Lecture 6- Adaptive Immune Responses
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What incites an immune response, especially antibody production?
anitgen or agent
What is immune surveillance?
cells are station or move through tissues to seek out target antigens
What are the two broad categories of immune response types?
cell-mediated, humoral
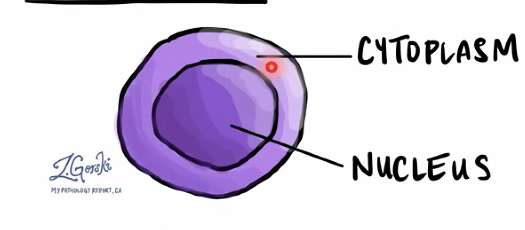
What is shown?
Lymphocyte (T lymphocytes)
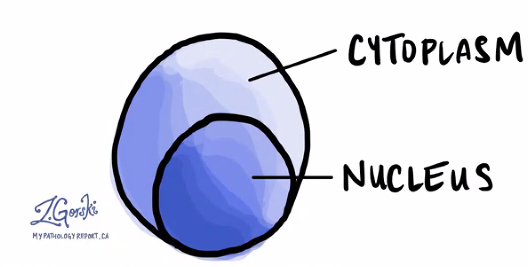
What is shown?
Plasma cell (B lymphocytes)
What is the role of lymphocytes?
respond to antigenic stimulation to kills cells or activate other immune cells
What happens as the lymphocytes start making antibodies and are activated?
they become plasma cells (B lymphocytes)
What do the regulatory T lymphocytes help us build?
tolerance to routine agents that maintain health
What T cells target and remove infected or foreign cells (like a viral infection)?
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Which cells help activate other immune cells, like B cells and macrophages?
Helper T cells
How do lymphocytes recognize self or non-self?
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)
The Major Histocompatibility Complex helps immune cells recognize invaders as ______.
non-self (Foreign)
What is the term for when cells that recognize self antigens are removed by apoptosis?
Clonal deletion
What does clonal deletion prevent?
response against own body
What are proteins secreted by plasma cells that target the antigen?
Antibodies or immunoglobulin
What part of the antigen does the antibody attach to?
the binding site on the Y of arms
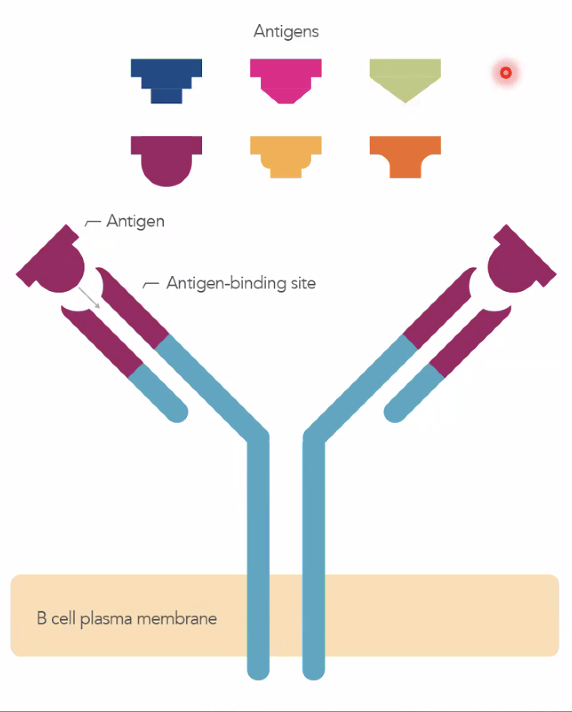
What is shown?
The antibody and antigen binding site
How can anitbodies flag cells for destruction?
sticking to target antigen on surface receptors
What does coating over agents/organisms to enhance phagocytosis by macrophages do?
Opsonization-another way to flag cells for destruction
What is clonal expansion?
copies of reactive cells made to respond uniquely to that pathogen in large numbers
How do lymphocytes adapt to any potential target?
produce an almost infinite number of unqiue sequences for antibody or T cell receptor
What is reassortment?
rearrangement of sequences in cell development to lead to more specific binding to target antigen
What are memory T cells?
some will stay around and adapt if antigen comes around again
T/F: Adaptive Immune responses are very speedy.
False
Is the primary or secondary immune response faster?
secondary
What can happen if the anitbody and antigen malfunction?
anemia (own blood cells attacked), amyloidosis, renal deposition→ kidney failure, blistering, demyelination of nerves
What is amyloid?
Protein is in places it should not be in, caused kidney to sort through
What is renal filtration antibody deposition?
antibody-antigen complexes get trapped in filtration system of kidney
What does demyelination cause?
slowed neuron function as myelin sheath breaks down