Filarial Worms
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
parts of the lymphatic system
lymph nodes
spleen
thymus
tonsils
bone marrow
what type of worm is the filarial worm
nematodes (round worm)
where do filarial worms reside in
lymphatic (immune system)
subcutaneous tissues
how are filarial worms transmitted
mosquitos
what are the mosquitos normally infected with
wolbachia spp
what do filarial worms cause
lymphatic filariasis
river blindeness
wuchereria bancrofti
lymphatic filariasis
life cycle of wuchereria bancrofti
mosquito takes blood meal and L3 larvae enter skin
adults in lymphatics
adults produce sheathed microfilariae that are in the blood (diagnostic)
if not picked up within a month by mosquito die
mosquito takes blood meal ingests microfilariae
microfilariae shed sheaths and go in midgut
microfilariae go to midgut then to migrate to thoracic muscles
L1 in thoarastic
L2 molt/ L3 from thorax to provoscus
L3 from blood skin

anopheles
culex
aedes
where are anophoeles found
rural
where are culex found
urban and semi urban
where are aedes found
pacific islands
what are 50% of all lymphatic filariasis infection
culex quinquefasciatus
what are culex quinquefasciatus
highly anthropophilic
rests and feeeds indoors and outdoors
stagnant and poluted water as breeding
in high density and urban areas
inflammatory Phase
acute filarial lymphangitis
due to death of adult worms
mild symptoms of inflammatory phase
malaise and chills
painful swollen local lymph nodes
fever
complications of inflammatory phase
adenolymphangitis (inflammation of lymph nodes and vessels)
Asymptomatic phase
high microfilaremia
endemic normals
no microfilariae circulating, no transmission exposed to pathogen continuously
what do casual visitors sufer from
acute lymphatic inflammation and no microfilaremia
child born with microfilaremic mother
likely to have no symptom but are microfilaremic in blood
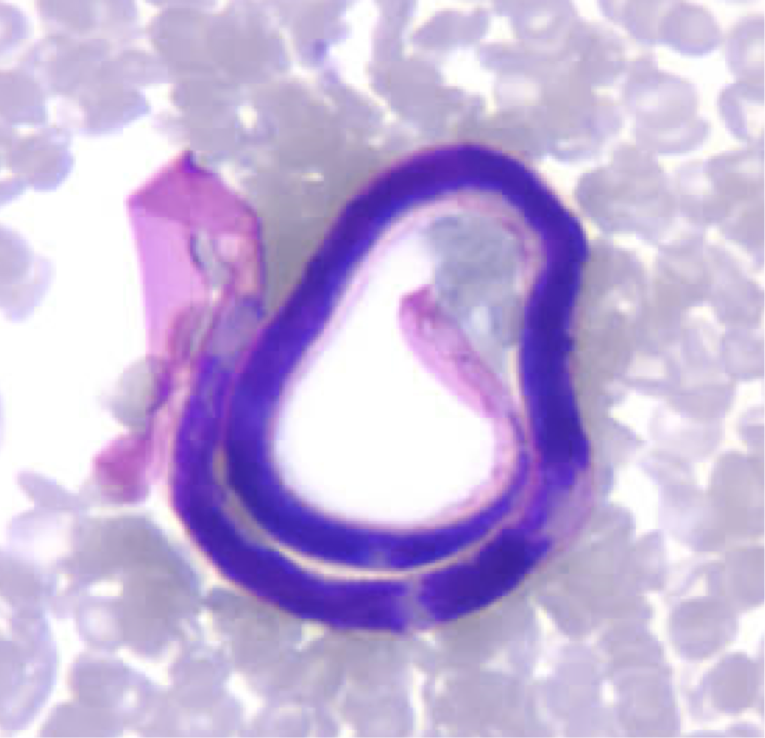
microfilaments in blood
different stages of lymphatic vessel
normal
slight impairment of lymphatic drainage in acute infection
filarial parasite
impaired lymphatic drainage and vessel remodeling during chronic infection/ elephantiasis
cause damage of valves
wolbachia
filarial parasite
pathogenesis
most infections acquired in child hood but then symptoms occur in adults
Multiple stages of filarial worms
asymptomatic
inflammatory
obstructive
clinical manifestations of filarial worms
lympho-edema of the limbs
genital disease
acute attacks
stages of pathogenesis of elephantiasis
swelling is soft, pits on pressure
