ENTM010 Final Study Guide
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
Adenotrophic viviparity
A reproductive strategy where insects give birth to live larvae that have been nourished internally by specialized glands.
- Fertilize one egg at a time and retain each egg within their uterus to have offspring develop internally
- Female feeds larva from modified uterine gland
- As 3rd instar, larvae leaves uterus and crawls into ground to pupate
- Emerges as adult and now must feed on own for first time
(Each female can produce only 8-10 offspring in her lifetime)
African trypanosomiasis
Also known as sleeping sickness; a parasitic disease transmitted by tsetse flies.
- sleeping sickness
- protozoan pathogen of species Trypanosoma brucei
- invade blood lymph central nervous system -> sleeping disorder
- nagana: animal form of sleeping sickness
Africanized “killer” bees
A hybrid of African and European honeybees known for aggressive behavior and strong colony defense.
cross between European honeybee and African honeybee
known for their increased defensiveness
Almond flower pollination in CA
A crucial ecosystem service where honeybees pollinate California's almond crops, essential for yield.
European honeybee used for pollination of almond flowers, honey bee hives are brought in from around the US (2 hives per acre), In almond bloom, >80% of all available commercial hives in the US are in CA
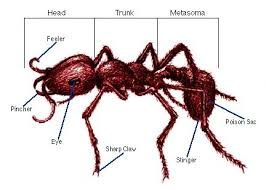
Ant antennae
Sensory organs used for detecting chemical signals (pheromones), touch, and environmental cues.
geniculate antennae / elbow-shaped
Used to smell, touch, feel, and communicate
Ant feeding habit
Varies by species; includes scavenging, farming fungi, or tending to aphids for honeydew.
omnivorous - eat everything
milk of aphids and other small Hemiptera, insects and small living or dead invertebrates, as well as the sap of plants and various fruits.
They also eat insect eggs
Some are parasitic of other ants
Many feed mouth to mouth (trophallaxis
(seed collectors, honeydew drinkers, predators)
Ant-decapitating phorid flies
Parasitoid flies that lay eggs in ants; their larvae decapitate the host as they develop.
Parasitoids of ants
Typically Species specific and often caste specific

Antlion larva habit
Predatory larvae that dig pit traps in sand to capture and consume ants and other small insects.
larvae: predator
require sandy soil/covered with something so they are protected from frequent /divert rain falls
larvae: build funnel - like trap in sandy soil use to catch insect preys

Aposematic coloration
Bright, warning coloration used by insects to signal toxicity or unpalatability to predators.
used by noxious organisms to signal their unprofitability to potential predators.
Bright warning colors in animals with a chemical defense.
Argentine ant biology
An invasive ant species known for forming massive supercolonies and displacing native ants.
Tend honeydew-producing plant pest: interferes w/ biological control
Displaces some native arthropods
Major urban / structural nuisance pest
Unicoloniality, individuals mix freely among separate nests
Vast population size / absence of intercolonial aggression in the introduced areas
similarity in cuticular hydrocarbon signature (colony odors)
Bite but cannot sting
Shallow nest in soil under rocks, logs, stepping stones, pavement

Army ant biology
Highly mobile, nomadic ants that form temporary nests and exhibit cooperative predatory behavior.
Aggressive predatory foraging raids
Life without a permanent nest: bivouac - making a "nest" with their bodies
Nomadic phase & Stationary phase: this depends on reproductive cycle of young ants (developmental)
Armyworm
The larval stage of certain moths, known for migrating in large numbers and damaging crops.
Lepidoptera
will eat anything in their path
nocturnal larvae
undergo seasonal migration

Biting midges
Family Ceratopogonidae (biting midges) aka no-see-ums
- Male and female feed on nectar, but females also feed from some kind of host animal for egg development
- Diverse feeding habit: vertebrate blood, insect hemolymph, etc
- Some are significant vectors of animal disease (ex: bluetongue virus in sheep )

Nonbiting midges
Family Chironomidae (non-biting midges)
- Common nuisance around bodies of water
- Frequently mistaken for mosquitoes (No bite, Wings are shorter than its body, Develops in mud on the bottom of lakes, ponds, Does not carry diseases)

