Mesopotamian and Egyptian Urban Planning, Architecture, and Culture
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What was the purpose of the immense effort to create canals and irrigation systems in Mesopotamia?
To consolidate the Mesopotamian cities.
What was the most available medium of expression in Mesopotamia?
Clay
Where and when did the earliest urban settlements in Mesopotamia appear?
In Sumer, around 5000 BCE
What were the ziggurats, and what did their design create?
Temples that rose on platforms, creating a stepped profile.
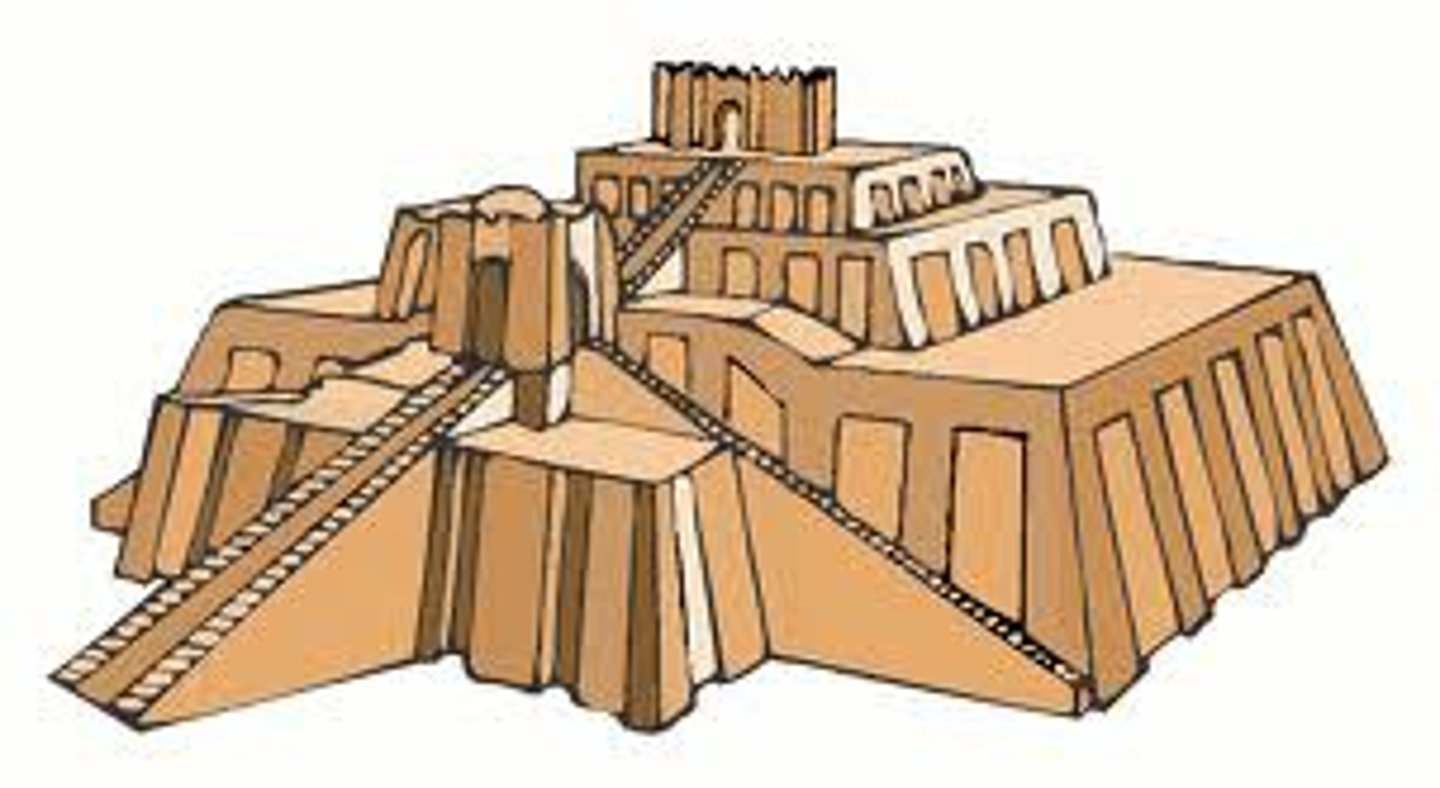
What is an axis mundi?
A sacred marker indicating a culture's center of the world.

What distinguished the temple district of Ur from the rest of the city?
Its orthogonal coordinates established an obvious contrast between order and disorder.
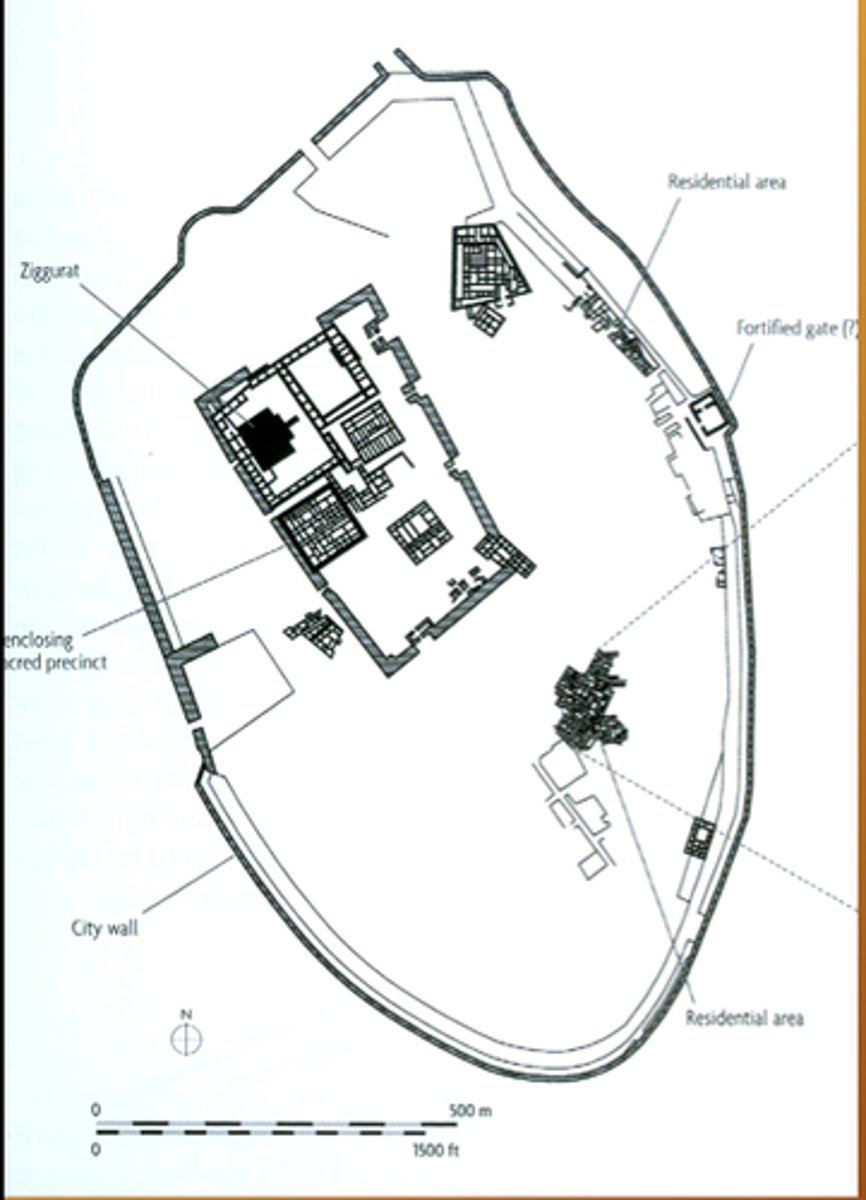
What was a tell and what did it serve as?
