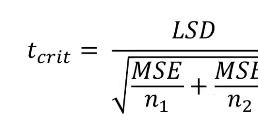Factorial ANOVA
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is a factorial ANOVA
A test with more than 1 independent variable
Allow us to test for interactions
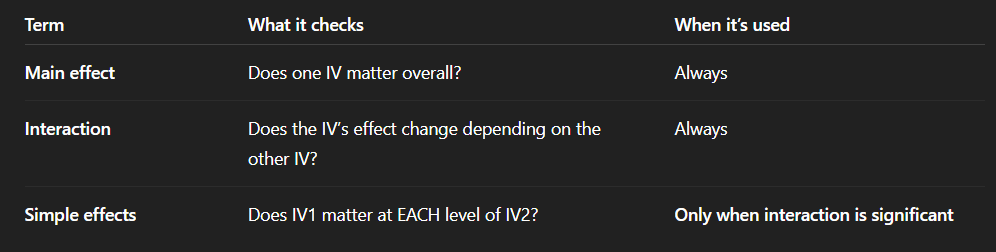
What is an interaction, main effect, simple effect
Interaction: - Examining if the effect of IV1 on the DV depends on the level of IV2 on DV (Level of A depends on B)
Main effect: overall effect of one variable - A main effect tests whether means differ across levels of one factor while collapsing across the other factor.
Simple effect: effect of that variable within one specific level of the other variable
Factors vs levels
Independent Variable
EG: Experiment to look at the effects of drug a vs drug b (assigned to 10mg, 20mg, 30mg)
Drug a and b would be the factors
Mg would be the 3 levels
What levels are compared in a factorial design?
Every level of every factor is paired with every level of every other factor (all combinations are included)
Eg: each person will have some level of drug b and drug a (12 different variations)
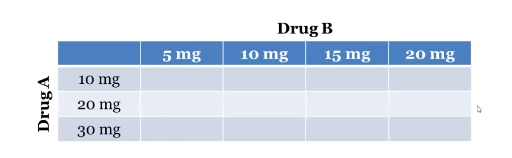

What kind of factorial design is this
Tow factor - 3×4 factorial design representing the number of levels
Factor with 3 levels fully crossed with a factor of 4 levels
What does it mean to have a between-subjects design in this context
Different participants in each cell (only one level of drug a and one level of drug b)
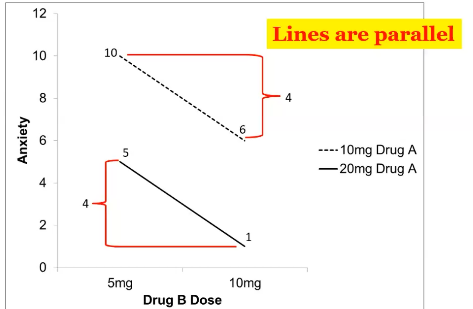
What does no interaction look like?
If the lines are parallel - EG: drug B dose and anxiety
As the dose increases by 4 on both drugs (the effect of drug b did not depend on the level of drug a)
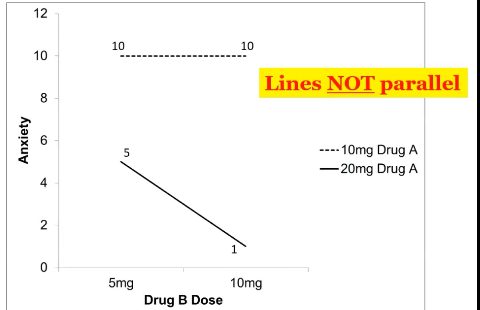
What does it look like when there is an interaction
Lines are not parallel - if you extended them out they would eventually cross
Effect of drug b depends on the effect of drug a - the change as we change from one condition to another depends on what is going on with the other
What does the source table look like?
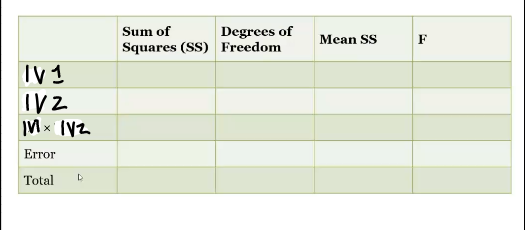
Different df
Group = k (levels) -1
Interaction = product of group df (group 1 df = group d df)
Error = df total - group and interaction terms (N - # of cells)
Total = N (total people in expirement) -1
ss total
look at each individual person and subtract their mean from the grand mean

