Introduction to MSK
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
True or False: One of the components of History taking includes the patient’s “Handedness”
True
In History Taking, “Patterns of Pain” falls under the ______. (4 words)
History of present illness

Physical & Social History include:
1. Home environment
2.__________ members
Work environment
Hobbies
Patient’s __________.
Family, preoccupations, goal
_____ test is used to assess __________ injuries in the knee.
Apley, meniscal
_____ is also known as "Looking" or Inspection phase
Ocular Inspection

The purpose of inspection in physical examination is to gain information on visible _____, __________, and functional deficits.
defects, malaligments

Guide questions during Observation (Type 1)
1

Guide questions during Observation (Type 1)
1
Used to confirm or refute the suspected diagnosis, based on the history and observation of the patient
Examination
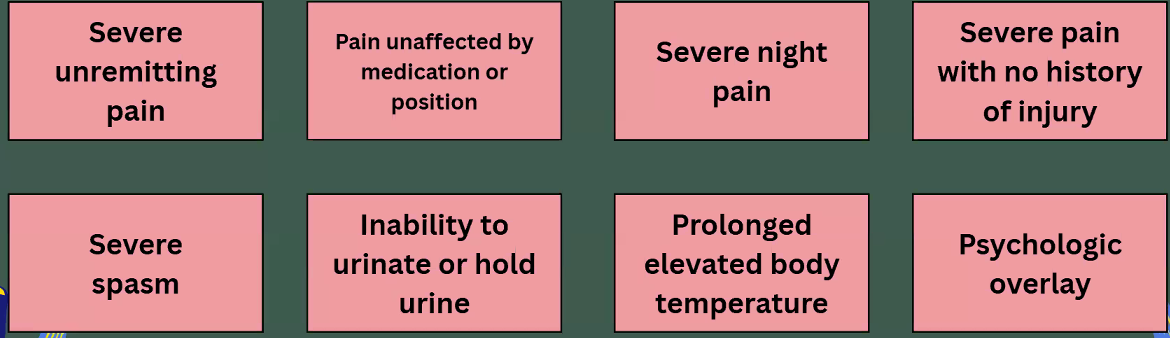
Red Flags for Medical Consultation:
Severe unremitting ___
Severe pain with no _____ of injury
Severe _____
Inability to hold ____
Prolonged elevated ___
_______ overlay
Pain, history, spasm, urine, temp, psychologic
Which side is tested first?…
Normal
When testing movement: _____ › Passive › ______ _______
Active, resisted isometric
True or False: Painful movements are usually done first
False
Resisted isometric movements are done with the joint in __________ position.
neutral
Passive or ligamentous tests should apply stress _____, gradually increasing but not beyond the point of __________.
gently, pain
When testing myotomes, hold each contraction for at least __________ seconds
