CONSTRUCTION: Masonry Walls
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Masonry wall
Consists of modular building blocks bonded together with mortar to form walls that are durable, fire-resistant, and structurally efficient in compression.
Unreinforced masonry walls
Also known as plain masonry walls. These incorporate horizontal joint reinforcement and metal wall ties to bond wythes of solid or cavity walls.
Reinforced masonry walls
These walls utilize steel reinforcing bars embedded in grout-filled joints and cavities to aid the masonry in resisting stresses.
Abang
Vernacular term for dowels.
Brick
Structural units of clay or shale are formed while plastic and subsequently fired.
3-3/4" x 2-1/4" x 8"
Standard size of brick
Building brick
Brick type used for all purposes including facing
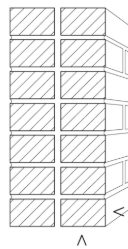
Facing brick
Specially processed to give certain specific surface characteristics. This brick is used for exposed masonry surfaces.
Glazed brick
These have a smooth outer surface with a dull satin or high gloss finish. These kinds of bricks are load-bearing, fire-resistant,t and impervious. Formed with vertical hollow cores through the body or scoring on the back.

Fire brick
Also known as refractory brick, it is used to line furnaces, fireplaces, and chimneys. It was originally made from a mixture of flint and plastic clay.

Bed
The horizontal surfaces on which the stones or bricks of walls lie in the courses.
Wythe
A vertical layer of masonry that is one masonry unit thick.

Course
A continuous horizontal layer of masonry units.
Bond
The connection between bricks, stones, or other masonry units formed by lapping them one upon another, carrying up the work, so as to form an inseparable mass of building by preventing the vertical joints from falling over each other.
Stretcher
A brick or block masonry laid lengthwise of a wall.
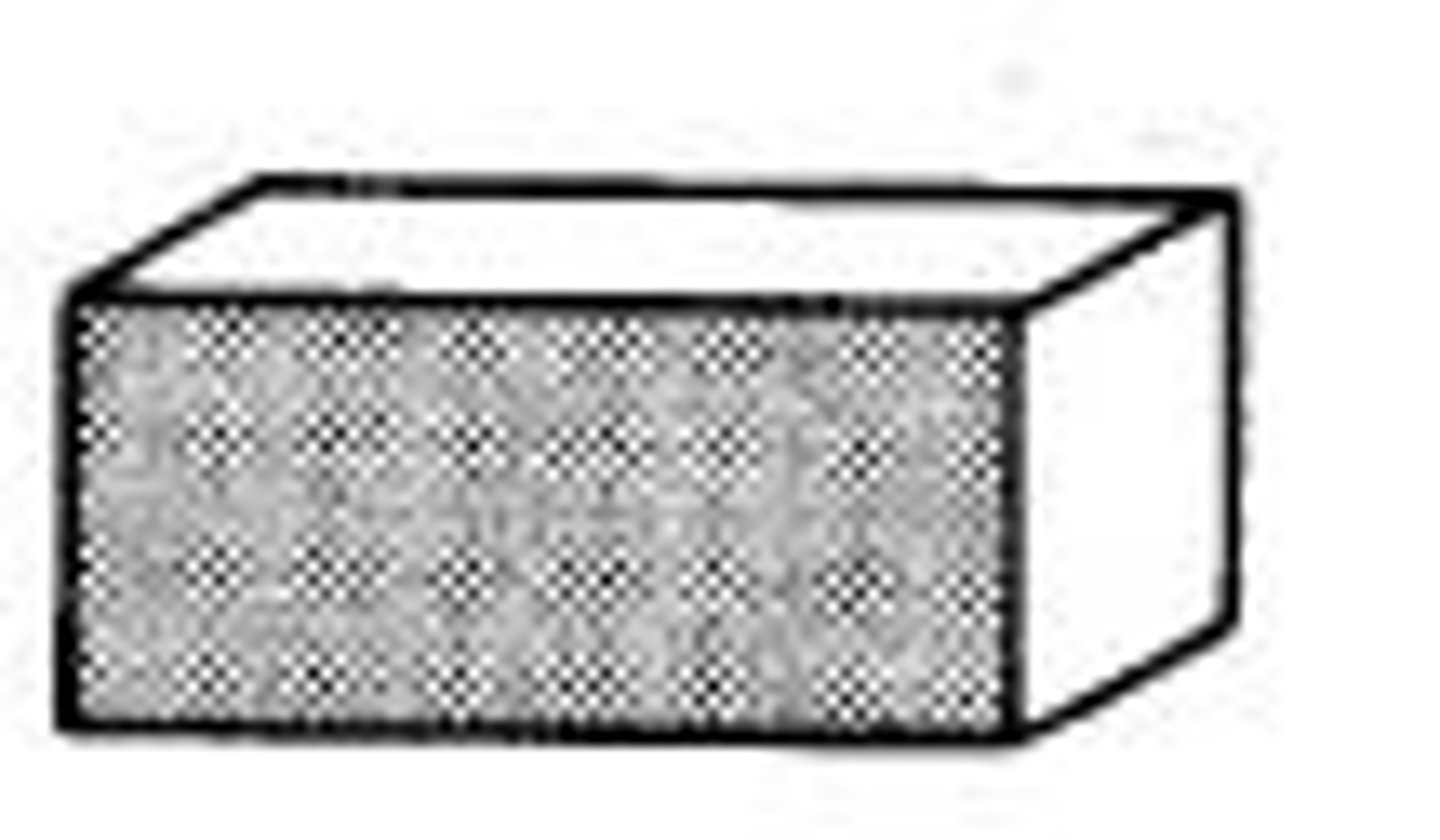
Header
A brick or block masonry extending over the thickness of the wall.
