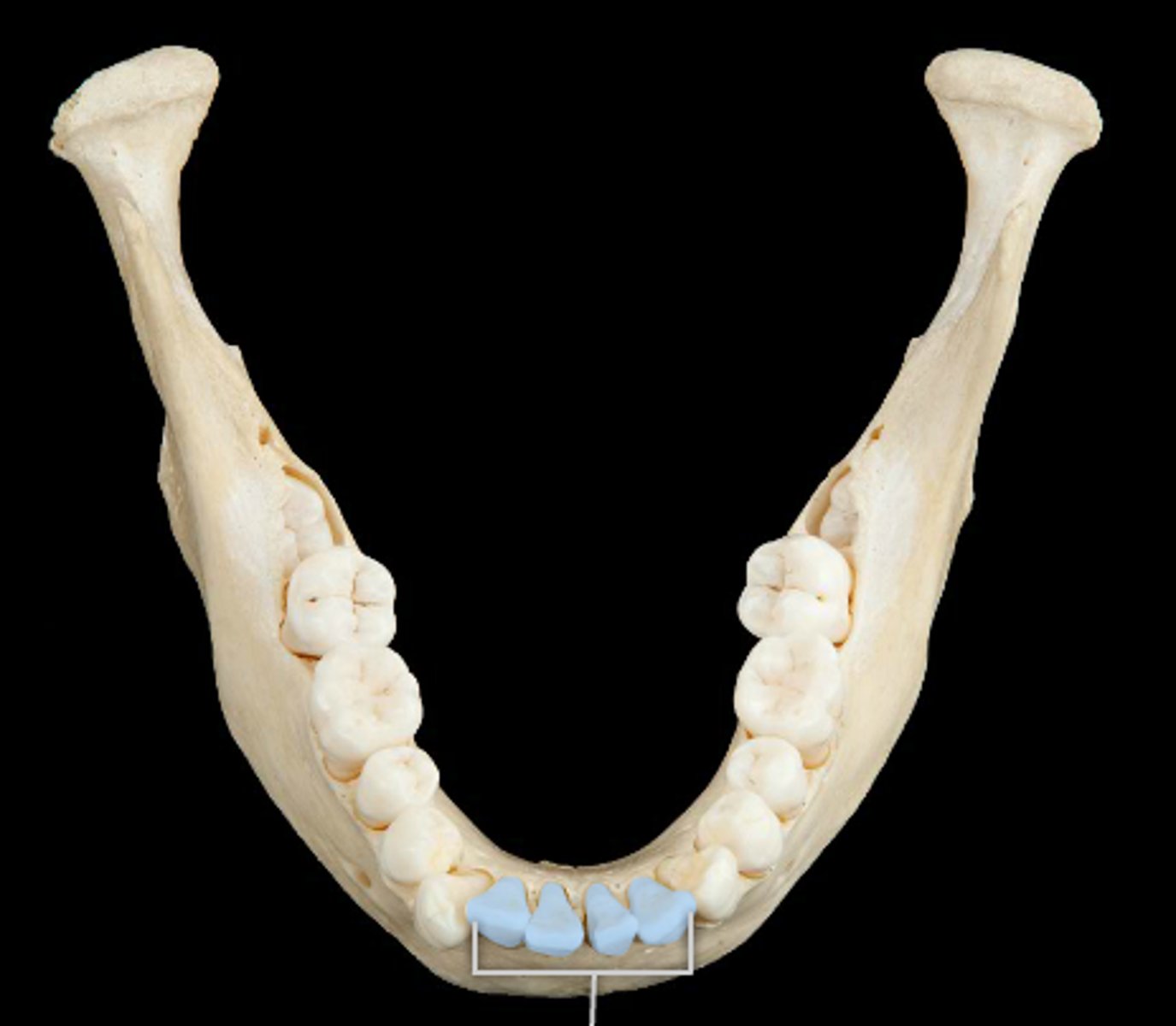
deciduous tooth
one of 20 "baby teeth"
dentition
set of tooth
Incisors
midline, chisel-shaped tooth used for cutting into food
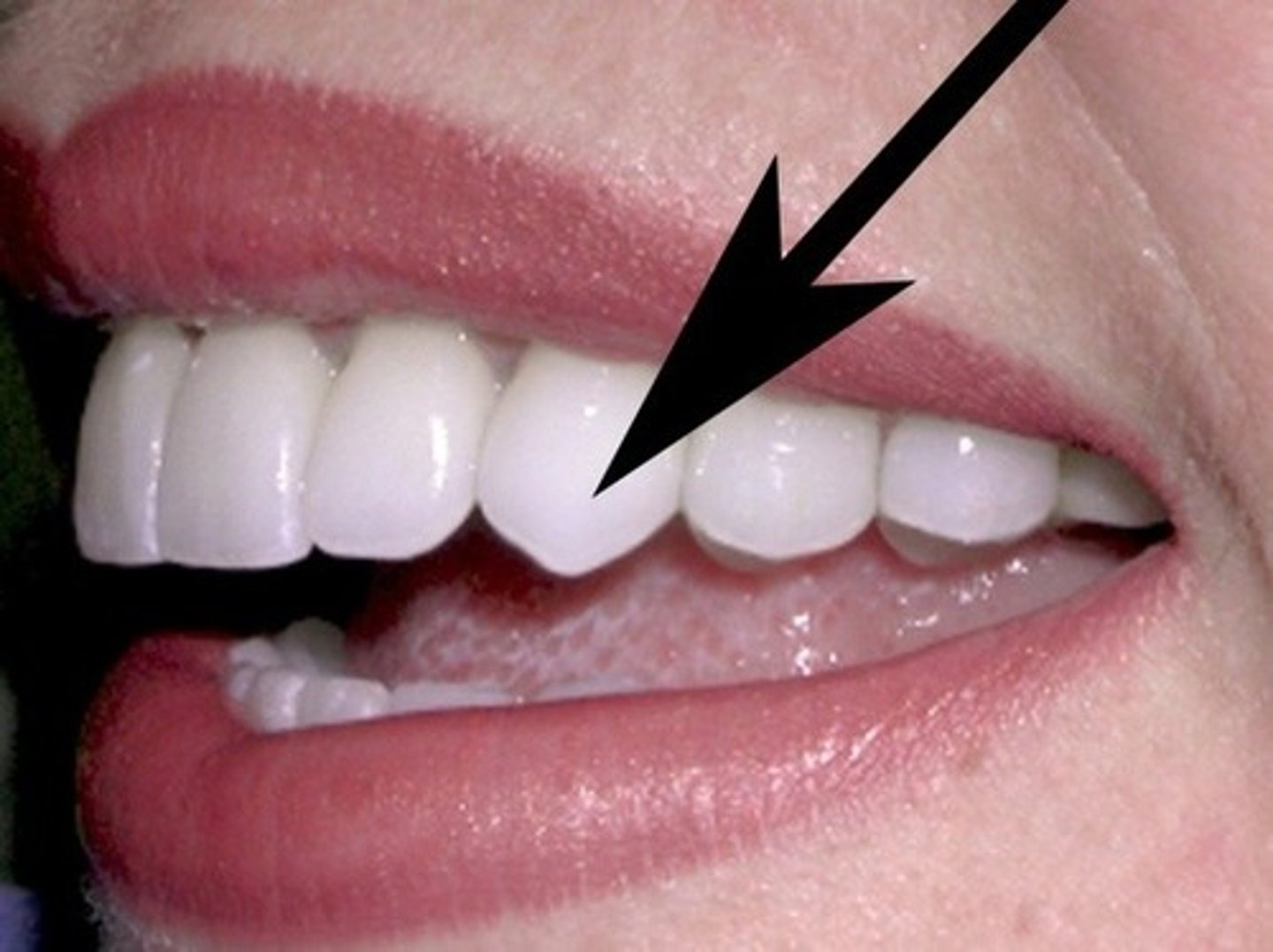
canine
pointed tooth used for tearing and shredding food
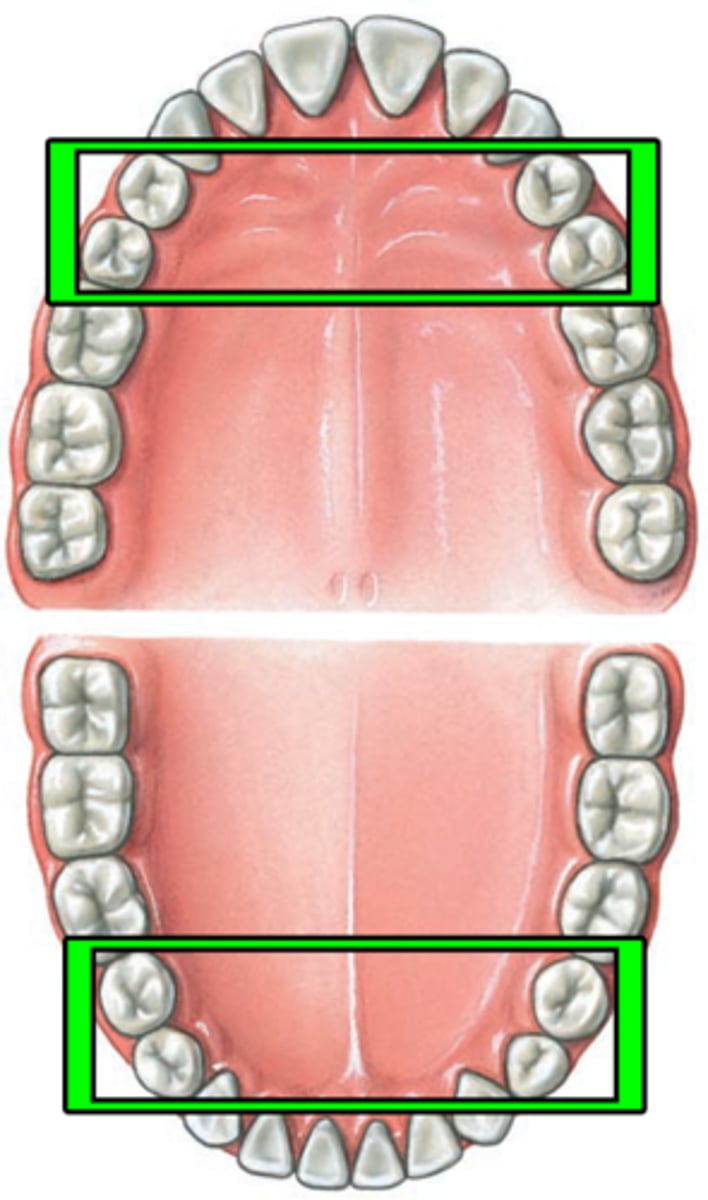