A human-made acropolis that served as the site for the royal palace and the primary temple.
What happened to the clay walls and cuneiform tablets of palaces in Ebla and Mari when they were destroyed by fire?
They were converted into the more permanent form of terra-cotta.
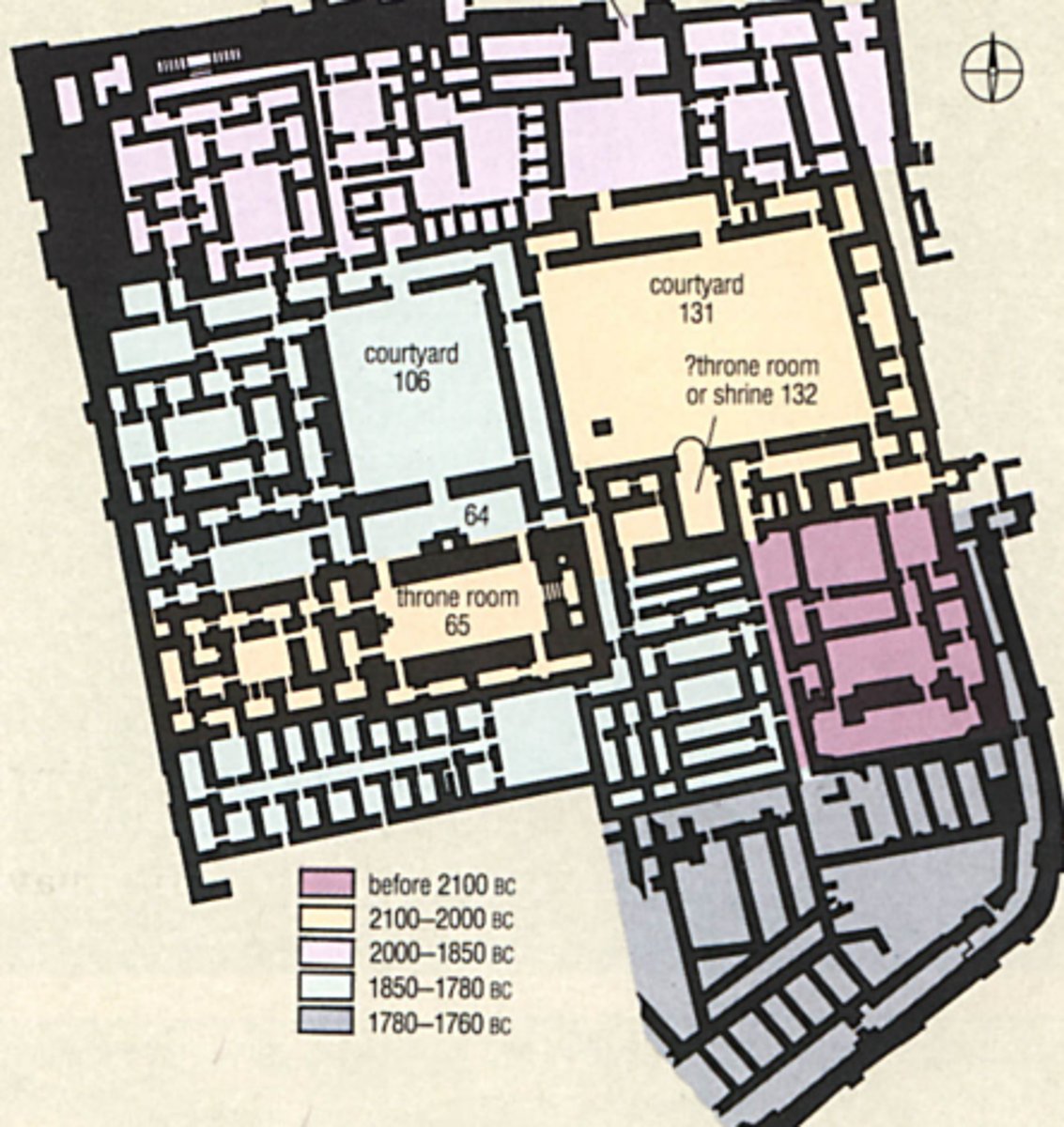
How was the approach to the great palace at Mari designed?
It had a twisting series of three antechambers to slow down entrants
What famous legal code was published by King Ur-Nammu of Ur's Third Dynasty?
The first code of laws.
What encouraged the Egyptians' belief in an eternal order?
The Nile's reliable annual floods
Why was orthogonal planning natural to the ancient Egyptians?
They had knowledge of right angles and proportional systems.
Where were all Egyptian burial grounds located and why?
On the west bank of the Nile, the land of the setting sun.