Heading course
A course in which the bricks or other masonry units are all headers.
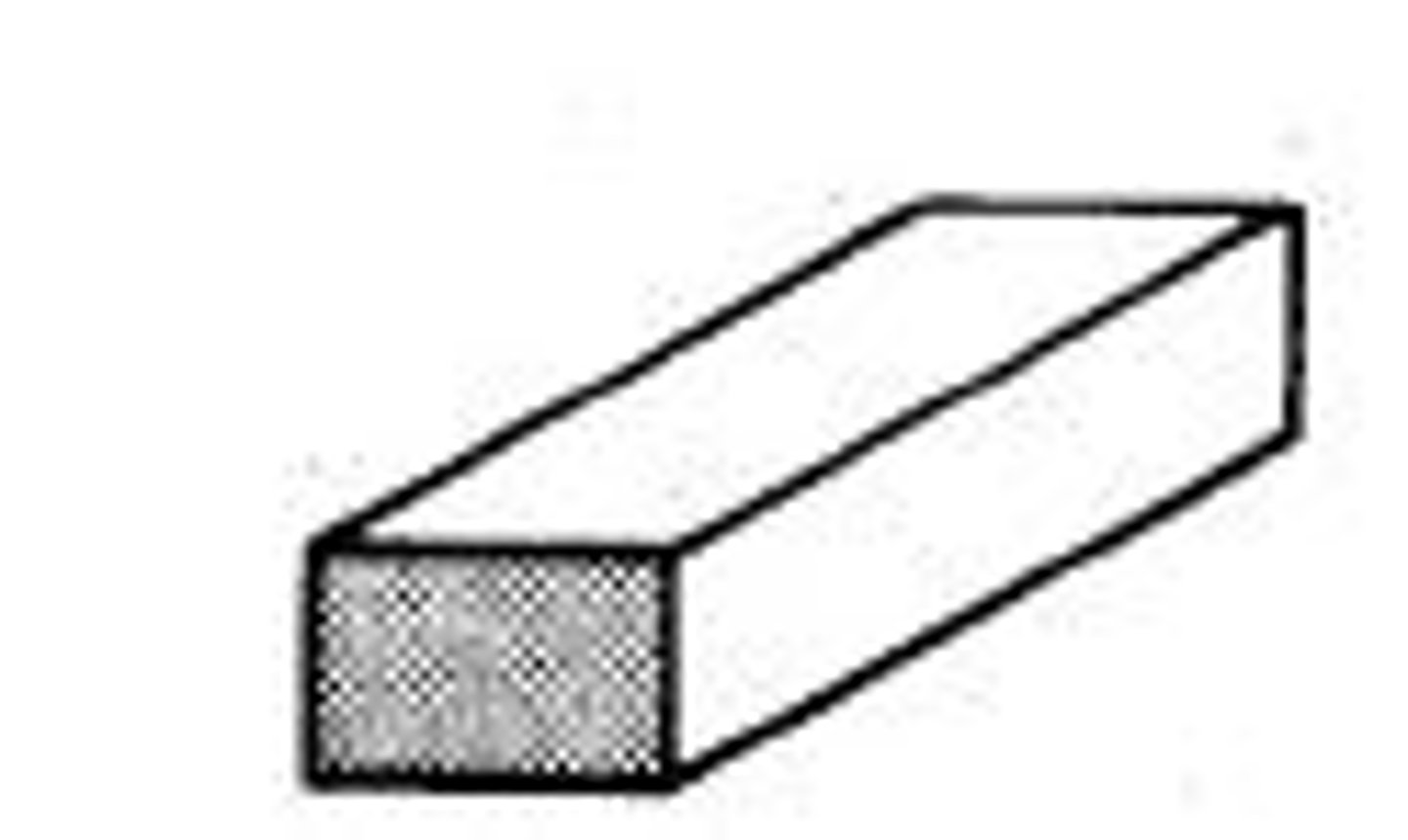
Soldier
A masonry unit laid (vertically) on its end with its face perpendicular to the face of the wall.