premolar
transitional tooth used for mastication, crushing, and grinding food
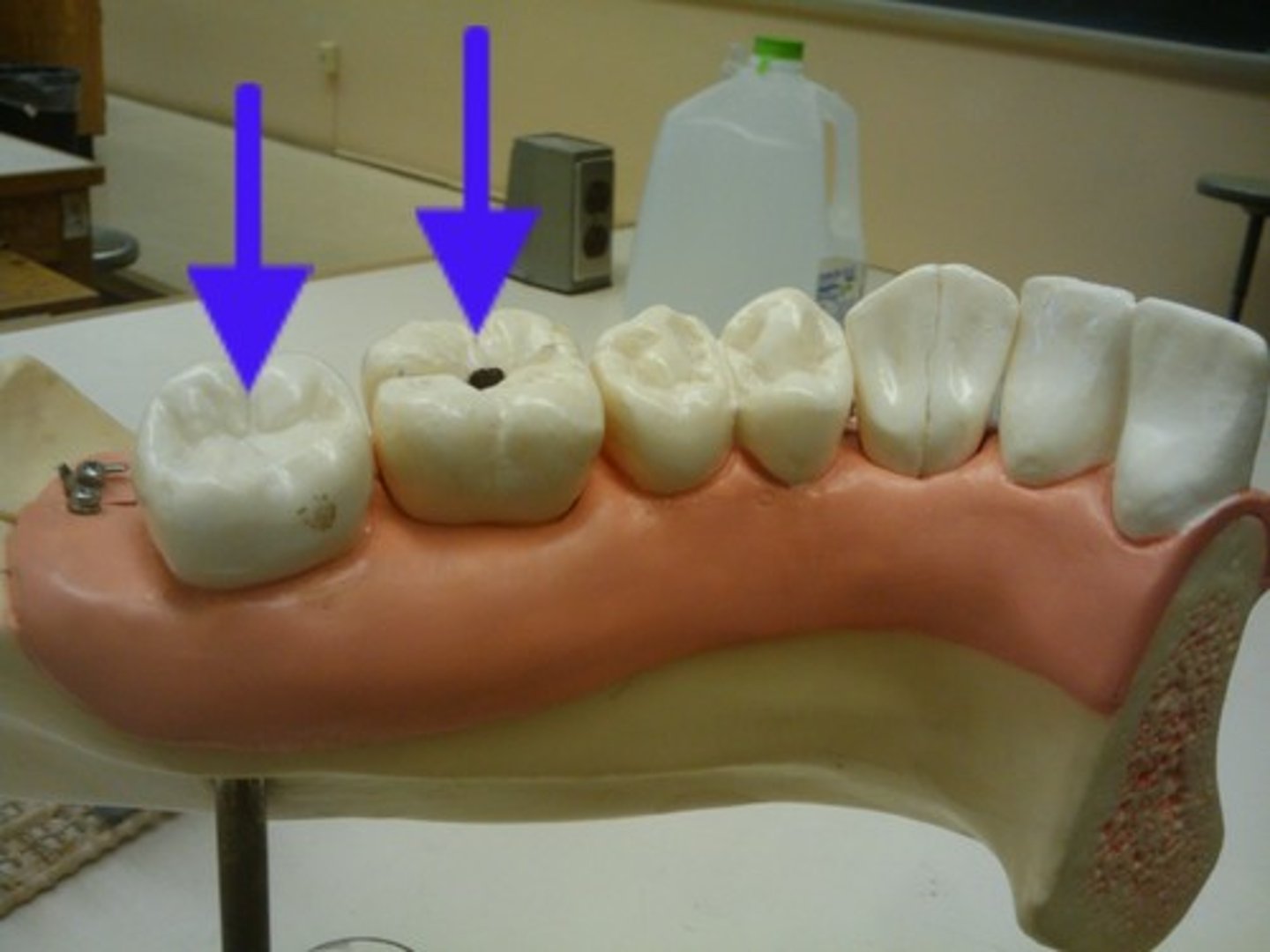
molar
tooth used for crushing and grinding food
salivary glands
an exocrine gland that secretes a digestive fluid called saliva directly into the oral cavity or indirectly through the ducts
