Biology Final
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Bio Study Guide
Last updated 7:57 PM on 6/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
1
New cards
What are the properties of a living organism?
1\. **Composed of at least 1 cel**l - *(basis unit of life)*
2\. **Organization** - *(Cells contain specialized parts that perform particular functions for life)*
3\. **Obtain and use energy** - (*energy provides organisms with the ability to carry out life functions.)*
4\. **Need stability / homeostasis -** *(maintain a stable internal environment and keep conditions suitable for life")*
5\*\*. **Respond to stimuli** -\*\* *(organisms respond to stimuli in . their environment like light, sound, etc. in order to survive)*
6\*\*. **Reproduce** -\*\* *(continue species, pass on DNA, Sexual & Asexual)*
7\. **Grow and develop -** *(all new cells develop from preexisting cells)*
8\*\*. **Evolve** -\*\* *(natural selection)*
2\. **Organization** - *(Cells contain specialized parts that perform particular functions for life)*
3\. **Obtain and use energy** - (*energy provides organisms with the ability to carry out life functions.)*
4\. **Need stability / homeostasis -** *(maintain a stable internal environment and keep conditions suitable for life")*
5\*\*. **Respond to stimuli** -\*\* *(organisms respond to stimuli in . their environment like light, sound, etc. in order to survive)*
6\*\*. **Reproduce** -\*\* *(continue species, pass on DNA, Sexual & Asexual)*
7\. **Grow and develop -** *(all new cells develop from preexisting cells)*
8\*\*. **Evolve** -\*\* *(natural selection)*
2
New cards
Explain Positive and Negative feedback loops and one example of each
Negative Feedback - most feedback loops are negative
ex : if glucose (sugar) is two low in blood, body works to improve sugar levels
Positive Feedback - usually destructive/ lethal
ex - blood clotting and labor two MAIN example
ex : if glucose (sugar) is two low in blood, body works to improve sugar levels
Positive Feedback - usually destructive/ lethal
ex - blood clotting and labor two MAIN example
3
New cards
What are the levels of organization from simplest to most complex level for up to the individual and biosphere
Atoms, molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, system, and organism
4
New cards
How does biology relate to everyday life?
Ex : when you wear sunscreen it protects you from skin cancer. This is because it protects you from mutations in your DNA
5
New cards
What is the classification scheme starting with Kingdom and ending in species? Which is most inclusive? Which is least inclusive?
Kingdom, biosphere, biome, ecosystem, community, population, species
\
most inclusive → biosphere
least inclusive → species
\
most inclusive → biosphere
least inclusive → species
6
New cards
What group uses the term division in the classification scheme?
plant uses the term division
7
New cards
What system can an organism live without? - how about a species?
Species can’t live without reproduction while organisms can live without
8
New cards
What are the three domains and their characteristics?
1. **Archaea** → contain organism that prob evolved first
2. **Eubacteria** → unicellular prokaryote (no nucleus or . membrane bound organelles)
3. **Eukarya** → more complex, have a nucleus & membrane, . and bound organelle
9
New cards
What are the six kingdoms and their characteristics?
**Bacteria**, → unicellular prokaryotes
**Protista**, → unicellular eukaryotes
**Fungi**, → are multicellular eukaryotes that obtain nutrients through absorption
**Plantae**, → are multicellular eukaryotes that perform photosynthesis
**Animalia**, → multicellular eukaryotes that obtain nutrients through ingestion.
**Archaea**, → thrive in hot and salty environments & believed to be the first kingdom
\
**Protista**, → unicellular eukaryotes
**Fungi**, → are multicellular eukaryotes that obtain nutrients through absorption
**Plantae**, → are multicellular eukaryotes that perform photosynthesis
**Animalia**, → multicellular eukaryotes that obtain nutrients through ingestion.
**Archaea**, → thrive in hot and salty environments & believed to be the first kingdom
\
10
New cards
What is binomial nomenclature? How do write the correct genus and species name of an organism?
Linnaus’s naming system. Two word naming (genus & species)
* italicized or underlined
* italicized or underlined
11
New cards
What can classification / scientific name tell you about the relationship between different organisms? About its evolution?
The closer they are in the classification scheme the lower down they are
12
New cards
Know what a dichotomous key is and how to use one
the tool used to differentiate between species
ex : has tentacles (go to 2)
ex : has tentacles (go to 2)
13
New cards
What are the step to the scientific method:
observation, hypothesis, experimental method, conclusion
14
New cards
Be able to determine the IV, DV, and CV’s
IV - a variable whose variation does not depend on that of another.
DV - a variable whose value depends on that of another.
CV - all must be the same
DV - a variable whose value depends on that of another.
CV - all must be the same
15
New cards
Understand the ionic, covalent and hydrogen bonds
**ionic bonds** → are formed by the transfer of electrons
**covalent bond**s → are formed when at least two or more atoms share one or more pairs of electrons
**hydrogen bonds** → are a weak bond between two molecules resulting from an electronegative atom in the other
**covalent bond**s → are formed when at least two or more atoms share one or more pairs of electrons
**hydrogen bonds** → are a weak bond between two molecules resulting from an electronegative atom in the other
16
New cards
What are the properties of water that make it important for life
a. cohesion
b. adhesion
c. high specific heat
d. high heat of vaporization
e. less dense as a solid
b. adhesion
c. high specific heat
d. high heat of vaporization
e. less dense as a solid
17
New cards
What does it mean to be polar?
polar mean that for example : with water the oxygen end “acts” negatively changed and the hydrogen end “acts” positively charged.
18
New cards
How does transpiration work in plants?
Transpiration is due to capillary action plants lose water through transpiration which is the evaporation of water from small pores on the underside of the leaves.
19
New cards
What does pH measure? What does it mean to be an acid? - a base - neutral?
pH measures how acidic /basic something is
neutral - 7 exactly
acid - below 7 → sour & corrosive
base - above 7 → bitter & slipper
neutral - 7 exactly
acid - below 7 → sour & corrosive
base - above 7 → bitter & slipper
20
New cards
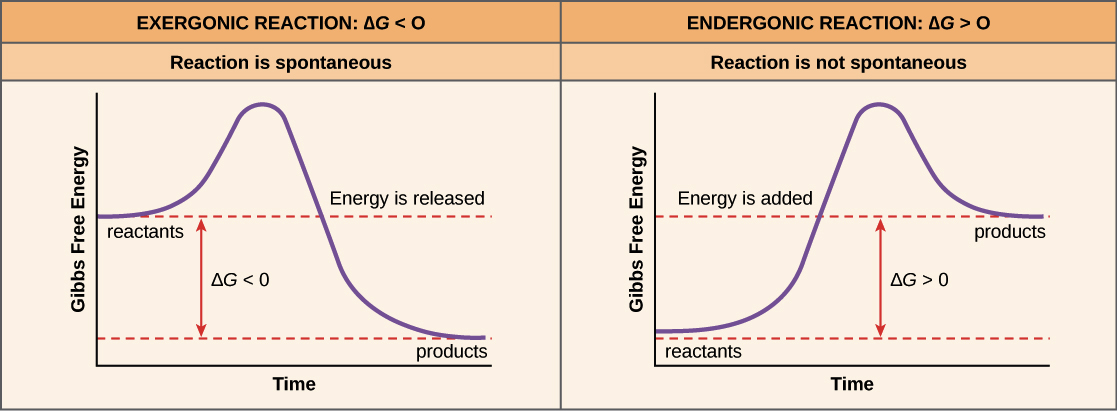
Understand the difference between exergonic (exothermic) and endergonic (endothermic) reactions and what the graphs of each looks like.
exergonic (exothermic) = energy released
*ex - burning of gasoline*
endergonic (endothermic) = energy absorbed
*ex - cooking pancakes*
*ex - burning of gasoline*
endergonic (endothermic) = energy absorbed
*ex - cooking pancakes*
21
New cards
What is an enzyme? How does it work? What is activation energy?