protein in fluid hardens- no pit on pressure
cant fight infection and prone to bacterial and fungal
accumulated fluid also causes tissue to expand and bulge. elephantiasis
definitive host of filarial worms
humans
intermediate host of filarial worms
mosquitos- aedes, anopheles, culex
reservoir host
none
mode of transmission of filarial worms
mosquito bite
blood transfussion —> microfilaments in blood
risk factors of getting filarial worms
living in urban or semi-urban areas, outdoor activities
Microfilariae periodicity
there are more microfilarie in blood at different times of day. higher during dawn
hawking’s hypothesis
parasites modify behavior to increase transmission
increase amount of microfilarie when vector’s eating habits
change in oxygen tension in lungs worms could tell night from day
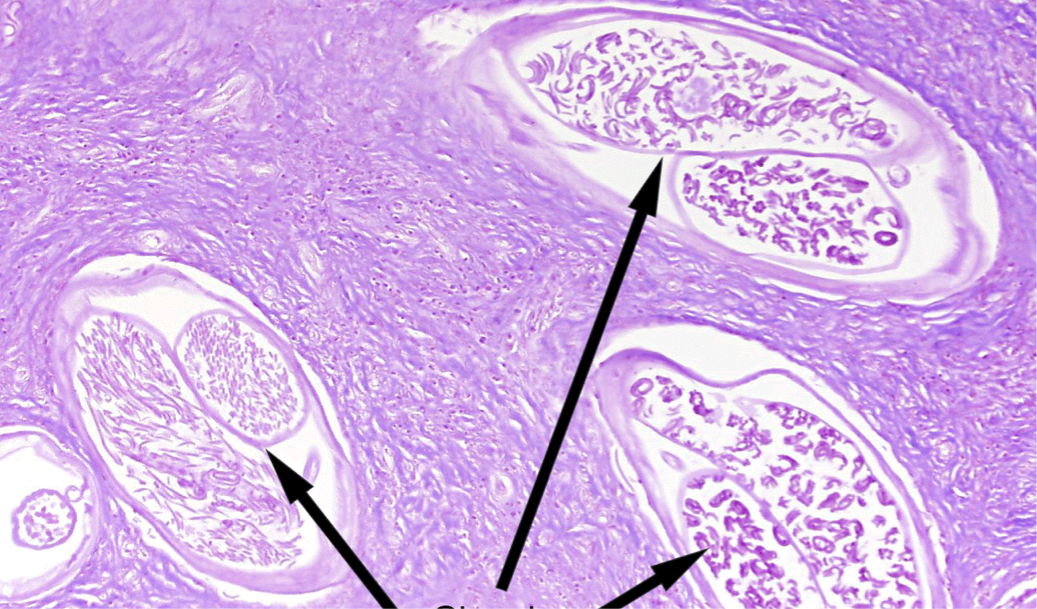
uterus of worms
L3
migrate to lymph system and are there 9-10 days before molt
L4
in lymph system molt to adult
adult filarial worms
lymphatic vessels
microfilariae
lymph and blood
Acute adenolymphangitis (ADL)
lymphatic vessel damage
bacterial infections
secondary infections cause acute attacks
local pain
swelling
fever and chills
obstructive phase
repeated ADL episode
damage to lymphatic vessels
usually lower limbs
arms, breast, genitalia
elephantiasis
who is more prone to the obstructive phase
women
Hydrocele
due to accumulation of fluid in the cavity of tunica vaginalis
chyluria
milky urin- excess fat in urine
blocked lymph leaks into kidney or bladder
malnutrition and viatmin deficiency
stigmatization
affects poor
social edclusion
discrimination
misconceptions
sad and hopeless, suicidal
treatment of filarial worms
Mass drug administration
interrupts transmission
given to population at risk
5 years
treatment via morbidity
Morbibity management and disability prevention
treats ADL
management of lymphoedema
self care and exercise
global programme to eliminate lymphatic filariasis
chemo
control morbidity
vector control
what does chemo do for filarial worms
interrupt transmission
what does control morbidity do for filarial worms
treat ADL
surgery for hyderocele
educate on how to manage
how to control vector
insecticide-treated nets
Mass drug administration give what for filarial worms
diethylcarbamazine
ivermectin
what is given to kill microfilariae
ivermectin
who eliminated lymphatic filariasis
china and korea
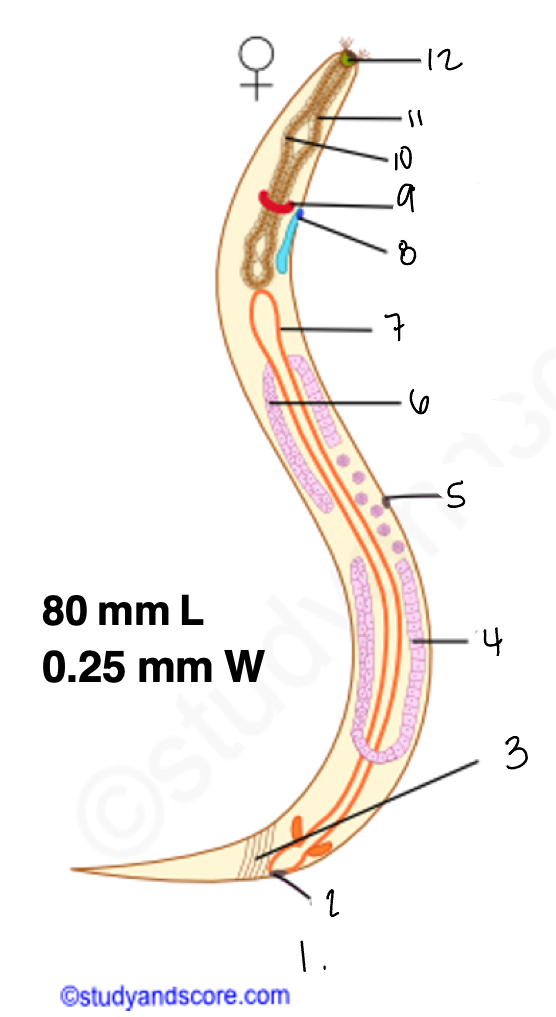
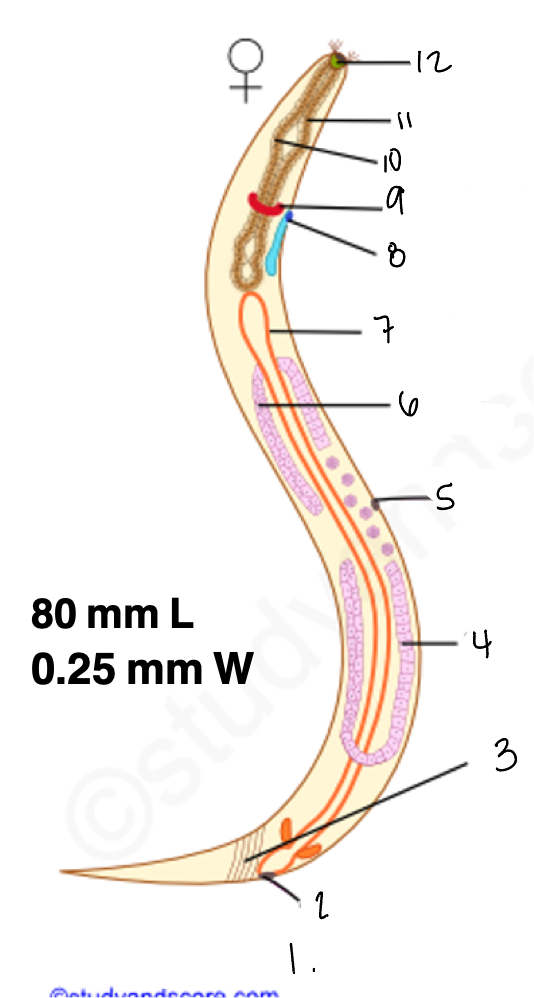
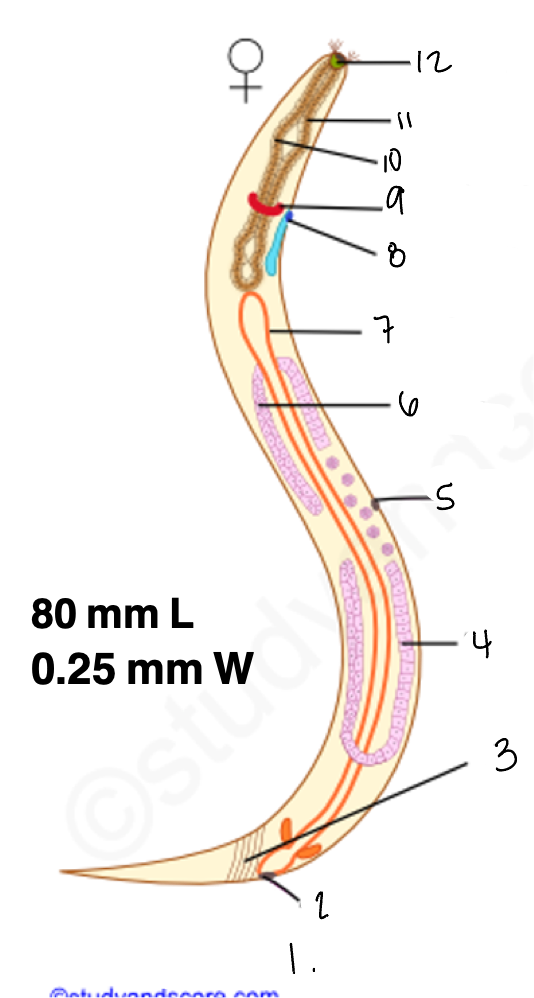
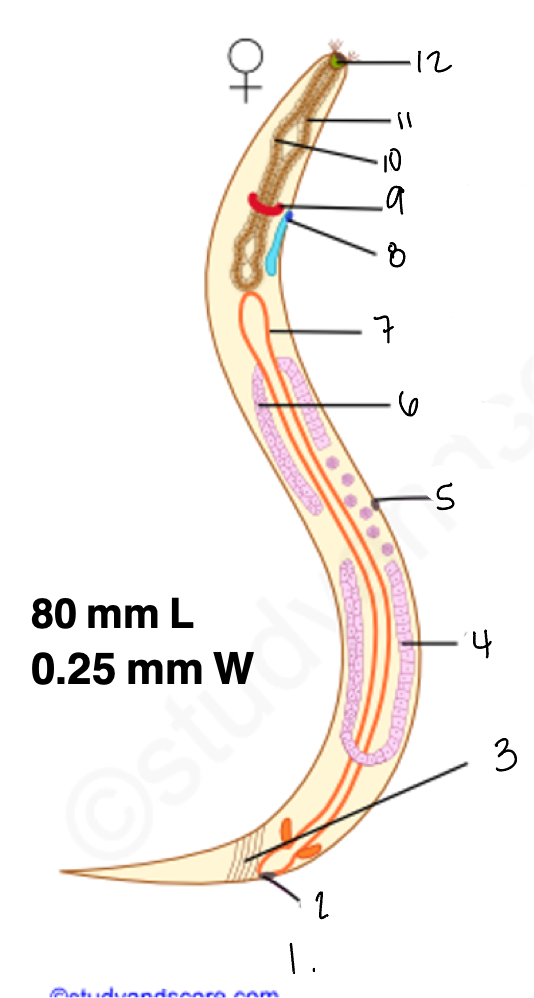
1.
wucereria adult female
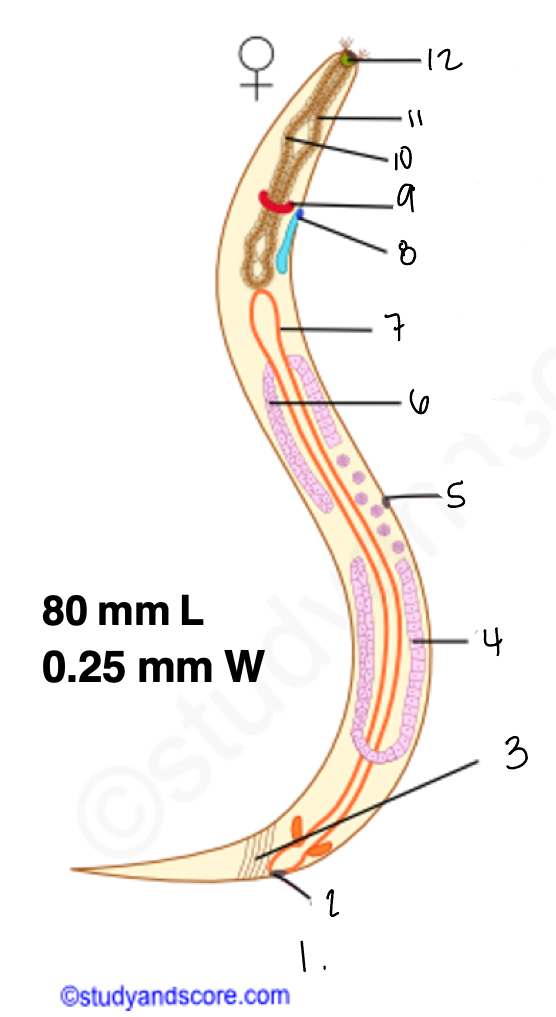
3.