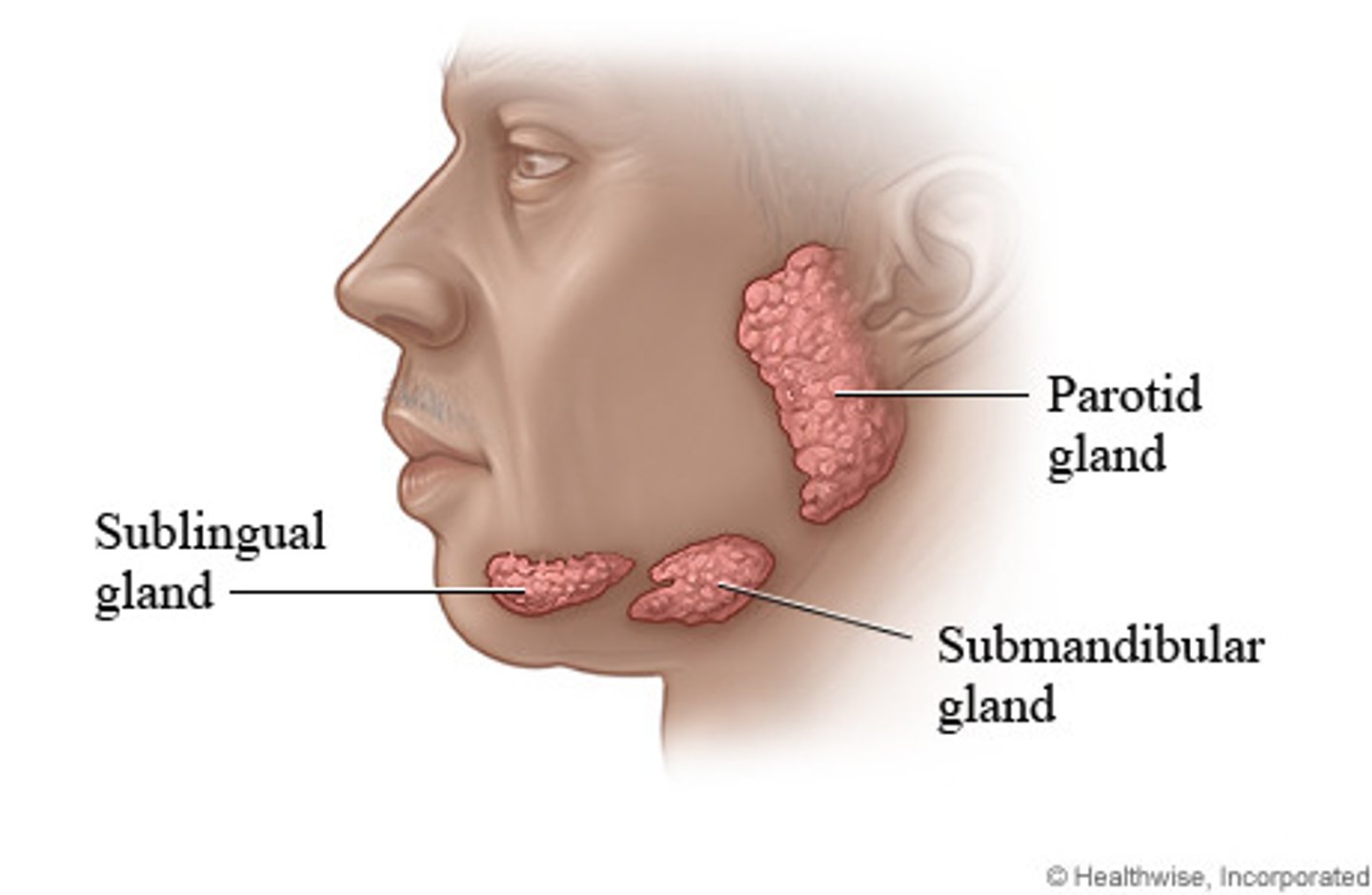
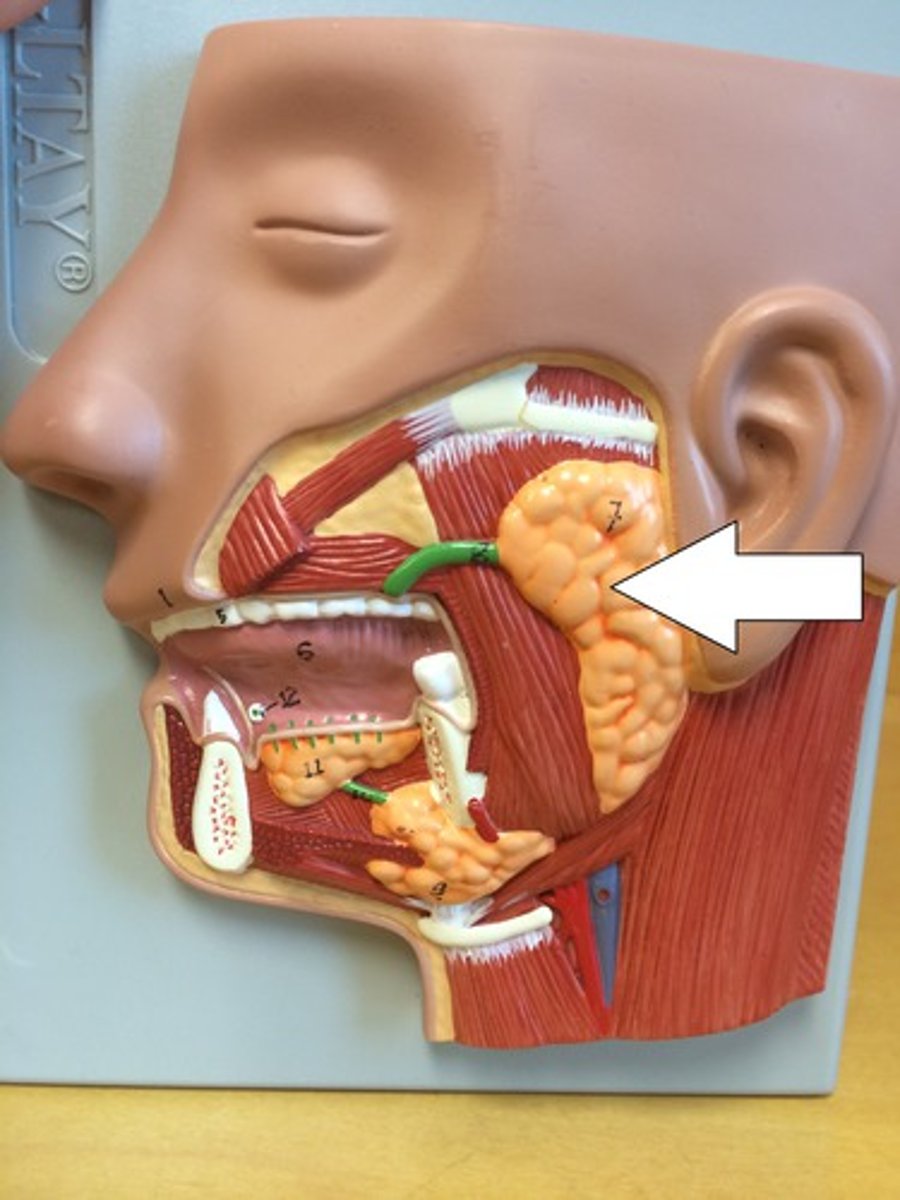
parotid glands
one of a pair of major salivary glands located inferior and anterior to the ears
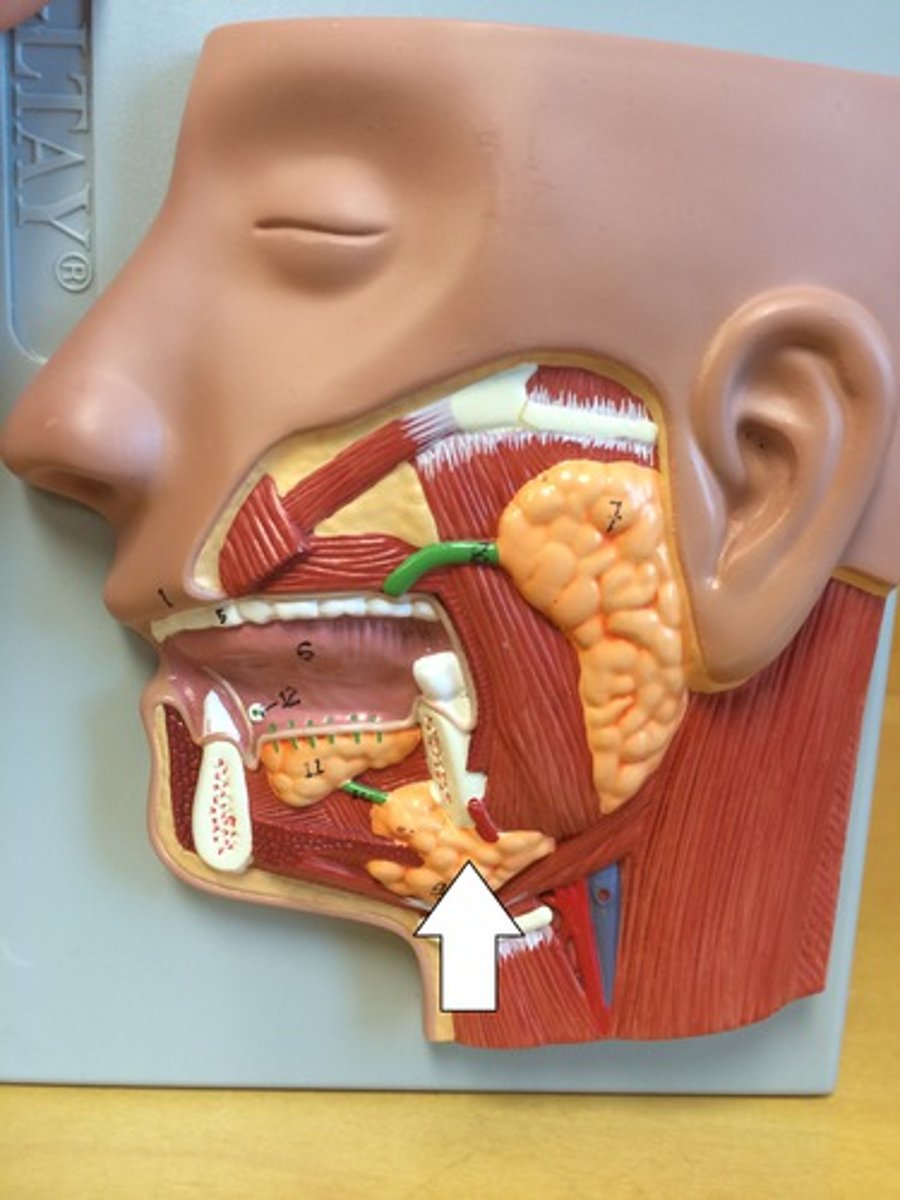
submandibular glands
one of a pair of major salivary glands located in the floor of the mouth