5
These examinations are done to ensure that ALL possible sources of pathology are assessed
Screening examinations
These examinations gives us a quick look or scan a part of the body from the spine to the extremities
Screening examinations
Performed to rule out (r/o)the possibility of refferal
of symptoms
Screening examinations
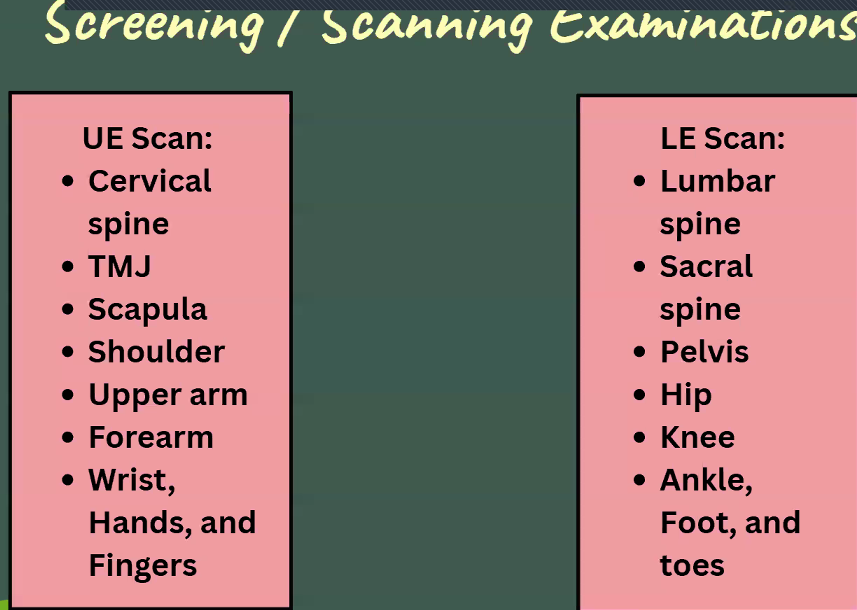
Screening Examination Guide: (Type 1)
1
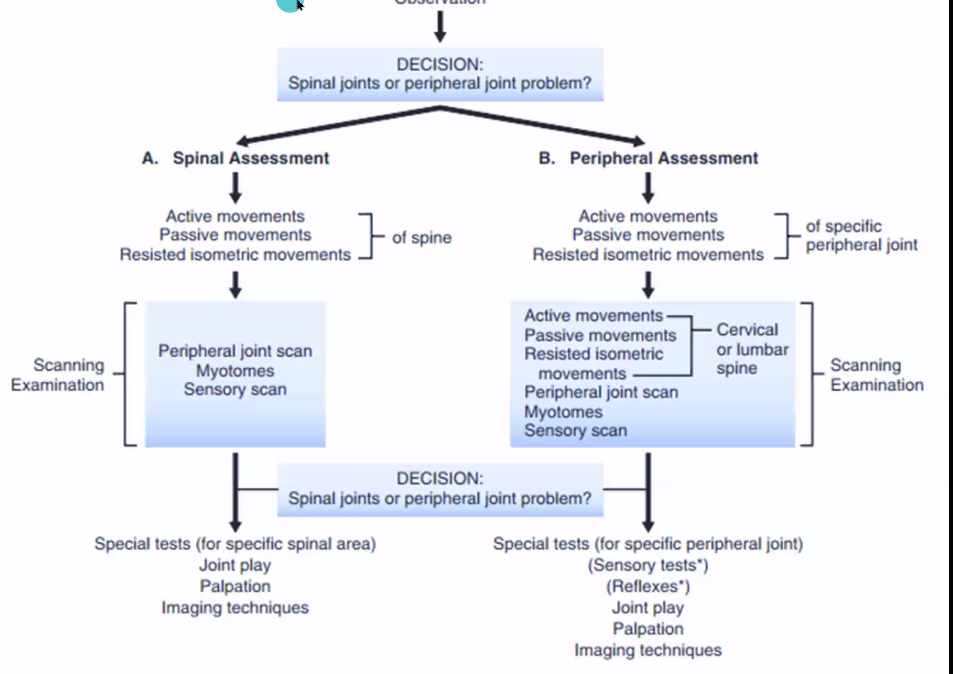
Scanning Examination Guide (Type 1)
1


_____ is also known as active psychological movements…
Active movements
True or False: You can perform active movements when you have a fracture, or newly repaired tissue…
False
Standard movements follow the _______ _____.
Cardinal planes
_______ may be carefully applied at the end of ____. (Type of ROM)
Overpressure, AROM

Guide Questions for Active Movement (Type 1)
1

Guide Questions for Active Movement (Type 1)
1

Guide Questions for Passive Movement (Type 1)
1
________ ______movement assesses static,voluntary muscle contraction, determines if the contractile tissue has pathology, and assigns muscle strength grades from 0–5.
Resisted isometric
When assessing contraction these 2 Qualities should be noted for pain:
1. _______ 2. ______
Intensity, quality
_____ issues indicate when the Amount of strength is usually determined by the amount of ____ the patient feels on contraction
Muscle, Pain
____ issues when contractions are not usually as strong as on the good side:
Pain is in or around the tendon
Partial avulsion fractures
Tendon

Contractile vs Nervous Tissue Lesions Guide (Type 1)
1