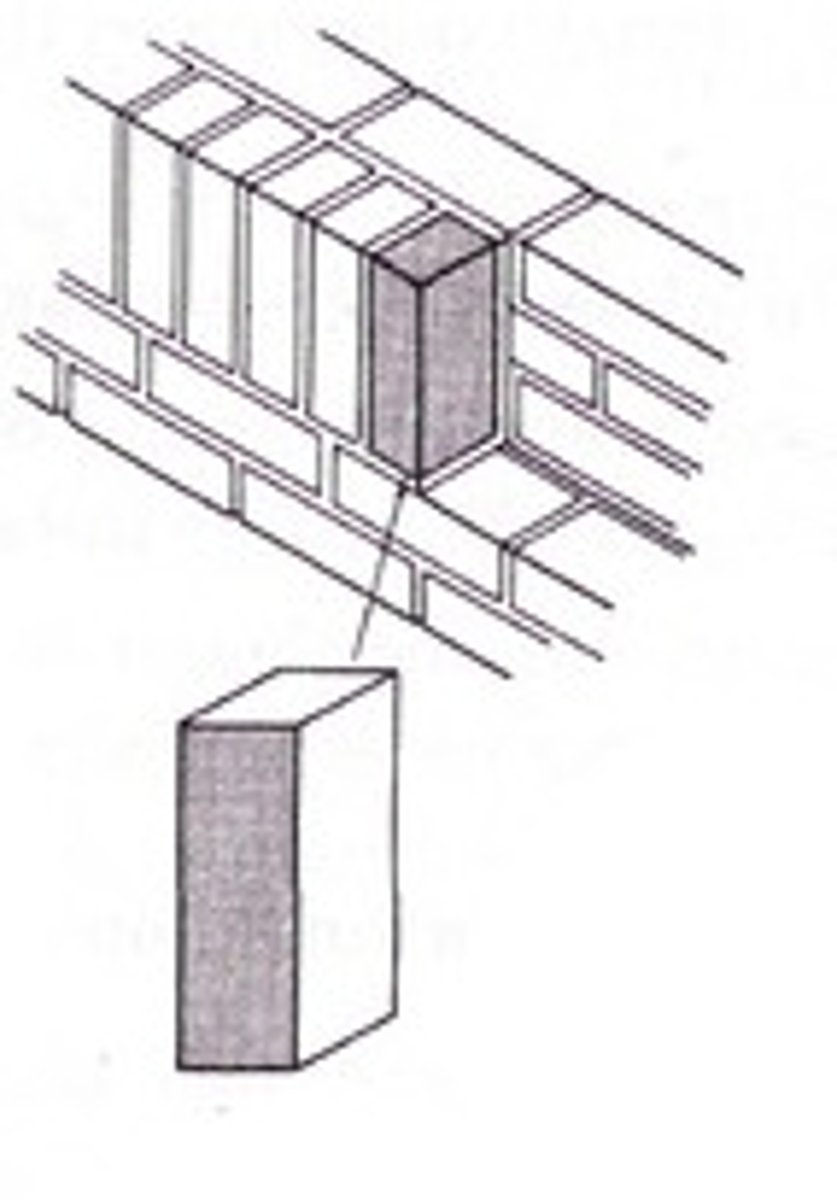
Quoins
The corner stones at the angles of buildings, usually rusticated to project from the normal surface of the wall.
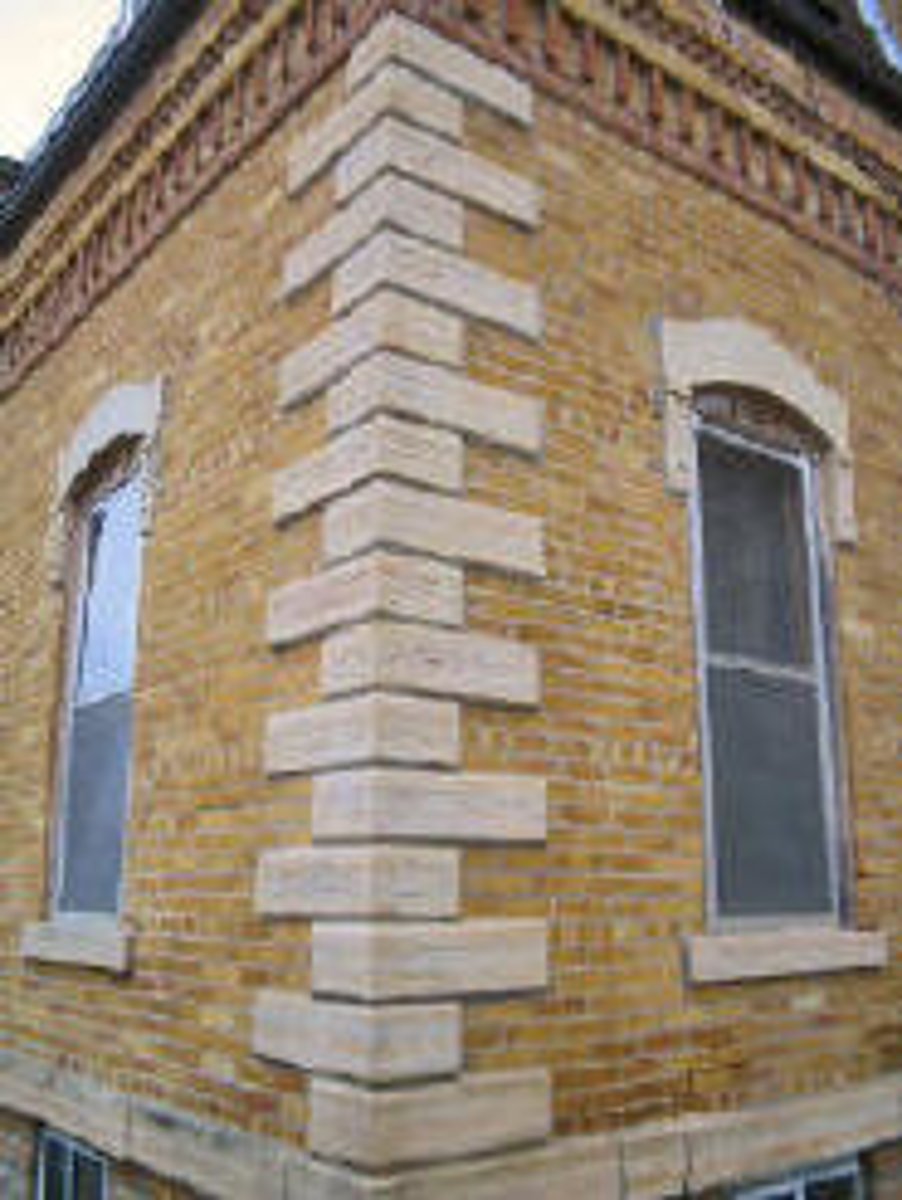

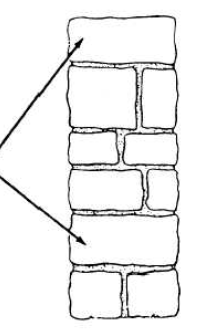
Bond stones
Stones running through the thickness of the wall at right angles to its face, to bind it together
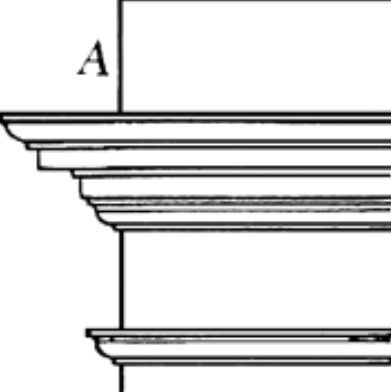
Blocking course
A course of stones is placed on top of the cornice crowning the walls.