saliva
aqueous solution of proteins and ions secreted into the mouth by the salivary glands
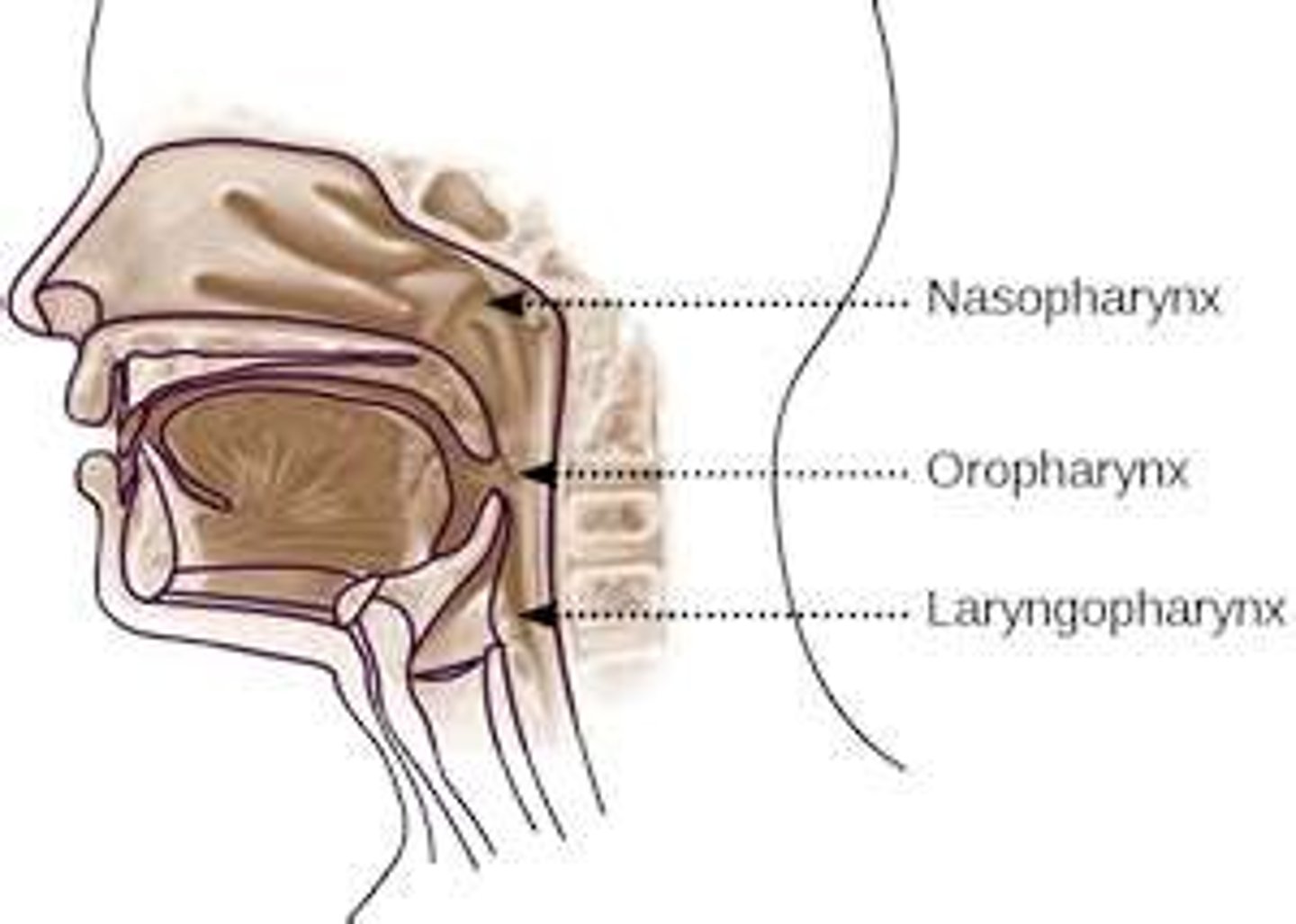
Pharynx
throat; passageway for food to the esophagus and air to the larynx
Mesothelium
the epithelium found in serous membranes lining the ventral body cavity and covering its organs