anal musculature
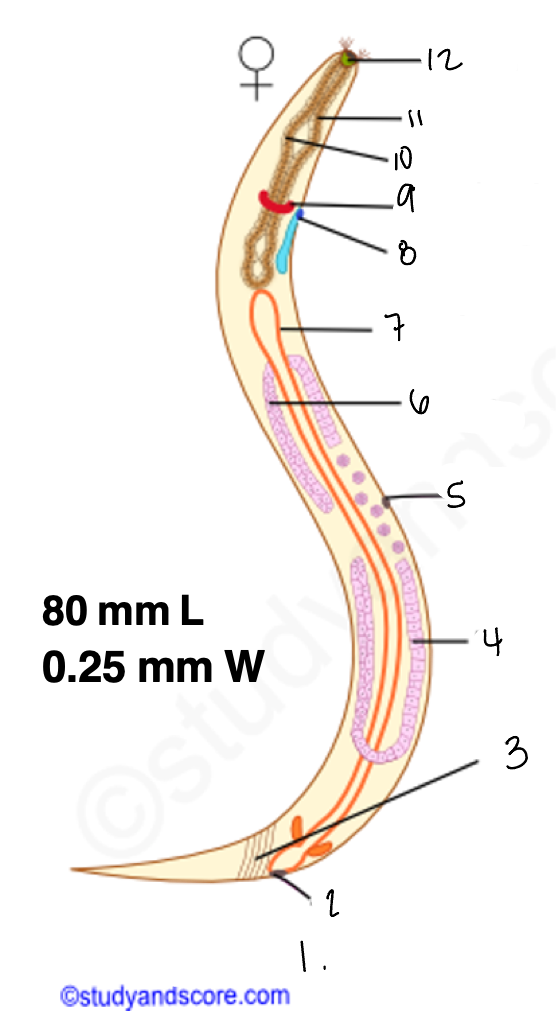
uterus
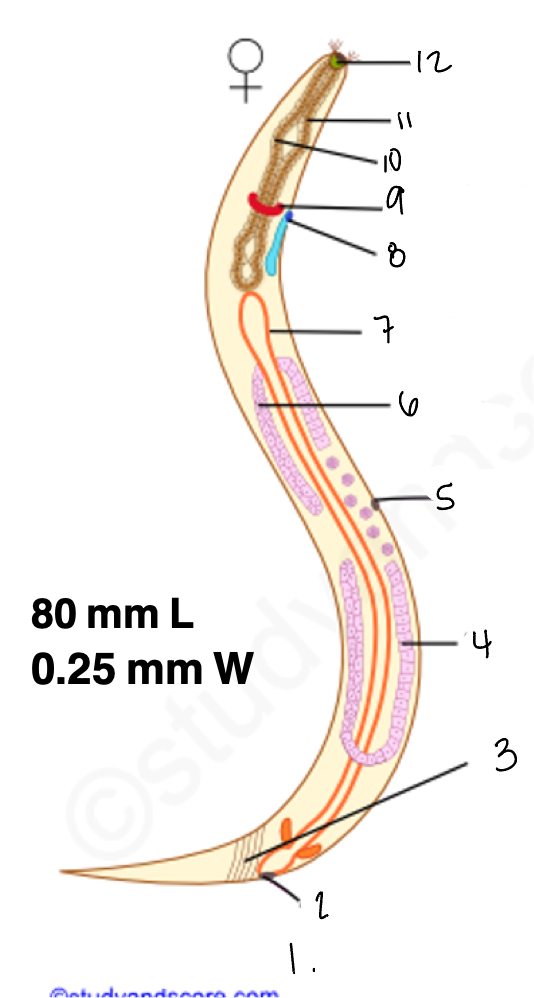
vulva
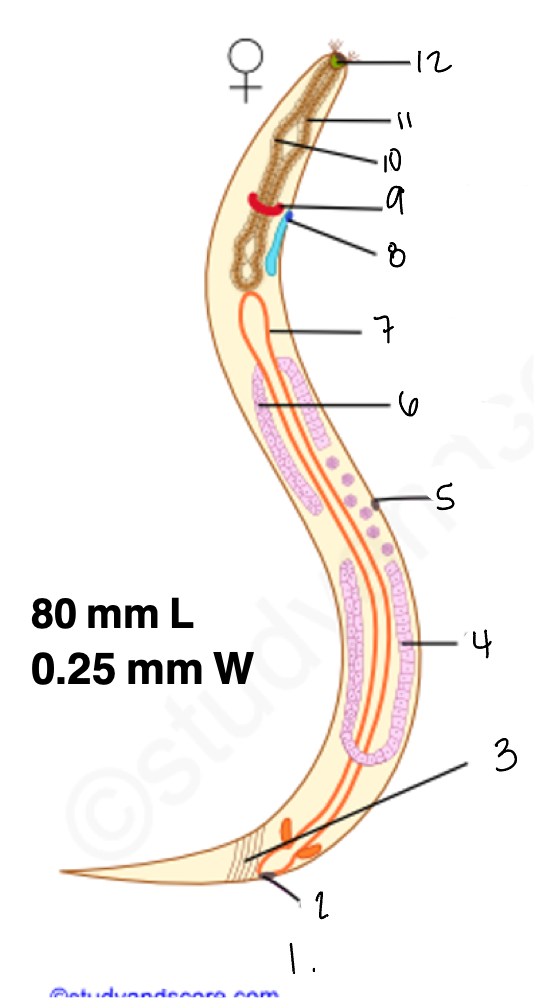
ovary
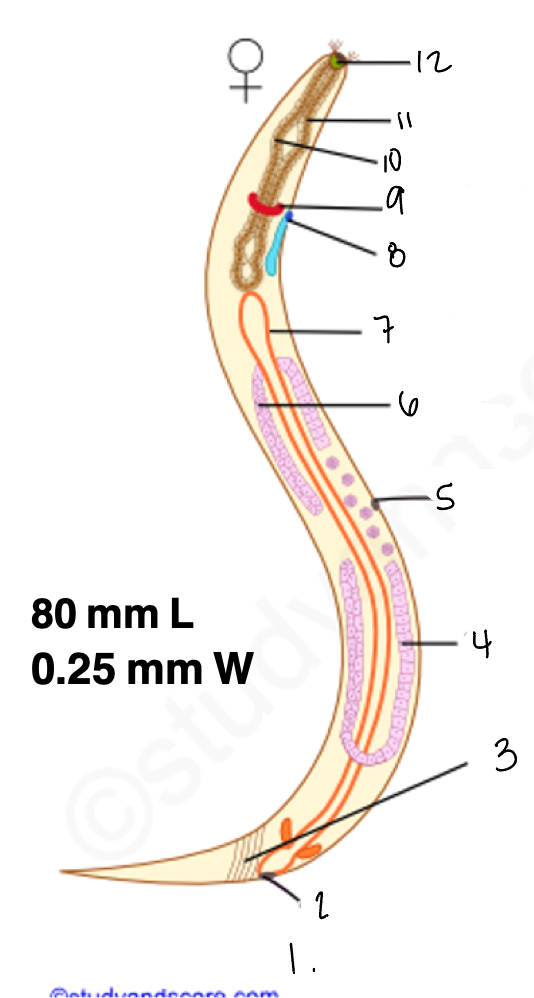
intestine
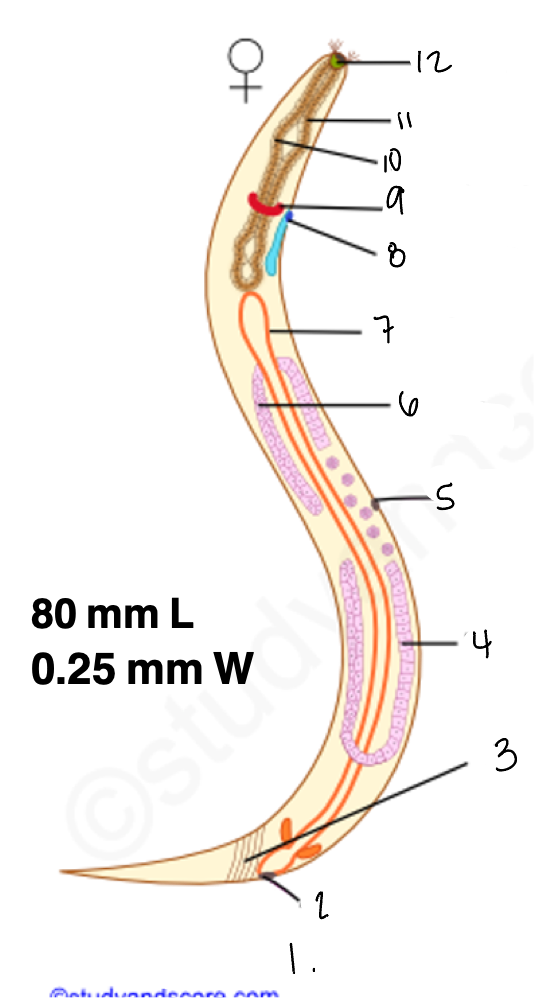
8
gonopore
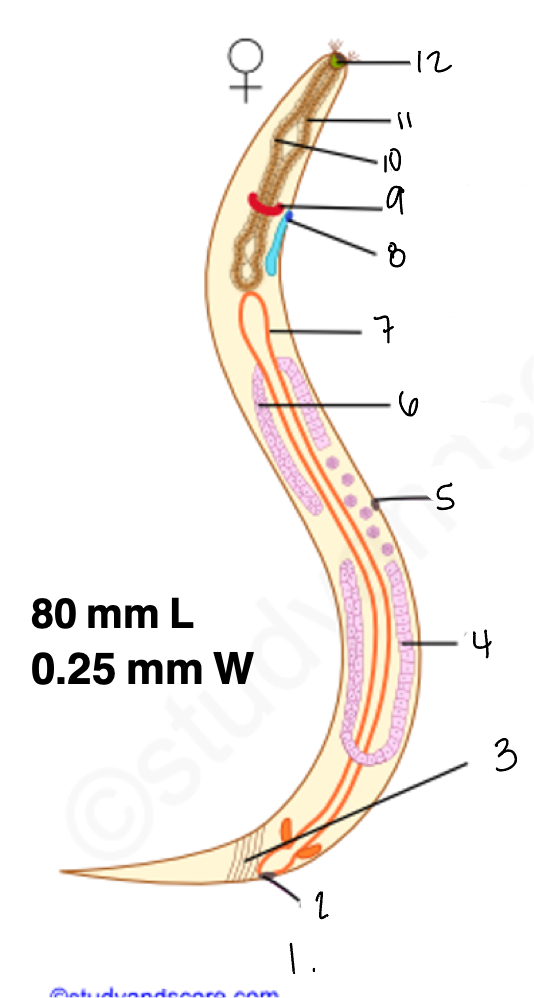
9.