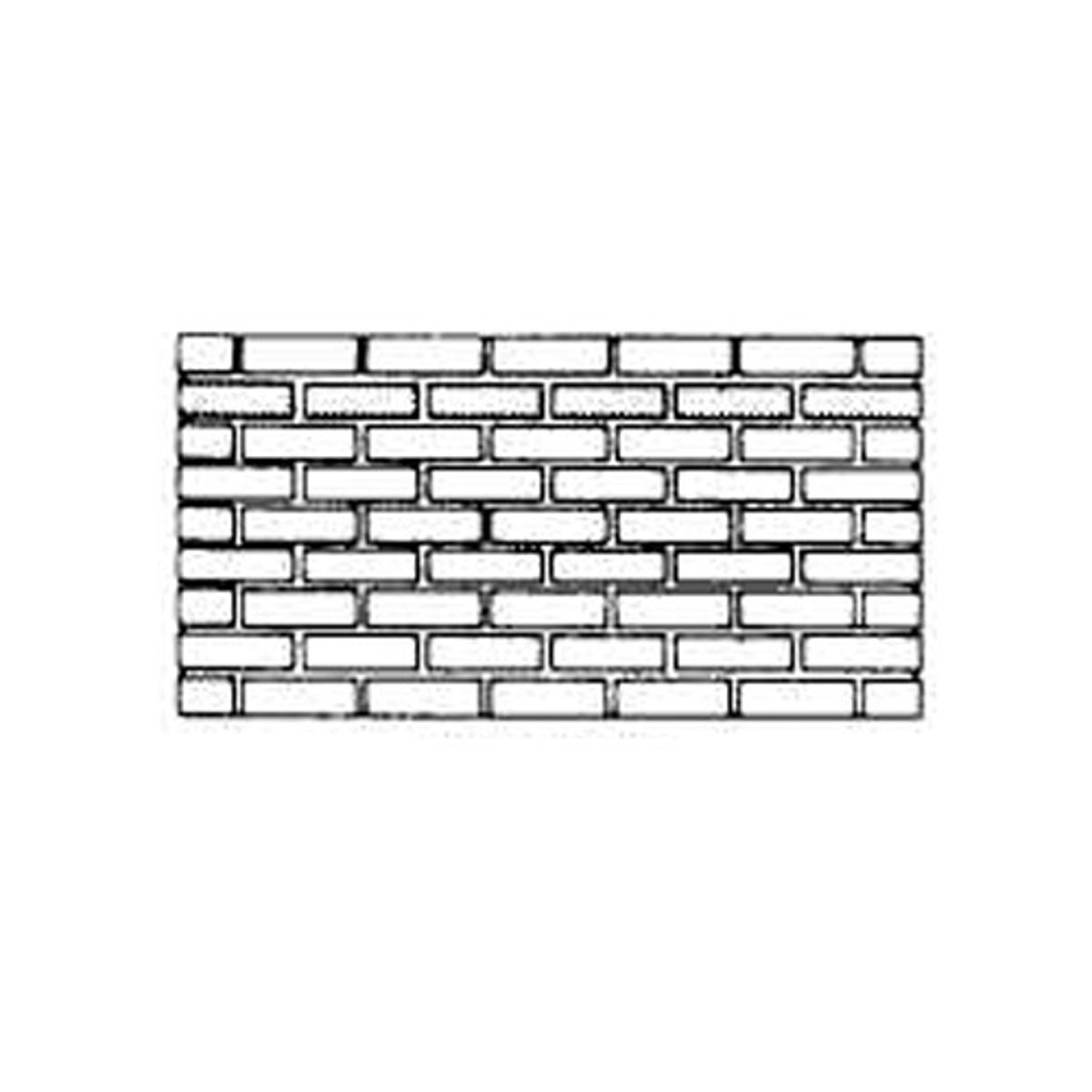
Running bond
This is the simplest bricklaying pattern which is used in cavity and veneer walls.