Blackflies
Small, bloodsucking flies; some species transmit diseases like river blindness.
Buffalo gnat (arched thorax, giving an appearance of miniature bison)
Females consume nectar and blood while males only feed on nectar
Bite: female only
Larvae: aquatic in flowing water
Feeding: fan-like labral from -> organic debris in flowing water
Attachment: silk -> starve or other substitutes w/ small hooks at end of their bodies
Adults are long distance flyers: Females in some species will fly several hundred kilometers in search of a blood meal
Adults are major nuisance pests in upper Midwest, New England and Canada
In NA, about 6 species are known to bite human
Pupae: pupate inside of a sunken shelter (cocoon)
aquatic - "spiracular gill"

Blackfly and disease
Blackflies (genus Simulium) transmit Onchocerca volvulus, the cause of river blindness.
River blindness (disease): aka onchocerciasis
Causative agent: microfilariae of a parasitic nematode (Genus Onchocerca)
Location: Equatorial Africa & Central America
Causative agent in parasitic nematode
Nematode enter wound → develop into worm→ mature and migrate through the skinSymptoms = severe itching, bumps under skin
Treatment: Ivermectin

Blackfly biology
Females require blood meals to reproduce; larvae live in fast-moving streams.
Blow flies in forensic entomology
Early colonizers of decomposing bodies; their development helps estimate time of death.
Tend to arrive first to the dead animal's body and lay eggs
ID species, determine where they are in life cycle then backtrack to get TOD

Bombardier beetle defensive strategy
Releases a hot, chemical spray from its abdomen to deter predators.
Hydrogen peroxide + Hydroquinone
chemical gas weapon

Book lung
A respiratory organ in some arachnids (not insects), composed of stacked, leaf-like structures.
respiratory organ for subphylum chelicerata (spiders, scorpions)
Cabbage butterfly
A white butterfly (e.g., Pieris rapae) whose larvae are agricultural pests of brassica crops.
Larvae only feed on / females lay eggs on plants containing glucosinolates
Defensive compounds characteristic of plant
Family Brassicaceae (cruciferous vegetables)
Pests on cabbage and its relatives

Cabbage looper
A green caterpillar known for its looping movement; damages cabbage and related plants.
Part of Noctuidae family
The caterpillar larvae are major pests

Caddisfly
Trichoptera
Related to butterflies & moths (lepidoptera)
Larvae have various feeding habits depending upon species (larval variability)
Shredders/scrapers/collectors - larvae mostly feed on periphyton (layer of algae)

California dogface butterfly
The state insect of California; males have a yellow and black pattern resembling a dog’s head.
only found in California
wings mimic a dog's face'
The state insect (CA) since 1972
Endemic range is limited to the state
Color and pattern on the underside of wings are simple

Canine heartworm
A parasitic worm (Dirofilaria immitis) transmitted by mosquitoes, affecting dogs' hearts and lungs.
The Anopheles Mosquito is a vector for this disease.
Cardenolid
A toxic chemical compound found in the milkweed plant that monarch butterflies eat and use against their predators
Carrion beetle
Scavengers that feed on dead animals; some help bury carcasses for their larvae to feed on.
Coleoptera
(Family Silphidae) diet: dead animal , colonize carrion during all stages (from early to late) of decomposition, recycling nutrients, chemical defense: excellent deterrent
aposematic coloration

Casemaking clothes moth
A moth species whose larvae build portable cases from silk and feed on wool or fabric.
Unique ability to digest keratin
Damages clothes and carpets
Pests on animal hair
Common in southern US, Georgia, and Florida
Larvae construct cases to hide with various fibers and other materials available in their habitats
Adult has 3 dark spots on wings
Larvae: pest on fabrics, prefer fabric that is old / contaminatedLarvae carry case. If separated, they will die. As the larvae grow, they lengthen the case by building onto old case at each molt.