nerve ring
10
oesophagus
pharynx
mouth
16.
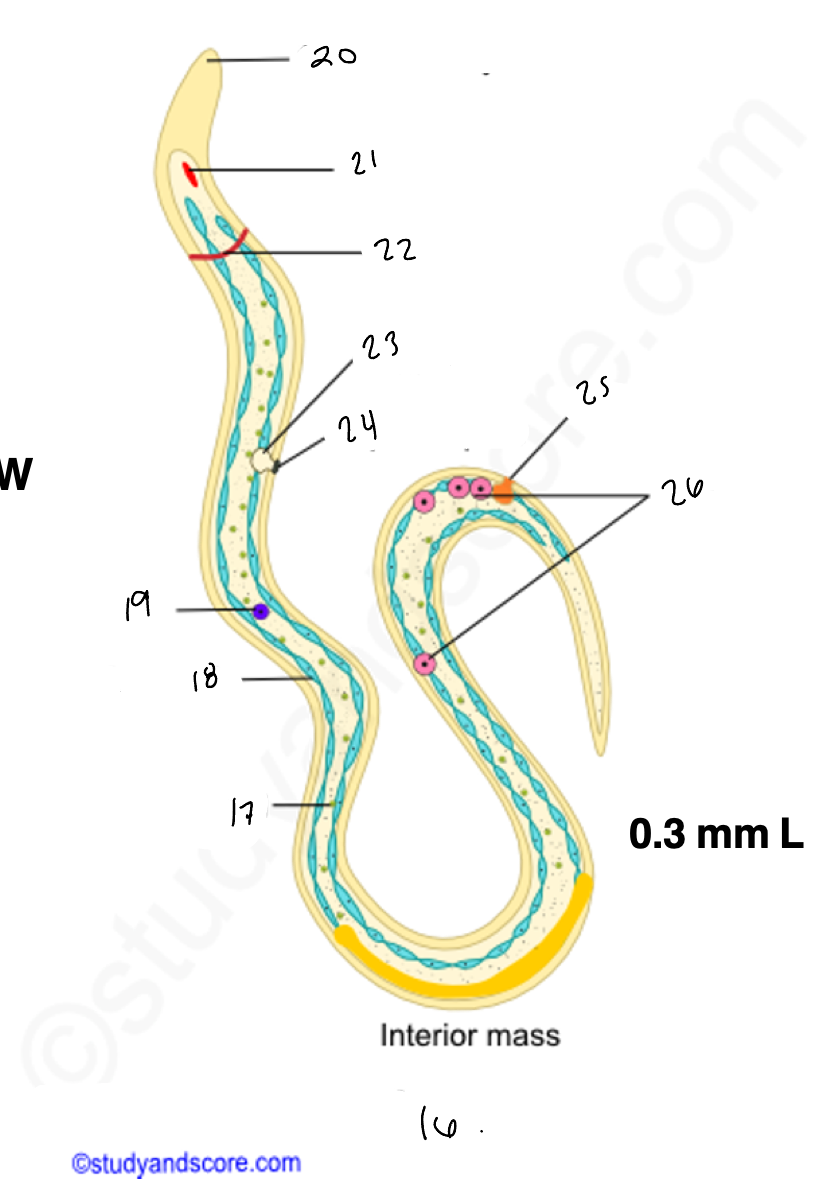
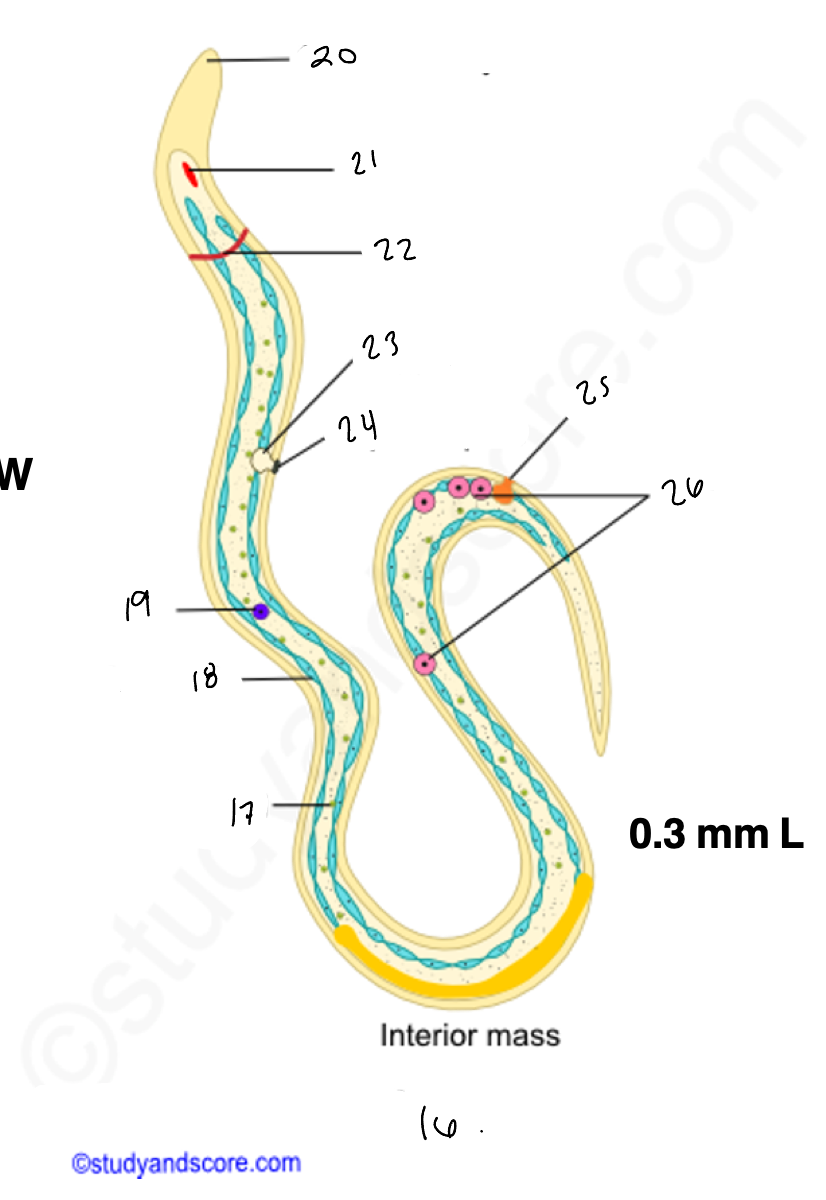
wuchereria microfilaria