**enzyme** -
* biological catalyst.
* Is a protein.
* Lowers activation energy & speeds up reaction.
* is denatured with heat & changed in pH (cold slows it down)
**Activation energy** - the amount of energy needed to start the reaction
* biological catalyst.
* Is a protein.
* Lowers activation energy & speeds up reaction.
* is denatured with heat & changed in pH (cold slows it down)
**Activation energy** - the amount of energy needed to start the reaction
22
New cards
What are monomers that make up carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, & lipids and what are their overall functions in cells (ex : phospholipids = cell membrane, cytoskeleton, central vacuole, flagella cilia, centrioles, etc.)
**carbohydrates** - monosaccharides = simple sugar
**proteins** - amino acids = build cells, act as hormones & enzymes, etc.
**nucleic acids** - nucleotides = store heredity info & info for making protein (RNA & DNA)
**lipids** - triglyceride = fats (store energy, insulate, protect organs)
**proteins** - amino acids = build cells, act as hormones & enzymes, etc.
**nucleic acids** - nucleotides = store heredity info & info for making protein (RNA & DNA)
**lipids** - triglyceride = fats (store energy, insulate, protect organs)
23
New cards
What are the four levels of protein structure and what denatures them?
==Primary==, ^^secondary^^, %%tertiary%%, & @@quaternary@@
Denatured by high temp & changes in pH
Denatured by high temp & changes in pH
24
New cards
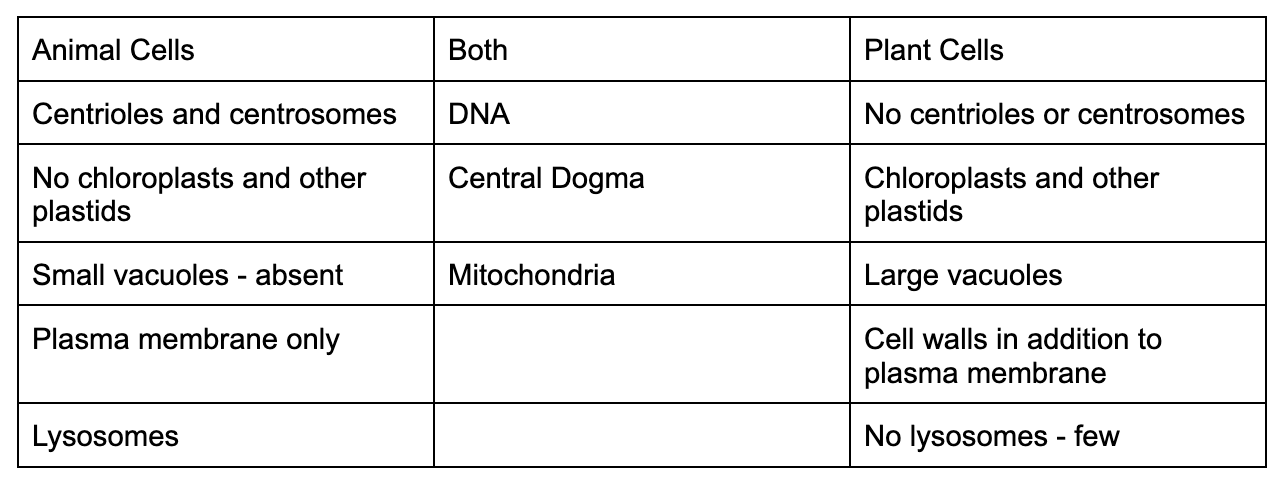
Compare and Contrast a plant and animal cell
\
25
New cards
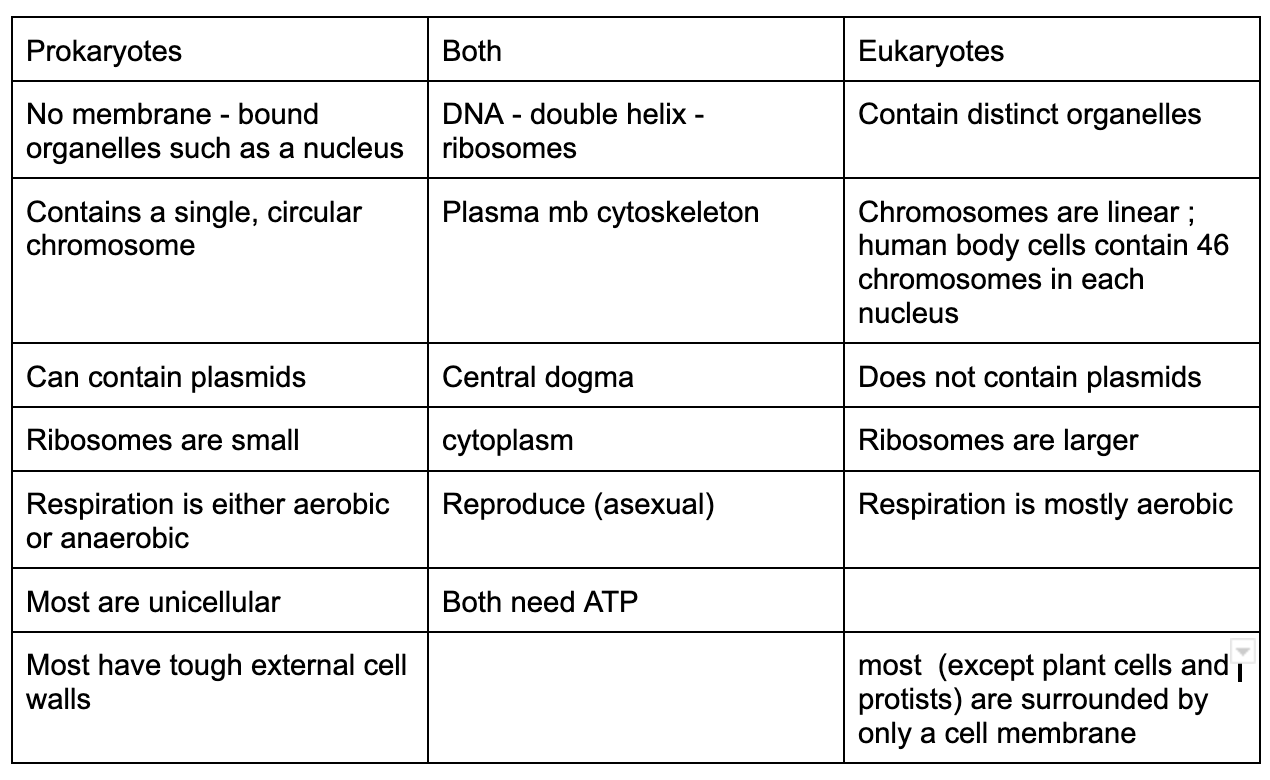
Compare & contrast eukaryotes and prokaryote cells?