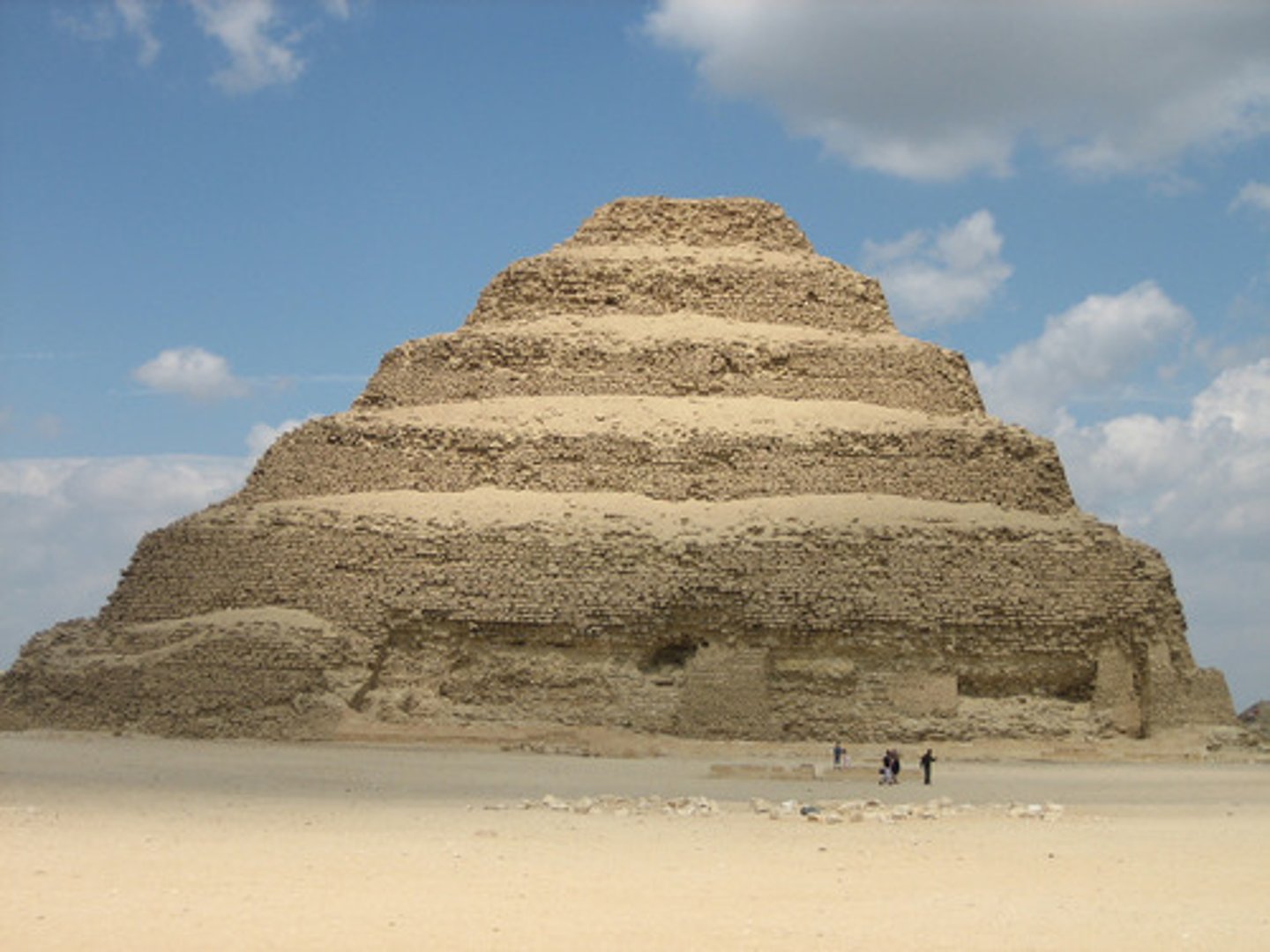
What was the first pyramid type?
The stepped pyramid.

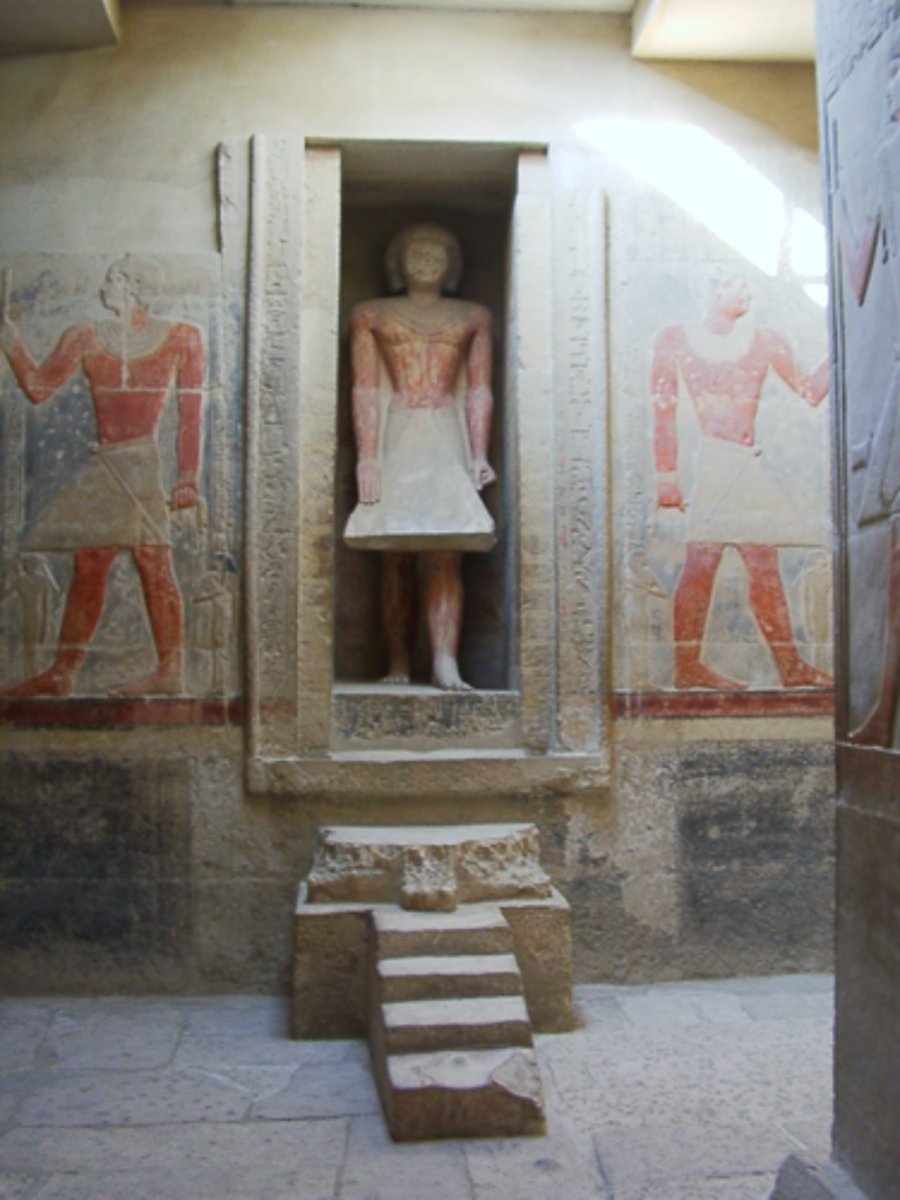
What was the serdab in a mastaba?
A sealed chamber containing a statue of the pharaoh.

