Energy - Sources, Conversion and Storage
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What are chemical fuels?
Chemical fuel is a combustible substance, containing carbon as main constituent, which on proper burning gives large amount of heat, which can be used economically for domestic and industrial purposes. Example: Wood, charcoal, kerosene, petrol, diesel etc.
General Reaction: CnH2n+2 + O2 → H2O + CO2 + heat
C oxidised to CO2
H oxidised to H2O
sulpher to sulper dioxide
mineral matter forms ash
What is calorific value?
It is defined as the total amount of heat liberated when a unit mass or volume of fuel is burnt completely in air or oxygen.
Gross (High) calorific value (GCV or HCV)
The total amount of heat liberated when a unit quantity of fuel is burnt completely in air and the products of combustion are cooled to room temperature. It is also called as higher calorific value (HCV).
Net (low) Calorific value (NCV or LCV)
It is the amount of liberated when a unit quantity of a fuel is burnt completely in air or oxygen and the products of combustion are allowed to escape.
Why GCV value is higher than NCV?
In case of GCV, on cooling the combustion products, steam gets condensed to water and liberates its latent heat.
The measured GCV includes the latent heat of steam. Therefore, it is always higher than the net calorific value.
Whereas in case of NCV, the products of combustion are let off in to the atmosphere
Two main reactions that occur during combustion are:
Carbon and hydrogen present in the fuel are converted in to carbon dioxide and steam respectively, on combustion
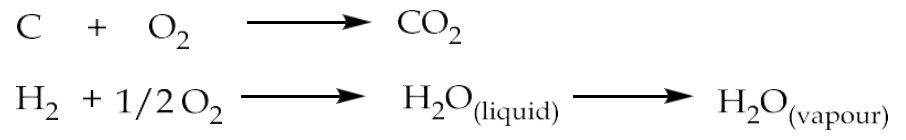
How is GCV different from NCV?
GCV is total heat liberated by fuel including heat of condensation of water and NCV is heat liberated by combustion of fuel excluding heat of condensation of water.
How is GCV and NCV related?
NCV = GCV – heat associated with steam
What is SI unit of calorific value for solids and liquids?
For solids, calorific value is expressed in KJ kg-1 (KiloJoules per kg).
For gaseous fuels it is expressed in J m-3 (Joules / m3).
Specific heat and units
Specific heat of water is the amount of heat energy required to increase the temperature of one kg of water by one degree C.
Units: J/kg/oC.
Latent heat of steam
Latent heat of steam is the amount of heat energy required to convert 1 Kg of liquid to vapor or steam
Units:KJ/kg.
Latent heat of steam(L) = ?
587 cal/g or 2457 KJ/Kg
1 Cal = ? J
4.186
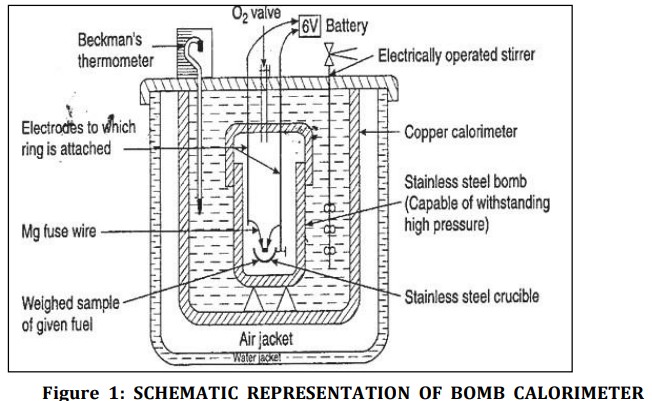
What is bomb calorimeter used for?
The calorific value of solid and non-volatile liquid fuels is determined by bomb calorimeter
What is the Principle of Bomb Calorimeter
→ Known mass of a solid/liquid fuel is burnt in excess oxygen
→ The surrounding water absorbs the heat liberated
→ Heat liberated by the fuel = The heat absorbed by the water
→ By recording the rise in temperature of the water and specific heat of water
We calculate Calorific value
Explain Construction of Bomb Calorimeter
Consists of Stainless-steel vessel with air-tight lid called Bomb
Bomb has inlet valve for providing oxygen atmosphere inside bomb
Placed inside insulated copper calorimeter
Calorimeter has mechanical stirrer for dissipation of heat and thermometer
A known mass of solid fuel is taken in crucible which is placed inside bomb which is placed inside calorimeter
A known mass of water is taken in calorimeter
Bomb is filled with oxygen at pressure of 25-30atm
Temp t1 is noted
Electric current is passed through ignition coil which ignites the fuel
Fuel burns and liberates heat
Stirrer continuously stirs water
Maximum temperature attained t2 is noted
Formula for GCV
W1 = mass of water in the calorimeter (kg)
W2= water equivalent of the calorimeter (kg)
S = specific heat of water (J kg-1 oC-1 )
t2-t1 = rise in temperature (oC )
m = mass of the fuel (kg)
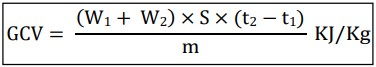
Formula for NCV

Water equivalent
The amount of water that would absorb the same amount of heat as the calorimeter per degree temperature increase.