26
New cards
Know the parts of the prokaryote cell and their function (like pili, capsule, plasmid)
* **pili** - used for attachment and conjunction
* **capsule** - active coding of prokaryote cell
* **plasmid** - extra piece of genetic material used in conjugation
* **nucleic region** (center) - contain the DNA
* surrounded by **cell membrane** and **cell wall**
* contain **ribosomes** (no membrane) in their cytoplasm to make protein
* **capsule** - active coding of prokaryote cell
* **plasmid** - extra piece of genetic material used in conjugation
* **nucleic region** (center) - contain the DNA
* surrounded by **cell membrane** and **cell wall**
* contain **ribosomes** (no membrane) in their cytoplasm to make protein
27
New cards
what are the ororganelles of the cell and their function (nucleus, chloroplast, mitochondira, RER, SER, ribosomes, Golgi apparatus, lysosmes, peroxisomes, cytoskeletonm central vacuole, flagella cilia, centrioles, etc.)
* Nucleus: contains genetic material and controls cell activities
* Chloroplast: site of photosynthesis in plant cells
* Mitochondria: produces energy for the cell through cellular respiration
* RER: involved in protein synthesis and transport
* SER: involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification
* Ribosomes: site of protein synthesis
* Golgi apparatus: modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for transport
* Lysosomes: contains enzymes for digestion and waste removal
* Peroxisomes: breaks down fatty acids and detoxifies harmful substances
* Cytoskeleton: provides structure and support for the cell
* Central vacuole: stores water and nutrients in plant cells
* Flagella and cilia: involved in cell movement
* Centrioles: involved in cell division
* Chloroplast: site of photosynthesis in plant cells
* Mitochondria: produces energy for the cell through cellular respiration
* RER: involved in protein synthesis and transport
* SER: involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification
* Ribosomes: site of protein synthesis
* Golgi apparatus: modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for transport
* Lysosomes: contains enzymes for digestion and waste removal
* Peroxisomes: breaks down fatty acids and detoxifies harmful substances
* Cytoskeleton: provides structure and support for the cell
* Central vacuole: stores water and nutrients in plant cells
* Flagella and cilia: involved in cell movement
* Centrioles: involved in cell division
28
New cards
What is a leukocyte and an erythrocyte? What does the suffix - cyte mean?
A **leukocyte** is a type of blood cell that helps the body fight infections and diseases.
An **erythrocyte** is a red blood cell that carries oxygen throughout the body.
The suffix -**cyte** means "cell".
An **erythrocyte** is a red blood cell that carries oxygen throughout the body.
The suffix -**cyte** means "cell".
29
New cards
why is surface area to volume ratio so important to cells
if a cell gets to big it will either divide or explode
30
New cards
How does the structure of the cell membrane relate to its function? What are integral & peripheral proteins and what are their functions? - glycoproteins? - glycolipids?
The cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins, glycoproteins, and glycolipids. The hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids face inward, while the hydrophilic heads face outward, creating a selectively permeable barrier.
Integral proteins span the entire membrane and aid in transport, while peripheral proteins are attached to the surface and provide structural support.
Glycoproteins and glycolipids are involved in cell recognition and communication. The structure of the cell membrane is essential for its function in regulating the movement of molecules in and out of the cell.
Integral proteins span the entire membrane and aid in transport, while peripheral proteins are attached to the surface and provide structural support.
Glycoproteins and glycolipids are involved in cell recognition and communication. The structure of the cell membrane is essential for its function in regulating the movement of molecules in and out of the cell.
31
New cards
What does it mean by phospholipid bilayer? Understand what is means to be polar or non-polar and how it relates to the transport of the substances.
The cell membrane is made of 2 layers of phospholipids called the lipid bilayer
* polar - hydrophilic (water loving )
* non-polar - hydrophobic (water fearing)
Makes the membrane “selective” in what crosses. (selectively permeable)
* polar - hydrophilic (water loving )
* non-polar - hydrophobic (water fearing)
Makes the membrane “selective” in what crosses. (selectively permeable)
32
New cards
what happens to a cell/RBC when placed in an isotonic, hypotonic, or hypertonic environment.
isotonic - at equilibrium
hypotonic - swell & burst
hypertonic -shrink & shrivel
hypotonic - swell & burst
hypertonic -shrink & shrivel
33
New cards
What type of environment do plant cells prefer and why? - animal cells?
==Plant cells== prefer a **hypotonic** environment because their cell wall prevents them from bursting
^^Animal cells^^, on the other hand, prefer an **isotonic** environment to maintain their shape and prevent bursting or shrinking due to osmotic pressure.
^^Animal cells^^, on the other hand, prefer an **isotonic** environment to maintain their shape and prevent bursting or shrinking due to osmotic pressure.
34
New cards
What are the principles involved in diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion?
**Diffusion** is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. (no membrane needed)
**Osmosis** is the diffusion of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration.
**Facilitated diffusion** is the movement of molecules across a membrane with the help of transport proteins.
All three processes are (high to low)
**Osmosis** is the diffusion of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration.
**Facilitated diffusion** is the movement of molecules across a membrane with the help of transport proteins.
All three processes are (high to low)
35
New cards
What is a proton pump? Na-k pump?
A **proton pump** is an integral membrane protein that transports protons across a cell membrane.
The **Na-K pump**, also known as the *sodium-potassium pump*, is an enzyme that pumps sodium ions out of cells while pumping potassium ions into cells, maintaining the cell's electrochemical gradient.How
The **Na-K pump**, also known as the *sodium-potassium pump*, is an enzyme that pumps sodium ions out of cells while pumping potassium ions into cells, maintaining the cell's electrochemical gradient.How
36
New cards
How is the disease cystic fibrosis related to the cell membrane (in general terms) and to frameshift mutations
Cystic fibrosis is a **genetic** disease caused by a **mutation** in the CFTR gene, which codes for a protein that regulates the movement of salt and water in and out of cells.
**Frameshift mutations** in the CFTR gene can disrupt the production of the CFTR protein, leading to a dysfunctional protein or no protein at all.
**Frameshift mutations** in the CFTR gene can disrupt the production of the CFTR protein, leading to a dysfunctional protein or no protein at all.
37
New cards
What are the three types of endcytosis?
1. simple diffusion
2. facilitated diffusion
3. active transport
38
New cards
How is the cell membrane related to the function of the immune system? How it work in organ transplants?
* the cell membrane contains proteins that help identify and destroy pathogens.
* In organ transplants, the immune system may recognize the transplanted organ as foreign and attack it.
* (Immunosuppressive drugs can be used to prevent this response by suppressing the immune system's activity.)
* In organ transplants, the immune system may recognize the transplanted organ as foreign and attack it.
* (Immunosuppressive drugs can be used to prevent this response by suppressing the immune system's activity.)
39
New cards
How do the bases in DNA & RNA match up? How many hydrogen bonds between bases?
Dna
* Adenine pairs with thymine (A-T)
* guanine pairs with cytosine (G-C)
Rna
* is the same except adenine pairs with uracil (A-U)
\
(A-T) = two hydrogen bonds
(G-C) = three hydrogen bonds
* Adenine pairs with thymine (A-T)
* guanine pairs with cytosine (G-C)
Rna
* is the same except adenine pairs with uracil (A-U)
\
(A-T) = two hydrogen bonds
(G-C) = three hydrogen bonds
40
New cards
Identify the structure of a nucleotide. Know the diffrent between pyrimidines and purins.
A nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a phosphate group.
Pyrimidines (cytosine, thymine, and uracil) have a single ring structure
purines (adenine and guanine) have a double ring structure.
Pyrimidines (cytosine, thymine, and uracil) have a single ring structure
purines (adenine and guanine) have a double ring structure.
41
New cards
What did Chargaff, Franklin, and Watson & Crick do?
**Chargaff** - showed the amounts of four bases on DNA . (A,T,C,G) in 1948
**Franklin** - took diffraction x-ray photos of DNA’s crystals
**Watson & Crick** - built the first model of DNA
**Franklin** - took diffraction x-ray photos of DNA’s crystals
**Watson & Crick** - built the first model of DNA
42
New cards
What is a chromosome, chromatin, chromatid, and a centromere?
* A **chromosome** is a structure in the nucleus of a cell that carries genetic information in the form of genes.
* **Chromatin** is the material that makes up chromosomes, consisting of DNA and proteins.
* A **chromatid** is one of the two identical copies of a chromosome that are joined at the centromere.
* A **centromere** is the region of a chromosome where the two chromatids are joined together.
* **Chromatin** is the material that makes up chromosomes, consisting of DNA and proteins.
* A **chromatid** is one of the two identical copies of a chromosome that are joined at the centromere.
* A **centromere** is the region of a chromosome where the two chromatids are joined together.
43
New cards
In protein synthesis what happens in transcription and translation and where does each process occur?
**Transcription** is the process of copying DNA into RNA, which occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells.
**Translation** is the process of using the RNA to synthesize a protein, which occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell.
**Translation** is the process of using the RNA to synthesize a protein, which occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell.
44
New cards
Explain what level of protein structure is made in protein synthesis and what things can denature proteins
* primary structure is the level of protein structure made in protein synthesis
* heat and changes in pH denature a protein
* heat and changes in pH denature a protein
45
New cards
What is the function of mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA
^^mRNA^^ - (messenger RNA) copies DNA’s code and carries the genetic info to the ribosomes
%%tRNA%% - (transfer RNA) transfers amino acids to the ribosomes where proteins are synthesized
==rRNA== - (ribosomal RNA) along with protiens, makes up the ribosomes
%%tRNA%% - (transfer RNA) transfers amino acids to the ribosomes where proteins are synthesized
==rRNA== - (ribosomal RNA) along with protiens, makes up the ribosomes
46
New cards
What are intron and exons? What is the difference between template strands and the complement strand of DNA?
**introns** = non-functional segments of DNA that are snipped out of the chain
\
**exons** = segment of DNA that code for proteins, are the rejoined by the enzyme RNA ligase
the difference is that the template strand does not have any complementary sequences.
\
**exons** = segment of DNA that code for proteins, are the rejoined by the enzyme RNA ligase
the difference is that the template strand does not have any complementary sequences.
47
New cards
What is the difference between pre-mRNA and mRNA?
pre-mRNA contains introns and exons while mRNA contains only exons
48
New cards
What does pre-mRNA, DNA polymerase, helicase, topoisomerase, DNA ligase, DNA primer, and primase do?
* **Pre-mRna** - generate multiple transcript isoforms from a single gene.
* **DNA polymerase** - proofreads DNA
* **helicase** - unwinds and separates the two DNA strands by breaking weak hydrogen bonds
* **topoisomerase** - relieve the strain in the DNA ahead of the replication fork
* **DNA ligase** - seals breaks in the sugar - phosphate backbones of the strand
* **DNA primer** - initiates synthesis of a new strand
* **primase** - synthesizes RNA primers during DNA replication
* **DNA polymerase** - proofreads DNA
* **helicase** - unwinds and separates the two DNA strands by breaking weak hydrogen bonds
* **topoisomerase** - relieve the strain in the DNA ahead of the replication fork
* **DNA ligase** - seals breaks in the sugar - phosphate backbones of the strand
* **DNA primer** - initiates synthesis of a new strand
* **primase** - synthesizes RNA primers during DNA replication
49
New cards
What are Okazaki fragments, the leading strand, and the lagging strand?
* **Okazaki fragments** - series of short segments on the lagging strand
* **leading strand** - from the point of origin to the opening replication fork (5’3’)
* **lagging strand** - many short segments. From the replication fork toward the origin (3’5’)
* **leading strand** - from the point of origin to the opening replication fork (5’3’)
* **lagging strand** - many short segments. From the replication fork toward the origin (3’5’)
50
New cards
Know that point mutations are like silent, nonsense, and missense and know about frameshift insertions and deletions. (gene mutations). Understand how sickle cell anemia relates to a point mutation and cystic fibrosis relates to a frameshift.
* ^^silent mutation^^ - 1 base pair gives new codon but still codes for original AA (amino acid) so make the same proteins
* @@nonsense mutation@@ - 1 base pair gives new codon that codes for an early stop (protein shorter)
* %%missense mutation%% - 1 base pair gives new codon & subsequently new AA & ultimately new protein
* ==Frameshift mutation== - the result of a gene deletion or insertion (can be lethal)
*insertion* (one or more nucleotides are added to gene)
*deletion* (one or more nucleotides are added to gene)
* @@nonsense mutation@@ - 1 base pair gives new codon that codes for an early stop (protein shorter)
* %%missense mutation%% - 1 base pair gives new codon & subsequently new AA & ultimately new protein
* ==Frameshift mutation== - the result of a gene deletion or insertion (can be lethal)
*insertion* (one or more nucleotides are added to gene)
*deletion* (one or more nucleotides are added to gene)
51
New cards
How does this relate to the Central Dogma?
the central dogma says DNA makes RNA, RNA makes proteins, if DNA is wrong then RNA is wrong so the proteins may have a major mistake
52
New cards
What is a mutagen?
What is a mutation and how can it affect an individual and/or species?
What is a mutation and how can it affect an individual and/or species?
**mutagen** - any agents in the environment that can change DNA (ex - uv radiation)
a mutation is a change in DNA that effects genetic information which effects individuals by changing their function or the function of their offspring
a mutation is a change in DNA that effects genetic information which effects individuals by changing their function or the function of their offspring
53
New cards
What is the difference between mutations in somatic cells and gametes and which type can be passed on to the next generation.
mutations in the somatic cells like skin cells are not passed on to the offspring, whereas mutations that happen in the gametes can be passed on to the offspring
54
New cards
What is an autosome? What is a sex chromosome?