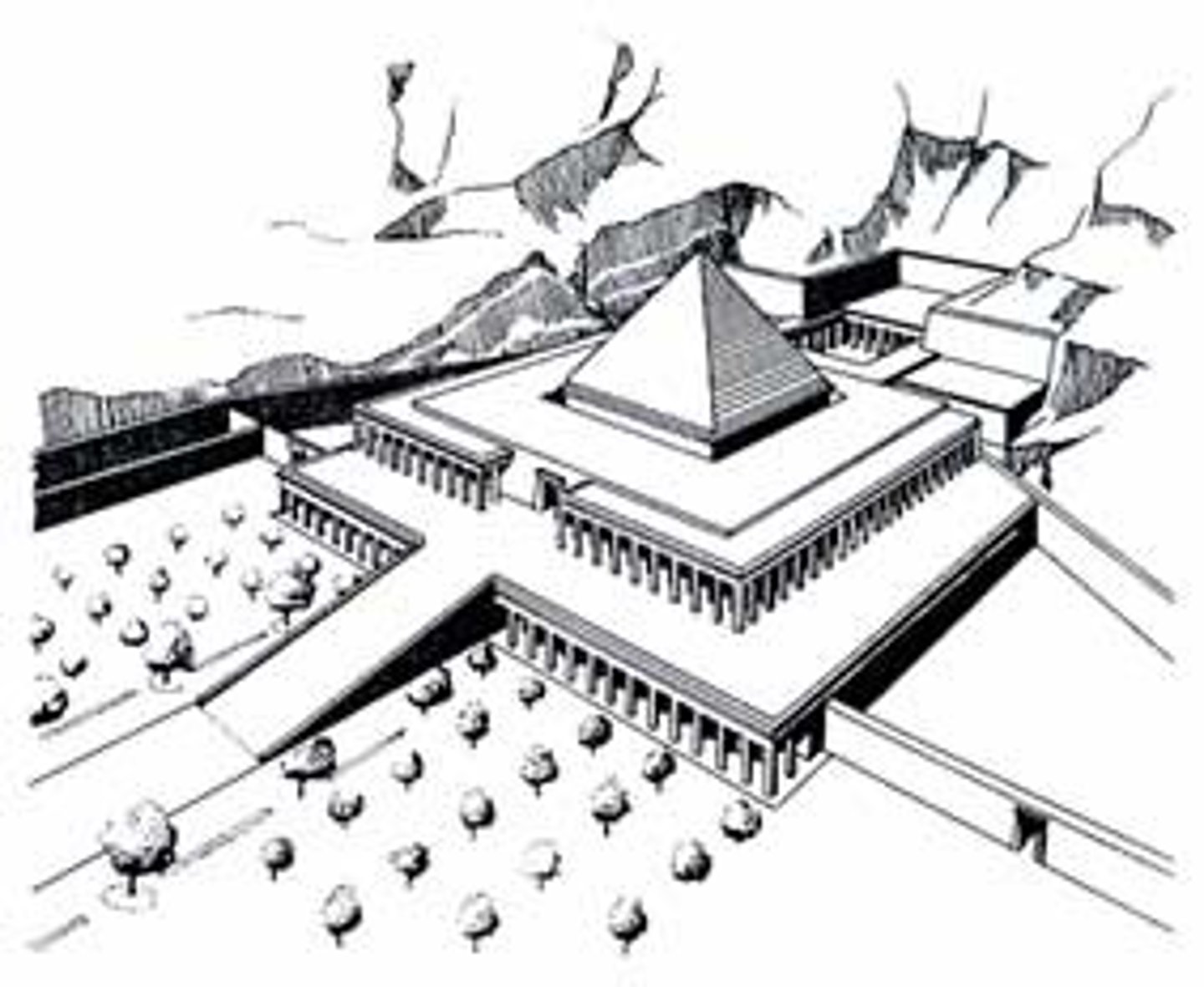
Who were Khufu, Khafre, and Menkaure?
The pharaohs who built the Great Pyramids at Giza.
What were the circumstances that led to the decline of the Old Kingdom in Egypt?
The Nile refused to flood, which led to famine, disorder, and political shifts.
What is a key characteristic of the Harappans' urban society in terms of monuments?
They intentionally avoided building them

What did the high degree of orthogonal order in Indus Valley cities indicate?
A sophisticated social organization and advanced engineering knowledge.
What did the Harappans use to seal the Great Bath at Mohenjo-daro?
Bitumen mortar and gypsum-based plaster.
What did the Harappans invest their surplus in instead of great architectural statements?
Defense against the elements, grain storage, and public assemblies.
What was the primary purpose of the towering temples in Mesopotamian cities?
Served as the center of the surrounding agricultural estates.
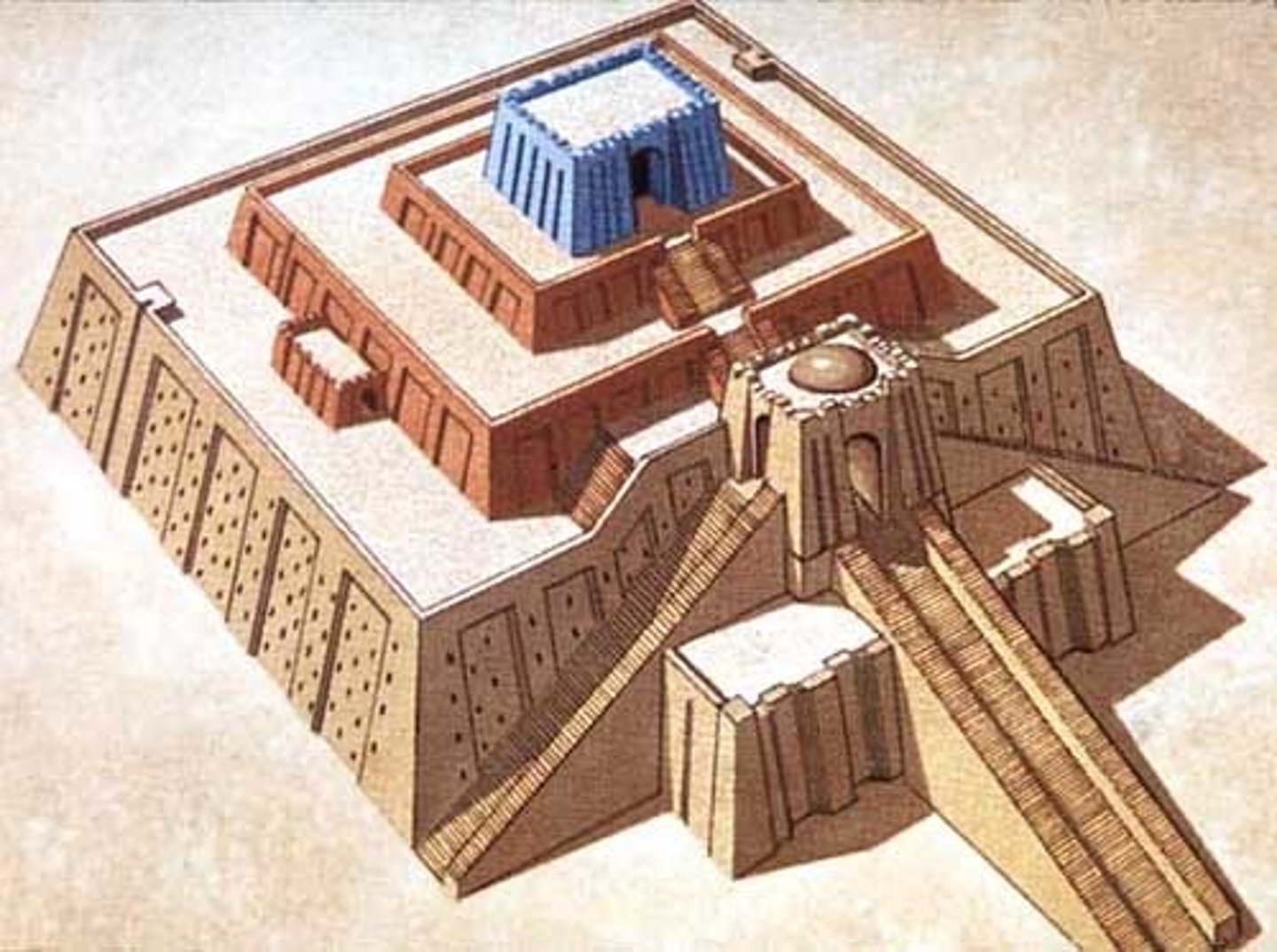
What was the primary purpose of the double walls in Mesopotamian cities?