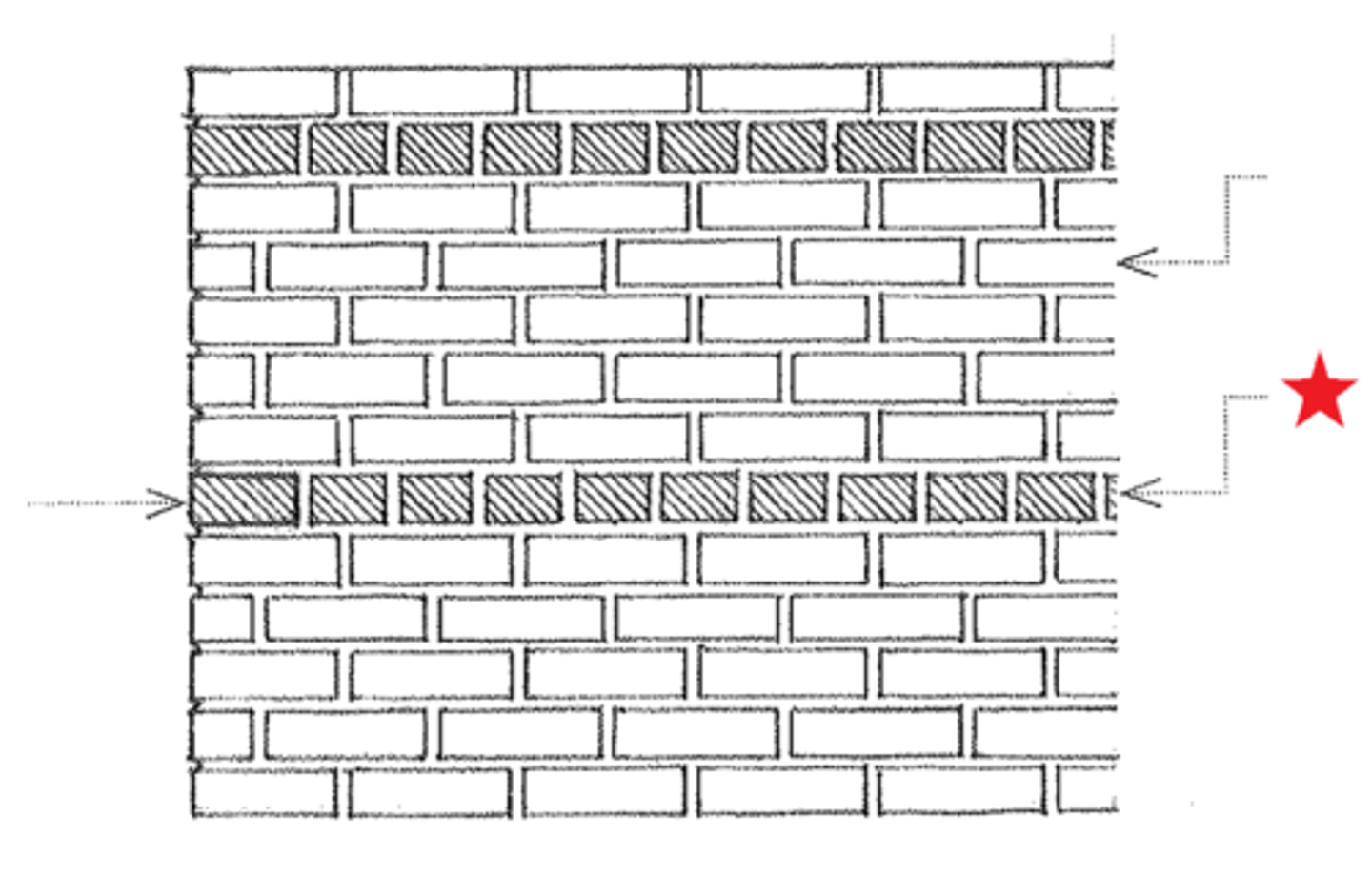
Common bond
This is similar to running bond except for a header course at every 5th, 6th, or 7th course (equal distance).
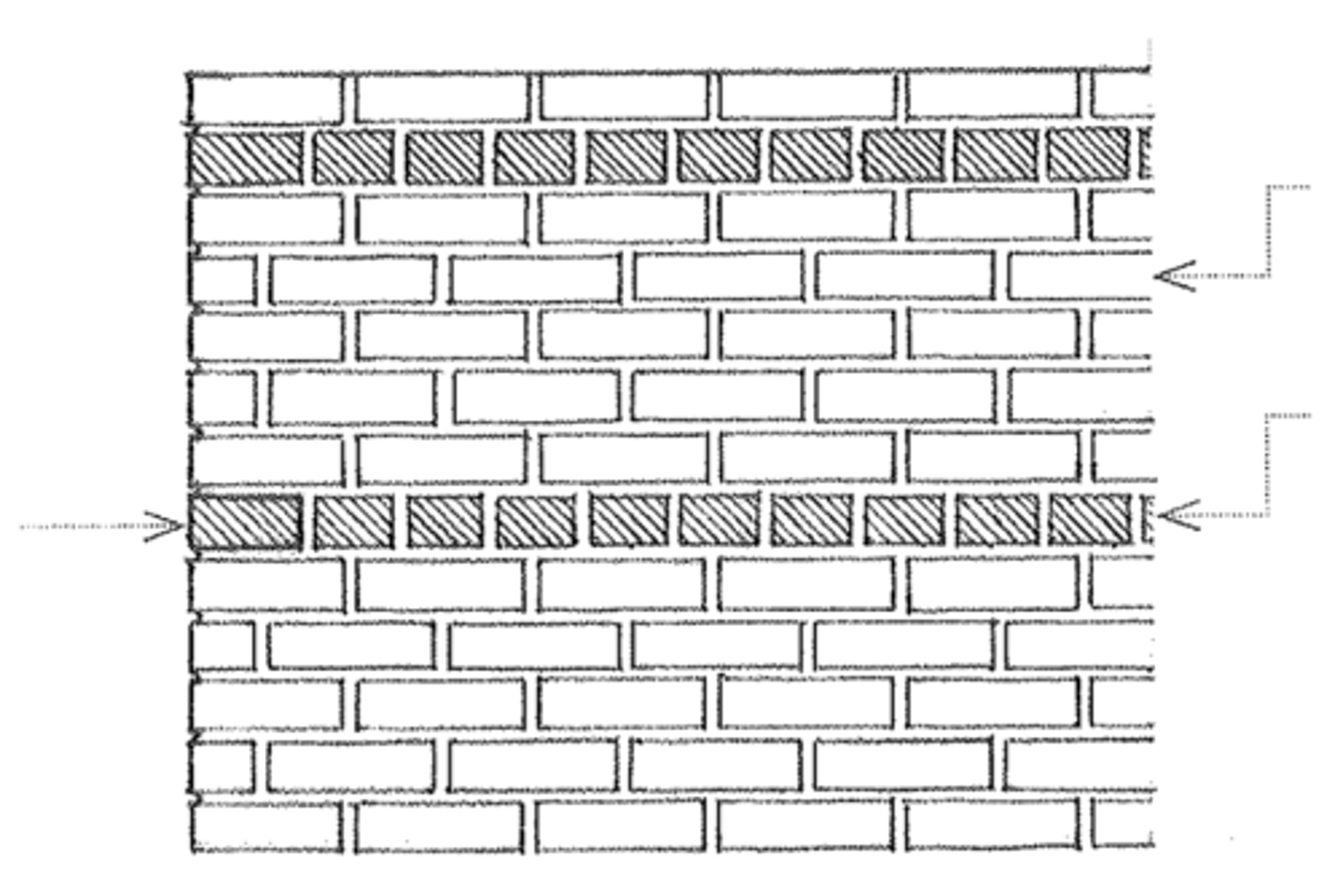