Characteristics of Insecta
Three body segments (head, thorax, abdomen), three pairs of legs, exoskeleton, and typically wings and antennae.
3 tagmata (head, thorax, abdomen)
wings: 2 pairs (always found in thorax)
compound eyes
1 pair of antennae
3 pairs of jointed legs
various mouthparts
Characteristics of Lepidoptera
Insects with scaled wings; includes butterflies and moths, undergoing complete metamorphosis.
siphoning mouthparts
proboscis
wings have scales
scales = modified hairs
larvae feed on plants
larvae spins silk
greatest color variation
major agricultural pests
Larvae have six true legs on thorax, plus abdominal and anal prolegs
adults feed on nectar
Cochineal
A scale insect used historically and commercially for producing carmine red dye.
Sessile parasites on plants
Lives on cacti in genus Opuntia
Natural dye carmine is derived

Colorado Potato Beetle
A major pest of potato crops; resistant to many insecticides.
Leaf Beetles (Family Chrysomelidae)
Major Crop pests
feed on several different plants within nightshade family
Quickly develops resistance to insecticides

Corixidae respiration
Water boatmen breathe through air stores held on their bodies and come to the surface to replenish them.
Lack gills, carry air bubble down into the water to take oxygen from water

Crane fly biology
Harmless, long-legged flies; larvae live in moist soil or water and feed on decaying organic matter.
Stilt-like legs may be easily shed (defensive mechanism)
Larvae are important soil engineers and either aquatic/terrestrial
Active during spring, after the rain, and at night
Emerges from the soil, flies low to mate and lay eggs
Lays eggs in the ground, the larva stays in the soul and looks like a maggot
Has halteres

Cryptic coloration
Camouflage that helps insects blend into their environment to avoid predation.
Camouflage; makes an organism difficult to spot.
Dance language of honeybee
A method of communication using movements to inform others about food sources.
wobble or waggle dance to tell other bees direction & distance to the food source (nectar, pollen)
The foragers that return from flower sources
Darkling beetle feeding habit
Scavengers; eat both fresh and decaying vegetation.
Feed on dried or rotting plant matter. In captivity, they feed on bran meal, apples, oranges, potatoes, cucumber, romaine lettuce, and pears. Remove uneaten food before it molds
Order Coleoptera
Fused Elytra
Flightless
Diapause
A type of dormancy in insects that is associated with a period of unfavorable environmental conditions.
Disease and body louse
Lice (Pediculus humanus corporis) transmit diseases like typhus and trench fever.
Human body lice transmits epidemic typhus fever
bacteria: rickettsia
develop off human body
Diversity in insects
~1M named insect species, 1.9 million total species
Based on the number of known species (all animals, all plants, all virus, all bacteria, all fungi...), of the approximately 1.9 million presently recognized, just over half are insects.
Diving beetle feeding habit
Predatory aquatic beetles; larvae and adults feed on small aquatic organisms.
predaceous
air bubble + natatorial legs

Dung beetle biology
Beetles that use dung as a food source or to lay eggs; important for nutrient recycling.
(Family Scarabaeidae): Adults eat soft dung
rollers & tunnelers & dwellers
Dung as provision for: developing larvae
Recyclers of animal dung
associated with Re, supreme being and sun god in Egyptian culture

Ecdysone
A hormone that promotes molting and the metamorphosis of a larva to a butterfly.
Ecological advantages of dipteran insects
Includes pollination, decomposition, disease vectoring, and as a food source.
Separate niches for life stages
Adults dispersal ability: Some black flies travel > 100 km!
Larvae specialize in rotting organic materials
Short generation times for many species (7-10 days)
Ephemeroptera
Order of insects known as mayflies; have short adult lives and aquatic nymph stages.
Hemimetabolous, yet has two stages (subimago and imago) after nymphal stage
Unique to only this order and fairly dies shortly after becoming an adult. large triangular wing, 1 caudal filament & 2 cerci. adult terrestrial, nymphs aquatic.
Epidemic Typhus Fever
Transmission of disease by human body lice
Caused by bacterium Rickettsia prowazekii
Symptom: sudden headache, chills, high fever, protration, coughing and severe muscular pain, skin rash
Typically occurs in conditions of overcrowding and poor hygiene aka prisons and refugee camps
Common in concentration camps in WWII
Etymology of Hymenoptera
Derived from Greek: “hymen” (membrane) + “ptera” (wings); includes bees, ants, wasps.
> 150,000 recognized species
Evolved ~ 250MYA
Diverse order!
Complete metamorphosis
Etymology of Lepidoptera
Greek origin: “lepido” (scale) + “ptera” (wings); refers to butterflies and moths.
butterflies and moths, "lepidpo" = scale, "ptera" = wing
Eusociality
Social organization with cooperative brood care, division of labor, and overlapping generations.
Live in groups as adults
Cooperative brood care
Reproductive division of labor
Overlapping generation in adults
Evolution of hexapods
Hexapods evolved from crustacean ancestors; includes all six-legged arthropods like insects.
class Entognatha- may be polyphyletic and have internal mouth parts.
Protura: cone headed soil organisms.
Diplura: two-pronged bristletails.
Collembola: springtails.
Furcula: "jumping fork"
Fire ant adaptation
Aggressive behavior, venomous sting, and the ability to form floating rafts during floods.
Seed harvesting (like harvester ants)

