Chemistry - Unit 1: States of Matter
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
describe the particle separation, arrangement and motion of solids
solid particles are arranged regularly
particles vibrate around fixed positions
particles are tightly packed together
describe the particle separation, arrangement and motion of liquids
particles are randomly arranged
particles slide past each other
particles are close together with some touching
describe the particle separation, arrangement and motion of gases
particles are randomly arranged
particles move quickly in all directions
particles are spread far apart
describe melting/boiling in terms of kinetic particle theory
particles in solid/liquid will absorb thermal energy when heated and convert it into kinetic energy
causes particles to move more
solid/liquid then expands until the intermolecular forces of attraction are overcome and structure becomes liquid/gas.
describe freezing/condensation in terms of kinetic particle theory
when cooled, liquid/gas particles slow down
eventually, particles will move slow enough for the intermolecular forces of attraction to hold the particles in a solid/liquid structure.
describe evaporation in terms of kinetic particle theory
particles near the surface of the liquid gain sufficient energy from the surroundings to overcome the intermolecular forces of attraction between molecules and evaporate.
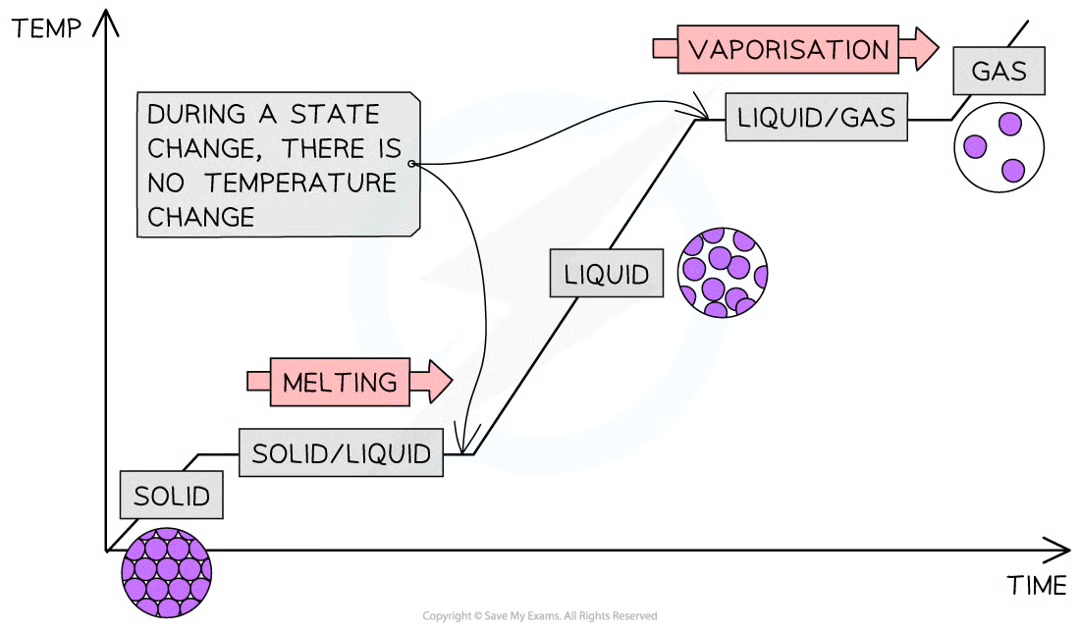
interpret and explain heating curve in terms of kinetic particle theory
as temperature rises, particles gain more energy, overcoming the forces of attraction between particles
line then becomes flat as the solid changes state to a liquid. the temperature at which this process occurs is called the melting point
once all the solid has melted, the temperature will increase again, increasing energy further
again, the line will become horizontal again as the liquid boils and the forces of attraction between the liquid particles are broken and changes state to a gas. this temperature is the boiling point.
temperature will continue to rise once all liquid has boiled.
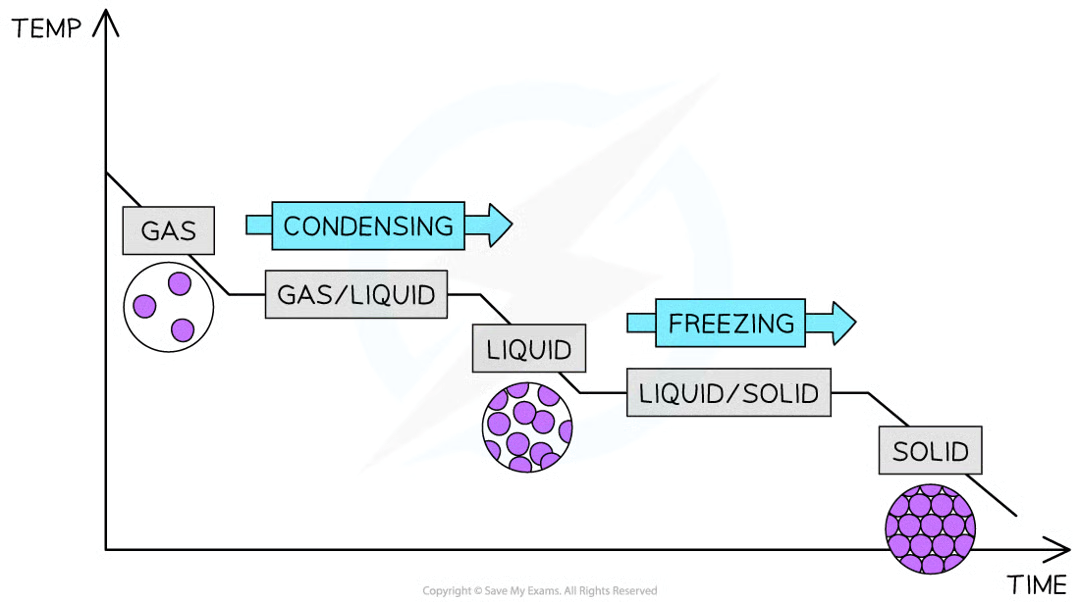
interpret and explain cooling curve in terms of kinetic particle theory
at the start of the graph, the substance is still in gaseous state, but the temperature decreases as energy is lost into the surroundings
the line then plateaus, new bonds are formed between the gas particles, turning them to liquid through condensation
the temperature decreases further as soon as all the gas particles have turned to liquid
the line becomes horizontal again as the freezing point is reaches and more bonds are formed, changing liquid to solid state.
explain the effects of temperature on the volume of a gas in terms of kinetic particle theory
as temperature increases, the volume of a gas will increase
increasing the temperature increases the kinetic energy of the gas particles
so the gas particles move and collide with the container more quickly, spreading further apart
explain the effects of pressure on the volume of a gas in terms of kinetic particle theory
as pressure increases, the volume of a gas will decrease
pressure refers to the number of particles in a fixed volume
increasing the pressure decreases the volume of the gas, as the gas particles are forced closer together
decreasing the pressure increases the volume of the gas, as the gas particles can spread further apart
describe and explain diffusion in terms of kinetic particle theory
diffusion is the process by which different gases or different liquids mix due to the random motion of their particles
diffusing particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
eventually the concentration of particles is even as they spread out to occupy all of the available space
diffusion happens on its own and no energy input is required although it occurs faster at higher temperatures
explain the effect of relative molecular mass on the rate of diffusion of gases.
gases with a smaller relative molecular mass diffuse faster as the smaller the relative molecular mass of the gas particles, the “lighter” the particles so particles move faster and the faster the rate of diffusion
gases with a larger relative molecular mass diffuse slower as the larger the relative molecular mass of the gas particles, the “heavier” the particles so particles move slower and the slower the rate of diffusion.