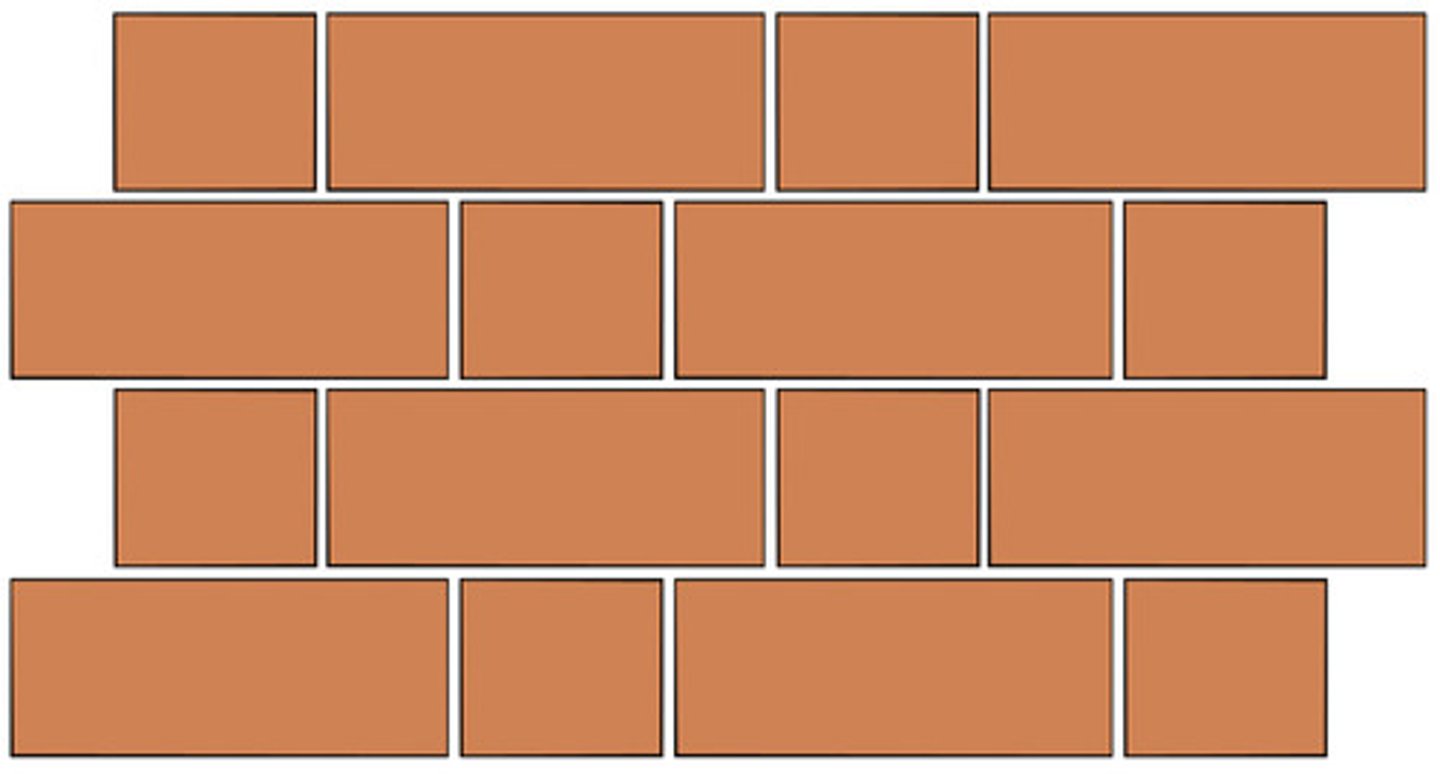
Stack bond
A brickwork or masonry bond having successive courses of stretchers with all head joints aligned vertically. Since units do not overlap, longitudinal reinforcements are needed for these.