Firefly bioluminescent organ
A light-producing structure in the abdomen, used for mating communication.
Luminescent organ on abdomen
Involves specialized cells, photocytes [responsible for producing light]
Luciferin, luciferase, energy, oxygen
Highly efficient [no heat created, energy goes into light production]
Lights used to attract mates [adults]
![<p><span> A light-producing structure in the abdomen, used for mating communication.</span></p><ul><li><p><span>Luminescent organ on abdomen</span></p></li><li><p><span>Involves specialized cells, photocytes [responsible for producing light]</span></p></li><li><p><span>Luciferin, luciferase, energy, oxygen</span></p></li><li><p><span>Highly efficient [no heat created, energy goes into light production]</span></p></li><li><p><span>Lights used to attract mates [adults]</span></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/cf6f2426-f424-416d-a6d9-fde64eba9c99.png)
Fly response to a corpse
Flies rapidly colonize decomposing bodies; species appear in predictable succession.
Tend to arrive first to the dead animal's body and lay eggs
Foraging strategies in Myrmicinae
Myrmicine ants show diverse foraging: trail following, group foraging, and solitary hunting.
seed harvesting and fungus growing

Forensic entomology
Study of insects in legal contexts, especially for determining postmortem intervals. (TOD)
Formic acid
A defensive chemical secreted by many ants, especially formicines.

Function of Malpighian tubules
Excretory organs in insects that remove nitrogenous waste and regulate water balance.
Main excretory organs in most insects.
Key role in the production of primary urine and osmoregulation, selectively reabsorbing water, ions, and solutes.
Filters hemolymph of metabolic wastes and transfer wastes to hindgut - comparable to kidney
Glucosinolates
Plant defensive chemicals; some insects sequester them to deter predators.
Larvae only feed on / females lay eggs on plants containing glucosinolates of cabbage butterfly
Defensive compounds characteristic of plant
Family Brassicaceae (cruciferous vegetables)
Gossamer-winged butterfly
A family (Lycaenidae) of small, delicate butterflies including blues, coppers, and hairstreaks.
small, less colorful
phytophagous or entomophagous (insect-feeding)
75% engage in an association with ant (some are parasitic)

Gulf fritillary
A butterfly with orange and silver markings; its larvae feed on passionflower vines.
Agraulis vanillae
Species of butterflies from Family Nymphalidae (brush-footed butterflies)
Bright orange, long narrow wings
family: nymphalida
eorder: lepidoptera
largest family of butterflies
larvae have defensive spikes on body

“Hair-pencils” in butterfly
Tufts of scent-emitting scales used in courtship by some male butterflies.
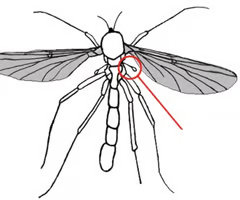
Haltere
Modified hindwings in flies used for balance during flight.
Small knob-like structure that exists behind each wing of flies and their relatives; function in stabilization during flight.
Hamulate wing-coupling mechanism
Tiny hooks on hindwings that latch onto forewings in Hymenoptera for synchronized flight.
Harvester ant
Ant species that collect, harvest, and store seeds; some are important for soil health and seed dispersal.