Provided defense.
What is the name for the sacred enclosures designed by Sumerian architects?
Temenos
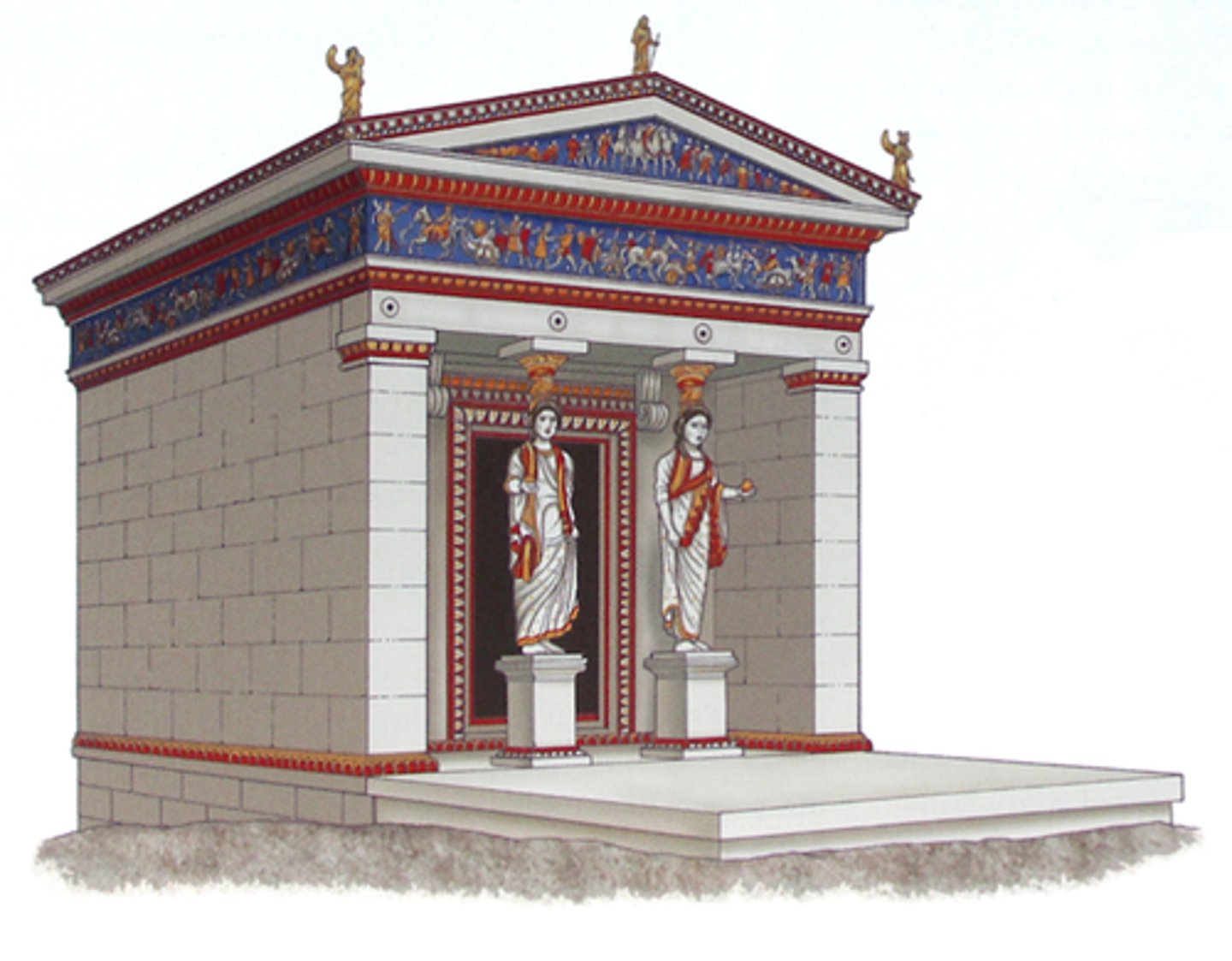

How was Uruk's White Temple used?
The focus of the city's religion and government.
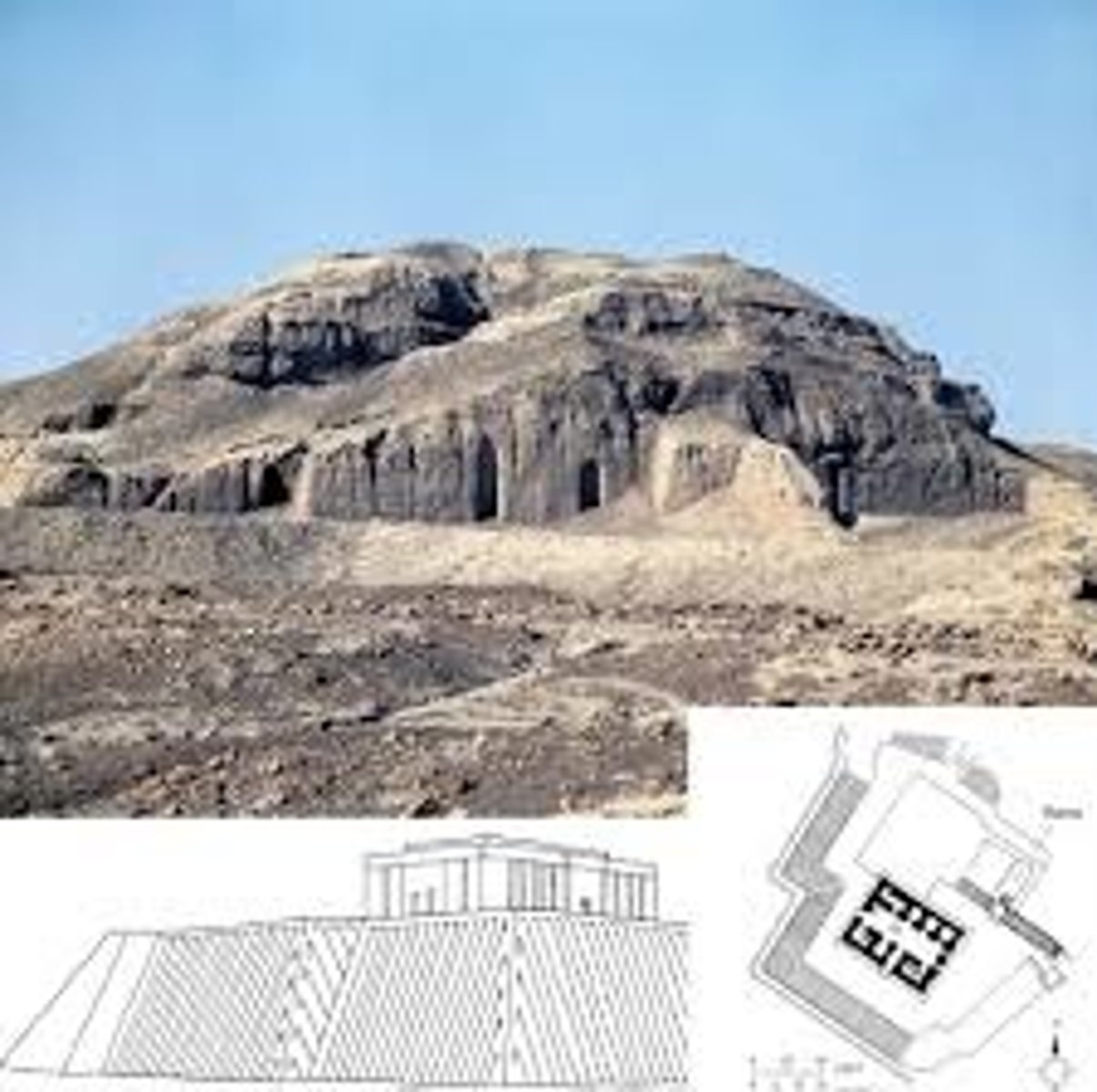
What was the palace at Mari used for?