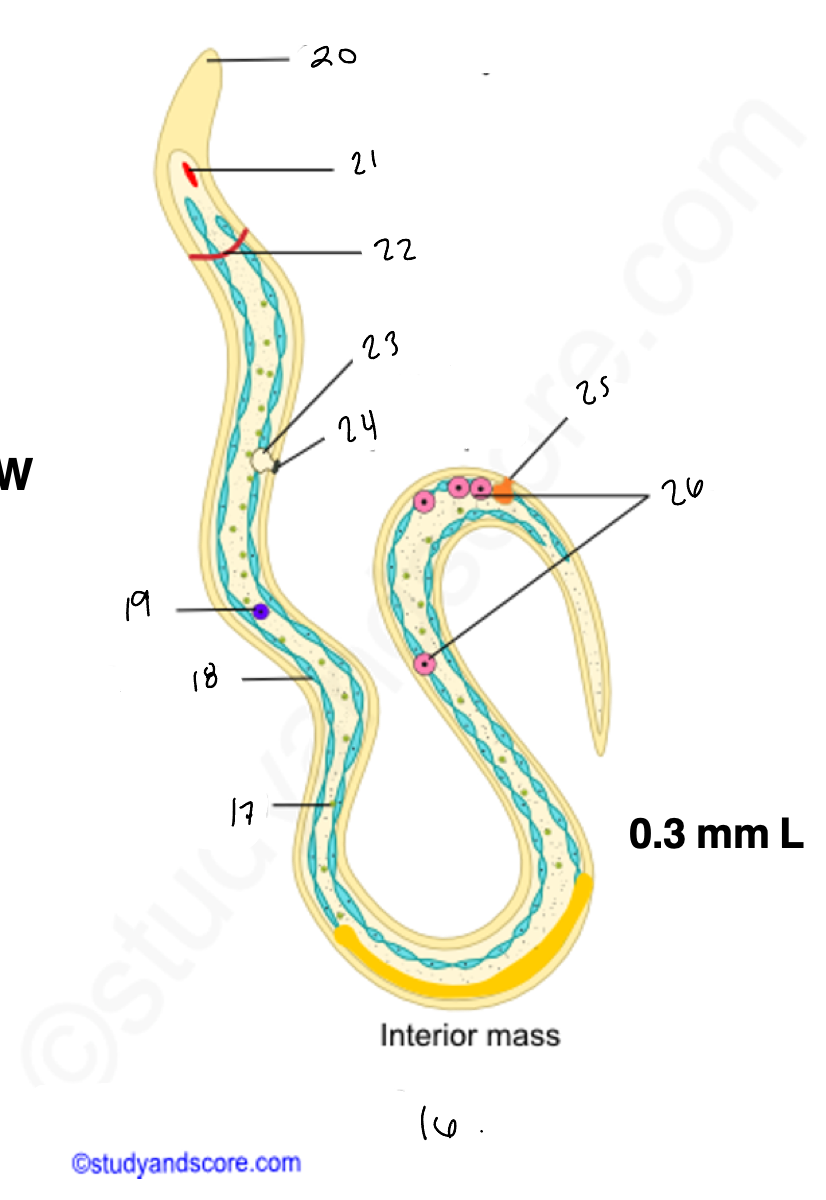
17.
somatic cell
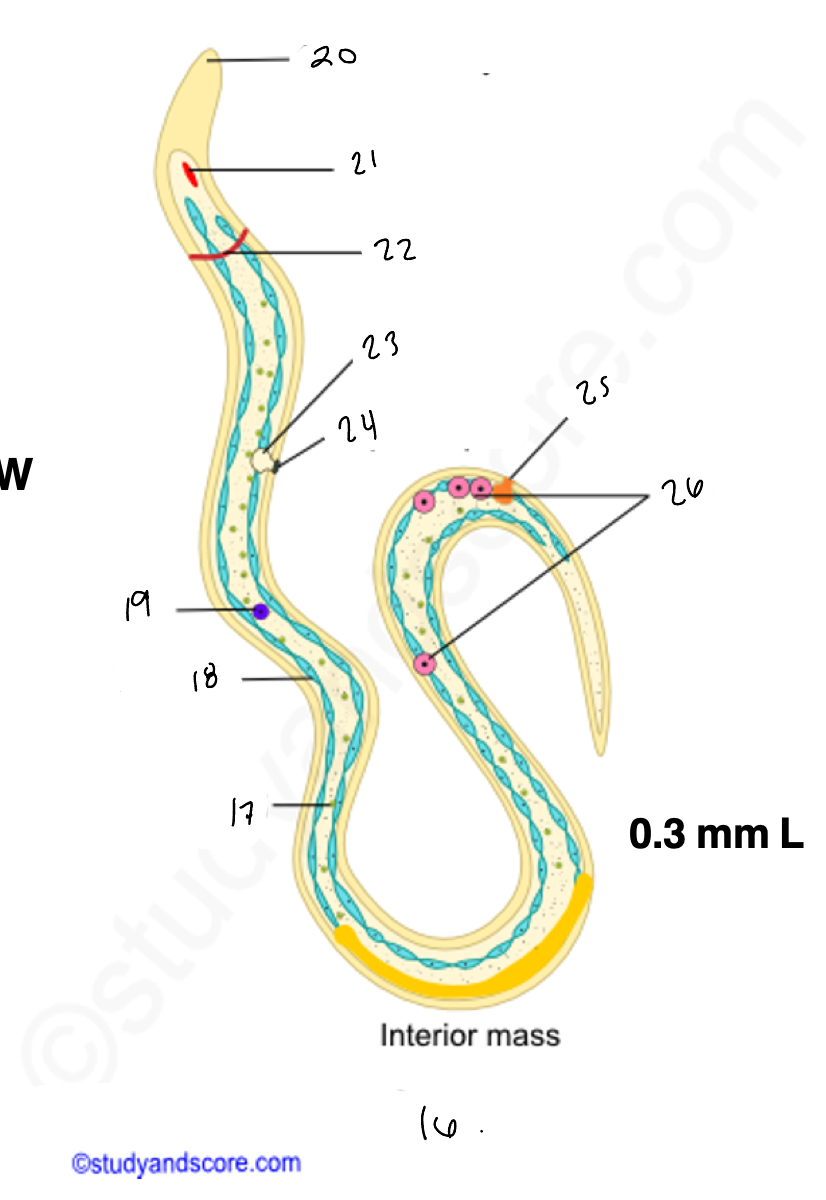
18
epidermis
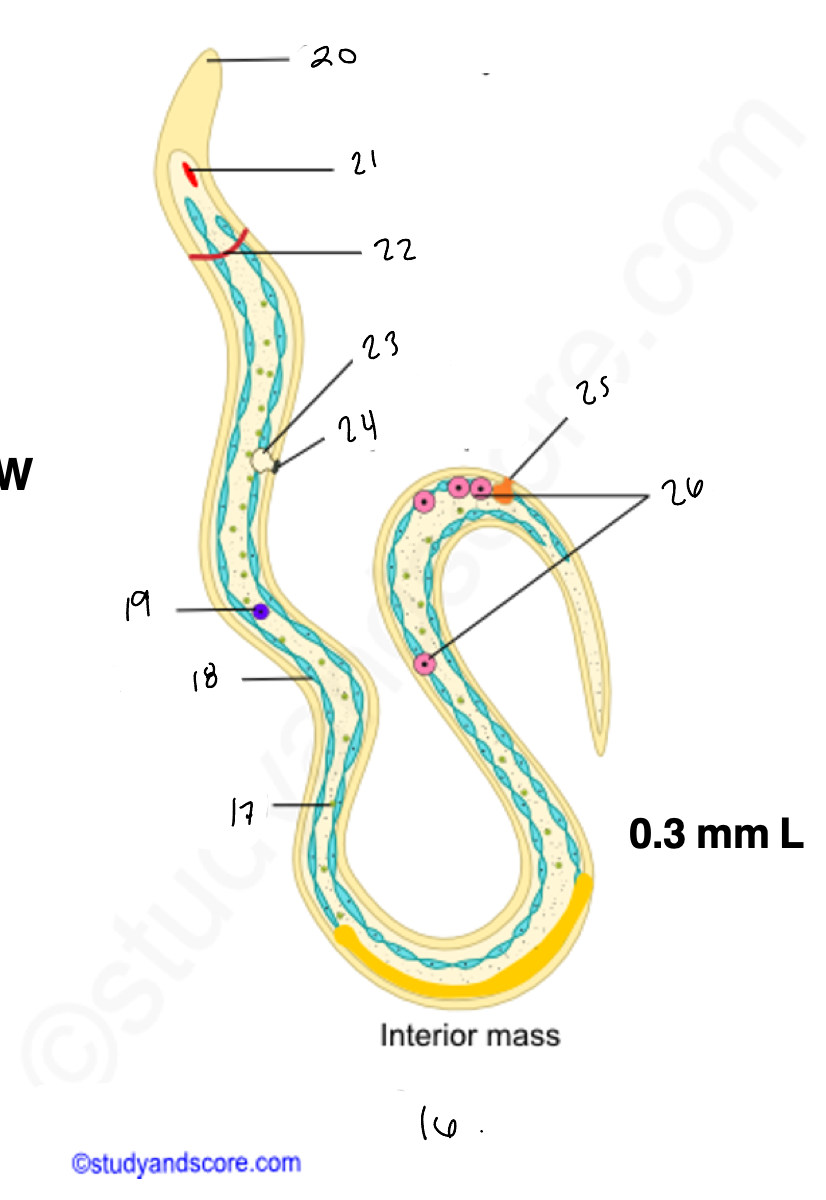