serous membrane
Membrane that lines a cavity without an opening to the outside of the body
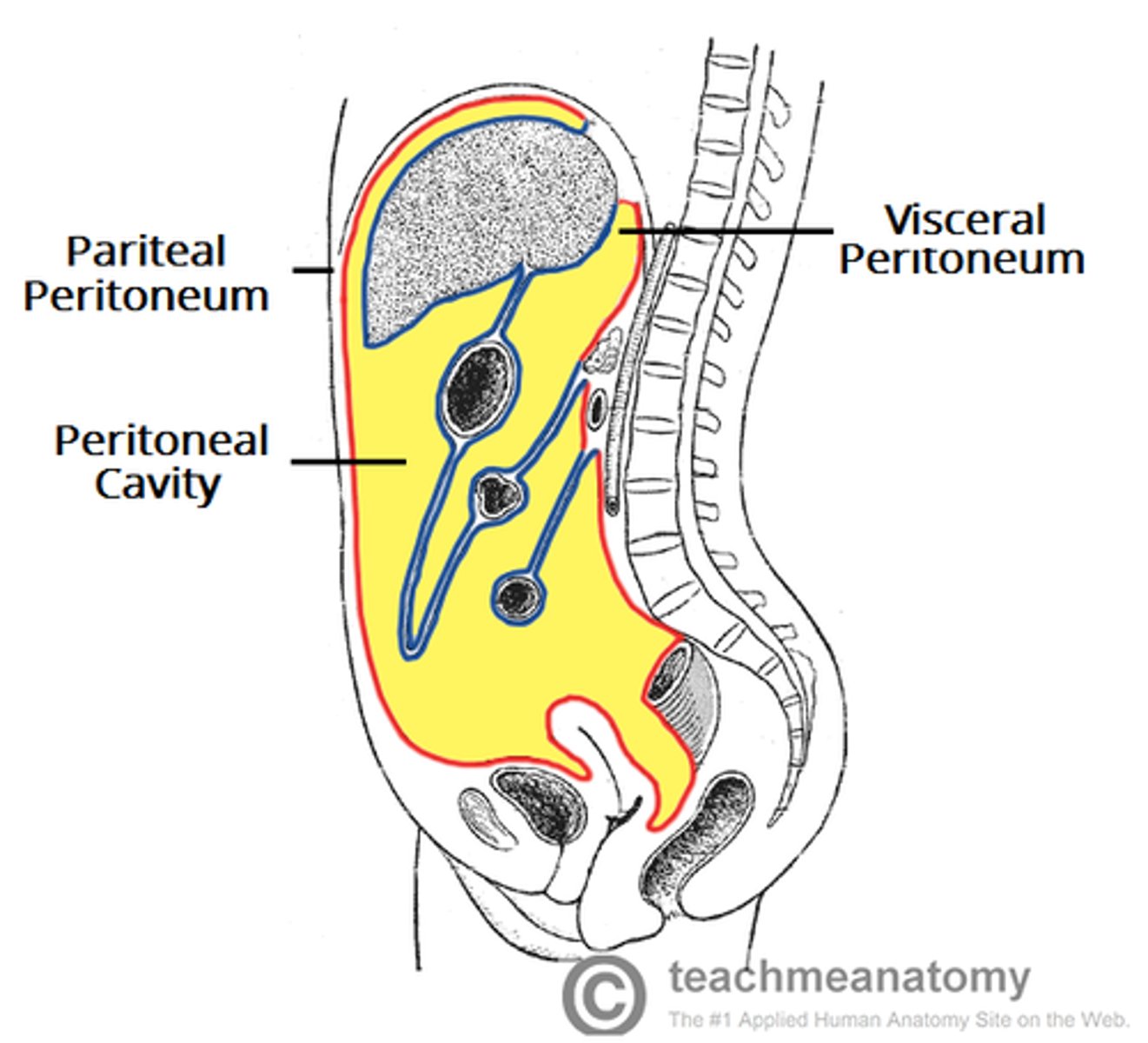
peritoneum
a serous membrane that lines the abdominopelvic cavity
mesentery
a fused double layer of the parietal peritoneum that attaches parts of the intestine