SS group
Sum of: nj (x hat - x hat)² on each side
(but them under each iv ss)
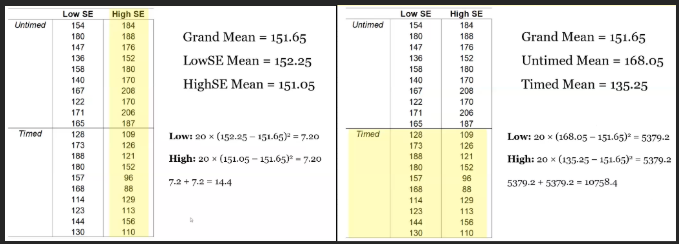
SS interaction
Have to compute ss cells ]
Compute the mean of each cell
Subtract this mean from the grand mean
SS IV1xIV2 = SScells - SSIV1 - SSIV2
![<p>Have to compute ss cells ]</p><ul><li><p>Compute the mean of each cell </p></li><li><p>Subtract this mean from the grand mean </p></li></ul><p>SS <sub>IV<sup>1</sup>xIV<sup>2</sup></sub> = SS<sub>cells</sub> - SS<sub>IV<sup>1</sup> </sub>- SS<sub>IV<sup>2</sup></sub></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/41d51d81-f047-4685-abf7-dad3bef515e9.png)
What is ss cells
Only a step of calqulating ss intercation, not the same thing
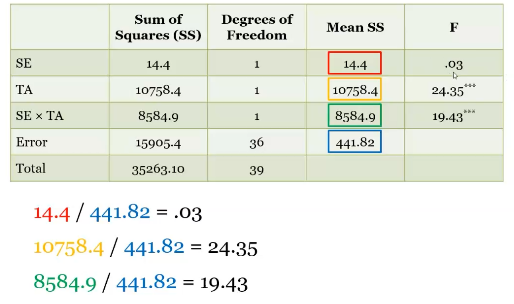
Mean SS and F
Mean ss: Divide Across
F: Divide each ss by the error term
Main Effects VS Simple effects
Main: The effect of one if the IVs averaged across the levels of the other IV
Imagine you’re looking at whether sleep affects test scores - You also have a second variable, caffeine, but you’re not thinking about it right now.
A main effect of sleep asks: “On average, does more sleep lead to higher scores?”
Simple: The effect of one of the IVs at one level of another IV - testing the little space
“Within high caffeine, does more sleep improve scores?”
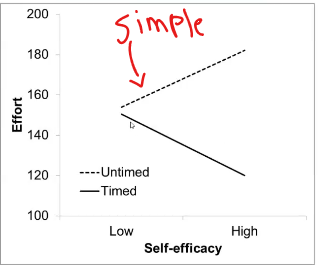
What does it mean when you find a significant effect
Means theres an interaction (lines arent horizontal)
We have to do a test to see if there is actually an interaction
Is the deviation from parallel significant
How to calculate simple effects (using MSE)
Use MSE and a new source table
*df and mean mse directly from omnibus table

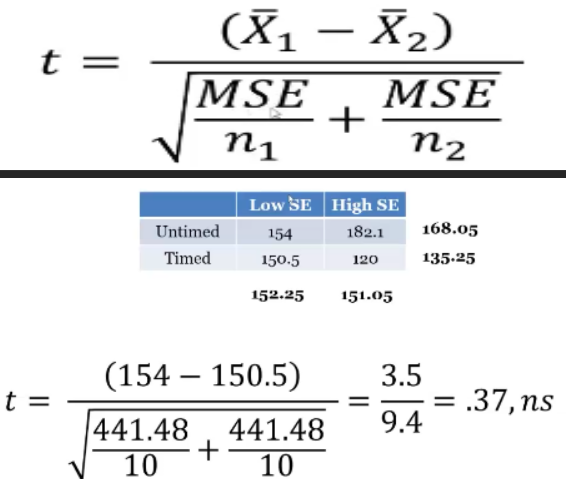
How to calculate simple effects (using t-test)
(do the same with the high end)
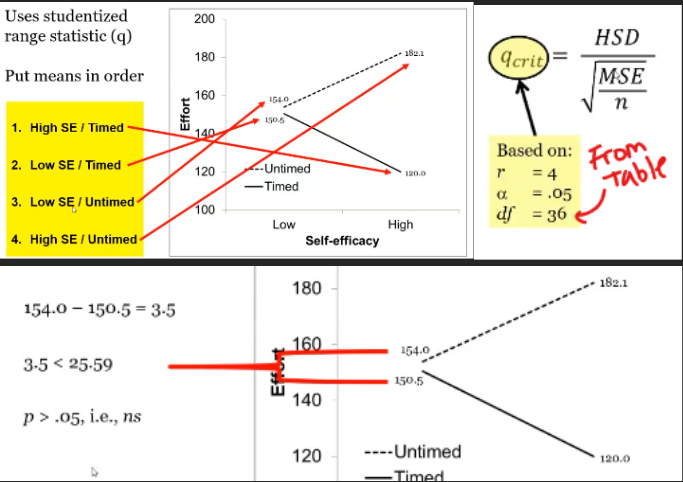
Calculate simple effects using Tukey
Put means in order
Calculate r= (largest position - smallest position) +1
Find q-crit
Compare each difference (is it sig)
ada² and partial ada²
Calculating Effect sizes
Ada² will always be smaller than partial ada²
partial ada² prefered bc it isolates variance for just that factor
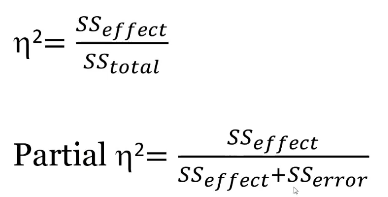
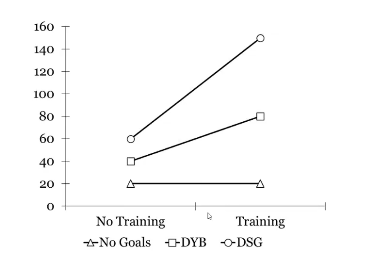
What is this an example of?
(two main effects and an interaction)
effects of training tends to depend on what type of goals you set
Strong effect on top and no effect on bottom
Calculating simple effects
SS = N (mean - mm)²
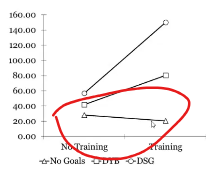
What happens when you have significant fs → don’t know which are significant (which are different from eachother)
You use a t-test as a follow up (with three means)