**autosomes** - any chromosomes that are not sex chromosomes (first 22 pairs)
**sex chromosome** - last chromosome (x = female, xy= male)
**sex chromosome** - last chromosome (x = female, xy= male)
55
New cards
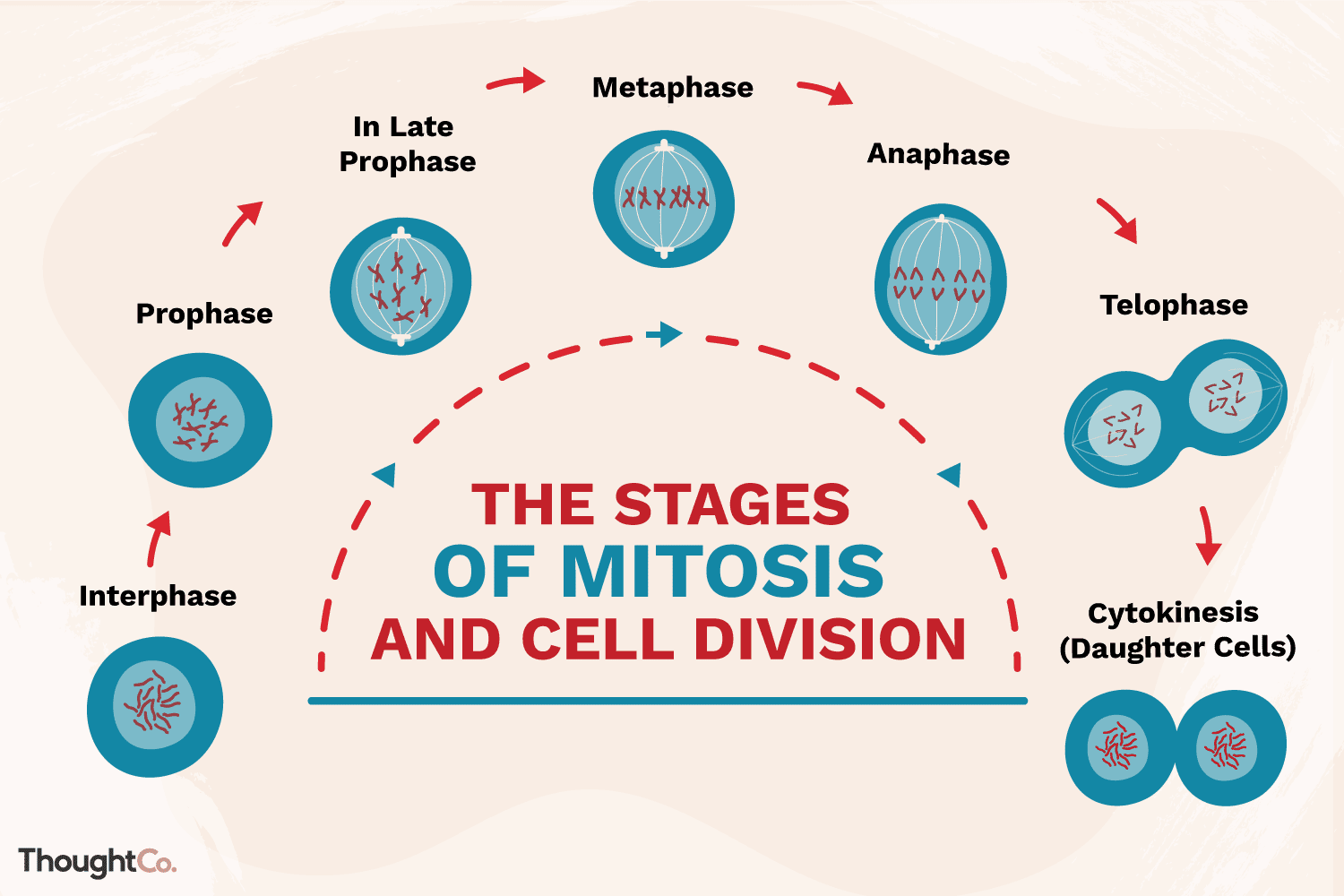
Understand what generally happens in mitosis during interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase & telophase. (be able to identify the stage of mitosis in a diagram or picture versus meiosis)
* **interphase** - chromsomes will align, separate and move into new daughter cells
* **prophase** - chromatin condenses, then coils and becomes increasingly compact , resulting in the formation of visible chromosomes
* **metaphase** - the nucleus dissolves and the cell’s chromosomes condense and move together
* **anaphase** - sister chromatids separate and are pulled to opposite ends of the cell
* **telephase** - nuclei re-form and the chromosomes decondense
* **prophase** - chromatin condenses, then coils and becomes increasingly compact , resulting in the formation of visible chromosomes
* **metaphase** - the nucleus dissolves and the cell’s chromosomes condense and move together
* **anaphase** - sister chromatids separate and are pulled to opposite ends of the cell
* **telephase** - nuclei re-form and the chromosomes decondense
56
New cards
What happens in binary fission? –conjugation? (bacteria)
**binary fission** - form of asexual reproduction where every organelle is copied & the organism divides in two (how bacteria reproduce)
**conjugation** - when one bacterium transfers genetic material to another through direct contact
**conjugation** - when one bacterium transfers genetic material to another through direct contact
57
New cards
Understand asexual reproduction: fragmentation, regenerations, spores, regeneration, cloning and budding?
* **fragmentation** - a parent organism splits into pieces, each which can grow into a new organism (seastars and flatworms)
* **regeneration** - when a body part has broken off so the organisms grow a new one (lizards)
* **budding** - part of original parent organism pinches off and forms another (hydra, yeast, sponge)
* **cloning** - copy of organism’s genetic material (no genetic variation (asexual reproduction)(snakes))
* **regeneration** - when a body part has broken off so the organisms grow a new one (lizards)
* **budding** - part of original parent organism pinches off and forms another (hydra, yeast, sponge)
* **cloning** - copy of organism’s genetic material (no genetic variation (asexual reproduction)(snakes))
58
New cards
Explain advantages and disadvantages of asexual versus sexual reproduction.
Asexual -
* advantages = don’t waste energy on finding a mate
* disadvantages = no genetic variation
Sexual -
* advantages = genetic variation
* disadvantages = waste enegry
* advantages = don’t waste energy on finding a mate
* disadvantages = no genetic variation
Sexual -
* advantages = genetic variation
* disadvantages = waste enegry
59
New cards
Why is surface area to volume ratio so important in cells? (repeat)
because if a cell gets to big it will either divide or explode
60
New cards
What is cytokinesis? – The cell cycle?
**cytokinesis** - the division of the cytoplasm into daughter cells
**cell cycle** - cells life
**cell cycle** - cells life
61
New cards
When is DNA replicated? What happens during each part of Interphase?
DNA is replicated during S/synthesis stage
interphase -
* G1 - primary growth phase
* S = synthesis ; DnA replicated
* G2 - secondary growth phase
interphase -
* G1 - primary growth phase
* S = synthesis ; DnA replicated
* G2 - secondary growth phase
62
New cards
What is G0?
cells that never divide (like brain cells)
63
New cards
How is cancer related to mitosis?
if mitosis is not controlled, unlimited cell division occurs causing cancerous tumors
64
New cards
What are stem cells?
cells that can develop into many different cell types
65
New cards
Know the difference between totipotent, pluripotent and multipotent stem cells?
**totipotent** - can grow into any other type of cell
**pluripotent** - can grow into anything but totipotent from embryos 3-5 days
**multipotent** - can give rise to closely related cells
**pluripotent** - can grow into anything but totipotent from embryos 3-5 days
**multipotent** - can give rise to closely related cells
66
New cards
What is apoptosis?
programmed cell death
67
New cards
Understand the difference between haploid, diploid and triploid.
haploid - 1 set of chromosomes
diploid - 2 sets of chromosomes
triploid - 3 sets of chromosomes
diploid - 2 sets of chromosomes
triploid - 3 sets of chromosomes
68
New cards
Understand what a karyotype is and how to use it.
a karyotype test looks for unusual change in the chromosome (think of down syndrome)
69
New cards
Be able to identify meiosis I and II in a diagram.