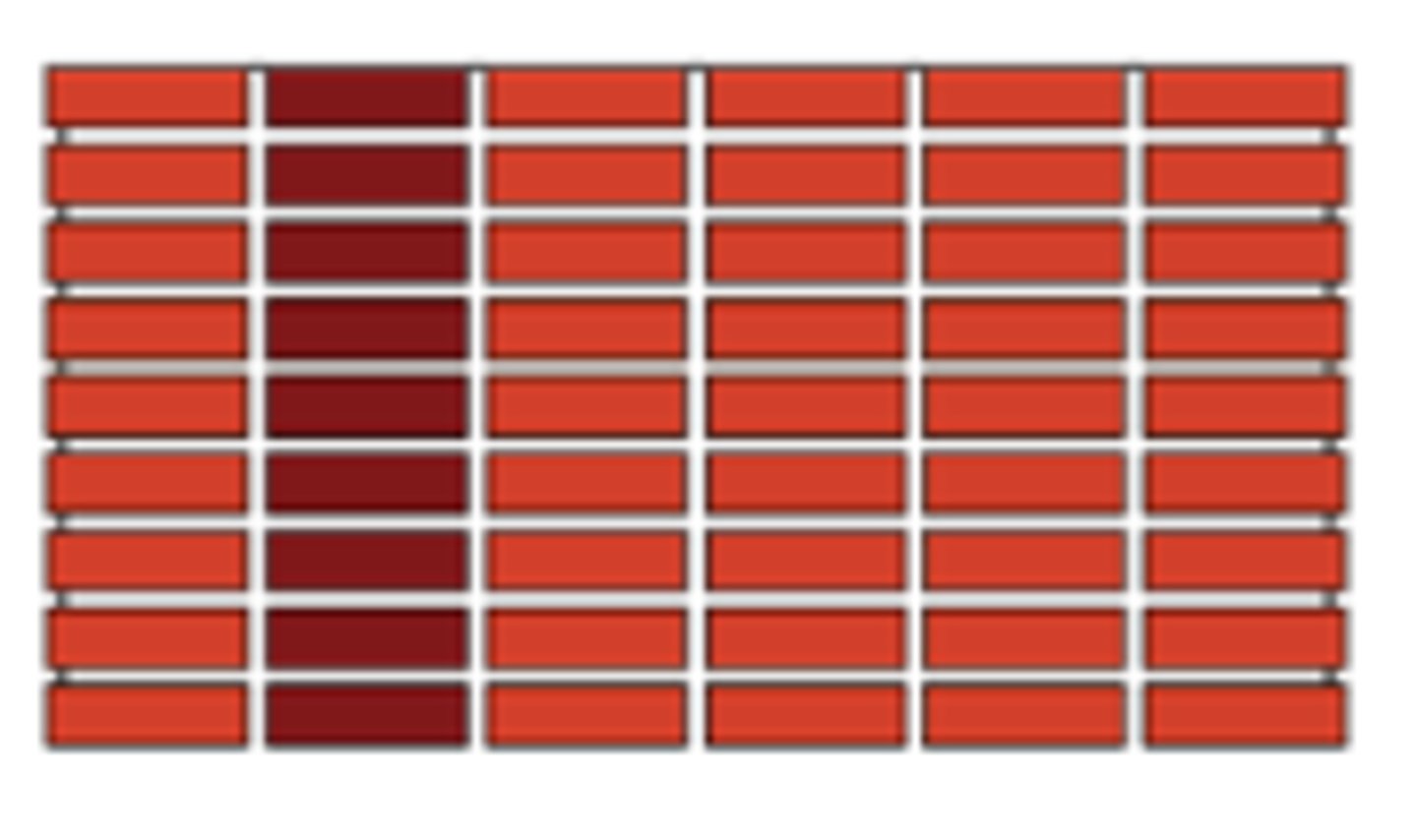

Flemish bond
Type of bond where each course consists of alternating headers and stretchers.
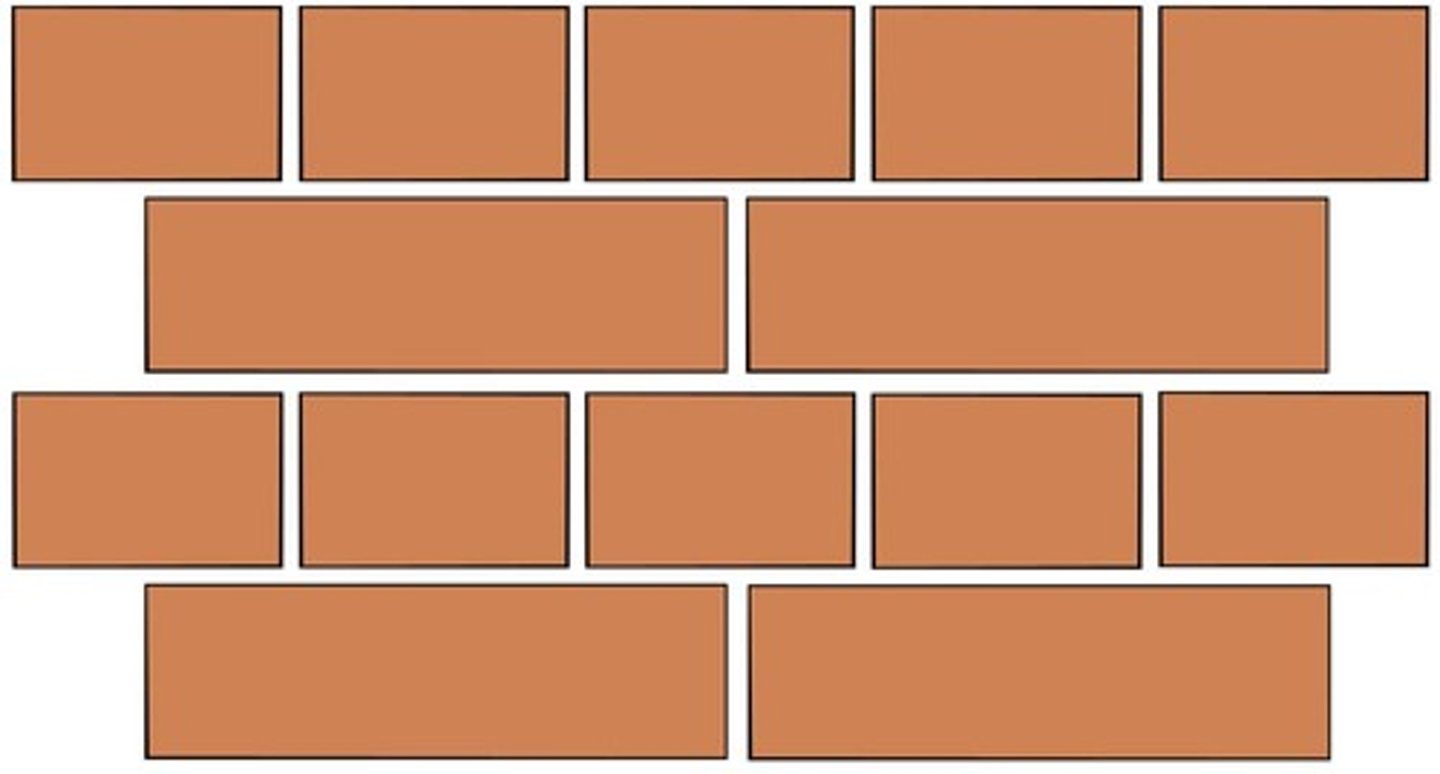
English bond
Pattern consists of alternating stretcher and header per course.