Hemolymph functions
Insect blood; circulates nutrients, hormones, and immune cells but does not carry oxygen.
used by invertebrates to deliver nutrients, transport materials, and remove waste.
Without hemolymph, the tissues and cells of these invertebrates would not be able to perform their intended functions, nor remove waste materials as they are produced.
Holometabolous
Complete metamorphosis with four life stages: egg, larva, pupa, adult.
Hornet
A large, social wasp known for powerful stings and aggressive nest defense.
Nesting: on trees
Diet: aggressively hunt bee hives

Hornworm
The larva of hawk moths; major pests of tomato and tobacco plants.
larvae of Tomato horn worm (Manduca quinquemaculata)
Major pests of tomatoes especially for organic gardeners (also potato, pepper, eggplant, tobacco - all members of nightshade family)
Cryptic but we can use UV to find them on host plants

Horsefly feeding
Female horseflies feed on blood; males feed on nectar.
Adults: stout bodied powerful fliers w/ large eyes and excellent vision/both sexes feed on nectars
Females use knife-like mandibles and maxillae to make an incision and then lap up the blood from the pool

Hydroquinone
A chemical involved in the bombardier beetle’s explosive defense.
Hymenoptera biology
Ants, bees, and wasps
complete metamorphosis
2 pairs of wings (hamulate- hooks) and compound eyes
chewing and lapping mouthparts
stingers (modified ovipositor)
larvae pupate in apocrita
Hymenoptera sex determination
Haplodiploid system: fertilized eggs become females, unfertilized become males.
females develop from fertilized eggs while males develop from unfertilized eggs
Females can reproduce haploid males without mating
Japanese beetle feeding habit
Adults feed on foliage and fruits of many fruiting trees and shrubs.

Jewel beetle characteristics
Family buprestidae
description = texture cuticle, shiny/metallic, thin film interference
diet = wood of trees-some are pryphils, organs sensitive to radiations
can detect radiation from heat and fires; forest fires
Larvae and adults in Diptera
Undergo complete metamorphosis; larvae often live in different habitats than adults.
No legs, sometimes spines diurnal , active but some are nocturnal or crepuscular (active at dusk or dawn)
larvae stay in or around their food source
primitive flies- caliciform type larvae (presence of distinct head capsule)vermiform type larvae- maggots (without head capsule reduced to hooks)
Halteres: gyroscope (excellent aeralists)
Leaf beetle
Herbivorous beetles that feed on leaves; includes pests like the Colorado potato beetle.
(Family Chrysomelidae)
Major Crop pests
feed on several different plants within nightshade family
Quickly develops resistance to insecticides
Leaf-cutter bee
Solitary bees that cut leaves to line their nests; important pollinators.
Uses hollow stems of plants, holes in solid wood, other protected natural cavities
Semi-domesticated (live in man-made nests (easy to domesticate)
have a tuft of hair on the abdomen used to collect pollen (scopae)

Leafcutter ant biology
Ants that farm fungus on cut leaves in underground colonies; highly social.
Unique farming of fungus. They collect leaf(leaves) to serve as the nutritional substrate of their fungus
Constantly taking out pathogenic fungus or molds & also produce antimicrobial compounds

Leishmaniasis
A disease caused by Leishmania parasites, transmitted by sandflies.
vector: sandfly
40 diff sand fly species (vector)
20 diff protozoan parasite species
very specific vector/parasite combo
Cutaneous (most common), visceral, mucocutaneous
Risk factors: malnutrition, poor hygiene, poverty, urbanization, deforestation
Prevention: sleep under mosquito nets treated with insecticide
Treatment: depends on the species parasite and where contracted
occur in US military
Lycaenidae biology
Small butterflies often associated with ants; some larvae are carnivorous.
gossamer-winged butterflies
small in body size and less colorful than other families
diverse in their food habits: phytophagy, entomophagy
(75%) larvae associated with ants
master manipulators = nest parasitism
Maggot therapy
Use of fly larvae to clean necrotic tissue from wounds.
use of larvae of a species of blow flies that secrete an enzyme that dissolves dead tissue
Debridement: removal of dead, damaged, or infected tissues to improve healing potential of remaining healthy tissue
Disinfection - secrete several different compounds that have broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity (uric acid, allantoin, ammonia; antibacterial peptide)