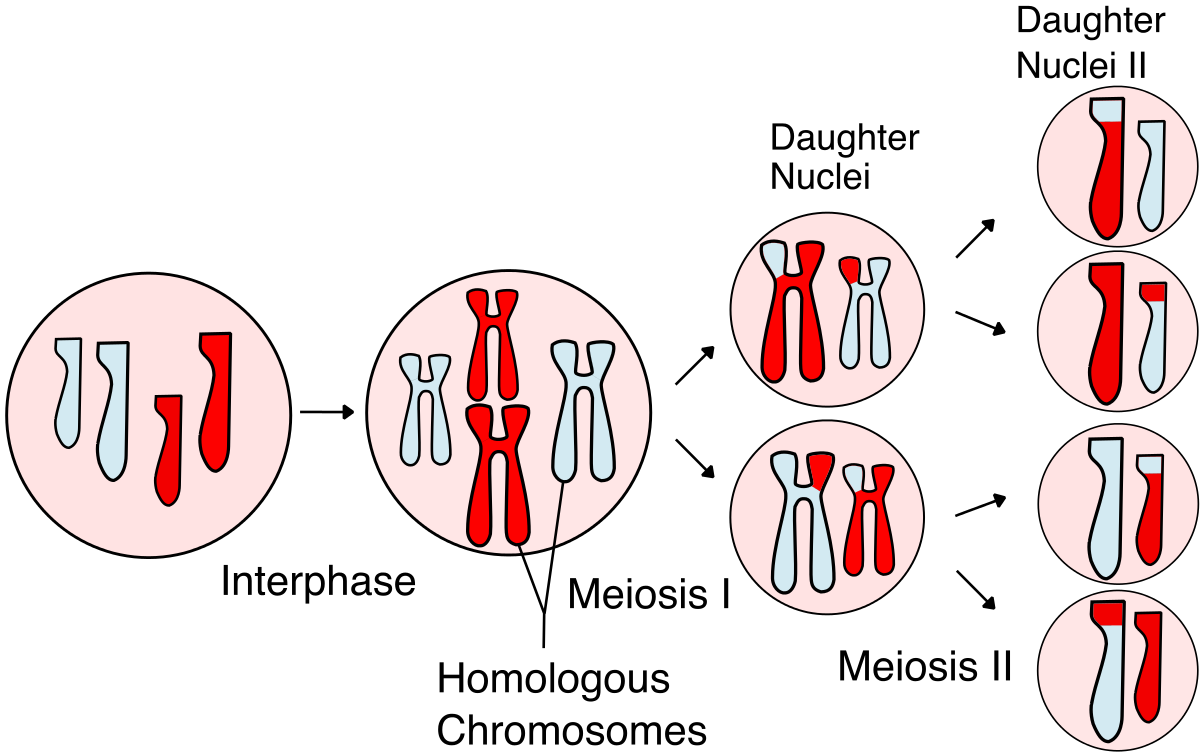
70
New cards
What is a trisomy? – an aneuploidy?
**trisomy** - condition in which an extra copy of a chromosome is present in the cell nuclei, causing development abnormalities
**aneuploidy** - one or more extra or missing chromosome
**aneuploidy** - one or more extra or missing chromosome
71
New cards
What is oogenesis and spermatogenesis? And what happens in each?
oogenesis -
* occurs in the ovaries
* starts at puberty, one oocyte (immature egg) matures into an ovum (egg) every 28 days
Spermatogenesis -
* occurs in the testes
* spermatids mature into sperm
* men produce 250,000,000 sperm per day
* occurs in the ovaries
* starts at puberty, one oocyte (immature egg) matures into an ovum (egg) every 28 days
Spermatogenesis -
* occurs in the testes
* spermatids mature into sperm
* men produce 250,000,000 sperm per day
72
New cards
Understand the overall events that happen in each stage of meiosis (I + II) include crossing over.
**meiosis 1** = chromosomes in a diploid cell resegregate, producing four haploid daughter cells
**meiosis 2** = the sister chromatids within the two daughter cells separate, forming four new haploid gametes, each with one copy of each chromosome
* *Meiosis I includes crossing over or recombination of genetic material between chromosome pairs, while meiosis II does not*
**meiosis 2** = the sister chromatids within the two daughter cells separate, forming four new haploid gametes, each with one copy of each chromosome
* *Meiosis I includes crossing over or recombination of genetic material between chromosome pairs, while meiosis II does not*
73
New cards
Understand how meiosis leads to variation.
meiosis leads to variation because it creates new combinations of genetic material in each of the 4 daughter cells
74
New cards
Understand chromosome mutations like a deletion, insertion, inversion, translocation and nondisjunction mutations? (and related diseases like Down Syndrome)
* deletion - one or more nucleotides are removed from a gene
* insertion - one or more nucleotides are added
* inversion - a chromosome segment breaks off, flips around and reattaches
* translocation - a piece of one chromosome breaks off and reattaches to a non- homologous chromosome
* nondisjunction - a chromosome fails to separate from its homologue during meiosis
ex = down syndrome - happens during meiosis when chromosome 21 fails to separate from its homologue in either the egg or the sperm (nondisjunction)
\
* insertion - one or more nucleotides are added
* inversion - a chromosome segment breaks off, flips around and reattaches
* translocation - a piece of one chromosome breaks off and reattaches to a non- homologous chromosome
* nondisjunction - a chromosome fails to separate from its homologue during meiosis