to the interior abdominal wall; in small intestines only jejunum and ileum
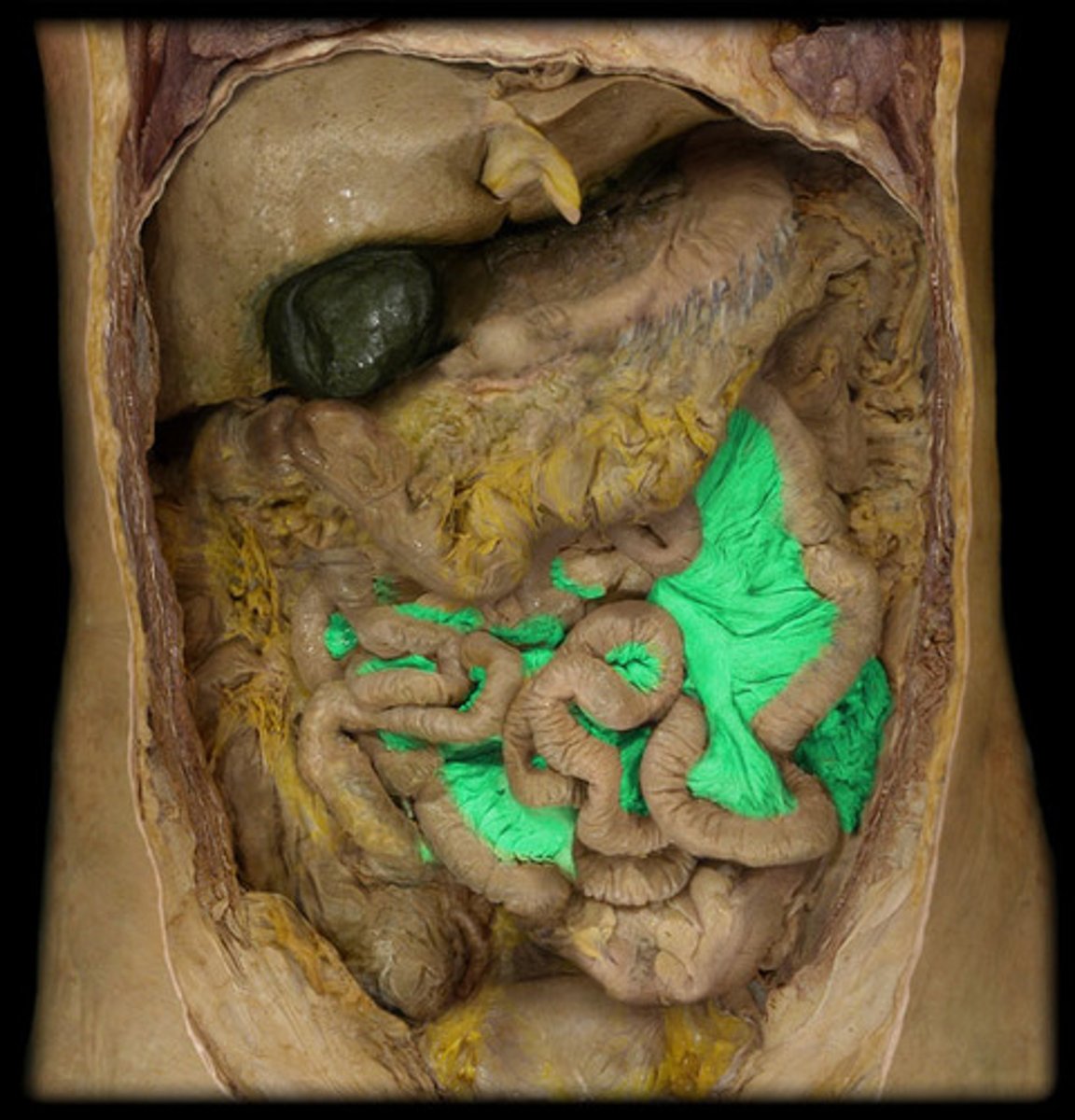
mesocolon
attaches the transverse and sigmoid colon to the posterior abdominal wall

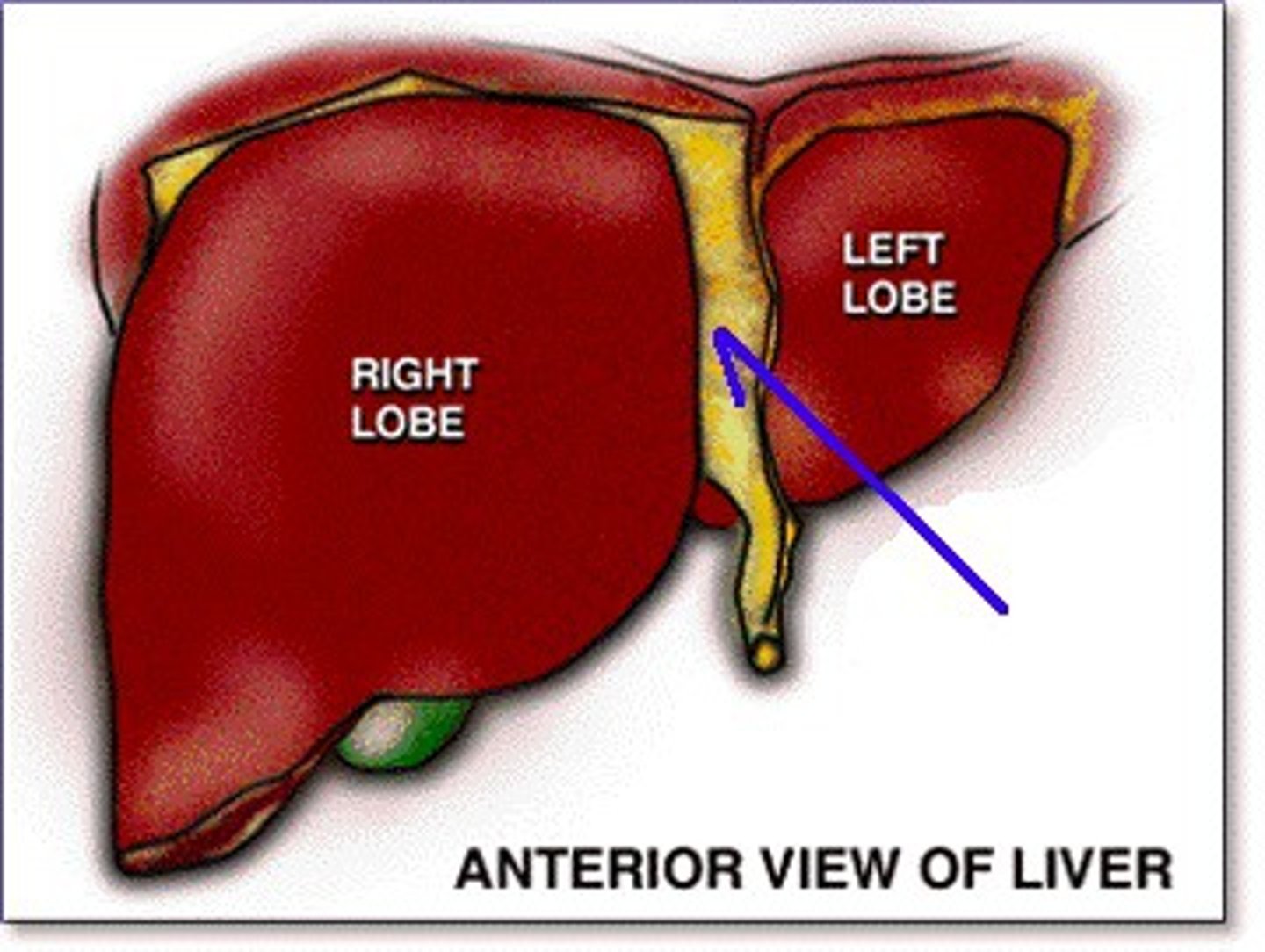
falciform ligament
attaches liver to anterior abdominal wall and diaphragm