renette cells
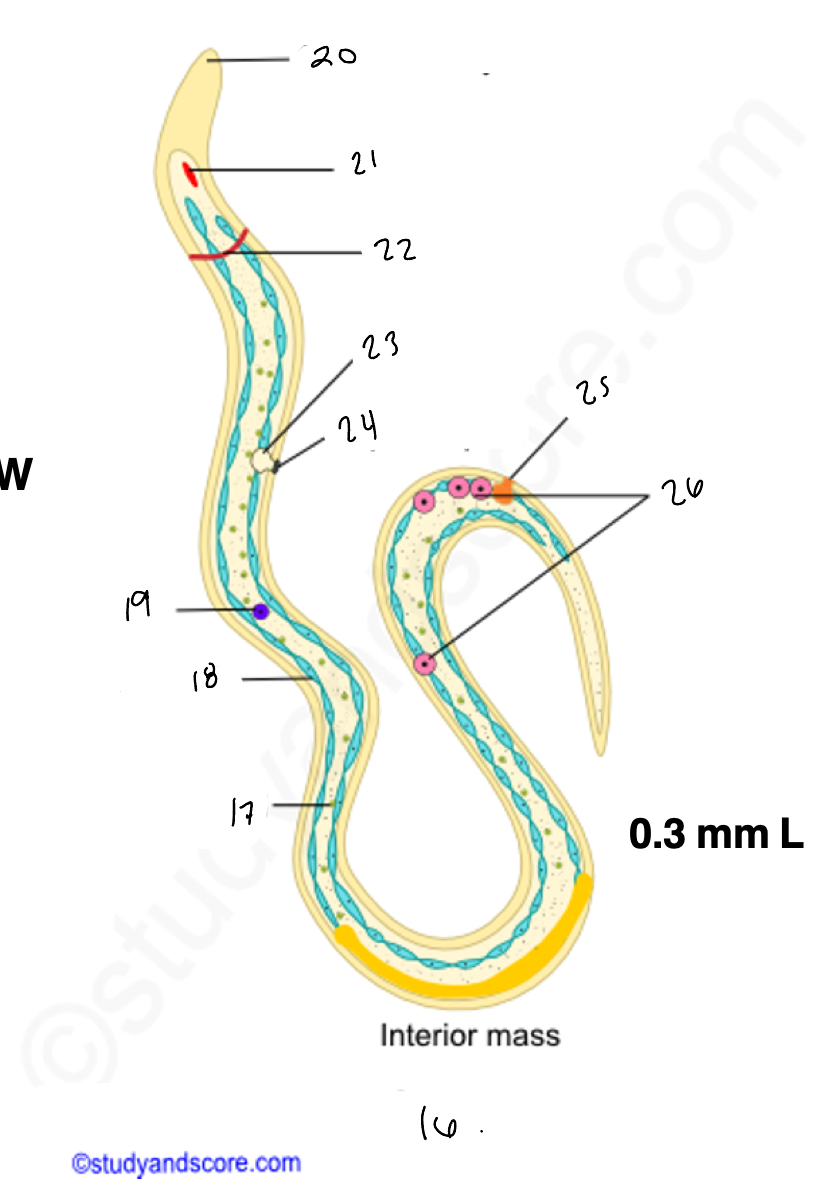
20
cuticular body sheath
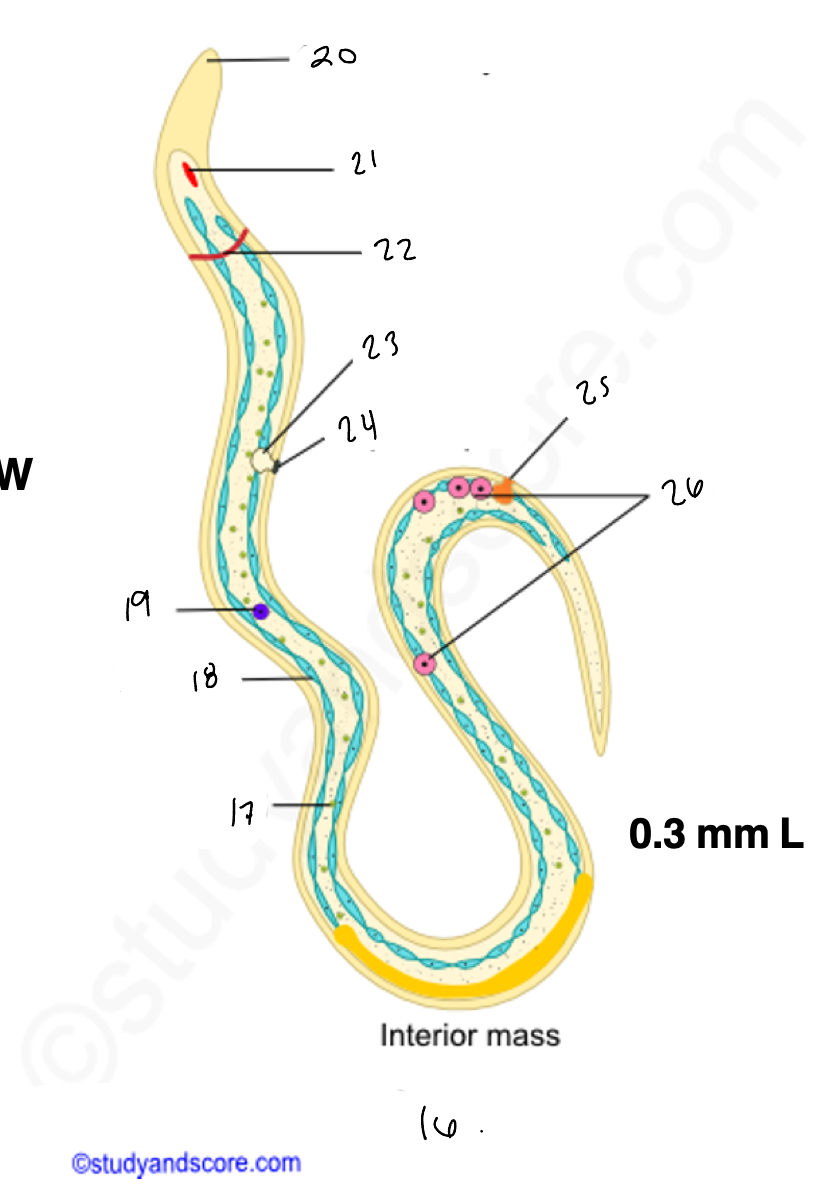
21.