It served as both a royal residence and a religious center.
What was the significance of the Great Ziggurat of Ur?
It was famous for being a "tangible axis mundi", serving as a vertical link to the supernatural.
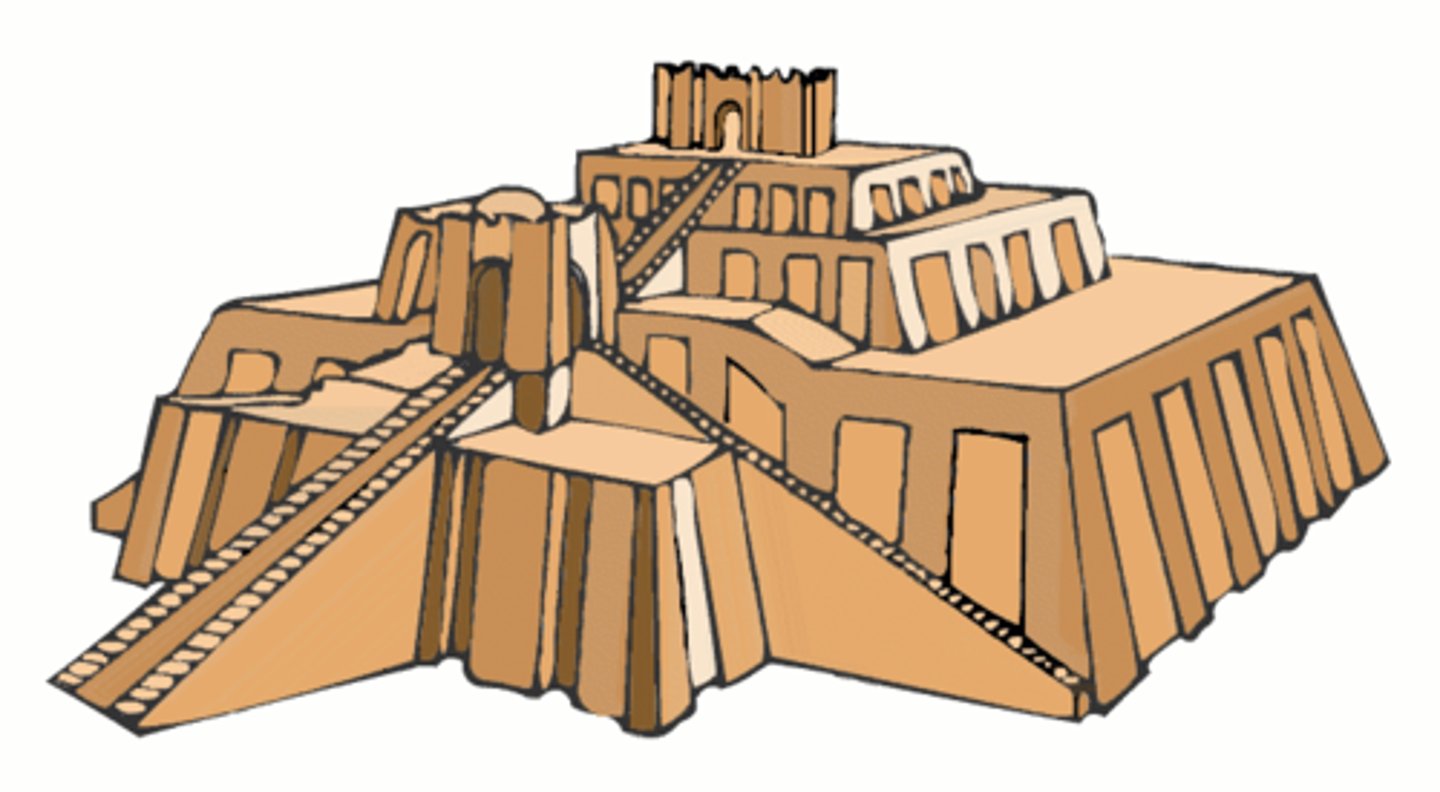
What were early royal tombs, known as mastabas, shaped like?
They were loaf-shaped rectangular tumuli.