Mayfly characteristics
Adults do not feed, only disperse, mate, and die
Large triangular front wings
1 median caudal filament and 2 cerci (long)
Adults terrestrial, nymphs aquatic (respire thru abdominal gills)
Relatively long life cycles (live as nymphs for months to years)
Subimago stage
final stage before molting to adult (imago)
Mass emergence swarms, lay eggs in water
Very important in food webs

Medico-legal forensic entomology
This is the study of how insects or their remains are used in the investigations of death, abuse, criminal, and neglect cases.
Mimicry
Imitation of one species by another for protection
"Classic" Mimicry: An insect blends in with its surroundings. Ex. Leaf insects, stick insects
Batesian mimicry: An unprotected species (mimic) evolves to look like a protected species (model)
ex: Coral Snake (venomous ) & Milk snake (non-venomous)Mullerian Mimicry: A chemically protected species (mimetic #1) evolves to look like another protected species (mimetic #2)
Mosquito and diseases
Mosquitoes transmit diseases like malaria, dengue, Zika, and West Nile virus.
Culex Mosquito: Disease Vector for West Nile Virus (WNV)
Aedes Mosquito: Disease Vector for Dengue, Yellow Fever, WNV, and Zika
Anopheles Mosquito: Vector for Mammalian Malaria and Canine Heartworm
Moths vs. butterflies
Moth: feather like (bipectinate) or thin antennae, Cocoon (silken case surrounding pupa), body robust, wings flat at rest, often nocturnal
Butterflies: Thicker antennae with bulbs or hooks on end
Chrysalis (is the pupa, with hardened protein exoskeleton as outer protection), body thinner, wings upright at rest, diurnal
Natatorial leg
A leg adapted for swimming, often flattened and fringed with hairs.

Nesting habits in wasps
new nest every year and is constructed out of wasp paper made by chewing wood and other plant debris mixed with saliva
no wax producing gland
Wasps lay eggs in caterpillars' body
As eggs hatch, they feed on caterpillars' internal organs
When ready to pupate, larvae emerge and spin cocoon on the
surface of the hornwormFrom these cocoons, new wasps will emerge
Neuropteran feeding habit
Lacewings (family Chrysopidae) and antlions (family Myrmeleontidae), are predatory and feed on other insects
Mantispids (family Mantispidae), feed on nectar and pollen as adults
Nymphalidae leg
Adults have reduced forelegs
stand only on 4 legs while the other two are curled up

Ocelli
Simple eyes on an insect used to sense light

Ommatidia
Light sensing units of compound eyes; each contributes to an insect’s mosaic vision.
Onychophora characteristics
Velvet worms; segmented, soft-bodied, terrestrial, and closely related to arthropods.
Bilaterally symmetrical
Gas exchange via trachea
Open circ system
Exoskeleton
Link between worms and arthropods
velvet/walking worm

Osmeterium
A gland in swallowtail caterpillars that emits foul odorous chemicals as a defense.
"Smelly horn" (chemical defense)

Parasitoid vs. predators
Parasitoids kill hosts slowly from within; predators kill multiple prey directly.
parasitoid: needs only one host to complete life cycle
predator: needs a lot of prey to complete one life cycle
Pentatomidae characteristics
Stink bugs; shield-shaped body and foul-smelling defense chemicals.
Shield and Stink bugs
Distinct angular shape
Brightly colored
Noxious odors (hence stink bugs!)
Some are agricultural pests

Pheromones
Chemical signals released by an animal that communicate information and affect the behavior of other animals of the same species.
Phorid flies and ants
Includes ant-decapitating species; also associated with decaying matter.
some are parasitoids of ants and can be used in biocontrol
ant decapitating (lay eggs on ants thorax → larvae migrate to the ant's head and feed on hemolymph, muscle, and nerve tissue
family formicidae
ants are eusocial (small workers- nurses, medium workers- colony maintenance and foraging, large workers- soldier)
Pollen basket
A structure on honeybee legs used to carry pollen back to the hive.
on hind leg tibia of European honey bee

Problems caused by invasive ants
Disrupt ecosystems, harm native species, damage electronics, and pose health risks.
threaten ecosystem stability = generate significant environmental and economic cost
threaten biodiversity, spread disease
alter stability and quality of ecosystem processes