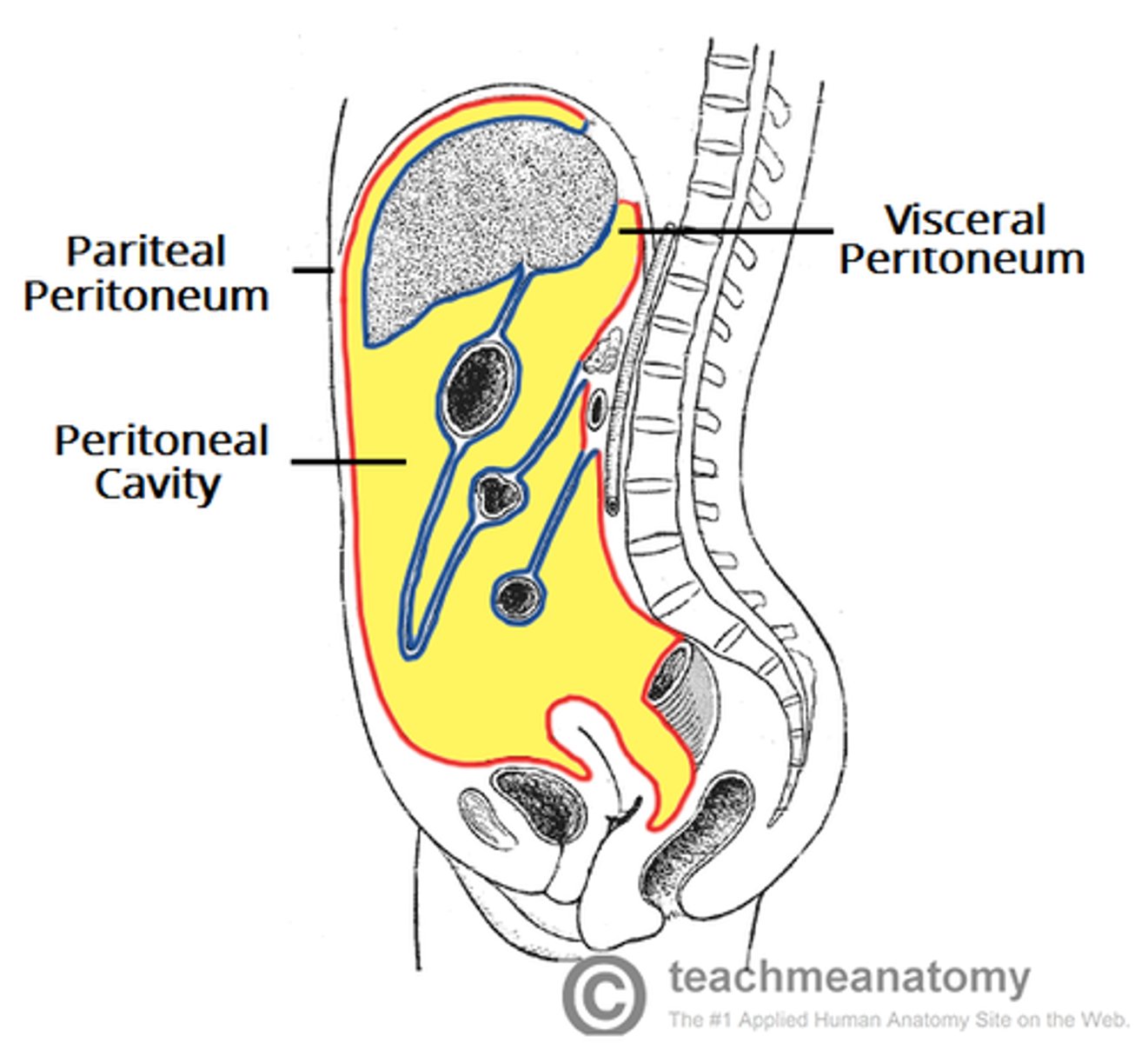
peritoneal cavity
space between the parietal and visceral peritoneum

parietal peritoneum
the outer layer of the peritoneum that lines the interior of the abdominal wall
visceral peritoneum (serosa)
covers organs within peritoneal cavity