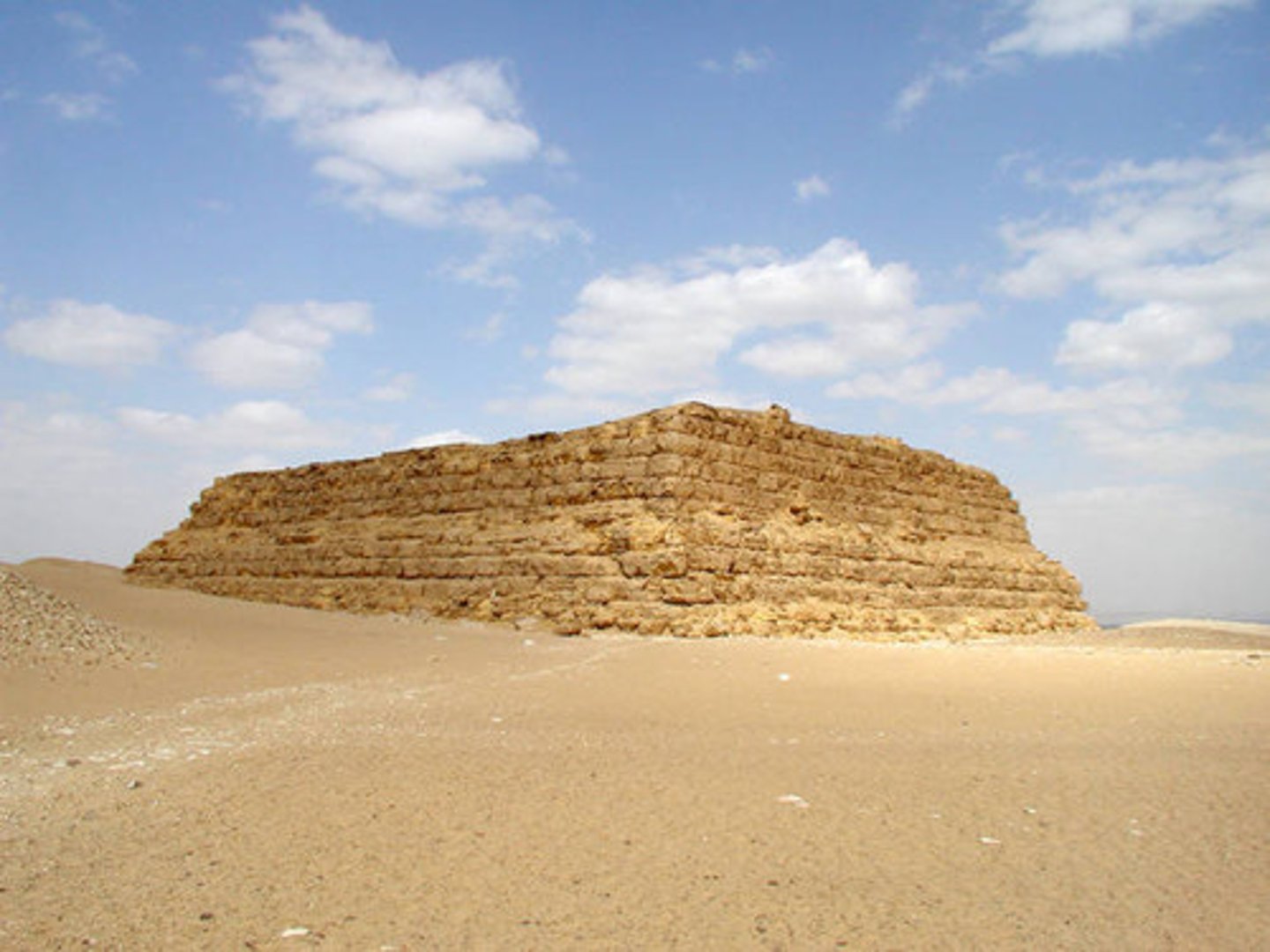

Tumuli
A mound of earth or stone raised over a grave or a graveyard.
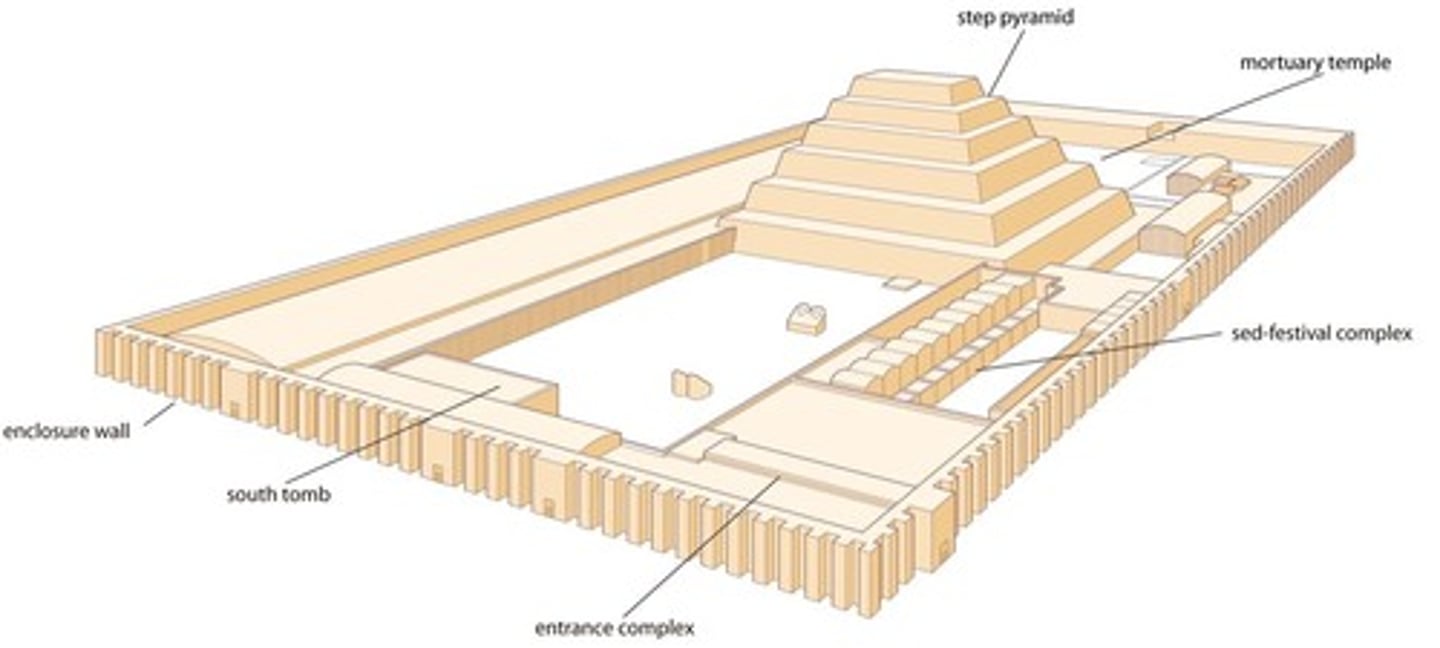
What was the purpose of the spaces surrounding Djoser's pyramid?
They served as the site of the Heb-Sed festival, which tested the pharaoh's capacity to rule.