oral style
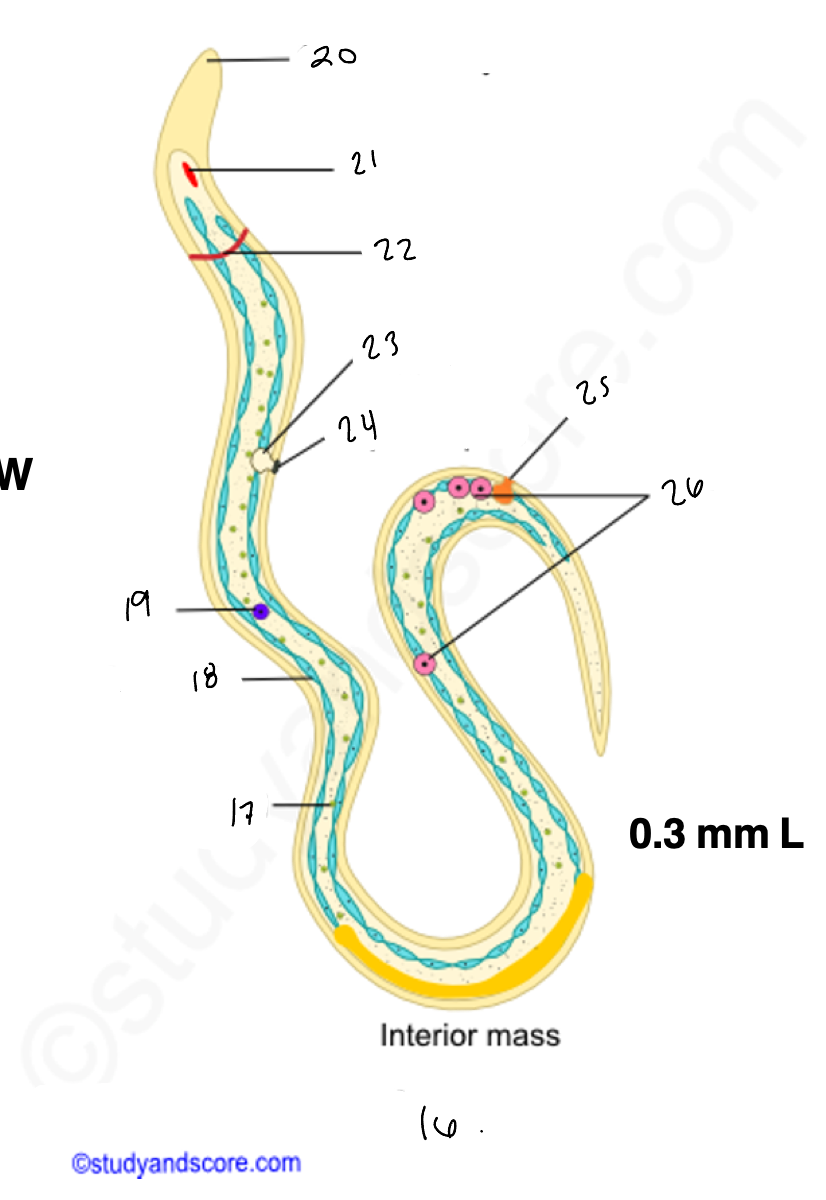
nerve ring
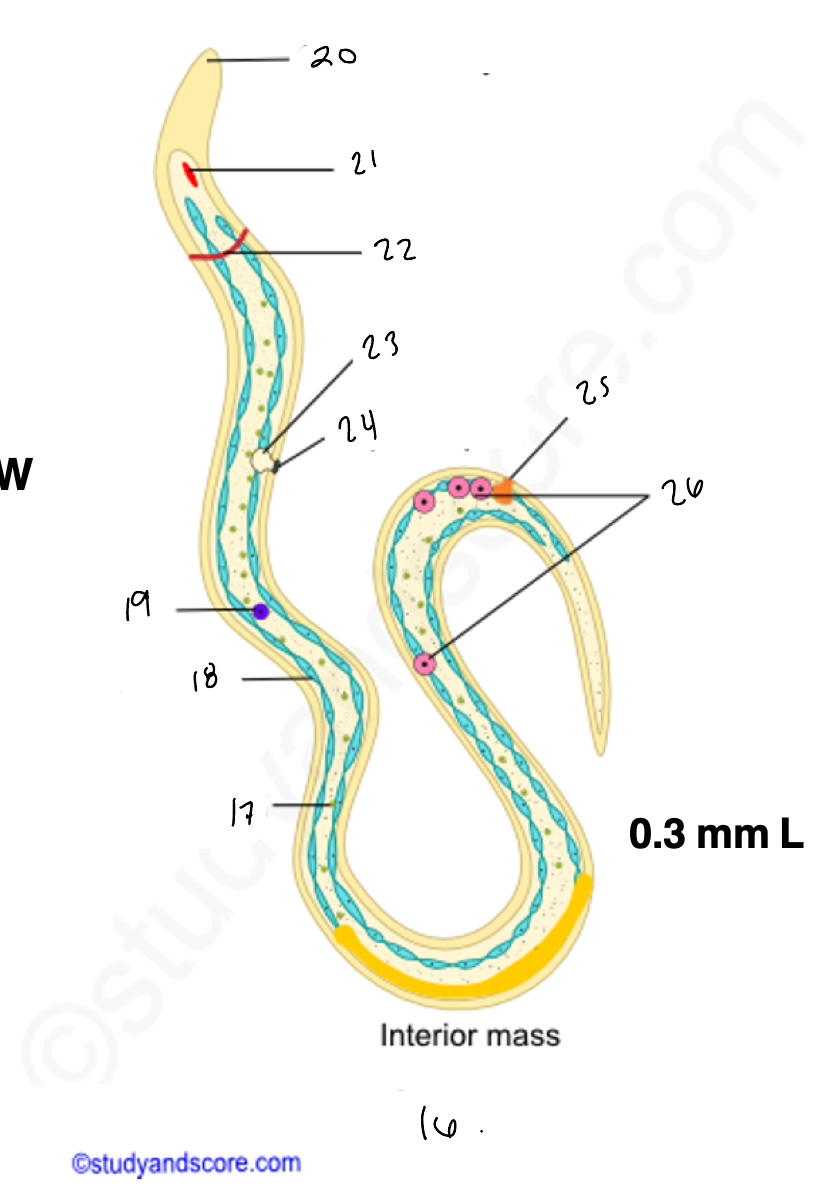
bladder
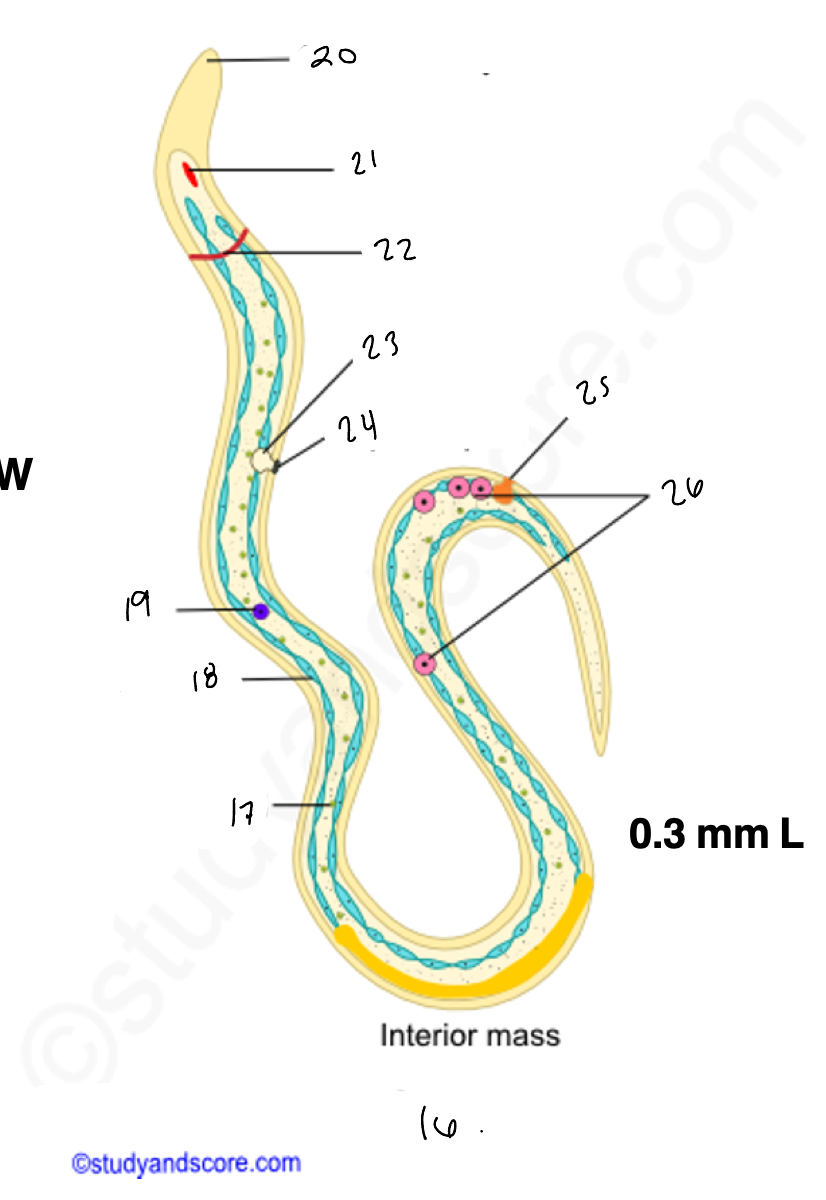
24
nephridiopore
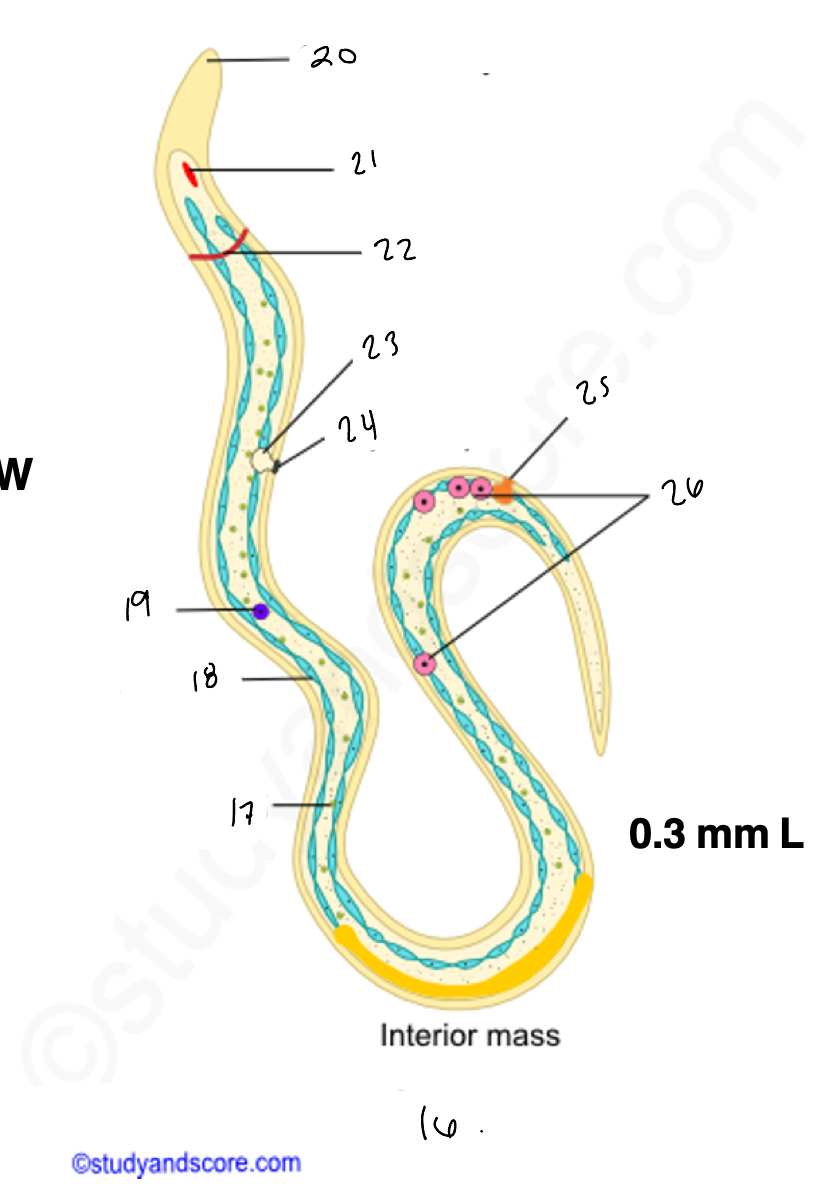
anus
4 large cells