ex = down syndrome - happens during meiosis when chromosome 21 fails to separate from its homologue in either the egg or the sperm (nondisjunction)
\
75
New cards
Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis.\*\*\*
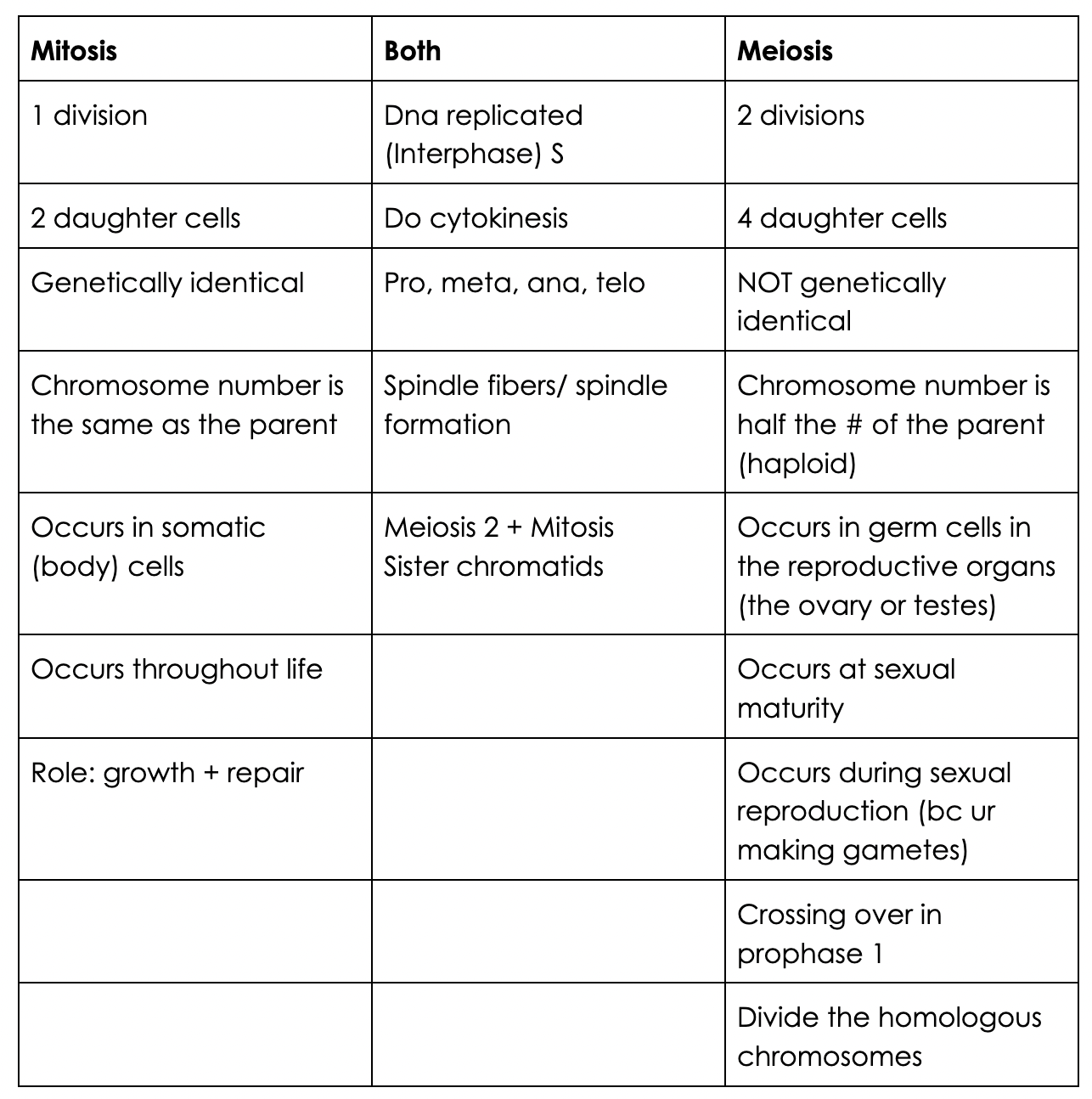
76
New cards
Who is Gregor Mendel?
father of genetics
77
New cards
What is a phenotype? What is a genotype?
* **phenotype** - observable characteristics (height, blood type, eye color)
* **genotype** - a person’s unique sequence of DNA (BB, Bb, bb)
* **genotype** - a person’s unique sequence of DNA (BB, Bb, bb)
78
New cards
Know how to do a Punnett Square using blood type or one trait.
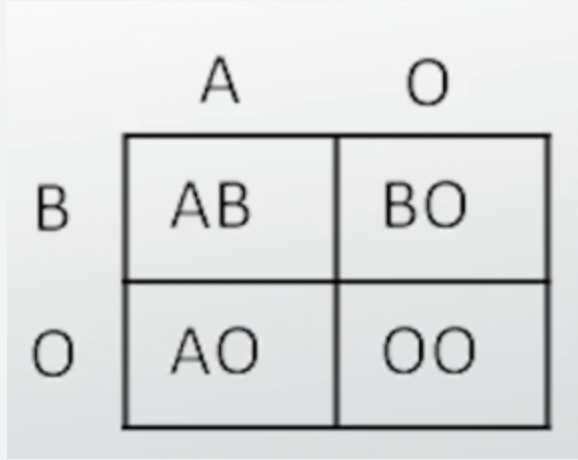
79
New cards
Understand dominant genetic diseases like Huntington’s disease.
* an allele of a gene is said to be dominate when it effectively overrules the other (recessive) allele
(Huntington’s disease develops later in life meaning the person is more likely to have reproduced by then) & a person only needs one copy of the gene to develop the disorder
(Huntington’s disease develops later in life meaning the person is more likely to have reproduced by then) & a person only needs one copy of the gene to develop the disorder
80
New cards
Know how to read pedigree charts
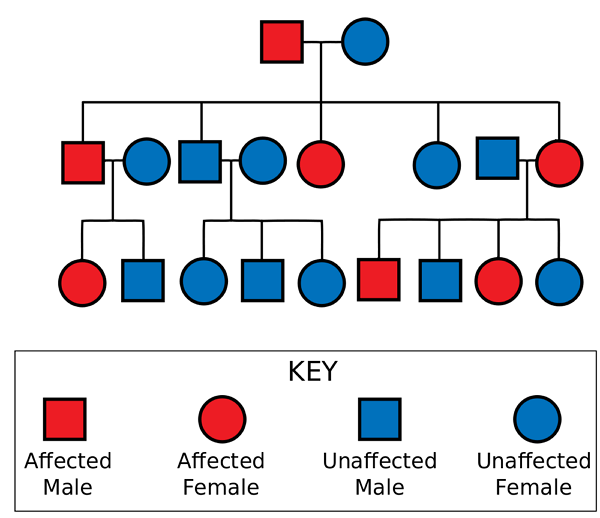
81
New cards
Who was Charles Darwin?
Father of Evolution
82
New cards
What are things that are evidence of evolution? What is a fossil?
* fossils, homologous features, embryological evidence and DNA & protein similarities are evidence of evolution
* fossils - remains of a once living organism
* fossils - remains of a once living organism
83
New cards
Relationship between behavioral, structural & physical characteristics & evolution.
phylogenetics - the analysis of evolutionary, or ancestral relationships between taxa
84
New cards
What are homologous and analogous structures?
__**homologous**__ = same structure as ancestors but serve completely diffrent function
__**analogous**__ = structure or feature of diffrent species that are similar in function but not always in structure which DO NOT derive from common ancestor (ex - bird, butterfly, bat)
__**analogous**__ = structure or feature of diffrent species that are similar in function but not always in structure which DO NOT derive from common ancestor (ex - bird, butterfly, bat)
85
New cards
What information can be used to determine evolutionary relationships?
phylogenetics
86
New cards
How can molecular biology, embryology and proteins show evolutionary relationships? \*\*\*
classification is based on evolutionary relationships
87
New cards
Determine from a phylogenetic tree what organisms are most likely related or have common ancestor etc.