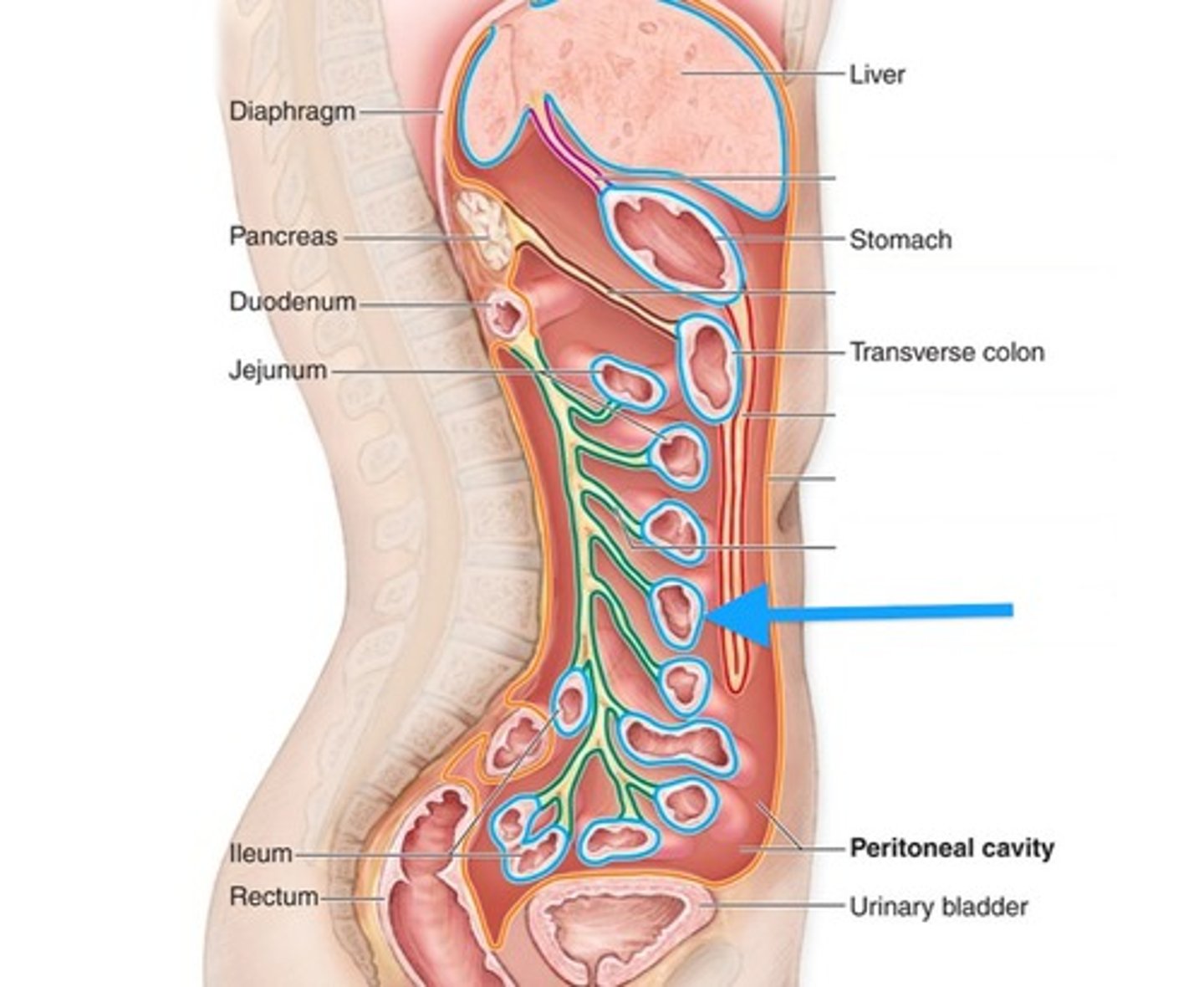
intraperitoneal organs
organs that are located within the peritoneum and surrounded by visceral peritoneum
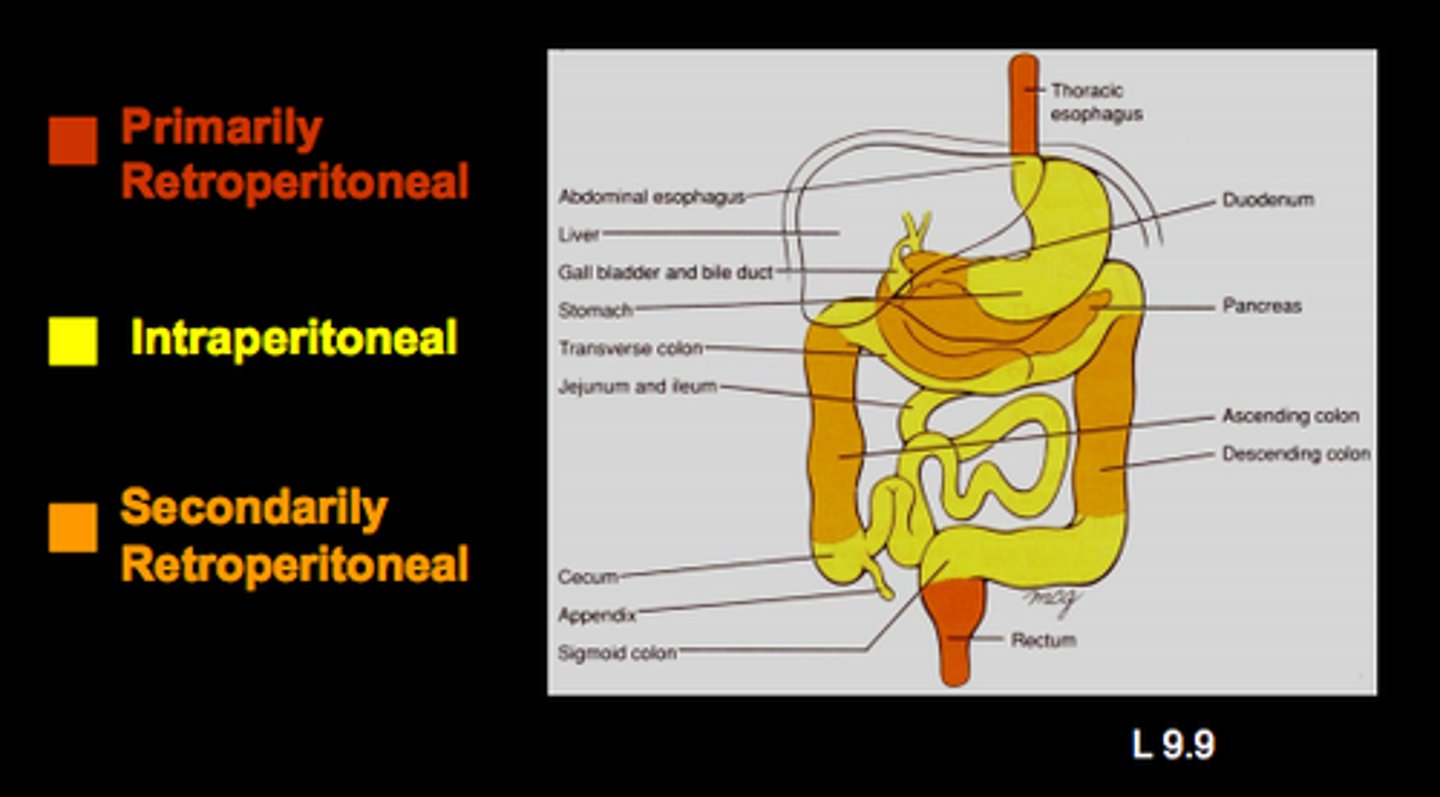
retroperitoneal organs
located outside, or posterior to, the peritoneum
Includes most of pancreas, duodenum, and parts of large intestine