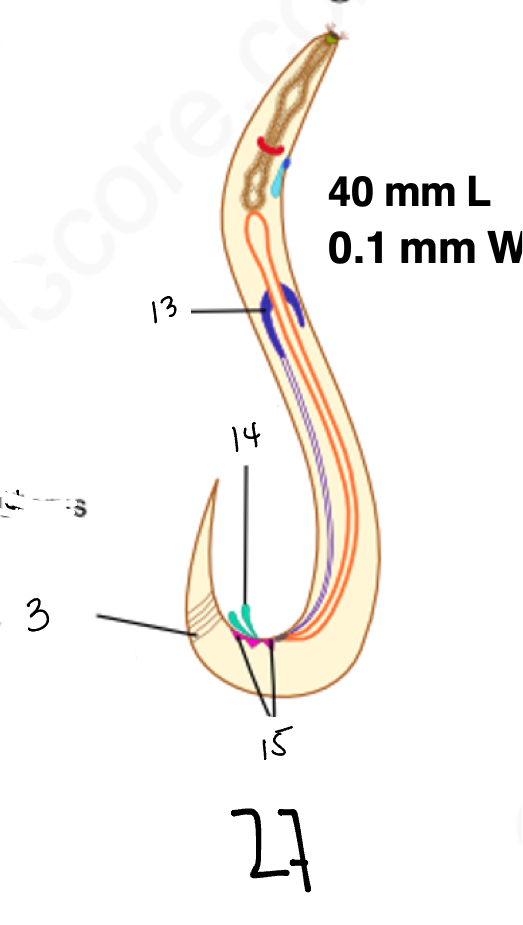
testes
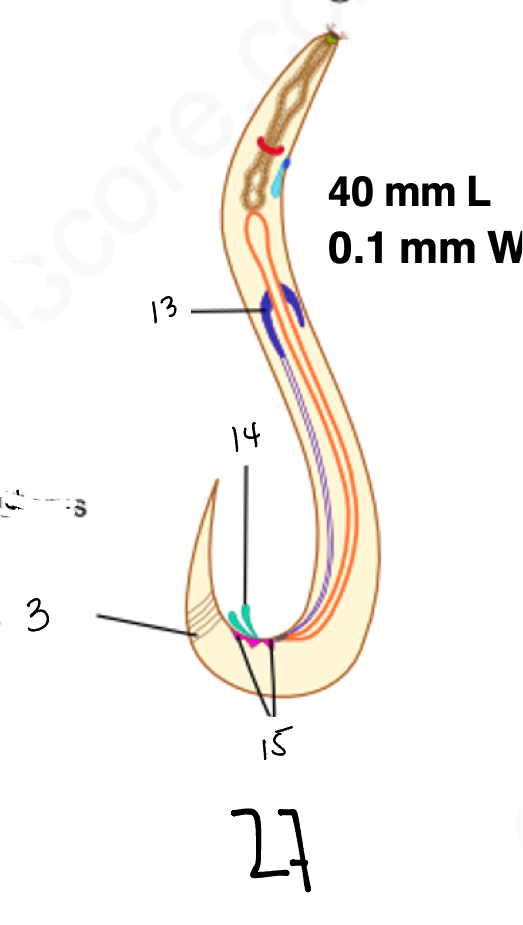
14
copulatory spicules
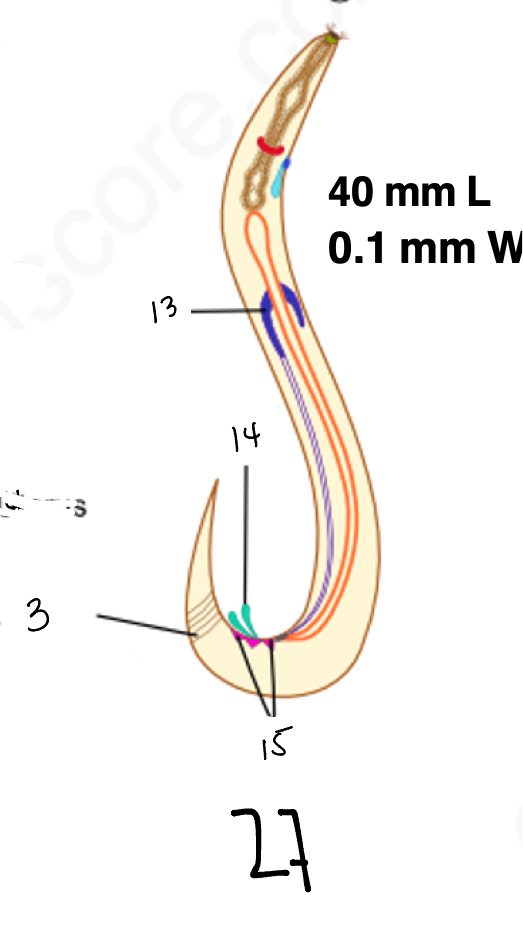
15
papillae
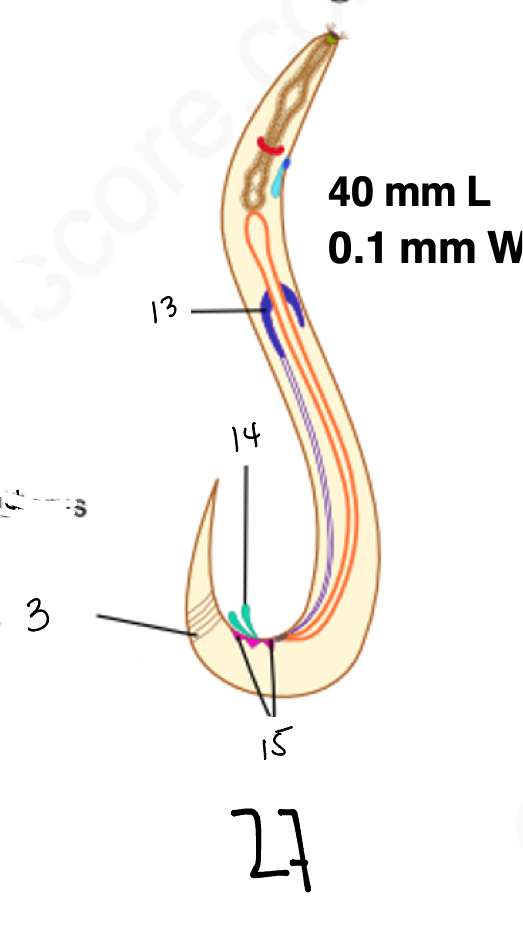
27
wucheria male