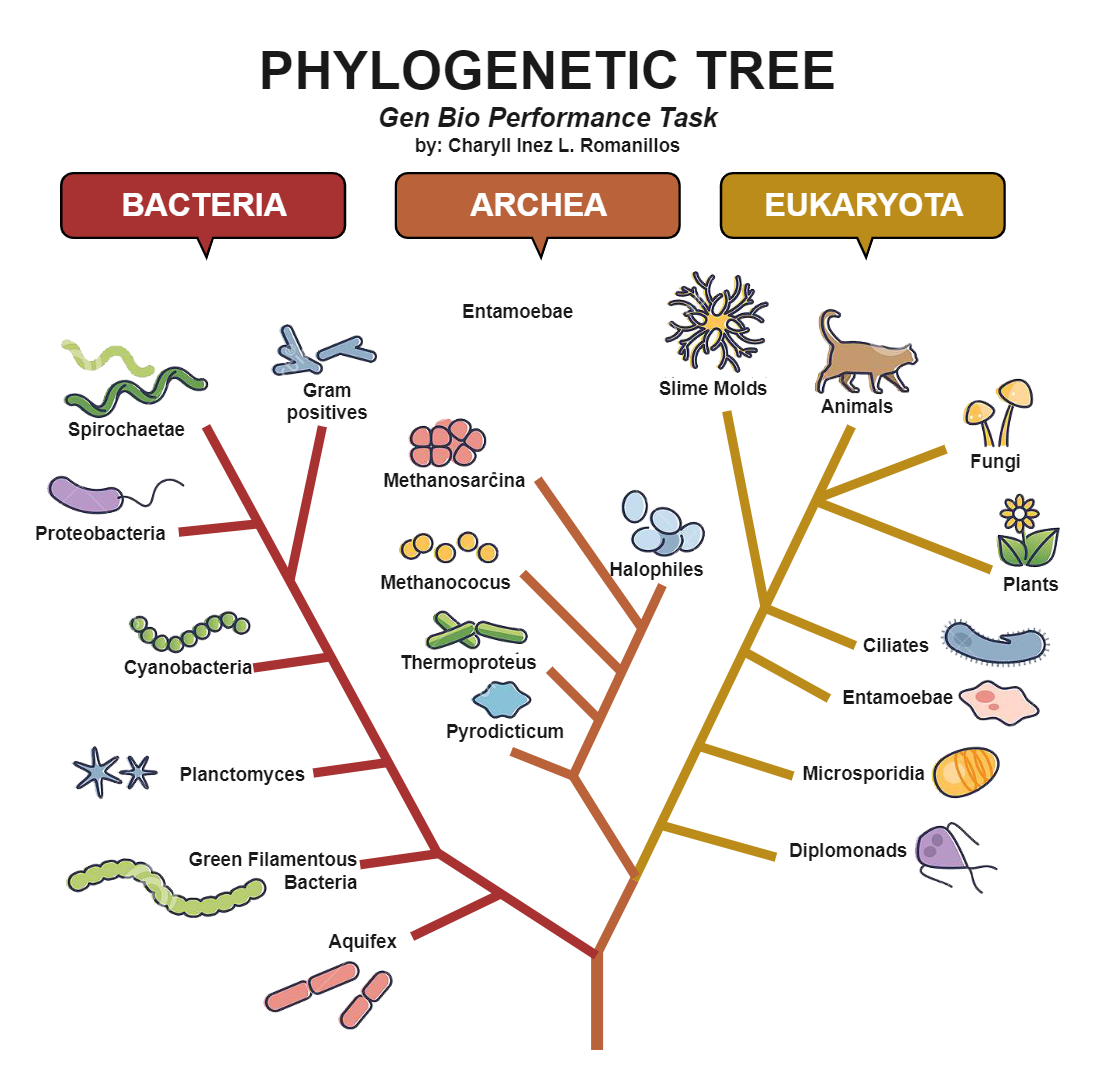
88
New cards
Understand what an isotope is and how it can be important in biology. (Use in evolution)
**isotope** - members of a family of an element that all have the same numbers of protons but different numbers of neutrons
89
New cards
What does survival of the fittest mean?
natural selection
the strongest live to pass on their gene pool
the strongest live to pass on their gene pool
90
New cards
Know the structure of a chloroplast.
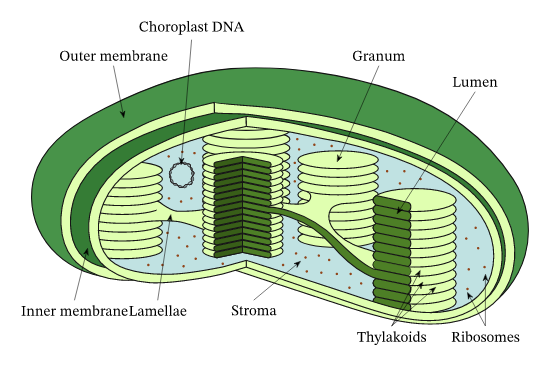
91
New cards
Know the structure of a mitochondria.
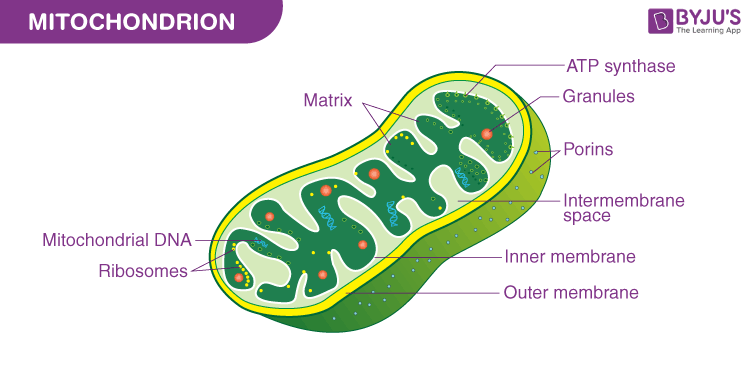
92
New cards
Relate adhesion, cohesion, evaporation, and capillary action to the process of transpiration in plants. (Be sure to know the difference between xylem and phloem)
Transpiration helps another process called capillary action to take place, which is how water moves through a plant. The movement of water inside vessels of the plant occurs due to cohesion and adhesion.
* *xylem* - carries water & minerals from the roots to the leaves
* *phloem* - carries food made by leaves to diffrent parts of the plants
* *xylem* - carries water & minerals from the roots to the leaves
* *phloem* - carries food made by leaves to diffrent parts of the plants
93
New cards
How does transpiration relate to photosynthesis?
plants absorb a lot of water and transpiration is a means by which excess water is removed
94
New cards
The cross-section of a leaf and where most of the chloroplasts located and why?
most chloroplast is found in the upper surface of a leaf, to trap the cross section of a leaf
95
New cards
What is ATP? What is the ATP-ADP cycle
**ATP** - an energy form that can be used in cells
**ATP-ADP cycle**- the process that recycles energy within a cell
**ATP-ADP cycle**- the process that recycles energy within a cell
96
New cards
Know the equations for each and whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic.
Photosynthesis (endo) -
* 6CO`2` + 6H`2`O → C`6`H`12`O`6` +6O`2`
Cellular Respiration (exo) -
* C`6`H`12`O`6` + 6O`2` → 6H`2`O + 6CO`2` + ATP
* 6CO`2` + 6H`2`O → C`6`H`12`O`6` +6O`2`
Cellular Respiration (exo) -
* C`6`H`12`O`6` + 6O`2` → 6H`2`O + 6CO`2` + ATP
97
New cards
What is an ETC (electron transport chain)?
A process that moves hydrogen ions across a membrane to produce large amounts of ATP
98
New cards
What are the levels of organization in the biosphere and levels of organization within an individual?
organism→population→community→ecosystem→biosphere
tertiary consumer → secondary consumers→ primary consumers → producers
tertiary consumer → secondary consumers→ primary consumers → producers
99
New cards
What are abiotic factors? – Biotic factors?
**abiotic factors** - nonliving parts of the environment
**biotic factors** - all living organisms inhabiting the earth
**biotic factors** - all living organisms inhabiting the earth
100
New cards
What is a trophic level and how much energy is transferred between levels?
producers (100%) → primary (10%) → secondary (1%)→ tertiary (0.1%)