4.5 mm to 12 mm
Mortar joint thickness between brick courses

Concrete Hollow Blocks
A hollow or solid concrete masonry unit (CMU) consisting of Portland cement and suitable aggregates combined with water. Also called a cement block.
100 mm (4”)
How thick should horizontal and vertical joints for CHB layouts be used in interior partition walls?
200 mm (height); 400mm (length)
What is the standard height and length of CHB blocks?
12.5
How many pieces of hollow blocks are needed to cover one square meter?
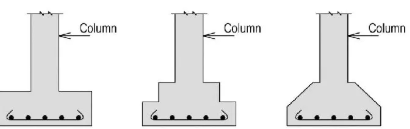
Wall footing
A strip of reinforced concrete wider than the wall, which distributes the load to the soil. It shall equal 0.2% to 0.3% of the cross-sectional area of concrete.
Hooked bar
A concrete reinforcing bar whose end is bent to improve its anchorage, generally through 90° or 180°. This anchors CHB to concrete.
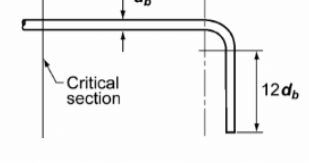
Dowel-bar reinforcement
Short, reinforcing bars of steel which extend approximately equally into two abutting pieces of concrete, to increase the strength of the joint; used in joint with columns or beams.
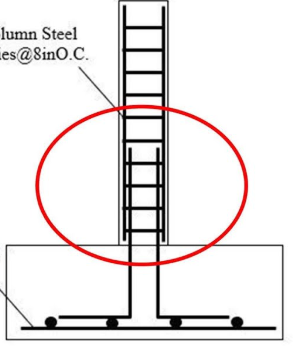
Stiffener columns
These support CHB partition walls from vertical lateral movements. It is located at the intersections of the CHB walls and at regular intervals of 3 meters for a long partition wall. It may take a form of an I, T, or L.

Stiffener beams
These support CHB partition walls from horizontal lateral movements.
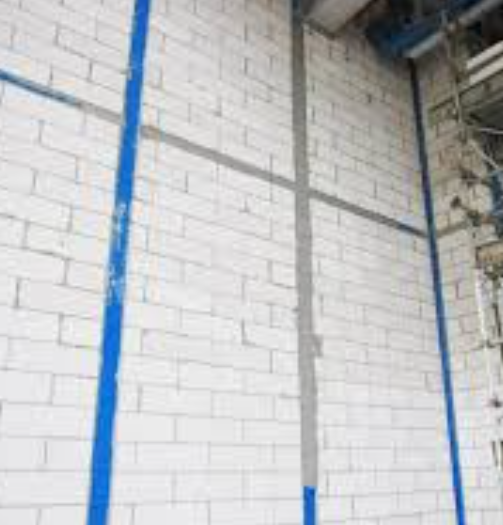

Lintel
A horizontal structural member (such as a beam) over an opening that carries the weight of the wall above it; usually of steel, stone, or wood.

Lintel Blocks
This is used to construct lintels. It has a single core with an open end and is usually placed with its open end upright. It forms a continuous beam when filled with grout and proper reinforcement. Also known as U-blocks.

Mortar
A plastic mixture of cement, lime, or a combination of both, with sand and water, used as a bonding agent in masonry construction.
Cement mortar
Type of mortar: Made by mixing Portland cement, sand, and water
Lime mortar
Type of Mortar: A mixture of lime, sand and water that is rarely used because of its slow rate of hardening and low compressive strength.
Cement-lime mortar
Type of Mortar: A cement mortar to which lime is added to increase its plasticity and water retentivity.
Masonry cement
A proprietary mix of Portland cement and other ingredients, such as hydrated lime, plasticizers, air-entraining agents, and gypsu,m requiring only the addition of sand and water to make cement mortar.
Scrim tape
It is also known as gypsum tape. It fills the gaps formed where gypsum boards join together. It is then covered with putty and smoothed over with sandpaper.