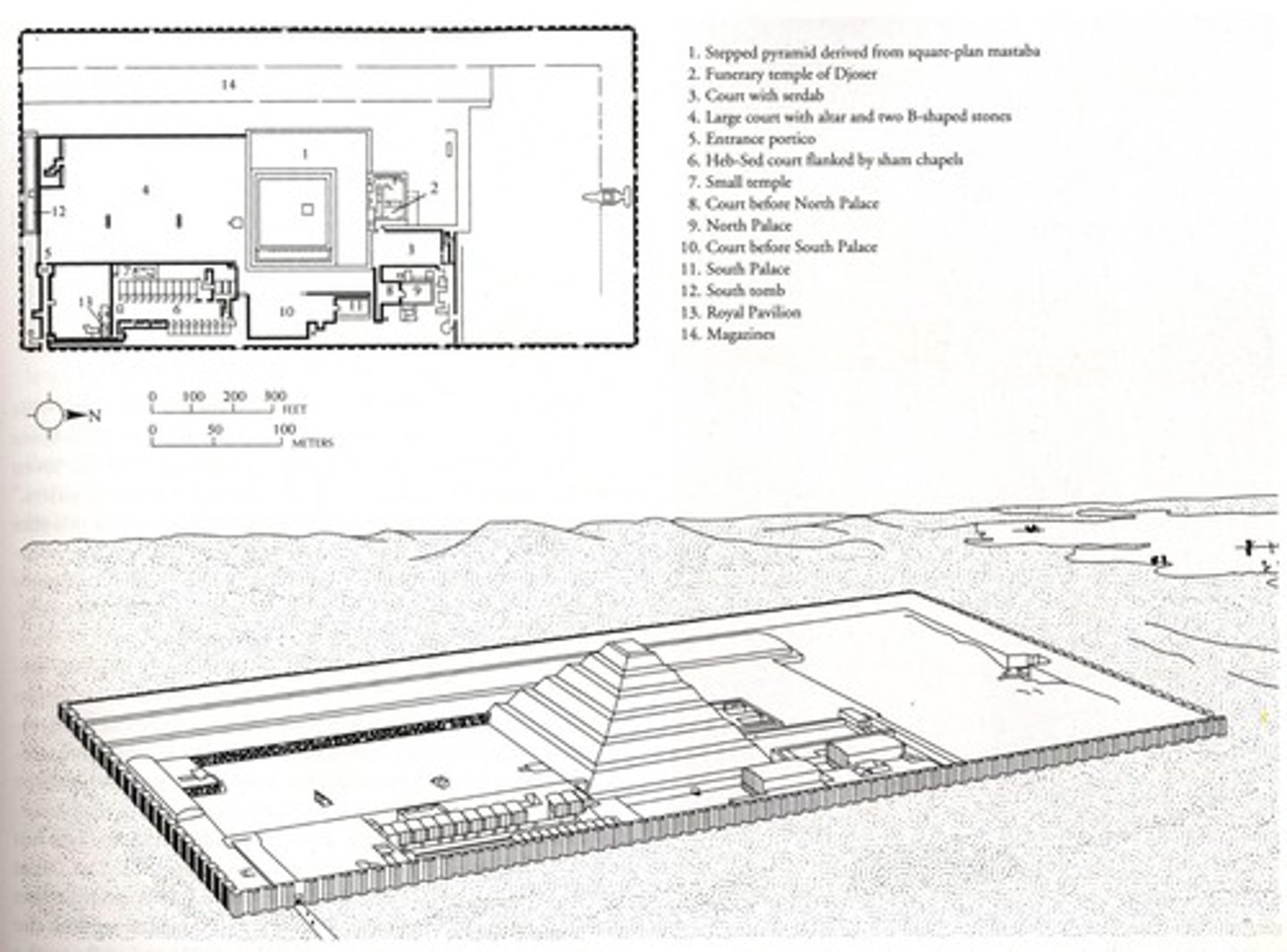
What was the design of the mortuary temple at Djoser's pyramid complex?
It stood adjacent to the north of the pyramid and was where sacrifices were regularly conducted.
What was the design of Mentuhotep I's new type of funeral memorial?
It combined a solar sanctuary terrace temple with a rock-cut tomb.
What was the primary purpose of the unusually thick city walls in Harappan cities?
They were built to defend against natural calamities like the periodic monsoon floods, rather than human invasions.
What was the purpose of the Great Bath at Mohenjo-daro?
It may have had religious functions as a structure for ritual bathing.
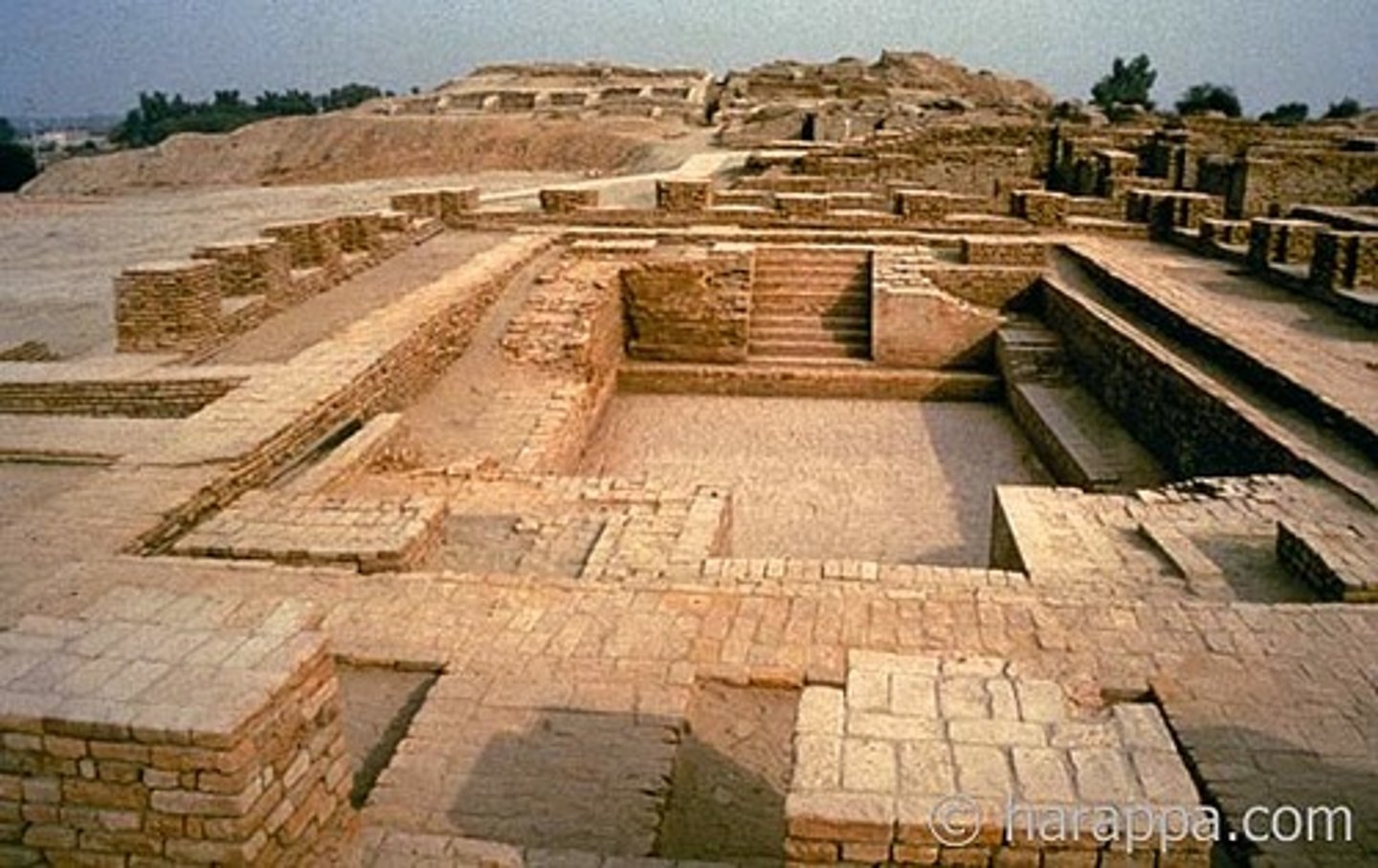

What types of structures were absent from the Harappan cities?
They left no traces of grand palaces, temples, or mausoleums